01. java多线程
01.线程概念
线程就是独立的执行路径;
在程序运行时, 即使没有自己创建线程, 后台也会有多个线程, 如主线程, gc线程;
main()称之为主线程, 为系统的入口, 用于执行整个程序;
在一个进程中, 如果开辟了多个线程, 线程的运行由调度器安排调度, 调度器是与操作系统紧密相关的, 先后顺序是不能认为的干预的。
对同一份资源操作时, 会存在资源抢夺的问题, 需要加入并发控制;
线程会带来额外的开销, 如cpu调度时间, 并发控制开销。
每个线程在自己的工作内存交互, 内存控制不当会造成数据不一致
02.创建方式
1)继承Thread类
1 public class MyThread extends Thread { 2 public void run(){ 3 // 线程执行的代码 4 } 5 } 6 7 // 使用 8 MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); 9 myThread.start();
2)实现Runnable接口
1 public class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 2 public void run(){ 3 // 线程执行的代码 4 } 5 } 6 // 使用 7 MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable(); 8 Thread thread = new Thread(myRunnable); 9 thread.start();
3)实现Callable接口
1 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 2 Future<String> future = executorService.submit(new Callable<String>() { 3 public String call() throws Exception { 4 // 线程执行的代码 5 return "结果"; 6 } 7 }); 8 9 try { 10 String result = future.get(); 11 } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { 12 // 处理异常 13 } 14 executorService.shutdown();
03.线程join
在Java中,join方法是线程间同步的一种手段,它允许一个线程等待另一个线程完成后再继续执行。具体来说,当某个线程调用另一个线程的join方法时,调用线程会被阻塞,直到被join的线程执行完毕(即线程终止)为止。

class Worker extends Thread { private String name; Worker(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println(name + " is starting."); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { if ("Worker 2".equals(name)) { Thread.sleep(1000); } System.out.println(name + " " + i); Thread.sleep(100); // 模拟一些工作 } System.out.println(name + " is finished."); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread worker1 = new Worker("Worker 1"); Thread worker2 = new Worker("Worker 2"); worker1.start(); worker2.start(); try { System.out.println("Main thread is waiting for workers to finish."); worker1.join(); System.out.println("All workers are finished. Main thread is continuing."); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
print:

Main thread is waiting for workers to finish. Worker 2 is starting. Worker 1 is starting. Worker 1 0 Worker 1 1 Worker 1 2 Worker 1 is finished. All workers are finished. Main thread is continuing. Worker 2 0 Worker 2 1 Worker 2 2 Worker 2 is finished.
在这个示例中:
- 我们创建了两个
Worker线程,每个线程都会在启动时打印一条消息,睡眠1秒钟(模拟工作),然后在结束时再打印一条消息。 - 在主线程中,我们启动了这两个
Worker线程。 - 主线程调用
worker1.join(),这会导致主线程等待worker1线程执行完毕后再继续执行,并不会等待worker2执行完毕。 - 当
Worker1线程都执行完毕后,主线程会打印"All workers are finished. Main thread is continuing."。
04.线程状态
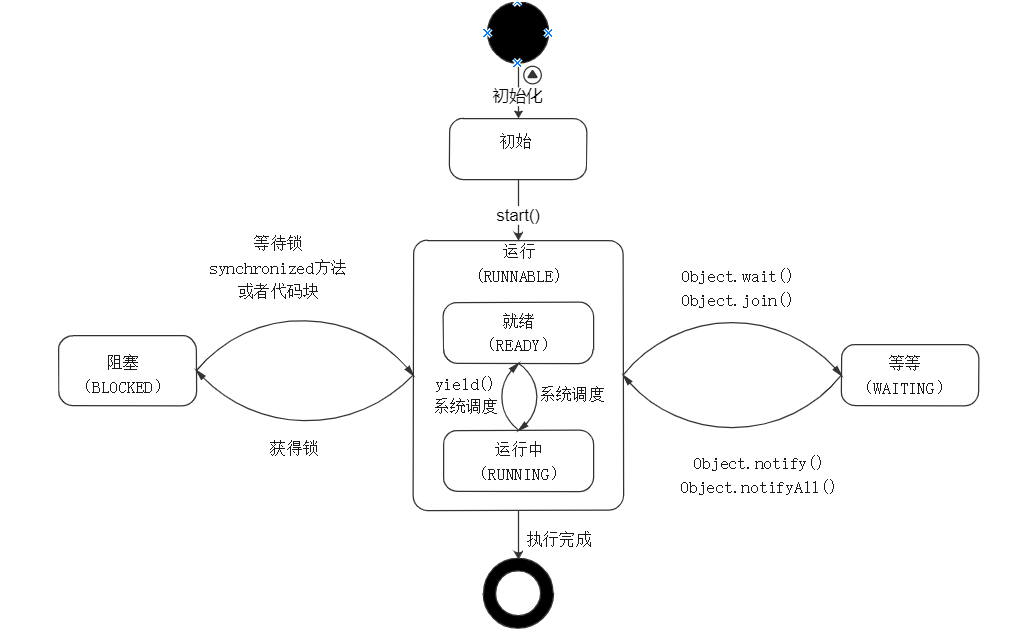
05.守护线程
在Java中,守护线程(Daemon Thread)是一种特殊的线程,它的主要特点是:当JVM中不存在任何非守护线程(即用户线程)时,JVM会自动退出,不会等待守护线程执行完毕。守护线程通常用于为其他线程或系统提供服务,如垃圾回收线程、后台日志记录线程等。
要创建一个守护线程,可以通过调用Thread对象的setDaemon(true)方法来实现

1 public class DaemonThreadExample { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Thread userThread = new Thread(new UserTask(), "UserThread"); 4 Thread daemonThread = new Thread(new DaemonTask(), "DaemonThread"); 5 6 // 将daemonThread设置为守护线程 7 daemonThread.setDaemon(true); 8 9 userThread.start(); 10 daemonThread.start(); 11 12 // 主线程虽然执行完毕,但是程序不会退出,直到用户线程执行完毕才会退出,并不会等待守护线程执行完毕 13 System.out.println("Main thread is exiting..."); 14 } 15 16 static class UserTask implements Runnable { 17 @Override 18 public void run() { 19 try { 20 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running..."); 22 Thread.sleep(1000); 23 } 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is finished."); 28 } 29 } 30 31 static class DaemonTask implements Runnable { 32 @Override 33 public void run() { 34 try { 35 while (true) { 36 //一直在这里守护你,你不走,我不走 37 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running in the background..."); 38 Thread.sleep(500); 39 } 40 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号