类和对象进阶 - 多态
1. 理解多态的前提
如果要理解多态,首先需要理解以下知识点
1. 理解什么是继承关系
2. 理解什么是向上转型
3. 理解什么是重写
4. 理解什么是动态绑定
什么是继承关系在上一章中已说明 在此不多叙述
1.1 什么是向上转型
父类引用 引用子类对象,也就是父类引用存储子类对象地址
观察下面这个例子
查看代码
class Animal {
public String name;
public int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public String color;
public Dog(String name,int age, String color) {
super(name,age);
this.color = color;
}
public void barks() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在狗叫");
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog("小白",2,"白色");
Animal animal = dog;
}
}
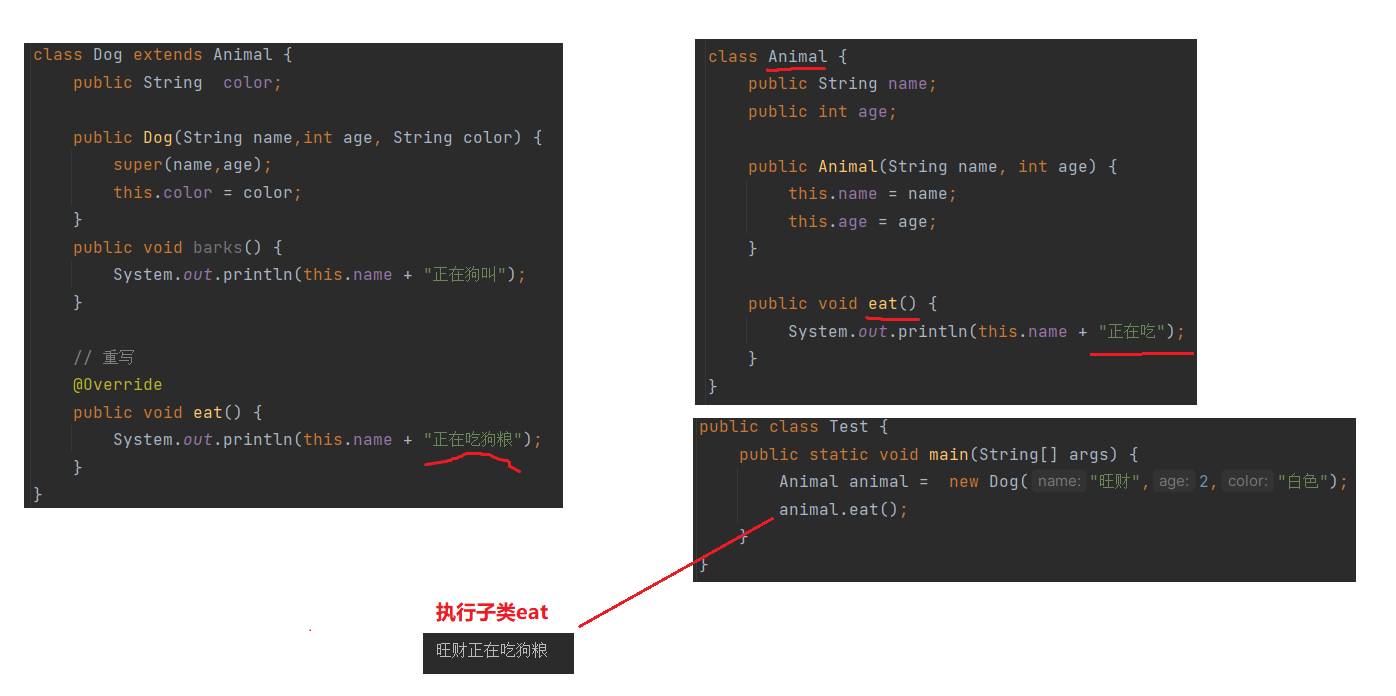
1.2 什么是重写
重写 就是在子类中重写父类中的成员方法
查看代码
class Animal {
public String name;
public int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public String color;
public Dog(String name,int age, String color) {
super(name,age);
this.color = color;
}
public void barks() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在狗叫");
}
// 重写
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Dog("旺财",2,"白色");
}
}
为什么需要重写 ? 重写有什么作用 ?
