了解Thread类
了解Thread类
1. Thread类中的构造方法
可以给线程起名字
查看代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread( () -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello t1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}, "自定义线程");
t1.start();
}
}
2. 设置/判断 后台进程
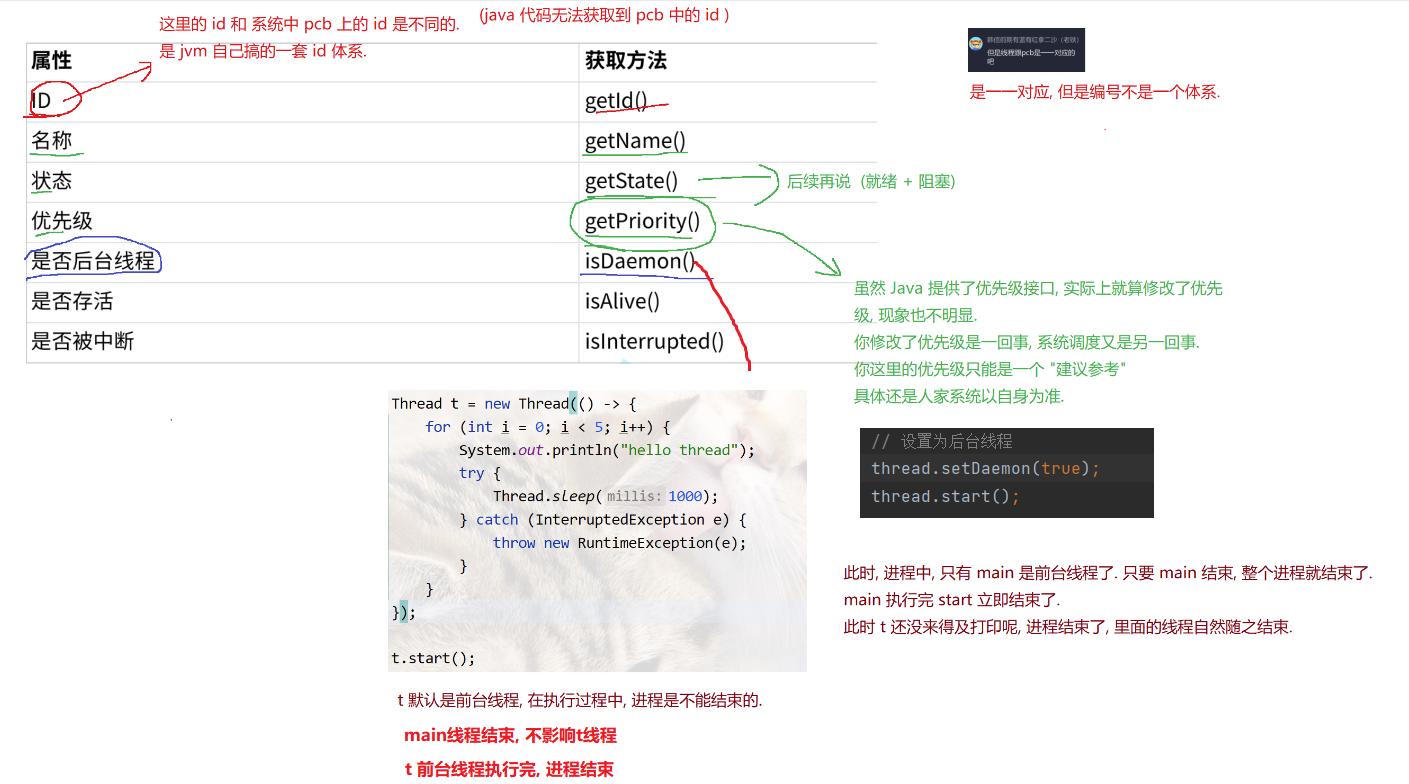
一个线程创建出来, 默认是前台线程, 所有前台线程执行完, 整个进程就结束了
后台线程不影响进程结束, 就算后台线程还没执行完, 只要前台线程执行完, 进程就结束

查看代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread( () -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello t1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}, "自定义线程");
// 把 t1线程 设置成后台线程
t1.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
}
}
3. 是否存活

查看代码
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread( () -> {
});
t.start();
// 主线程 睡1s
Thread.sleep(2000);
// 判断 t线程是否存在
// false
System.out.println(t.isAlive());
}
}
查看代码
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread( () -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
t.start();
// 主线程 睡1s
Thread.sleep(2000);
// 判断 t线程是否存在
System.out.println(t.isAlive());
}
}
4. 终止一个线程
在 java 中, 线程自己控制, 是否结束

例子1:
查看代码
class Demo10 {
private static boolean isRunning = true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (isRunning) {
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("t 线程已经结束了");
});
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 3s 之后, 主线程修改 isRunning 的值, 从而通知 t 结束.
System.out.println("控制 t 线程结束");
isRunning = false;
}
}

