nginx服务配置
-
特点
-
工作进程抢占机制
-
同时保持长连接和接收新的请求
-
模块体系,很多
-
lb只是用于网站
-
正向代理,代理的客户端,知道自己访问的地址
a客户端,访问谷歌
中间是一个欧美的服务器代理浏览器,从而实现访问
- 反向代理 ,代理的是服务器,不知道真实的地址
a客户端 从下载服务器上面下载rpm包,真实的包的地址在cetos官网
这个下载地址就将这个请求给centos官网了,反向代理
客户端不知道真正的地址在哪里
-
端口的映射
-
yum 安装的nginx,不支持热升级,
-
本身启动或者systemctl启动
nginx详解
1、nginx了解
1、nginx的特性
-
支持高并发
- 单机的nginx可以支持十万的并发连接,优化后还可以连接更多的
-
内存资源消耗低
- 在同级的web服务器中,nginx占用的内存的少,一万非活跃的长连接,仅消耗2.5m内存
-
高扩展性
- 支持丰富第三方模块
-
高可靠性
- nginx采用master-worker模式,如果worker出现故障,master可以快速的开启新的worker提供服务
2、nginx运行的架构
-
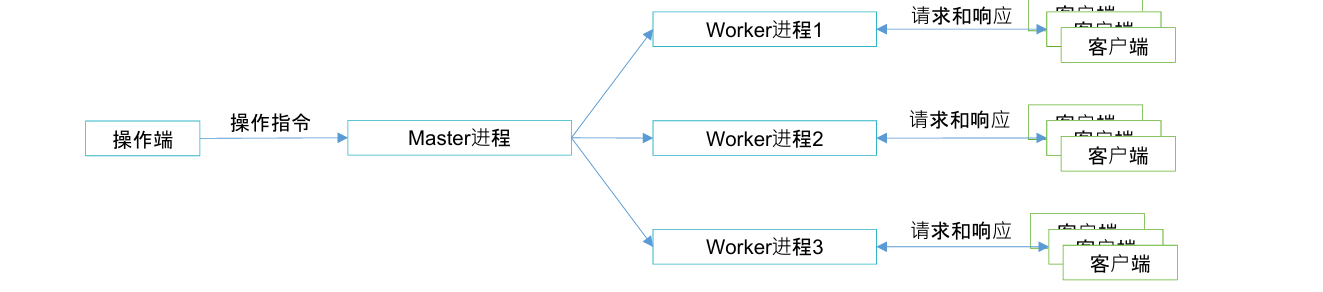
主进程:master,检查nginx配置是否正确,接收对nnginx的指令
-
工作进程:worker,处理客户端请求,接收master发来的指令,做出对应的操作
3、nginx关键工作机制
-
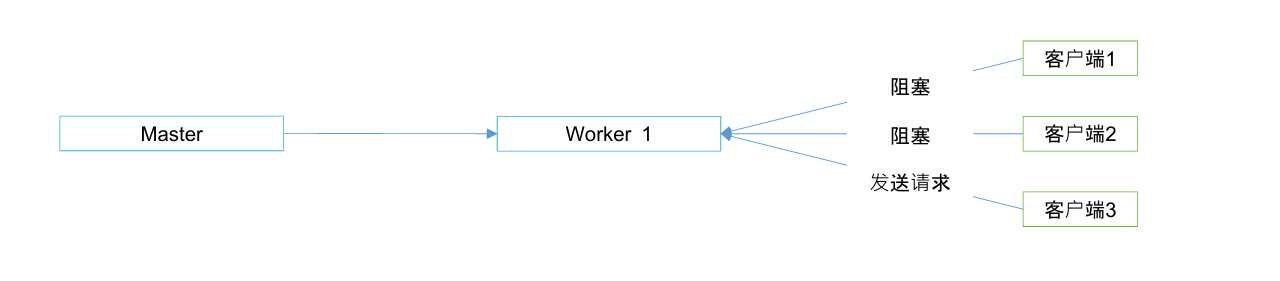
worker的抢占机制,就是工作进程会抢占请求
-
异步非阻塞处理机制,同时保持长连接和接收新的请求
4、nginx的模块体系
- lb模块适用于web服务器
5、反向代理功能
-
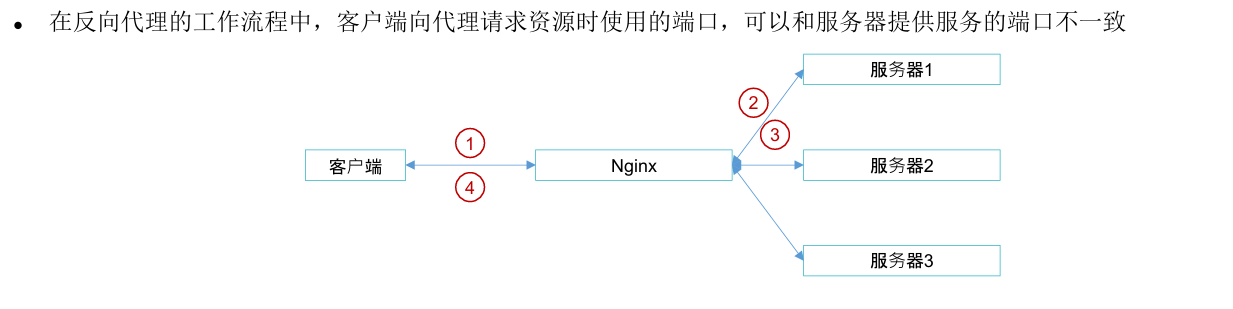
客户端反向代理的工作流程
-
客户端向nginx发送请求
-
nginx在接收到客户端请求后,将请求转发给后端服务器
-
后端服务器将客户端请求资源回复给nginx
-
nginx将资源返回给客户端
-
-
nginx反向代理通过location中的proxy_pass实现
6、负载均衡功能
-
nginx可以提供四层和七层的负载均衡
-
通过http中的upstream实现
-
算法为轮询或者权重
-
轮询会将请求发送给不同的服务器,均等的提供服务
2、nginx安装和使用的命令
1、yum安装
yum -y install nginx
2、编译安装
3、常见的命令
-
nginx -t 检查配置文件
-
nginx -v 查看nginx版本
-
nginx 启动nginx
-
nginx -s stop 强制停止nginx
-
nginx -s quit 优雅停止nginx
-
nginx restart 重启nginx
-
nginx -s reload 重新加载nginx
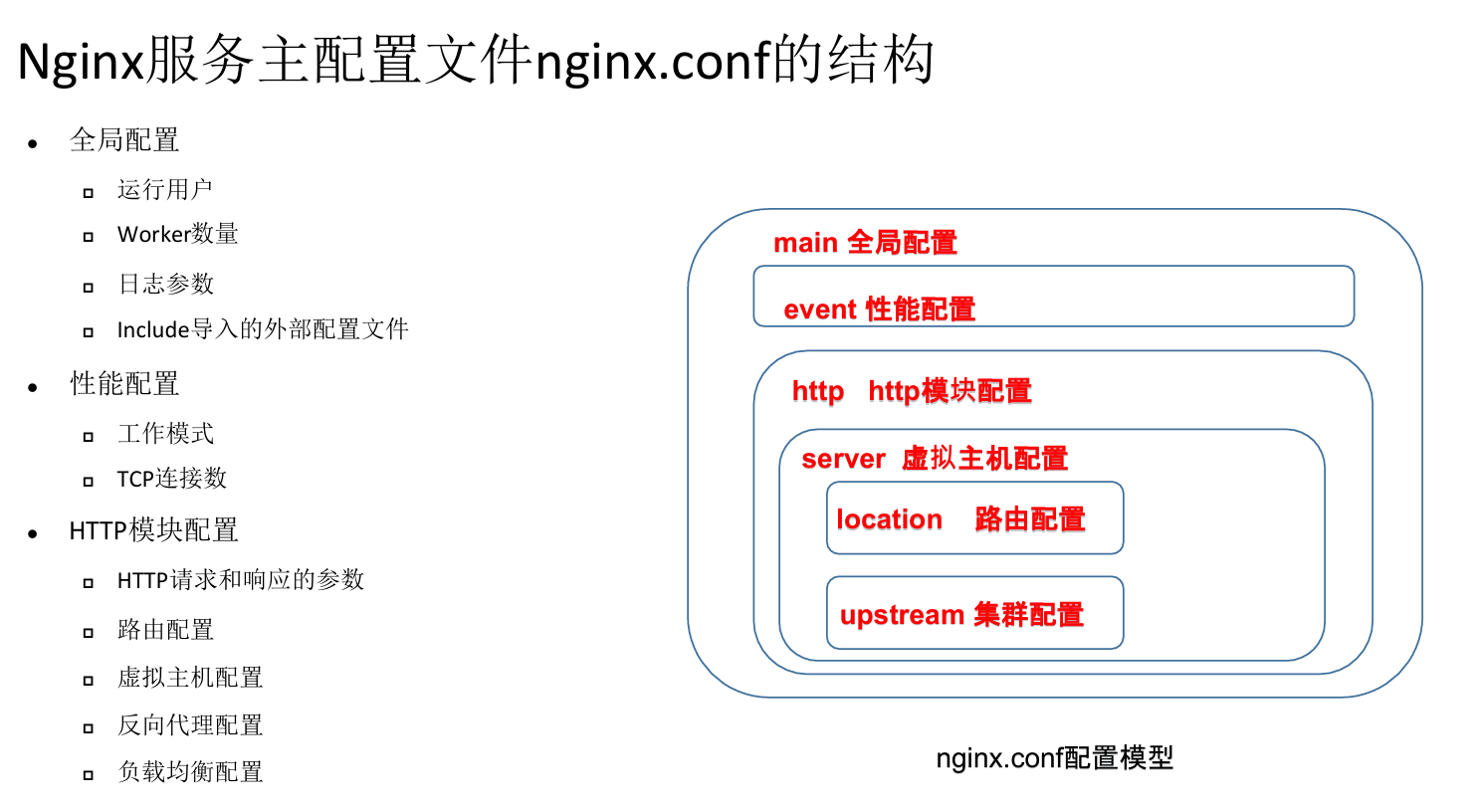
3、nginx配置文件详解
-
/etc/nginx/conf.d 为子配置文件目录
-
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf 为主配置文件
-
/etc/nginx/fastcgi_params 用来翻译nginx的变量供php识别
-
/etc/nginx/mime.types 用来配置支持的媒体文件类型
-
/etc/nginx/uwsgi_params用来翻译nginx的变量供python识别
-
/usr/share/nginx/html 为默认的nginx网站根目录
-
/var/log/nginx 为默认的nginx日志目录
1、查看主配置文件内容
- 配置文件都是 ; 结尾的,apache都是标签对的
[root@server nginx]# grep -Ev "^$|#" nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 4096;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
}
2、全局配置
-
user 设置worker进程所属用户
-
worker_processes 设置worker进程数量,这个默认是跟cpu数量一致
-
error_log 错误日志存放路径
-
pid 进程文件对应的路径
-
include 加载的功能模块路径
-
events块,主要配置服务器与用户的网络连接
- worker_connections 每个worker进程最大连接数
3、 http块
-
配置的核心,所有与http服务相关的功能都定义在这里
-
log_format 错误日志格式
-
access_log 接入日志路径
-
sendfile 启用高效文件传输,默认是开启
-
tcp_nopush 性能优化参数,对于数据是否立刻发送
-
tcp_nodelay 性能优化参数,对于小数据包是否延时发送
-
keepalive_timeout 持久连接时间或超时时间
-
gzip 启用gzip压缩
-
default_type application/octet-stream; 二进制的文件可以直接下载
4、server块
-
就是一个单独的虚拟主机,在http块中配置
-
主要就是配置网站根目录和监听端口的
-
listen 监听的端口
-
server_name 域名
-
root 网站主页存放的路径,也就是根目录
