vue源码分析(一)>>: props
今天记录一下研究props流程,由于工作需要,研究了几天vue实现props方式,为了看props是什么时候将驼峰命名或者羊肉串命名转化成子组件props中统一的驼峰命名的,如下图:
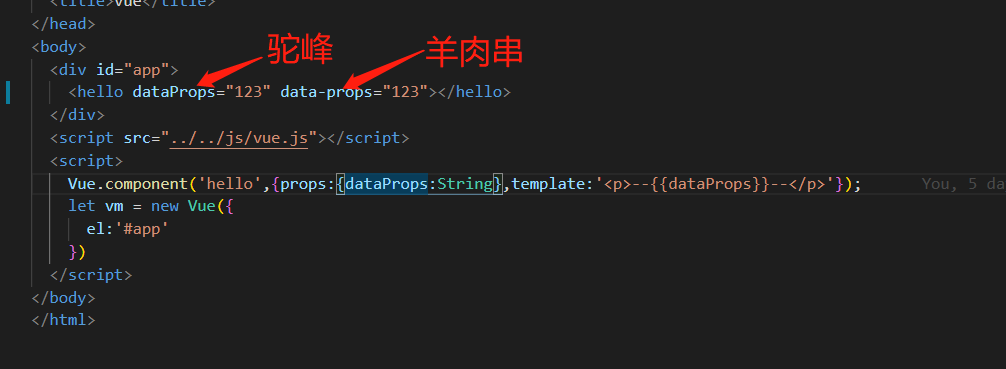
带着这个问题我一顿看呀,看到最后也没看到是什么时候转化的,因为一开始就想错了,并不是dataProps或者data-props转成dataProps了,而是子组件拿着props里边的dataProps,通过一个方法把字符串转换成data-props然后去匹配<hello>的attrs里边的属性,如果匹配到了,就将值123赋值过来,然后将<hello>attrs里边该条数据(属性)删除了 ,所以F12你会看到,渲染后p标签上还有dataProps这个属性只不过被变成dataprops了,但是data-props这个属性已经不存在了,就是这个原因。
看到这里可能有人会笑我,人家说了推荐羊肉串写法,但是驼峰也是支持的呀,官网确实是这样说的,但我测试确实驼峰不行,这怎么回事?原来文档上指的是.vue文件,就是说脚手架搭起来的项目,html里边引入vuejs这种不行。原因是.vue文件通过vue-loader编译过一遍,将dataProps编译成data-props了。
以上研究结果满足工作了,接下来将源码分析一遍,方便以后复习,也加深自己的印象。
step1:当用户声明组件时候,即Vue.component()时候,调用Vue.extend()。在这里规范了一下组件相关的东西,校验组件名字合理不合理,合并一下options,initProps$1,然后对每一个props执行proxy方法设置代理;然后对每个computed执行defineComputed给她defineProperty,这里主要看一下合并options;
function mergeOptions ( parent, child, vm ) { debugger console.log('mergeOptions :parent>> ', parent); console.log('mergeOptions :child>> ', child); console.log('mergeOptions :vm>> ', vm); { // 校验子组件的组件 checkComponents(child); } if (typeof child === 'function') { child = child.options; } // 检查props合法性 合法化props // 你用数组定义的props也会转化成对象形式 // 用非驼峰命名也会转化成驼峰命名 normalizeProps(child, vm); //格式化Inject normalizeInject(child, vm); //格式化Directives normalizeDirectives(child); // Apply extends and mixins on the child options, // but only if it is a raw options object that isn't // the result of another mergeOptions call. // Only merged options has the _base property. // 如果有_base属性,就合并继承和混入 if (!child._base) { if (child.extends) { parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.extends, vm); } if (child.mixins) { for (var i = 0, l = child.mixins.length; i < l; i++) { parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.mixins[i], vm); } } } var options = {}; var key; for (key in parent) { mergeField(key); } for (key in child) { if (!hasOwn(parent, key)) { mergeField(key); } } // 继承合并属性 function mergeField (key) { var strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat; options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key); } return options }
normalizeProps方法如下:
function normalizeProps (options, vm) { console.log('options :>> ', options); var props = options.props; if (!props) { return } var res = {}; var i, val, name; if (Array.isArray(props)) {// 是数组 i = props.length; while (i--) { val = props[i]; if (typeof val === 'string') {//必须是字符串 name = camelize(val);// 转化成驼峰 res[name] = { type: null }; } else { warn('props must be strings when using array syntax.'); } } } else if (isPlainObject(props)) {// 是对象 for (var key in props) { val = props[key]; name = camelize(key); res[name] = isPlainObject(val) ? val : { type: val };// 不是对象也转对象 } } else { warn( "Invalid value for option \"props\": expected an Array or an Object, " + "but got " + (toRawType(props)) + ".", vm ); } console.log('res :>---> ', res); options.props = res; }
就是说你还没有用组件只是创建了个组件,他会做这么多的操作。
step2:接下来再看测createElement方法,然后走_createElement方法,然后主要看createComponent方法,里面有这么一行:
// extract props 提取props var propsData = extractPropsFromVNodeData(data, Ctor, tag);
继续跟踪往下看
/* * 根据组件上的属性集合 和定义的组件内的prop集合 实现值传递 即赋值操作 */ function extractPropsFromVNodeData ( data,// 组件上的属性集合 Ctor, // 组件对象 tag // 组件名称 ) { console.log('-------------------6----------------'); // we are only extracting raw values here. // validation and default values are handled in the child // component itself. var propOptions = Ctor.options.props; if (isUndef(propOptions)) {// 是不是undefind return } var res = {}; var attrs = data.attrs; var props = data.props; if (isDef(attrs) || isDef(props)) {//是不是undefind for (var key in propOptions) { var altKey = hyphenate(key);//字符串驼峰转羊肉串 { var keyInLowerCase = key.toLowerCase();//直接大写转成小写 if ( key !== keyInLowerCase && attrs && hasOwn(attrs, keyInLowerCase) ) { tip( "Prop \"" + keyInLowerCase + "\" is passed to component " + (formatComponentName(tag || Ctor)) + ", but the declared prop name is" + " \"" + key + "\". " + "Note that HTML attributes are case-insensitive and camelCased " + "props need to use their kebab-case equivalents when using in-DOM " + "templates. You should probably use \"" + altKey + "\" instead of \"" + key + "\"." ); } } checkProp(res, props, key, altKey, true) || checkProp(res, attrs, key, altKey, false);// --- 7 } } return res }
然后再看checkProp
