了解包装类
1. 了解包装类
什么是包装类 ?
包装类是java提供的类 每一个基本类型都有对应的包装类
| 基本类型 | 包装类 |
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
为什么要有包装类 ?
1. 包装类是一个类类型 类中会有成员方法 使用这些方法写代码会很方便 可以提高效率
比如:字符串转整数
直接使用 包装类Integer中parseInt方法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123";
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(a);
}
}2. 为了支持泛型 基本类型无法作为参数传递给 泛型类, 所以 Java给每个基本类型都对应了一个包装类型
装箱和拆箱是什么 ?
装箱是把一个基本类型 转变为包装类型
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
Integer b = a; // 基本类型 a ——》 包装类型 b
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}拆箱是把一个包装类型 转为基本类型
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = new Integer(1);
int b = a; // Integer包装类型 ——》 int基本类型
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
装箱和拆箱的原理是什么 ?
装箱原理:调用Integer类中valueOf 方法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
Integer b = a;
Integer c = Integer.valueOf(a); // 装箱原理: 是调用ValueOf方法
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
}
}拆箱原理: 调用intValue方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = new Integer(1);
int b = a;
int c = a.intValue();
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
}证明:

如图,调用了valueOf intValue方法 证明装箱和拆箱的确是调用这两个方法实现的
自动/手动 装箱拆箱是什么 ?
如果是自己调用对应方法实现装箱拆箱操作就是手动
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 基本类型 转 包装类型
int a = 1;
Integer b = a; // 自动装箱
Integer c = Integer.valueOf(a); // 手动装箱
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
}public static void main(String[] args) {
// 包装类型 转 基本类型
Integer a = new Integer(1);
int b = a; // 自动拆箱
int c = a.intValue(); // 手动拆箱
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
}
一道包装类面试题
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = Integer.valueOf(100);
Integer b = Integer.valueOf(100);
Integer c = Integer.valueOf(200);
Integer d = Integer.valueOf(200);
System.out.println(a == b);
System.out.println(c == d);
}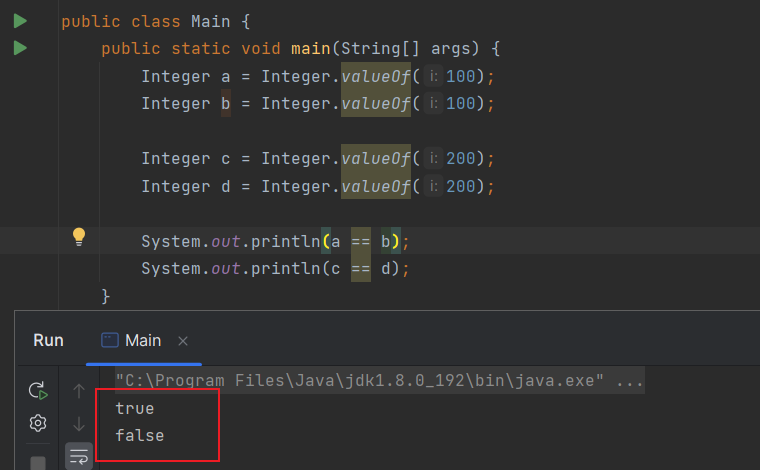
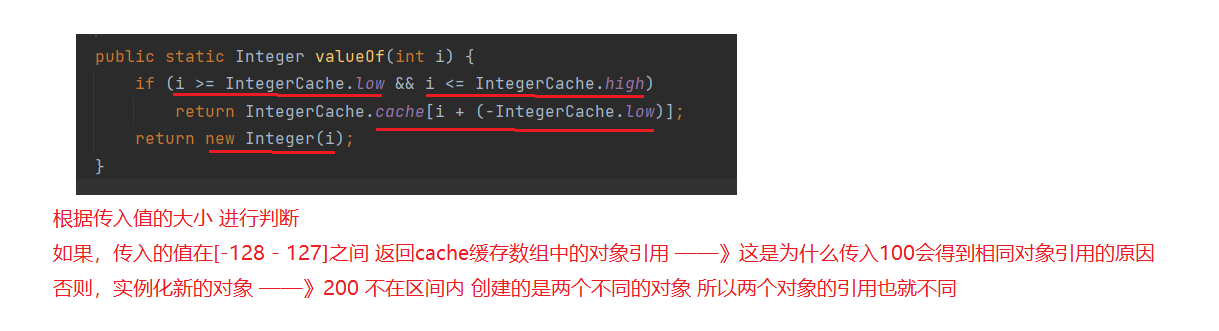
为什么 a == b 为真,c == d 为假 ?
原因在于valueOf这个方法


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号