Linux 文件夹、文件、inode、fd
1.Linux 文件夹
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
Linux 中一切皆文件,对文件夹的操作本质上也是对文件的操作。
/* Open a directory stream on NAME.
Return a DIR stream on the directory, or NULL if it could not be opened.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern DIR *opendir (const char *__name) __nonnull ((1));
打开一个文件夹。
/* Read a directory entry from DIRP. Return a pointer to a `struct
dirent' describing the entry, or NULL for EOF or error. The
storage returned may be overwritten by a later readdir call on the
same DIR stream.
If the Large File Support API is selected we have to use the
appropriate interface.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
#ifndef __USE_FILE_OFFSET64
extern struct dirent *readdir (DIR *__dirp) __nonnull ((1));
#else
读取文件夹的内容。
/* Close the directory stream DIRP.
Return 0 if successful, -1 if not.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int closedir (DIR *__dirp) __nonnull ((1));
关闭文件夹。
/* Get file attributes for FILE and put them in BUF. */
extern int stat (const char *__restrict __file,
struct stat *__restrict __buf) __THROW __nonnull ((1, 2));
获取文件夹的属性。
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
void folder_func()
{
DIR* dirp = opendir(".");
if(dirp != NULL)
{
struct dirent* dp = NULL;
while((dp=readdir(dirp)) !=NULL)
{
struct stat sb={0};
if(stat(dp->d_name,&sb) != -1)
{
printf("name : %s,type : %d,size bytes : %ld,mtime : %s\n",dp->d_name,dp->d_type,sb.st_size,ctime(&sb.st_mtime));
}
}
}
closedir(dirp);
}
int main()
{
folder_func();
return 0;
}2.Linux 文件定义
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
/* Open FILE and return a new file descriptor for it, or -1 on error.
OFLAG determines the type of access used. If O_CREAT or O_TMPFILE is set
in OFLAG, the third argument is taken as a `mode_t', the mode of the
created file.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int open (const char *__file, int __oflag, ...) __nonnull ((1));
打开文件
/* Read NBYTES into BUF from FD. Return the
number read, -1 for errors or 0 for EOF.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t read (int __fd, void *__buf, size_t __nbytes) __wur;
读取 __nbytes 字节到 __buf 中。
/* Write N bytes of BUF to FD. Return the number written, or -1.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t write (int __fd, const void *__buf, size_t __n) __wur;
写入 __n字节到 __buf 中。
/* Close the file descriptor FD.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int close (int __fd);
关闭文件。
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
void file_func(const char* dst,const char* src)
{
int dfd = open(dst,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0600);
int sfd = open(src,O_RDONLY);
if((dfd != -1) && (sfd != -1))
{
char buf[512]={0};
int len=0;
while((len=read(sfd,buf,sizeof(buf)))>0)
{
write(dfd,buf,len);
}
}
close(dfd);
close(sfd);
}
int main()
{
file_func("new_test.cpp","test.c");
return 0;
}3.Linux inode,fd
#include <sys/stat.h>
struct stat
{
__dev_t st_dev; /* Device. */
#ifndef __x86_64__
unsigned short int __pad1;
#endif
#if defined __x86_64__ || !defined __USE_FILE_OFFSET64
__ino_t st_ino; /* File serial number. */
#else
__ino_t __st_ino; /* 32bit file serial number. */
#endif
#ifndef __x86_64__
__mode_t st_mode; /* File mode. */
__nlink_t st_nlink; /* Link count. */
#else
__nlink_t st_nlink; /* Link count. */
__mode_t st_mode; /* File mode. */
#endif
__uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of the file's owner. */
__gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of the file's group.*/
#ifdef __x86_64__
int __pad0;
#endif
__dev_t st_rdev; /* Device number, if device. */
#ifndef __x86_64__
unsigned short int __pad2;
#endif
#if defined __x86_64__ || !defined __USE_FILE_OFFSET64
__off_t st_size; /* Size of file, in bytes. */
#else
__off64_t st_size; /* Size of file, in bytes. */
#endif
__blksize_t st_blksize; /* Optimal block size for I/O. */
#if defined __x86_64__ || !defined __USE_FILE_OFFSET64
__blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number 512-byte blocks allocated. */
#else
__blkcnt64_t st_blocks; /* Number 512-byte blocks allocated. */
#endif
#ifdef __USE_XOPEN2K8
/* Nanosecond resolution timestamps are stored in a format
equivalent to 'struct timespec'. This is the type used
whenever possible but the Unix namespace rules do not allow the
identifier 'timespec' to appear in the <sys/stat.h> header.
Therefore we have to handle the use of this header in strictly
standard-compliant sources special. */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access. */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification. */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change. */
# define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility. */
# define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
# define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
#else
__time_t st_atime; /* Time of last access. */
__syscall_ulong_t st_atimensec; /* Nscecs of last access. */
__time_t st_mtime; /* Time of last modification. */
__syscall_ulong_t st_mtimensec; /* Nsecs of last modification. */
__time_t st_ctime; /* Time of last status change. */
__syscall_ulong_t st_ctimensec; /* Nsecs of last status change. */
#endif
#ifdef __x86_64__
__syscall_slong_t __glibc_reserved[3];
#else
# ifndef __USE_FILE_OFFSET64
unsigned long int __glibc_reserved4;
unsigned long int __glibc_reserved5;
# else
__ino64_t st_ino; /* File serial number. */
# endif
#endif
};/* Get file attributes for the file, device, pipe, or socket
that file descriptor FD is open on and put them in BUF. */
extern int fstat (int __fd, struct stat *__buf) __THROW __nonnull ((2));
1.第一个参数是 fd,第二个参数是 stat 对象指针。
2.在stat 结构中,__ino_t st_ino; /* File serial number. */ 就是具体的inode。
3.fd 是根据进程来的,每一个进程不同,fd也就不同;inode 是唯一确定的。
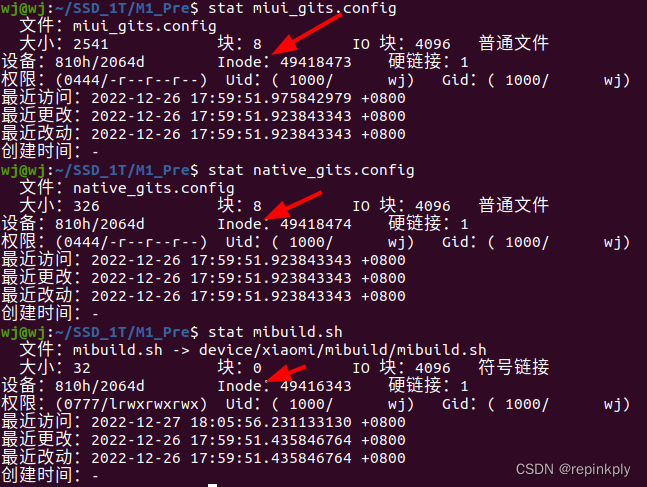
4.Linux下,获取某个文件的inode值的方式为:stat fileName。如下所示:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号