2.2数据结构
1.链表
1)单链表:邻接表
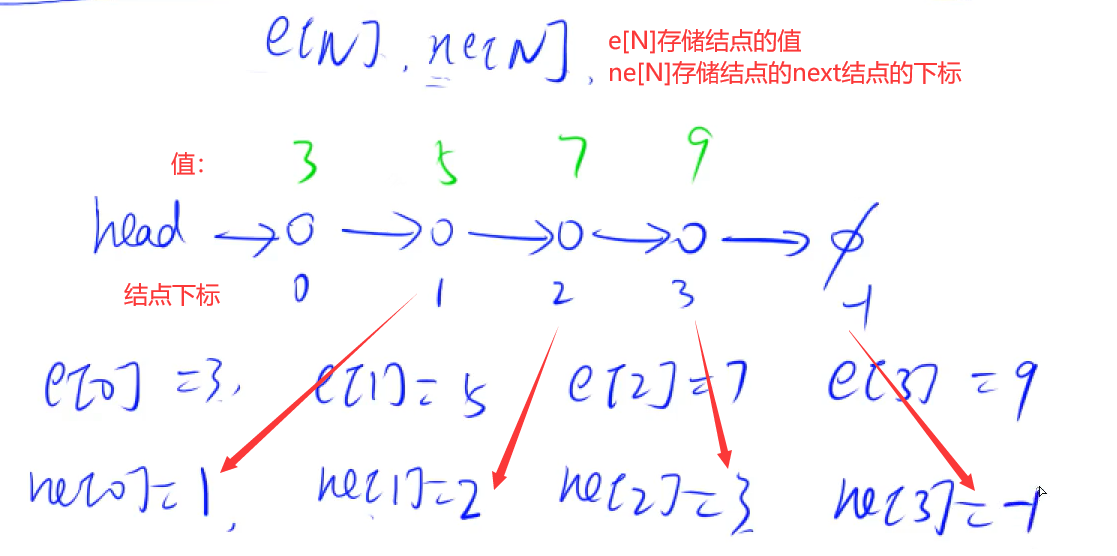
数组实现单链表:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
//e[N]存储数组
//ne[N]存储每个数的下一个数的下标
//head表示头结点,指向第一个点
//idx表示下一个要存储的点是第idx+1个点
int e[N] , ne[N] , head , idx;
//初始化,head指向空,下一个要输入的是第1个点
void init(){
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
//在链表头处插入值为x的点
void add_to_head(int x){
e[idx] = x;//在e中存入第idx-1个点为x
ne[idx] = head;//该点的下一个点为原来的head头结点表示的点
head = idx;
idx++;
}
//在第k个插入的点后面插入x
void add(int k , int x){
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx;
idx++;
}
//删除第k+2个插入的数
void remove(int k){
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
int main()
{
init();
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
while (m -- ){
char r;
int k,x;
cin>>r;
if(r=='H'){
scanf("%d", &x);
add_to_head(x);
}
else if(r=='D'){
scanf("%d", &x);
if(!x) head = ne[head];
else remove(x-1);
}
else{
scanf("%d%d", &k, &x);
add(k-1,x);
}
}
for(int i = head ; i!=-1 ; i = ne[i]) cout<<e[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
2)双链表:优化某些问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int e[N], r[N] , l[N] ,idx;
int m;
void init(){
r[0] = 1;
l[1] = 0;
idx = 2;
}
void add(int k , int x){
e[idx] = x;
l[idx] = k;
r[idx] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = idx;
r[k] = idx;
idx++;
}
void remove(int k){
r[l[k]] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = l[k];
}
int main(){
init();
scanf("%d" , &m);
while(m--){
int k,x;
string c;
cin>>c;
if(c=="L"){
scanf("%d" , &x);
add(0,x);
}
else if(c=="R"){
scanf("%d" , &x);
add(l[1],x);
}
else if(c=="D"){
scanf("%d" , &k);
remove(k+1);
}
else if(c=="IL"){
scanf("%d%d" , &k ,&x);
add(l[k+1],x);
}
else{
scanf("%d%d" , &k ,&x);
add(k+1,x);
}
}
for(int i = r[0] ; i!=1; i = r[i]) printf("%d " , e[i]);
return 0;
}
3.模拟栈
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int stk[N] , tt ;
void push(int x){
stk[++tt] = x;
}
void pop(){
tt--;
}
void empty(){
if(tt==0) cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
void query(){
cout<<stk[tt]<<endl;
}
int main(){
int m;
cin>>m;
while(m--){
int x;
string p;
cin>>p;
if(p=="push"){
scanf("%d" , &x);
push(x);
}
else if(p=="pop"){
pop();
}
else if(p=="empty"){
empty();
}
else{
query();
}
}
return 0;
}