-
index 默认首页文件,按照顺序查找
-
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf 子配置文件存放路径
-
ssl_certificate 证书路径
-
ssl_certificate_key 私钥路径
-
error_page 自定义错误页面,返回给客户端页面
5、location块
-
位于server块里面,对于特定的url路径进行更加精细的配置
-
配置文件权限和目录的,用于访问控制的
-
return 返回重定向,只能写在location中的参数
-
alias 重写,url跳转到真实的网站存储位置
6、upstream块
-
定义后端服务器,用于负载均衡
-
server 后端服务器地址
-
weight 权重
-
backup 备份服务器
4、配置nginx虚拟主机
1、基于端口的配置
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
listen 81;
root /web/81;
}
server {
listen 82;
root /web/82;
}
[root@server conf.d]# ls /web/
81 82
# 访问
curl localhost:81
curl localhost:82
2、基于ip地址配置
- 127.0.0.1和本机ip地址
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
listen 81;
root /web/81;
}
server {
listen 82;
root /web/82;
}
server {
listen 127.0.0.1:80; # 基于127.0.0.1配置
root /web/web1;
}
server {
listen 192.168.50.20; # 基于ip地址配置
root /web/web2;
}
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost
web1
[root@server conf.d]# curl 192.168.50.20
web2
3、基于域名配置
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server{
listen 80;
server_name a.com;
root /web/web1;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name b.com;
root /web/web2;
}
[root@server conf.d]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.50.20 server
192.168.50.20 a.com
192.168.50.20 b.com
[root@server conf.d]# curl a.com
web1
[root@server conf.d]# curl b.com
web2
5、location配置
- 设置目录和文件访问权限的
location 修饰符 匹配模式
- 基于这个匹配的,就是匹配上了,就实现这个规则
-
= /index.html 精确匹配
-
~ .php 区分大小写,匹配php
-
~* .php 不区分大小写
-
^~pass 优先前缀匹配
-
/ 通用匹配,如果没有其他匹配,任何请求都会匹配到,都匹配
-
/url 普通的前缀匹配
-
如果url是一个目录,后面/结尾
-
root 写相对路径,完整路径就是/usr/share/nginx+location的root目录+location匹配的路径
-
alias 绝对路径,一个重写,访问url跳转到真实的网页存储文件,在location中配置
-
location 中可以开启autoindex功能,表示对访问的目录进行索引
-
proxy_pass 反向代理,转发到后端服务器
location详解和root配置
-
location就是一个匹配的url的配置,如果存在,就执行这个规定即可
-
如果后面带有斜杠的话/ 就是目录,否则就是文件
-
第一种情况,location没有root的话
- 没有root的话,继承server中的root定义的路径即可
# 网站根目录授root
# /web/123.html 其他文件路径
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /123.html {
}
}
curl loclahost
curl localhost/123.html
-
第二种情况 location中有root的情况,是相对的路径的
-
无论server中有没有root的话,就是/usr/share/nginx/location root路径/
-
但是这个是欧拉的版本,如果是centos版本的话,这个默认的路径是/usr/share/nginx/html这个目录下面
-
# 22.html路径在/usr/share/nginx/pub/22.html
# 网站的根目录在/web
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /123.html {
}
location /22.html {
root pub;
}
}
-
第三种情况,location有root的情况,是绝对路径