向上转型和重写都是为了发生动态绑定 执行子类方法,直接看例子
查看代码
class Animal {
public String name;
public int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public String color;
public Dog(String name,int age, String color) {
super(name,age);
this.color = color;
}
public void barks() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在狗叫");
}
// 重写
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃狗粮");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Dog("旺财",2,"白色");
animal.eat();
}
}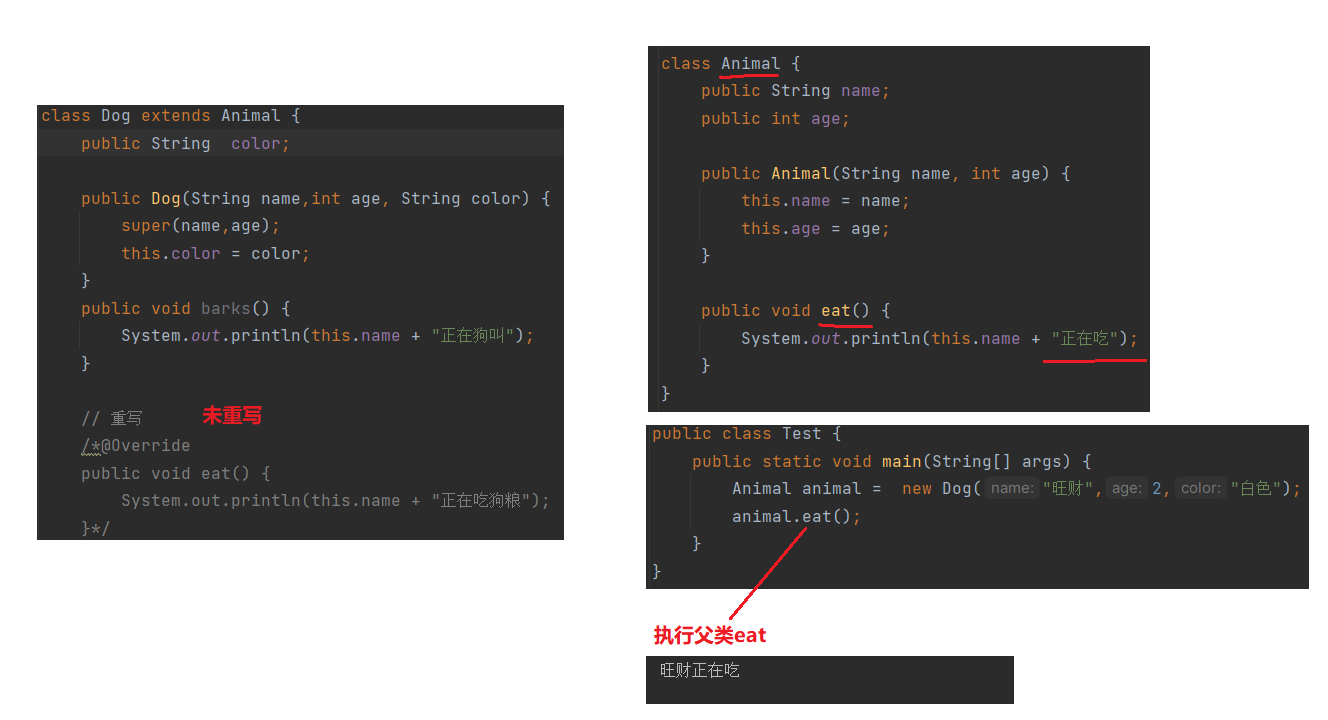
注意: animal对象虽然引用的是dog子类对象,但是animal对象的类型是Animal,只能调用Animal父类中的成员
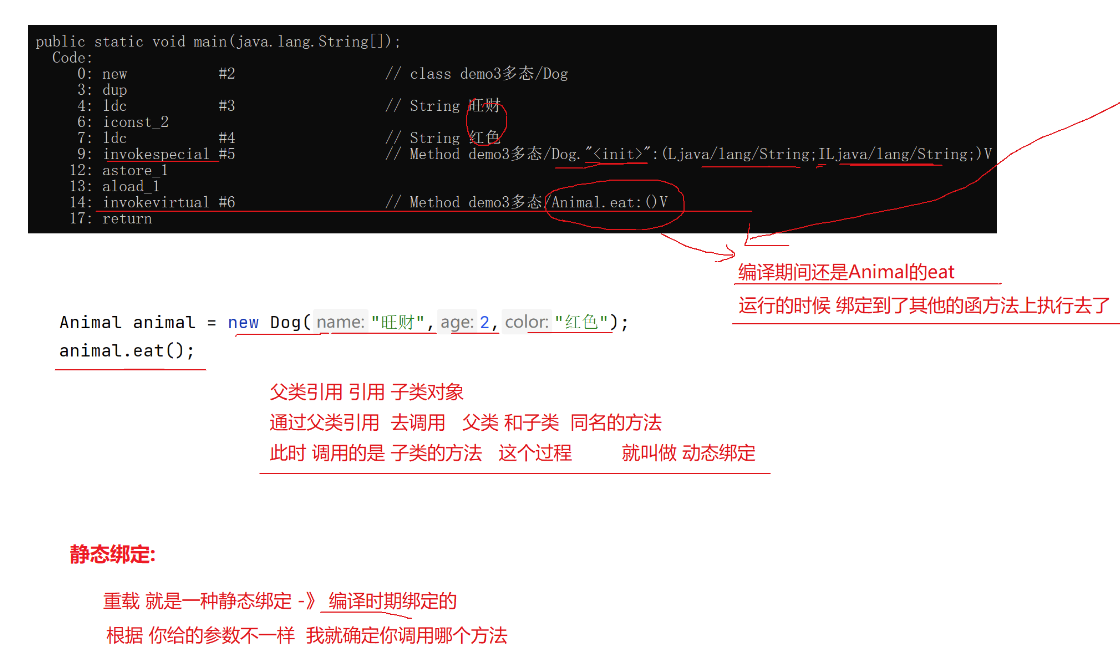
为什么在Dog子类中 重写了父类eat方法 就会去调用子类eat方法 ?
因为发生了动态绑定, 什么是动态绑定 ?
在编译的时候还是执行父类的方法 但是在实际运行时 绑定执行子类的方法
1.3 什么是多态
直接看代码来 理解多态
查看代码
class Animal {
public String name;
public int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public String color;
public Dog(String name,int age, String color) {
super(name,age);
this.color = color;
}
public void barks() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在狗叫");
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + " 正在吃狗粮");
}
}
class Bird extends Animal {
public Bird(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + " 正在吃鸟粮");
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void func(Animal animal) {
animal.eat();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog("小白",2,"白色");
Animal bird = new Bird("布谷鸟",1);
func(dog);
func(bird);
}
}
前面理解多态的前提 继承关系 向上转型 重写 动态绑定 都可以理解为 发生多态的条件
2. 重写注意点
1. 子类在重写父类的方法时,必须与父类方法原型一致: 返回值类型 方法名 (参数列表) 要完全一致
2. final static 关键字修饰的父类方法 子类不能重写
3. 重写的子类方法访问权限 一定 >= 父类方法访问权限
判断规则(public > protected > default)
private 关键字修饰的父类方法 子类不能重写
4. 父类构造方法不能被写
5. 被重写的方法返回值类型可以不同,但是必须是具有父子关系的