4.模拟队列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int stk[N] ,ss, tt=-1 ;
void push(int x){
stk[++tt] = x;
}
void pop(){
ss++;
}
void empty(){
if(tt<ss) cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
void query(){
cout<<stk[ss]<<endl;
}
int main(){
int m;
cin>>m;
while(m--){
int x;
string p;
cin>>p;
if(p=="push"){
scanf("%d" , &x);
push(x);
}
else if(p=="pop"){
pop();
}
else if(p=="empty"){
empty();
}
else{
query();
}
}
return 0;
}
5.单调栈
创建一个单调的栈
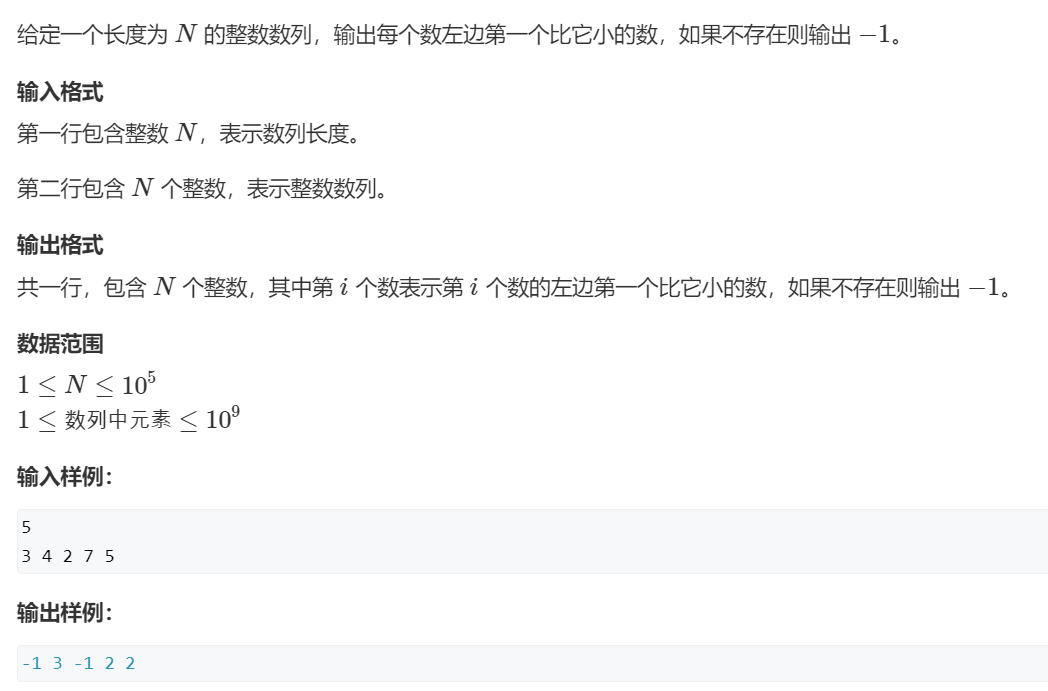
这题主要是找关系,只要之前存在比后面某数大的数字,这个数就绝对不会再被使用了,我们就得到了一个单调递增的数列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int stk[N] , tt;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
int x;
scanf("%d" , &x);
while(tt and stk[tt]>=x) tt--;
if(tt==0) cout<<-1<<" ";
else cout<<stk[tt]<<" ";
stk[++tt] = x;
}
return 0;
}
6.单调队列(典型题目:滑动窗口)
还是主要是找关系,创建一个单调的数组
(找个样例,实际题目是输出最小和最大):

代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int a[N] , q[N] ;
int n,k;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d" , &n, &k);
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) scanf("%d" , &a[i]);
int hh = 0 , tt = -1;//hh是q中存储的最左边的点的下标,tt是q中存储的最右边的点的下标
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if(hh<=tt and i-k+1>q[hh]) hh++;//判断是否头部已滑出
while(hh<=tt and a[q[tt]]>=a[i]) tt--;//删除尾部较大的数
q[++tt] = i;//读入i
if(i>=k-1) printf("%d " , a[q[hh]]);//只有i>=k-1才用输出
}
cout<<endl;
hh = 0 , tt = -1;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
if(hh<=tt and i-k+1>q[hh]) hh++;
while(hh<=tt and a[q[tt]]<=a[i]) tt--;
q[++tt] = i;
if(i>=k-1) printf("%d " , a[q[hh]]);
}
return 0;
}
7.kmp算法
很好的教程地址:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/discussion/content/1604/
先创建一个next数组,每个下标 i 存放的 j 表示存放每个数之前最大的前 j 个数等于后 j 个数
然后进行 s 数组的遍历
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010 ,M = 1000010;
char s[M] , p[N];
int ne[M] , n , m;
int main(){
cin>>n>>p+1>>m>>s+1;
//计算ne数组
for(int i = 2 , j = 0 ; i <= n ; i++){//一定不要忘了等于
while(j and p[i]!= p[j+1]) j = ne[j];//
if(p[i]==p[j+1]) j++;
ne[i] = j;
}
for(int i = 1 , j = 0 ; i <= m ; i++){//也不要忘了等于
while(j and s[i]!=p[j+1]) j = ne[j];
if(s[i]==p[j+1]) j++;
if(j==n) printf("%d " , i-n) , j = ne[j];
}
return 0;
}
这个 s + 1 和 p + 1表示从下标是 1 开始读入。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号