查看代码
class Demo10 {
// private static boolean isRunning = true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean isRunning = true;
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (isRunning) {
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("t 线程已经结束了");
});
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 3s 之后, 主线程修改 isRunning 的值, 从而通知 t 结束.
//System.out.println("控制 t 线程结束");
//isRunning = false;
}
}
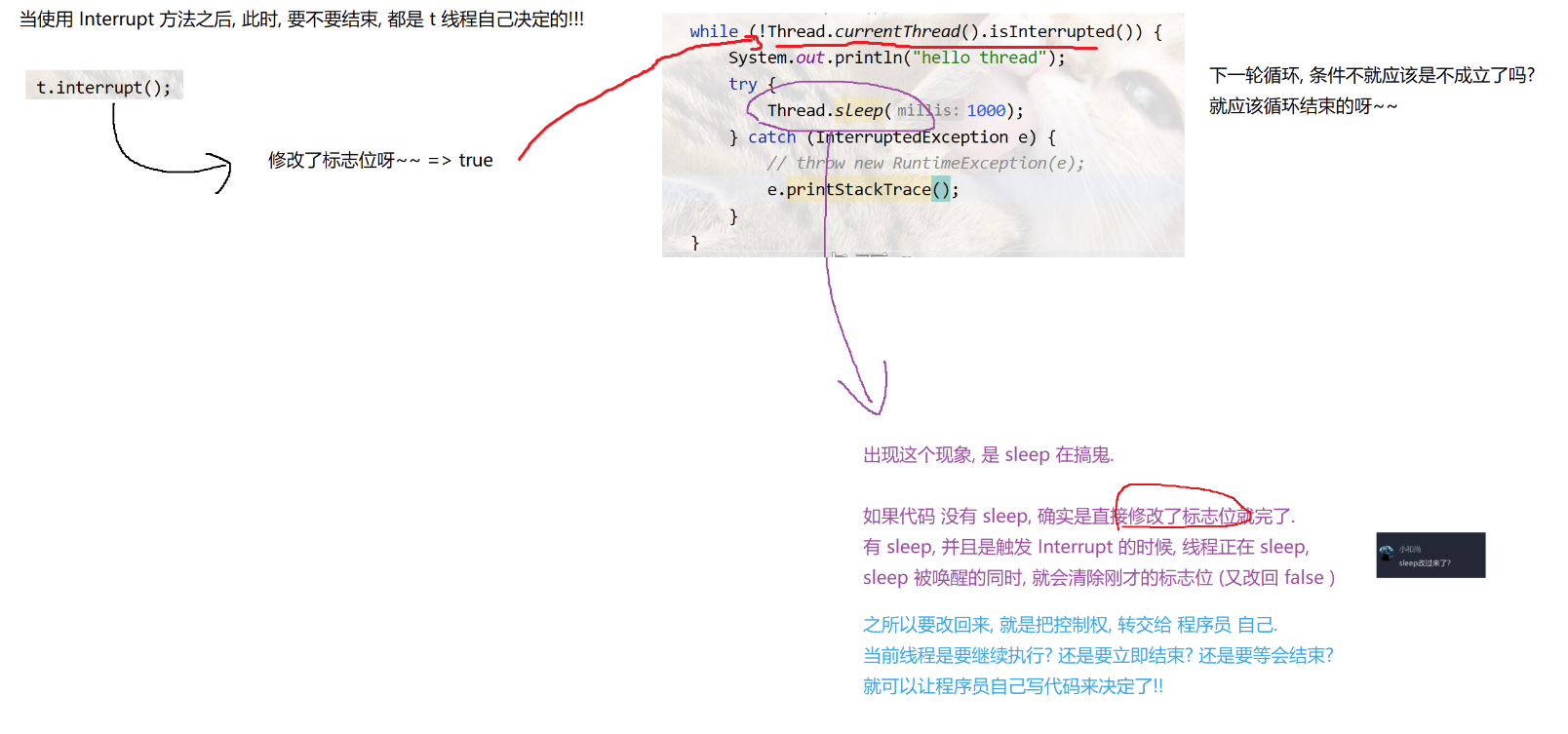
例子2:
class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread( () -> {
// 不能这么写, 因为t还未初始化
//t.isInterrupted();
// Thread.currentThread() 获取当前 线程对象t
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
// 线程休眠被打断, 标志位重新设置为true
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// 这里自己决定, 线程是继续执行,立即结束,还是等会结束
throw new RuntimeException(e);
// e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//throw new RuntimeException(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 设置标志位为true, 中断线程
t.interrupt();
}
}
5. 设置线程之间的结束顺序
多个线程之间是抢占式执行, 哪个线程先执行完,哪个线程最后执行完, 这是不确定的
通过线程等待, 确定线程结束的先后顺序
例子1:
查看代码
package demo2;
class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread( () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("thread end");
});
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// main方法内部调用 t.join(), main线程阻塞, 等待 t 线程执行完
t.join();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
例子2:
查看代码
class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("t1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("t2");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
// main 线程阻塞, 等待 t1 线程执行完
// t2线程会执行的, main 线程阻塞 不影响 t2线程执行
t1.join();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}

查看代码
class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
System.out.println("t2");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
// t1 一进来先等待 t2 结束
try {
// 这里的sleep是必要的, 因为得确保t2线程启动
//Thread.sleep(500);
// t1阻塞, 等待t2执行完
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("t1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t1.start();
//Thread.sleep(500);
t2.start();
// main 只等 t1
// main等待t1线程执行完
t1.join();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
6. 了解线程的状态

查看代码
class Demo17 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("hello");
});
System.out.println(t.getState());
t.start();
// main线程死等, 等待t线程执行完
t.join();
// t线程执行完后, 内核中pcb对象销毁
System.out.println(t.getState());
}
}


查看代码
class Demo18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
// 死等版本的 join -> waiting
//t.join();
// 有时间版本 -> time-wainting
// t.join(3600 * 1000);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号