Tarjan复建
写在前面:
我 \(C_aO\) 了全™的忘干净了于是步了鱼鱼的后尘开始切黄绿DP绿蓝 \(Tarjan\) 。
哎呀呀反正肝硬化不受人待见没人看就随便写写了。
强连通分量:
这个没忘干净,当年为了写 \(2-sat\) 特意写了写,先直接存板子。
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int _ = 10010, __ = 100010;
int b[_], low[_], dfn[_], num, cnt, lian[_], s[_], top, n, m, x, y, to[__], nxt[__], h[_], tot;
bool v[_];
vector<int> kuai[_];
inline void add(int x, int y){
to[++ tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = h[x];
h[x] = tot;
return ;
}
inline void tarjan(int x){
s[++ top] = x;
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ num;
v[x] = 1;
for(int i = h[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int y = to[i];
if(! dfn[y]){
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
}
else if(v[y]){
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if(dfn[x] == low[x]){
cnt ++;
do{
kuai[cnt]. emplace_back(s[top]);
lian[s[top]] = cnt;
v[s[top]] = 0;
}while(s[top --] != x);
}
return ;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", & n, & m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){
scanf("%d%d", & x, & y);
add(x, y);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! dfn[i]){
tarjan(i);
}
}
printf("%d\n", cnt);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! v[lian[i]]){
v[lian[i]] = 1;
int cur = 0;
for(auto h : kuai[lian[i]]){
b[++ cur] = h;
}
sort(b + 1, b + cur + 1);
for(int j = 1; j <= cur; j ++){
printf("%d ", b[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
然后是板子题:
上白泽慧音:
哇哇哇好萌欸!
依旧板子,没有细节,直接拿 \(set\) 存的每个强连通分量里点的编号并且从一遍历然后没了。
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int _ = 5010, __ = 50010;
int cnt, da, lian[_], s[_], dfn[_], low[_], top, num, n, m, to[__ << 1], nxt[__ << 1], h[_], tot, x, y, op;
bool v[_];
set<int> miao[_];
inline void add(int x, int y){
to[++ tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = h[x];
h[x] = tot;
return ;
}
inline void tarjan(int x){
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ num;
s[++ top] = x;
v[x] = 1;
for(int i = h[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int y = to[i];
if(! dfn[y]){
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
}
else if(v[y]){
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if(dfn[x] == low[x]){
cnt ++;
do{
miao[cnt]. insert(s[top]);
v[s[top]] = 0;
lian[s[top]] = cnt;
}while(s[top --] != x);
da = max(da, (int)miao[cnt]. size());
}
return ;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", & n, & m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){
scanf("%d%d%d", & x, & y, & op);
add(x, y);
if(op == 2){
add(y, x);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! dfn[i]){
tarjan(i);
}
}
printf("%d\n", da);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(miao[lian[i]]. size() == da){
for(auto r : miao[lian[i]]){
printf("%d ", r);
}
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
割点:
首先割点就是顾名思义在一个连通块中把它和连着那个点的边扔了然后发现剩下的不连通了的点。
