1.7类、结构体、指针与引用
1.类的定义
在类的大括号后面要加分号。
private:加私有的变量,方法等
public:加公开的变量方法等
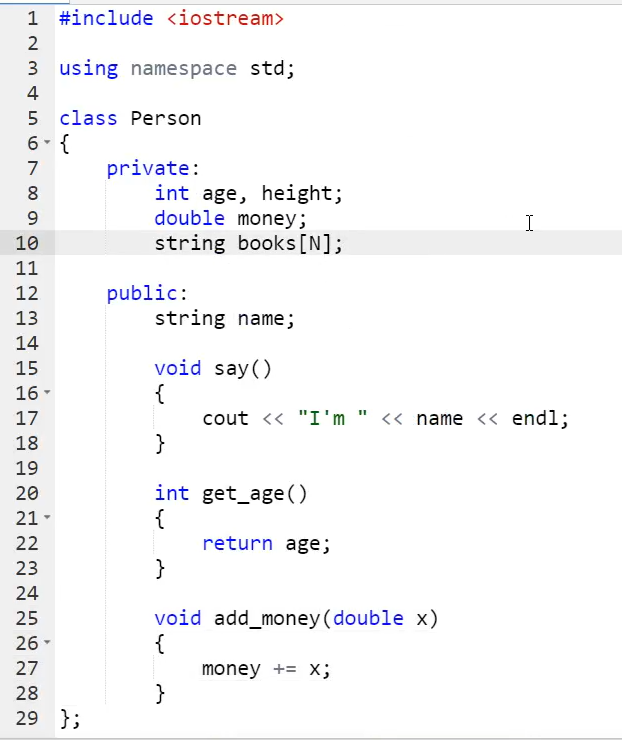
类的调用:直接写类的名字就行

2.结构体和类
在类中没有声明是private还是public则默认为private,class count
在结构体中默认为pubic,struct count

3.结构体构造函数
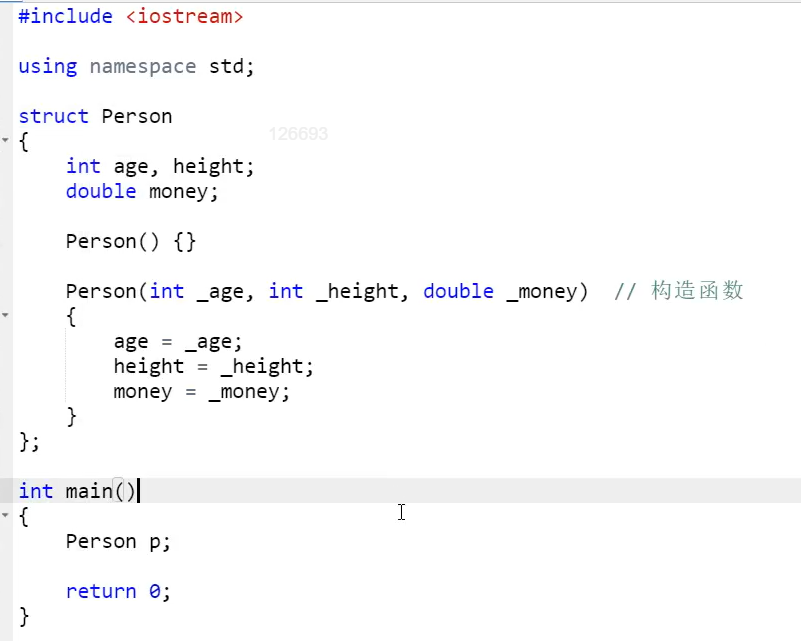
另一种更快的写法:

不加分号
4.指针和引用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char m,n;
int main(){
char a = 's',b;
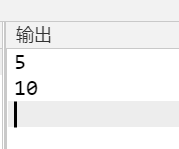
cout<<(void*)&a<<endl;
cout<<(void*)&b<<endl;
cout<<(void*)&m<<endl;
cout<<(void*)&n<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
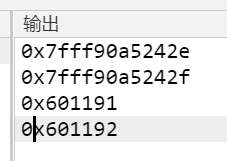
指针:
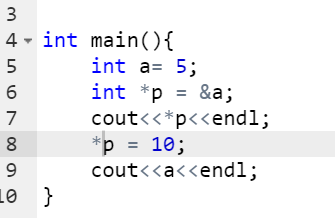
更改了*p后,a 的值也会变化
地址变化:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[5] = {0,1,2,3,4};
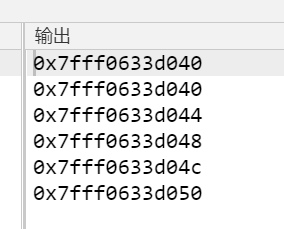
cout<<a<<endl;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) cout<<(void*)&a[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出的a是a[0]的地址,后面每个元素的地址都隔了4,因为int是4个字节
当int转为char,每个就变成隔了1
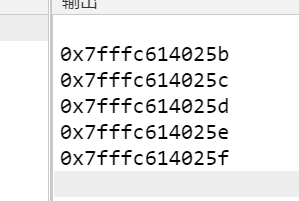
因为char是一个字节
依此类推,longlong就是相隔8
指针的用法:

指针的用法:

int &p = a就是一个p跟a存到一起,p变了a也会变,a变了p也会变,相当于是给a起了一个别名p
5.链表
struct Node{
int val;
Node* next;
Node(int _val) : val(_val),next(NULL) {}
};
int main(){
auto p = new Node(1);//Node *p = new Node(1);
auto q = new Node(2);
auto o = new Node(3);
p->next = q;
q->next = o;
}
链表用head存链表的头结点的地址,头结点指的是第一个节点的地址,而不是它的值
指针的方法用->,之前用的.(点)
遍历链表:
Node *head = p;
for(Node *i = head ; i ; i = i -> next) cout<<i->val<<endl;
链表添加第一项
Node *u = new Node(4);
u->next = p;
head = u;
链表的删除是指遍历的时候,这个点遍历不到就是删除了,跳过那个数就行,并不是真的删除
head->next = head->next->next;
(删除第二个结点)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号