set
\(update2022.9.20\) 更新一个代码以便加深记忆
用处
\(set\)更多的用在可以用平衡树做的题目中,换句话说,平衡树的题用\(set\)一般都可以做。\(set\)支持查找一序列的长度、是否为空,可以随时插入、删除元素,可以查找某个点的前驱后继等。
用法
调用
\(set\)作为\(STL\),要用到专门的头文件。
#include<set>
\(set\)的调用与\(queue\)等类似:\(set<\)类型\(>\) 名称,如:
set<int> a;
注意,\(set\)中的元素不可重复,若有重复,应用\(multiset\)。
常用操作(以名称为\(a\)的\(set\)为例)
- 插入:\(a.insert(x)\),向\(a\)中插入一个元素\(x\)。
- 删除:\(a.erase(x)\),把\(a\)中所有值为\(x\)的元素全部删除。
- 查找:\(a.find(x)\),查找\(a\)中第一个值为\(x\)的元素的地址。
- 是否为空:\(a.empty()\),判断是否为空,用法与\(queue\)一样。
- 大小:\(a.size()\),返回\(a\)的大小,即元素个数。
- 前驱:\(a.upper\)_\(bound(x)\),返回第一个大于\(x\)的元素的地址。
- 后继:\(a.lower\)_\(bound(x)\),不是真正意义上的后继,是返回第一个大于等于\(x\)的元素的地址,要想求后继要将地址\(-1\)。
- 第一个值:\(a.rbegin()\),返回\(a\)中的第一个值,即最大值。
- 末一个值:\(a.end()\),返回\(a\)中的最后一个值,即最小值。
10
1 4 5 5 6 6 7 8 8 9
Now put them in a multiset 'a'
The result of *a.find(5) is 5
The result of *a.upper_bound(5) is 6
The result of *a.upper_bound(7) is 8
The result of *a.lower_bound(5) is 5
The result of *(a.lower_bound(5)--) is 4
The result of *a.lower_bound(7) is 7
The result of *(a.lower_bound(7)--) is 6
The result of *a.rbegin() is 9
The result of *a.end() is 10
Now a.erase(4) and a.erase(6)
Now...
The result of a.size() is 7
The result of *a.upper_bound(5) is 7
The result of *a.upper_bound(7) is 8
The result of *a.lower_bound(5) is 5
The result of *(a.lower_bound(5)--) is 1
The result of *a.lower_bound(7) is 7
The result of *(a.lower_bound(7)--) is 5