然后就是找的时候如果 \(low[y] >= dfn[x]\) 并且当前的搜索树根不是 \(x\) 那么 \(x\) 就是割点,如果根是 \(x\) ,有大于等于两个 \(y\) 满足条件那么它也是割点。
然后就是存板子。
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int _ = 100010, __ = 20010;
int x, y, tot, root, n, m, to[_ << 1], nxt[_ << 1], h[__], num, dfn[__], low[__];
set<int> cut;
inline void add(int x, int y){
to[++ tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = h[x];
h[x] = tot;
return ;
}
inline void tarjan(int x){
int r = 0;
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ num;
for(int i = h[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int y = to[i];
if(! dfn[y]){
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
if(root != x && low[y] >= dfn[x]){
cut. insert(x);
}
if(x == root){
r ++;
}
}
else{
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if(r >= 2){
cut. insert(x);
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin. tie(0), cout. tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){
cin >> x >> y;
add(x, y);
add(y, x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! dfn[i]){
root = i;
tarjan(i);
}
}
cout << cut. size() << '\n';
for(int h : cut){
cout << h << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
边双连通分量:
边双联通分量顾名思义就是边·双联通·分量,就是一个极大的没有割边的连通块。
求法就是要么跑 \(Tarjan\) 求割边的时候就顺便统计好边双连通分量;要么标记一下割边然后单独写个 \(DFS\) 统计边双连通分量。
依旧存板子。(这个是单独写一个 \(DFS\) 的)
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int _ = 500010, __ = 2000010;
int cnt, num, dfn[_], low[_], n, m, x, y, tot = 1, nxt[__ << 1], h[_], to[__ << 1];
bool v[__ << 1], c[_];
vector<int> miao[_];
inline void add(int x, int y){
to[++ tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = h[x];
h[x] = tot;
return ;
}
inline void tarjan(int x, int bfr){
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ num;
for(int i = h[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int y = to[i];
if(! dfn[y]){
tarjan(y, i);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
if(low[y] >= dfn[x]){
v[i] = v[i ^ 1] = 1;//割边。
}
}
else if(i != (bfr ^ 1)){
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
return ;
}
inline void dfs(int x){
miao[cnt]. emplace_back(x);
c[x] = 1;
for(int i = h[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int y = to[i];
if(! v[i] && ! c[y]){
dfs(y);
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin. tie(0), cout. tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){
cin >> x >> y;
add(x, y), add(y, x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! dfn[i]){
tarjan(i, 0);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! c[i]){
cnt ++;
dfs(i);
}
}
cout << cnt << '\n';
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++){
cout << miao[i]. size() << ' ';
for(int r : miao[i]){
cout << r << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
然后是板子题:
有机化学之神偶尔会做作弊
Q:有机会吗?
A:有机?不会!
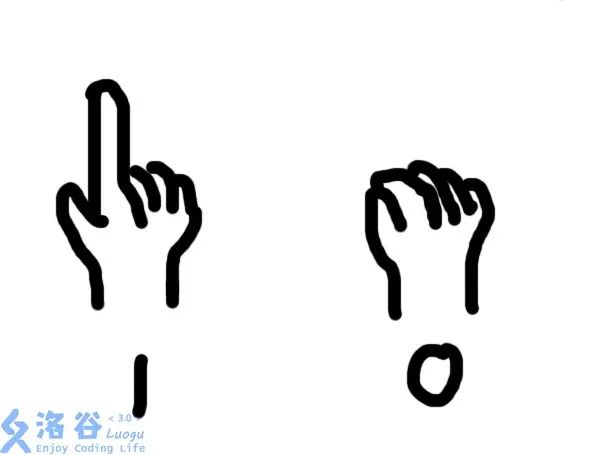
挑衅我?