3. 向下转型
什么是向下转型 ? 向下转型有什么作用 ?
先来回顾向上转型,向上转型是父类引用引用子类对象 向上转型是发生多态的条件之一
此时 由于向上转型 子类对象的引用类型为父类 所以只能调用父类的成员方法 无法调用子类

如何让 在不重写的情况下 让父类引用调用子类成员方法 ?
使用向下转型 将父类引用强制转换为子类类型

查看代码
class Animal {
public String name;
public int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public String color;
public Dog(String name,int age, String color) {
super(name,age);
this.color = color;
}
public void barks() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在狗叫");
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + " 正在吃狗粮");
}
}
class Bird extends Animal {
public Bird(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + " 正在吃鸟粮");
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void func(Animal animal) {
animal.eat();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Dog("小白",2,"白色");
Dog dog = (Dog)animal;
dog.barks();
}
}
instanceof 关键字
查看代码
class Animal {
public String name;
public int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public String color;
public Dog(String name,int age, String color) {
super(name,age);
this.color = color;
}
public void barks() {
System.out.println(this.name + "正在狗叫");
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + " 正在吃狗粮");
}
}
class Bird extends Animal {
public Bird(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.name + " 正在吃鸟粮");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println(this.name + " 正在飞");
}
}
class TestDemo {
public static void func(Animal animal) {
animal.eat();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Bird("布谷鸟",1);
// instanceof 判断 animal这个对象 是否引用Bird对象
if (animal instanceof Bird) {
((Bird) animal).fly();
}
}
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号