Now a.erase(a.find(8))
Now...
The result of a.size() is 6
例题:CF528A Glass Carving
题意
有一块长\(n\)宽\(m\)的玻璃,现进行若干次横向(\('H'\))或纵向(\('V'\))的切割,问每次切割后的得到的最大玻璃是多少。
思路
显然,切割后剩下的玻璃中,最大的那块一定是横向最长边与纵向最长边构成的,如图:
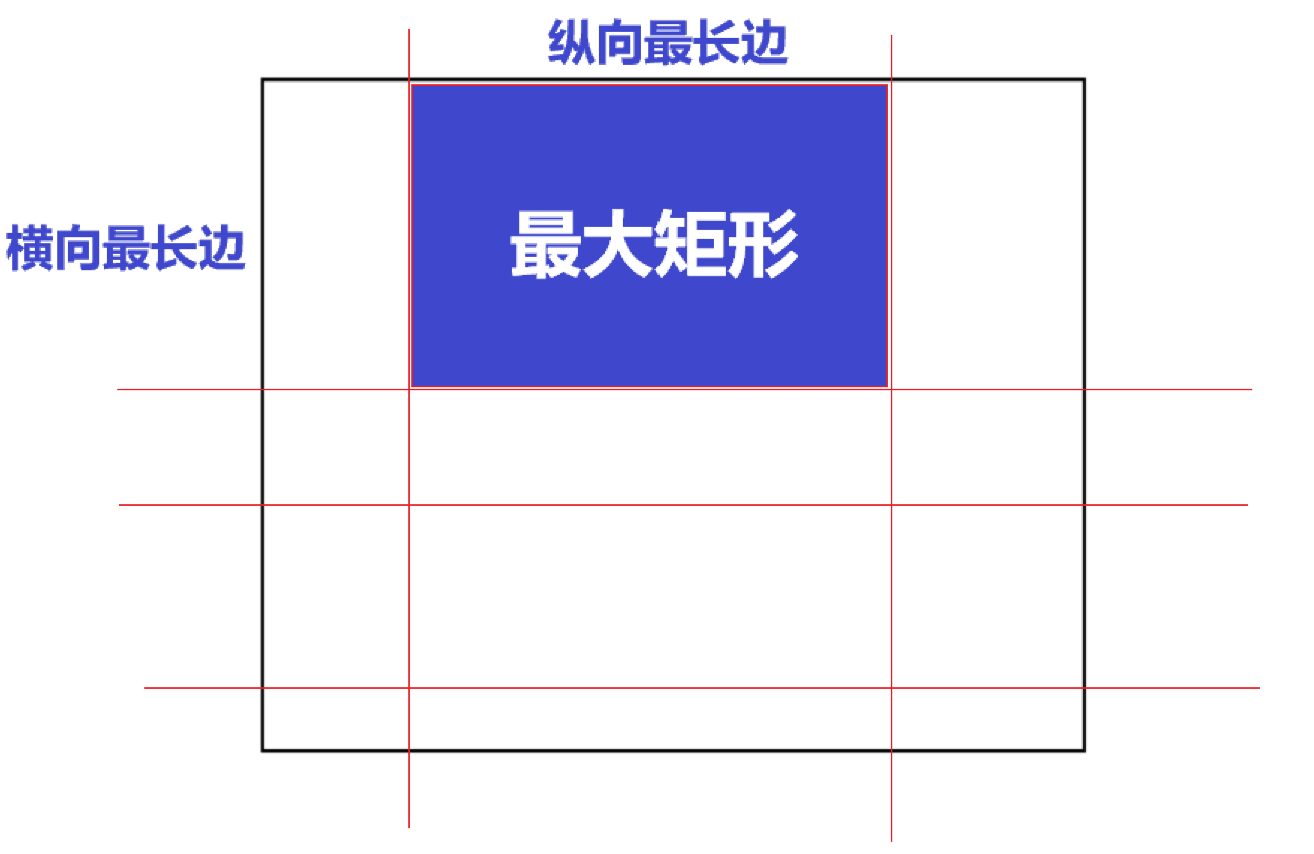
那么,我们只要在每次操作后计算横向及纵向的最大值的积即可。
注意到我们使用的数据结构应支持删除(删去被切割的边)、插入(添加新得到的两条边)、找最值(横向及纵向的最大长度)、找前驱后继(确定切割点所在边的长度及得到的边的长度)操作,很容易就能想到\(set\)。具体解释如下:
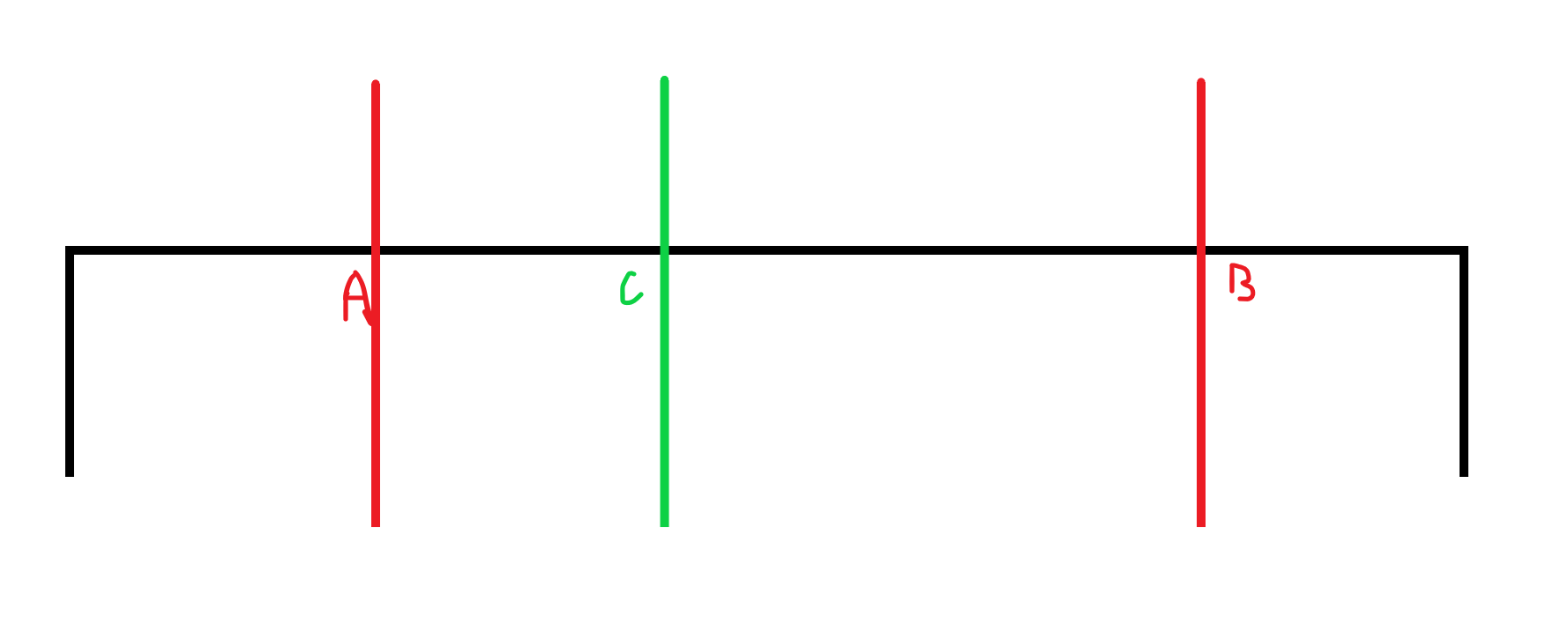
如图,红色为已切割处,当要在绿色部分切割时:对于点来说,只是新增了一个点\(C\),而对于边来说,我们要先找到点\(C\)的前驱\(A\)和后继\(B\),然后在边中减去一条长为\(AB\)的边,因为它被切割了,而插入两条长为\(AC\)和\(CB\)的边。根据这些,我们可以得出代码。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int n,m,q,x;//'V'->n 'H'->m
char opt;
set<int> point1,point2;
multiset<int> edge1,edge2;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
point1.insert(0);
point1.insert(n);
edge1.insert(n);
point2.insert(0);
point2.insert(m);
edge2.insert(m);
while(q--){
scanf("\n%c%d",&opt,&x);
if(opt=='V'){
set<int>::iterator pre=point1.upper_bound(x),nex=point1.lower_bound(x);
nex--;
edge1.insert(x-*nex);
edge1.insert(*pre-x);
edge1.erase(edge1.find(*pre-*nex));
point1.insert(x);
}else if(opt=='H'){
set<int>::iterator pre=point2.upper_bound(x),nex=point2.lower_bound(x);
nex--;
edge2.insert(x-*nex);
edge2.insert(*pre-x);
edge2.erase(edge2.find(*pre-*nex));
point2.insert(x);
}
printf("%lld\n",(long long)(*edge1.rbegin())*(*edge2.rbegin()));
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号