Hadoop(五):HDFS的JAVA API基本操作
HDFS在生产应用中主要是客户端的开发,其核心步骤是从HDFS提供的api中构造一个HDFS的访问客户端对象,然后通过该客户端对象操作(增删改查)HDFS上的文件。
主要类
Configuration
-
其实就是我们Java项目的core-site.xml文件,就像安装Hadoop时要配置core-site.xml文件一样,我们的java项目也要正确配置才能连接Hadoop。
-
在实例化的时候,Configuration类会自动读取:
-
core-default.xml(不需要我们增加)
-
core-site.xml(我们配置)
-
其实和Hadoop配置一样,core-site没配置的时候,就取默认的core-default.xml里的配置。
-
-
Configuration类除了自动读取配置文件以外,还提供了一系列操作配置的方法,可以在程序里修改配置(而不是修改配置文件)。
FileSystem
-
类似Hadoop shell,对文件操作,通过该类可以对文件进行CRUD。
-
和Hadoop shell一样,可以对Hadoop支持的文件系统操作。
-
无参构造器是protected的,一般使用get方法获取该类的对象。
-
get方法获取对象有4种重写,一般我们只会用两种,见下文。
-
示例代码
1.建立Maven项目,导入基本依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId> <version>3.2.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-hdfs</artifactId> <version>3.2.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId> <version>3.2.1</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
2.在resources文件夹下建立core-site.xml文件
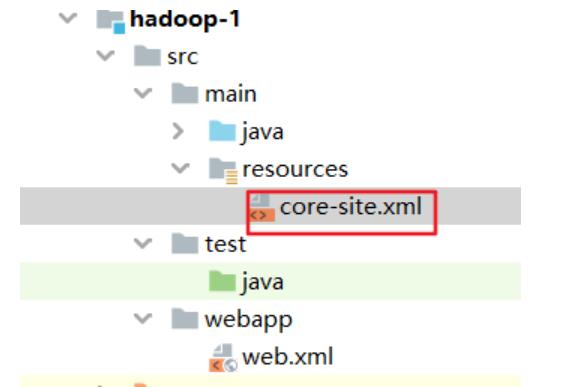
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?>
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://192.168.98.129:9000</value>
</property>
</configuration>
-
备注:Hadoop中似乎已经封装了log4j日志,可以把log4j.properties也添加进去,否则log4j就一直报找不到配置文件。不加也可以。
3.建立测试类
1.基本使用
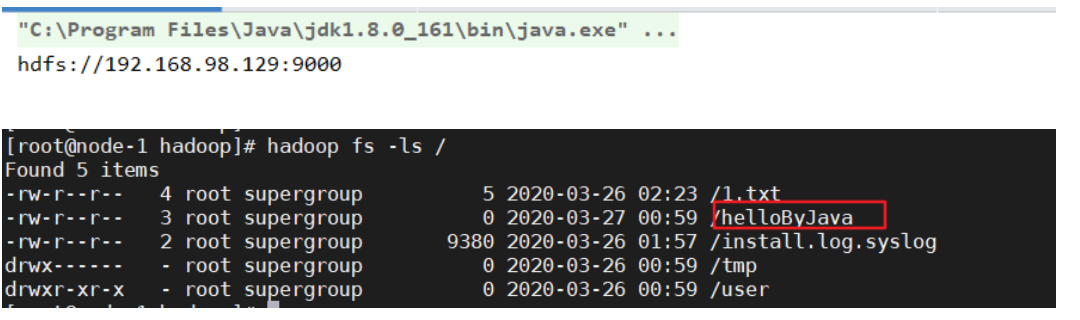
package com.rzp.hdfs; //注意导入的包一定要正确 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; import java.net.URISyntaxException; public class TestHDFSClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, URISyntaxException, InterruptedException { //实例化Configuration Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //使用root用户登录,如果不写,会用当前程序运行环境的用户登录,比如windows的Administrator用户导致报错 System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME","root"); //查看core-site.xml文件中fs.defaultFS的值 System.out.println(conf.get("fs.defaultFS")); //第一种获取FileSystem的对象的方式,通过get(conf)方法, FileSystem fs1 = FileSystem.get(conf); //在根目录下增加/helloByJava文件夹 fs1.create(new Path("/helloByJava")); //关闭连接 fs1.close; } }
-
测试结果:输出了配置中的值,Hadoop根目录下也增加对应文件夹,说明连接成功。
2.通过set方法,修改conf的参数
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, URISyntaxException, InterruptedException { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //set方法,修改conf的参数,可以把core-site.xml文件删除测试 conf.set("fs.defaultFS","hdfs://192.168.98.129:9000"); System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME","root"); System.out.println(conf.get("fs.defaultFS")); FileSystem fs1 = FileSystem.get(conf); fs1.create(new Path("/helloByJava")); }
3.第二种FileSystem实例化的方法,指定用户的get方法