- 绝对路径的话,会覆盖掉这个server中的root路径
# 33.html路径在 /pub/33.html这个路径下面
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /123.html {
}
location /22.html {
root pub;
}
location /33.html {
root /pub;
}
}
- 没有写root,就继承
2、拒绝访问
- 拒绝访问/test.html
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web
location /test.html {
return 403;
}
}
- 创建test.html文件和访问
[root@server web]# echo test > test.html
[root@server web]# curl localhost/test.html
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
- 拒绝了访问,如果是拒绝所有test开头的文件呢
3、拒绝访问test开头的所有文件
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
location ^~ /test { # 拒绝以/test开头的所有文件
return 403;
}
}
# 创建了三个test文件
[root@server web]# ls
test.1 test.2 test.html
- 访问
[root@server web]# curl localhost/test.1
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@server web]# curl localhost/test.2
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@server web]# curl localhost/test.html
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
# 访问一个不存在的文件
# 返回的也是一个权限拒绝,因为是以test开头的文件
[root@server web]# curl localhost/test123
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
- 但是我访问Test呢,不会拒绝
[root@server web]# curl localhost/TESt
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
# 显示404
4、忽略大小写
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
location ~* /test {
return 403;
}
}
# 那么所有以test开头的都会被拒绝
[root@server web]# curl localhost/TESt
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
5、alias配置
-
这个是绝对路径,会覆盖掉server端的设置
-
只能在location中配置
-
这个location这个是虚拟的目录或者文件
location /请求路径/ {
alias /服务器本地路径/;
}
# 请求路径,客户端请求的url路径,/结尾的话,就是一个目录,否则是一个文件
# /服务器本地路径、 服务器实际对应的文件目录,与上面的请求路径保持一致 /结尾
1、映射目录(最常用的)
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /qq/ { # 这个可以是虚拟的,也就是不存在的即可
alias /pub/;
}
}
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost/qq/33.html
welcome 33.html
# 实际访问的是/pub/33.html这个文件
2、映射文件
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /qq/ {
alias /pub/;
}
location 66.html {
alias /pub/66.html;
}
}
# 实际访问的是/pub/66.html这个文件
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost/66.html
welcome 66.html
6、return
- 直接返回指定的响应的状态码,404,或者403,响应的内容或者重定向的地址
1、临时重定向(302,默认)
# 访问curl localhost/123.html 会自动的跳到/11.html这个文件
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /123.html {
return 302 11.html;
}
}
2、403禁止访问
# 会显示禁止访问的信息
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /123.html {