// 校验prop 如果定义的组件内有prop属性 赋值然后删除调用组件的属性 function checkProp ( res, hash, key, altKey, preserve ) { console.log('-------------------7----------------'); if (isDef(hash)) { if (hasOwn(hash, key)) { res[key] = hash[key]; if (!preserve) { delete hash[key]; } return true } else if (hasOwn(hash, altKey)) { res[key] = hash[altKey]; // 赋值 if (!preserve) { delete hash[altKey];// 删除 } return true } } return false }
这里就是说,实例中拿着props里边的key去调用者的attrs上匹配,先匹配正常的,找不到再去匹配转成羊肉串的,一旦匹配成功,就将值赋值过来,然后将调用者对象attrs里边关于本属性删除了
step3:然后关注initState,这里可以看到函数执行顺序,钩子函数调用;
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
。。。
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)// 初始化数据相关
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
。。。
}
然后看initState方法,先不看其他的,只关注props相关的:
export function initState (vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)// 初始化props
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm)
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}
然后进入到initPrpos方法里:这里操作的东西就多了,遍历组件props里边的属性,一个一个的赋值,并且加上getter和setter方法
function initProps (vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {
const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}
const props = vm._props = {}
// cache prop keys so that future props updates can iterate using Array
// instead of dynamic object key enumeration.
const keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []
const isRoot = !vm.$parent
// root instance props should be converted
if (!isRoot) {
toggleObserving(false)
}
// 这里的propsOptions就是vm.$options.props也就是组件里props的value
for (const key in propsOptions) {
keys.push(key)
//校验prop值 返回传过来的值 或者默认值
const value = validateProp(key, propsOptions, propsData, vm)
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
const hyphenatedKey = hyphenate(key)
if (isReservedAttribute(hyphenatedKey) ||
config.isReservedAttr(hyphenatedKey)) {
warn(
`"${hyphenatedKey}" is a reserved attribute and cannot be used as component prop.`,
vm
)
}
defineReactive(props, key, value, () => {
if (!isRoot && !isUpdatingChildComponent) {
warn(
`Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be ` +
`overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders. ` +
`Instead, use a data or computed property based on the prop's ` +
`value. Prop being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
}
})
} else {
// 添加defineProperty geter seter那一套东西
defineReactive(props, key, value)
}
// static props are already proxied on the component's prototype
// during Vue.extend(). We only need to proxy props defined at
// instantiation here.
if (!(key in vm)) {
proxy(vm, `_props`, key)
}
}
toggleObserving(true)
}
再看看valiateProp方法:
/**
* 校验prop
* key 要校验的prop的key
* propOptions 定义的props对象
* propsData 调用者传进来的props对象
* vm 组件实例对象
*/
export function validateProp (
key: string,
propOptions: Object,
propsData: Object,
vm?: Component
): any {
const prop = propOptions[key]
//判断propsData有没有key这个属性,换句话说就时组件定义的props调用者有没有传进来
const absent = !hasOwn(propsData, key)
let value = propsData[key]
// 判断定义的prop类型是不是Boolean
const booleanIndex = getTypeIndex(Boolean, prop.type)
if (booleanIndex > -1) {
// 用户也没有传值 也没有定义default值 那就给你按false整
if (absent && !hasOwn(prop, 'default')) {
value = false
} else if (value === '' || value === hyphenate(key)) {
// 传进来的值时空的, 或者 value和key转成羊肉串命名一样
// 定义prop时候还定义了其它类型
const stringIndex = getTypeIndex(String, prop.type)
if (stringIndex < 0 || booleanIndex < stringIndex) {
// 就是说 调用的地方传递了空值 (类似于checked disabled等类似);接收的地方只定义了是Boolean类型,那value就是true;或者定义了String类型但是Boolean写在了String之前,那也是true
value = true
}
}
}
// check default value
if (value === undefined) {
// 获取默认值
value = getPropDefaultValue(vm, prop, key)
// since the default value is a fresh copy,
// make sure to observe it.
const prevShouldObserve = shouldObserve
toggleObserving(true)
observe(value)
toggleObserving(prevShouldObserve)
}
if (
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
// skip validation for weex recycle-list child component props
!(__WEEX__ && isObject(value) && ('@binding' in value))
) {
assertProp(prop, key, value, vm, absent)
}
return value
}
这个流程是vue初始化时候props整体过程
最后总结一下就是:当你创建一个组件,底层会给你把组件的props属性规范化,将数组形式定义的props转化成对象形式,将非驼峰命名的转化成驼峰命名;然后创建vnode时候将调用者attrs里边对应的prop剪切到组件实例上;然后初始化状态时候,将值一个个挂载,设置默认值,添加数据劫持等操作。
over!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号