public void test1() throws URISyntaxException, IOException, InterruptedException { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //直接指定操作该对象的用户名 FileSystem fs1 = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://192.168.98.129:9000"),conf,"root"); fs1.create(new Path("/helloByJava")); //关闭连接 fs1.close; }
FileSystem的主要方法
-
copyToLocalFile--下载文件到本地
@Test public void test2() throws URISyntaxException, IOException, InterruptedException { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://192.168.98.129:9000"),conf,"root");
//第一个地址是Hadoop路径,第二个地址是本地路径
fs.copyToLocalFile(new Path("/install.log.syslog"),new Path("./log"));
}
-
copyFromLocalFile 上传文件
static FileSystem fs = null; public static void init() throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); fs = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://192.168.98.129:9000"), conf, "root"); } @Test public void testAddFileToHdfs() throws Exception { HdfsClient.init();
//第一个地址是本地路径,第二个地址是Hadoop的路径
fs.copyFromLocalFile(new Path("D:\\log.log"), new Path("/")); fs.close();
}
-
文件CRUD
@Test public void testMkdirAndDeleteAndRename() throws Exception { HdfsClient.init(); // 创建目录 fs.mkdirs(new Path("/a1/b1/c1")); fs.mkdirs(new Path("/d1")); // 删除文件,如果是非空文件夹,参数2必须给值true fs.delete(new Path("/a1"), true); // 重命名文件或文件夹 fs.rename(new Path("/d1"), new Path("/d2")); fs.close(); }
-
查看目录(该部分笔者还没梳理完,所以没有注释,梳理完再修改)
/** * 查看目录信息,只显示文件 * * @throws IOException * @throws IllegalArgumentException * @throws FileNotFoundException */ @Test public void testListFiles() throws Exception { HdfsClient.init(); RemoteIterator<LocatedFileStatus> listFiles = fs.listFiles(new Path("/"), true); while (listFiles.hasNext()) { LocatedFileStatus fileStatus = listFiles.next(); System.out.println(fileStatus.getPath().getName()); System.out.println(fileStatus.getBlockSize()); System.out.println(fileStatus.getPermission()); System.out.println(fileStatus.getLen()); BlockLocation[] blockLocations = fileStatus.getBlockLocations(); for (BlockLocation bl : blockLocations) { System.out.println("block-length:" + bl.getLength() + "--" + "block-offset:" + bl.getOffset()); String[] hosts = bl.getHosts(); for (String host : hosts) { System.out.println(host); } } System.out.println("--------------打印的分割线--------------"); } } /** * 查看文件及文件夹信息 * * @throws IOException * @throws IllegalArgumentException * @throws FileNotFoundException */ @Test public void testListAll() throws Exception { HdfsClient.init(); FileStatus[] listStatus = fs.listStatus(new Path("/")); String flag = ""; for (FileStatus fstatus : listStatus) { if (fstatus.isFile()) { flag = "f-- "; } else { flag = "d-- "; } System.out.println(flag + fstatus.getPath().getName()); System.out.println(fstatus.getPermission()); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号