return 302 11.html;
}
location /99.html {
return 404 "forbidden:access denied \n";
}
}
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost/99.html
forbidden:access denied
3、404页面不存在
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /123.html {
return 302 11.html;
}
location /99.html {
return 404 "forbidden:access denied \n";
}
location /22.html {
return 404 "page not found\n";
}
}
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost/22.html
page not found
4、200成功
# 显示ok即可
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
listen 80;
location /123.html {
return 302 11.html;
}
location /99.html {
return 200 "ok\n";
}
location /22.html {
return 404 "page not found\n";
}
}
# 显示ok
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost/99.html
ok
7、反向代理
-
就是你访问一个网站下的/,然后我就将其代理到baidu.com,你以为我就是百度,其实不是的,只是将你的请求转发给了baidu.com
-
你是不知道真实的物理地址的
server {
listen 80;
root /www;
location / {
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com;
}
}
curl ip # 就会跳转到百度上面去
- 但是如果location中的有路径的话,就是添加到代理路径后面了
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
listen 80;
root /www;
location /index.html {
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com;
}
}
# 访问的就是baidu.com/index.html
# 因此的话,百度后面加上/,就能将index.html替换为/即可
- 带上了斜杠
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
listen 80;
root /www;
location /77.html {
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com/;
}
}
# 77.html被替换掉了
# 访问的就是 baidu.com
-
proxy_pass 带了斜杠的话,会将location中匹配的规则替换为斜杠
-
没有带斜杠的话,就会将location中匹配到的路径追加到目标地址后
6、https配置
- 只需要告诉这个证书文件在哪里就行了
[root@ceph nginx]# vim nginx.conf
server {
listen 443 ssl http2; # ssl 表示开启https访问,http2增强版
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
ssl_certificate "/etc/nginx/server.crt"; # 证书文件
ssl_certificate_key "/etc/nginx/server.key"; # 私钥文件
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
7、nginx热升级
1、热升级的原理和流程
-
所谓的热升级就是不停止服务升级nginx版本
-
低版本和高版本的能够共存一个特点就是nginx支持USR2信号
-
想要热升级nginx版本的话,nginx最好是源码包安装,而不是yum安装,yum的话,比较麻烦
-
源码安装的流程比较简单
-
下载源码包和解压
-
执行预编译 ./configure 也可以自定义安装在哪一个目录上
-
编译 make
-
编译安装 make install
-
-
热升级的流程
-
首先编译安装低版本的nginx版本,然后编译高版本的nginx
-
高版本的nginx发送一个USER2信号,低版本个高版本就能同时工作
-
新的请求转发到高版本的nginx,低版本的nginx仍然能运行,处理旧的请求
-
测试高版本的可以正常运行后,杀死低版本的进程
-
实现了无缝切换
-
2、热升级实现的过程
1、编译安装旧版本的nginx
-
nginx的下载地址 https://nginx.org/en/download.html
-
版本为1.26.1 ,升级到1.27.0
# 清理已经存在的nginx
yum remove -y nginx
-
编译安装低版本的nginx