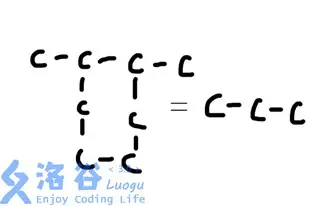
我连环C尼玛。
要用 \(map\) 判重边。(你根本不是清真的饱和烃呜呜呜…)
还要求 \(LCA\) 。
输出要转换成二进制。
很多细节………
没了。
(这个是在 \(Tarjan\) 里面算边双连通分量的)
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int _ = 1e5, __ = 1e5;
int s[_], top, nw, kuai[_], cnt, lian[_], l, dep[_], lg[_], father[_][33], tot, n, m, q, x, y, to[__ << 1], nxt[__ << 1], h[_];
bool v[__ << 1];
unordered_map<int, bool> mp[_], mm[_];
inline void add(int x, int y){
to[++ tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = h[x];
h[x] = tot;
return ;
}
void dfs(int root, int bfr){
father[root][0] = bfr;
dep[root] = dep[bfr] + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= lg[dep[root]]; i ++){
father[root][i] = father[father[root][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for(int i = h[root]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int sroot = to[i];
if(sroot != bfr){
dfs(sroot, root);
}
}
return ;
}
inline int lca(int x, int y){
if(dep[x] < dep[y]){
swap(x, y);
}
while(dep[x] > dep[y]){
x = father[x][lg[dep[x] - dep[y]] - 1];
}
if(x == y){
return x;
}
for(int i = lg[dep[x]] - 1; i >= 0; i --){
if(father[x][i] != father[y][i]){
x = father[x][i];
y = father[y][i];
}
}
return father[x][0];
}
namespace rain{
int to[__ << 1], nxt[__ << 1], h[_], tot = 1, dfn[_], low[_], num;
inline void tarjan(int x, int bfr){
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ num;
s[++ top] = x;
for(int i = h[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int y = to[i];
if(y == bfr){
continue;
}
if(! dfn[y]){
tarjan(y, x);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
}
else if(! lian[y]){
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if(low[x] == dfn[x]){
cnt ++;
while(s[top] != x){
lian[s[top --]] = cnt;
}
lian[s[top --]] = cnt;
}
return ;
}
inline void add(int x, int y){
to[++ tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = h[x];
h[x] = tot;
return ;
}
}
inline void w(int x){
if(! x){
return ;
}
w(x >> 1);
printf("%d", x & 1);
return ;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", & n, & m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){
scanf("%d%d", & x, & y);
if(x == y){
continue;
}
if(mp[x][y] && mp[y][x]){
continue;
}
mp[x][y] = mp[y][x] = 1;
rain :: add(x, y), rain :: add(y, x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! rain :: dfn[i]){
rain :: tarjan(i, 0);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
for(int j = rain :: h[i]; j; j = rain :: nxt[j]){
int k = rain :: to[j];
if(lian[i] != lian[k]){
if(! mm[lian[i]][lian[k]]){
add(lian[i], lian[k]);
add(lian[k], lian[i]);
}
mm[lian[i]][lian[k]] = mm[lian[k]][lian[i]] = 1;
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
lg[i] = lg[i - 1] + (1 << lg[i - 1] == i);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++){
if(! dep[i]){
dfs(i, 0);
}
}
scanf("%d", & q);
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i ++){
scanf("%d%d", & x, & y);
x = lian[x], y = lian[y];
l = lca(x, y);
w(dep[x] + dep[y] - (dep[l] << 1) + 1);
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
点双连通分量:
顾名思义就是点·双连通·分量,就是一个极大的没有割点的连通块。
求法就是跑 \(Tarjan\) 的时候求出割点就顺便求了,但是要注意割点会存在于多个点双连通分量中,不要忘了。
仍然存板子。
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int _ = 500010, __ = 2000010;
int root, n, m, x, y, to[__ << 1], nxt[__ << 1], h[_], tot, dfn[_], low[_], num, s[_], top, cnt;
vector<int> miao[_];
inline void add(int x, int y){
to[++ tot] = y;
nxt[tot] = h[x];
h[x] = tot;
return ;
}
inline void tarjan(int x){
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ num;
s[++ top] = x;
if(x == root && h[x] == 0){
miao[++ cnt]. emplace_back(x);
return ;
}
for(int i = h[x]; i; i = nxt[i]){
int y = to[i];
if(! dfn[y]){
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
if(dfn[x] <= low[y]){
cnt ++;
do{
miao[cnt]. emplace_back(s[top]);
}while(s[top --] != y);
miao[cnt]. emplace_back(x);
}
}
else{
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
return ;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", & n, & m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){
cin >> x >> y;
if(x != y){
add(x, y), add(y, x);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(! dfn[i]){
root = i;
tarjan(i);
}
}
printf("%d\n", cnt);
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++){
printf("%d ", miao[i]. size());
for(auto r : miao[i]){
printf("%d ", r);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
不知道不知道不知道这些长难句看的人看着怎么样反正我写高兴了嗯对…
对不起!
本文来自博客园,作者:养鸡大户肝硬化,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/rain20100708/p/19223643



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号