-
编译时,需要安装c编译器,gcc或者cc,make
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.26.1.tar.gz
tar -xf nginx-1.26.1.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.26.1/
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make #安装编译环境
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx # 检查环境,生成编译规则Makefile 指定安装的目录
# 缺什么就安装指定的软件包即可
- 输出为下面就是没有错误了
Configuration summary
+ using system PCRE library
+ OpenSSL library is not used
+ using system zlib library
nginx path prefix: "/usr/local/nginx"
nginx binary file: "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
nginx modules path: "/usr/local/nginx/modules"
nginx configuration prefix: "/usr/local/nginx/conf"
nginx configuration file: "/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf"
nginx pid file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
nginx error log file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log"
nginx http access log file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log"
nginx http client request body temporary files: "client_body_temp"
nginx http proxy temporary files: "proxy_temp"
nginx http fastcgi temporary files: "fastcgi_temp"
nginx http uwsgi temporary files: "uwsgi_temp"
nginx http scgi temporary files: "scgi_temp"
# 编译源代码,生成可执行文件
# -j 指定同时编译的进程数量
[root@server nginx-1.26.1]# make -j 2
# 将编译好的文件复制到系统的指定目录
make install
2、启动旧版本的nginx
- 指定目录下有一个二进制的文件,可以启动nginx
[root@server sbin]# ./nginx
# 版本为1.26.1
[root@server sbin]# ./nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.26.1
3、下载新版本的nginx
- 下载nginx版本为1.27.0
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.27.0.tar.gz
tar -xf nginx-1.27.0.tar.gz
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx/ # 指定目录与旧版本的保持一致即可
make -j 2
# 不要执行make install 因为会覆盖掉之前的旧版本的nginx
- 找一下新版本的nginx命令在哪里,并同时备份旧版本的nginx命令
# 在objs目录下面,先不要启动,将之前的旧版本的nginx进行备份即可
[root@server nginx-1.27.0]# cd objs/
[root@server objs]# ls
autoconf.err nginx ngx_auto_config.h ngx_modules.c src
Makefile nginx.8 ngx_auto_headers.h ngx_modules.o
# 将旧版本的nginx进行备份
[root@server sbin]# cp nginx nginx.bak
[root@server sbin]# ls
nginx nginx.bak
[root@server sbin]# cp /opt/nginx-1.27.0/objs/nginx . -f
cp: overwrite './nginx'? y
- 查询nginx的进程id
[root@server sbin]# ps -aux | grep nginx
root 7671 0.0 0.0 4444 372 ? Ss 20:30 0:00 nginx: master process ./nginx
nobody 7672 0.0 0.1 5196 2624 ? S 20:30 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 10380 0.0 0.0 22096 2304 pts/1 S+ 20:40 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
-
发送一个USER2信号,对这个旧版本的nginx,发现新版本的nginx会自动的起来
-
这个信号支持旧和新版本同时存在
[root@server sbin]# kill -s USR2 7671
[root@server sbin]# ps -aux | grep nginx
root 7671 0.0 0.0 4444 1968 ? Ss 20:30 0:00 nginx: master process ./nginx
nobody 7672 0.0 0.1 5196 2624 ? S 20:30 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 10385 0.0 0.1 4448 2816 ? S 20:41 0:00 nginx: master process ./nginx
nobody 10386 0.0 0.1 5196 2684 ? S 20:41 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 10388 0.0 0.0 22096 2436 pts/1 S+ 20:41 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
- 测试新版本的nginx是否可用
[root@server nginx]# curl -I localhost
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.27.0
Date: Sat, 15 Nov 2025 12:43:19 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 615
Last-Modified: Sat, 15 Nov 2025 12:28:17 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "691871e1-267"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
- 删除旧版本的nginx,这样的话,新版本的nginx就能接收所有的请求了
[root@server nginx]# kill 7671
[root@server nginx]# ps -aux | grep nginx
root 10385 0.0 0.1 4448 2816 ? S 20:41 0:00 nginx: master process ./nginx
nobody 10386 0.0 0.1 5196 2684 ? S 20:41 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 10432 0.0 0.0 22096 2236 pts/1 S+ 20:45 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
8、yum热升级
实验
1、开启目录索引
[root@server conf.d]# cat v.conf
server {
root /web;
location /web1{
autoindex on;
}
}
# 访问
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost/web1/
<html>
<head><title>Index of /web1/</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Index of /web1/</h1><hr><pre><a href="../">../</a>
<a href="1.txt">1.txt</a> 28-Oct-2025 13:49 0
<a href="2.txt">2.txt</a> 28-Oct-2025 13:49 0
</pre><hr></body>
</html>
- 访问/web目录是没有权限的,寻找index.html没有找到,默认是没有目录浏览权限的
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.21.5</center>
</body>
</html>
- 但是访问/web下面的test.1可以访问
[root@server conf.d]# curl localhost/test.1
test
2、综合实验
-
访问一个data目录有首页文件,访问一个目录可以看到下面的内容,但是里面的以pass开头的文件任何人都访问不到,这个不能实现,需要安装扩展模块
-
但是httpd可以随便实现
3、实验3
-
默认首页文件
-
data1目录下面开启索引功能
-
dat2目录下面不允许访问
-
启动nginx的时候,默认读的是nginx.conf文件
- apache的题目,nginx也能实现
问题
-
增删改查思维
-
编译安装了,那么怎么删除了
-
停止服务
-
删除安装目录,也就是编译指定的安装目录
-



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号