HSP——队列、栈
队列
队列介绍
队列是一个有序列表,可以用数组或是链表来实现。
遵循先入先出的原则。即:先存入队列的数据,要先取出。后存入的要后取出
示意图(使用数组模拟队列示意图)

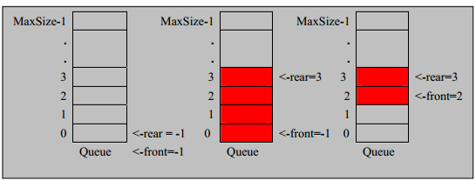
数组模拟队列思路
-
队列本身是有序列表,若使用数组的结构来存储队列的数据,则队列数组的声明如下图, 其中 maxSize 是该队 列的最大容量。
-
因为队列的输出、输入是分别从前后端来处理,因此需要两个变量 front 及 rear 分别记录队列前后端的下标, front 会随着数据输出而改变,而 rear 则是随着数据输入而改变,如图所示:
![image]()
-
当我们将数据存入队列时称为”addQueue”,addQueue 的处理需要有两个步骤:
- 思路分析
-
- 将尾指针往后移:rear+1 , 当 front == rear 【空】
-
- 若尾指针 rear 小于队列的最大下标 maxSize-1,则将数据存入 rear 所指的数组元素中,否则无法存入 数据。rear == maxSize - 1[队列满]
代码实现
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个队列
ArrayQueue arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue(3);
char key = ' ';
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):推出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列中取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0); //接受一个字符
switch (key) {
case 's':
arrayQueue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
arrayQueue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = arrayQueue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int res = arrayQueue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e': //退出
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~");
}
}
//使用数组模拟队列-编写一个ArrayQueue类
class ArrayQueue {
private int maxSize; //数组最大容量
private int front; //头
private int rear; //尾
private int[] arr; //该数据用于存放数组,模拟队列
public ArrayQueue(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
//判断队列是否为满
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == maxSize - 1;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
//添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n) {
//判断队列是否为满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满,不能加入数据!");
return;
}
rear++; //后移
arr[rear] = n;
}
//获取队列的数据,出队列
public int getQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据!");
}
front++;
return arr[front];
}
//显示队列所有数据
public void showQueue() {
//遍历
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列空,没有数据!");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
}
//显示队列的头数据
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,没有数据!");
}
return arr[front + 1];
}
}
数组模拟环形队列
对前面的数组模拟队列的优化,充分利用数组. 因此将数组看做是一个环形的。(通过取模的方式来实现即可)
分析说明
- 尾索引的下一个为头索引时表示队列满,即将队列容量空出一个作为约定,这个在做判断队列满的
时候需要注意 (rear + 1) % maxSize == front [满] - rear == front [空]
思路如下
1.front变量的含义做一个调整:front就指向队列的第一个元素,也就是说arr[front]就是队列的第一个元素。 (front的初始值为0)
2.rear变量的含义做一个调整:rear指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置。该位置空间作为一个约定。
(rear的初始值为0)
3.当队列为满的时候,(rear+1) % maxSize = front [满]
4.当队列为空的时候,rear == front [空]
5.队列中的有效的数据个数 (rear+maxSize-front) % maxSize
代码实现
public class CircleArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("测试数组模拟环形队列的案例~~~");
// 创建一个环形队列
CircleArray queue = new CircleArray(4); //说明设置 4, 其队列的有效数据最大是 3
char key = ' '; // 接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
// 输出一个菜单
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);// 接收一个字符
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输出一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g': // 取出数据
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h': // 查看队列头的数据
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e': // 退出
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~");
}
}
class CircleArray {
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public CircleArray(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
public void addQueue(int n) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满,不能添加数据!");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
public int getQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取数据");
}
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空,没有数据!");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxSize, arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
// 求出当前队列有效数据的个数
public int size() {
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空的,没有数据~~");
}
return arr[front];
}
}
栈
介绍
1) 栈的英文为(stack)
2) 栈是一个先入后出(FILO-First In Last Out)的有序列表。
3) 栈(stack)是限制线性表中元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的同一端进行的一种特殊线性表。允许插入和删 除的 一端,为变化的一端,称为栈顶(Top),另一端为固定的一端,称为栈底(Bottom)。
4) 根据栈的定义可知,最先放入栈中元素在栈底,最后放入的元素在栈顶,而删除元素刚好相反,最后放入的元 素最先删除,最先放入的元素最后删除
栈的应用场景
1) 子程序的调用:在跳往子程序前,会先将下个指令的地址存到堆栈中,直到子程序执行完后再将地址取出,以 回到原来的程序中。
2) 处理递归调用:和子程序的调用类似,只是除了储存下一个指令的地址外,也将参数、区域变量等数据存入堆 栈中。
3) 表达式的转换[中缀表达式转后缀表达式]与求值(实际解决)。
4) 二叉树的遍历。
5) 图形的深度优先(depth 一 first)搜索法。
数组模拟栈
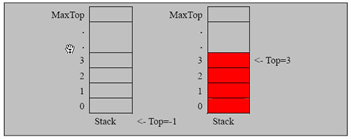
实现栈的思路分析
使用数组来模拟栈
定义一个 top 来表示栈顶,初始化 为 -1
入栈的操作,当有数据加入到栈时, top++; stack[top] = data;
出栈的操作, int value = stack[top]; top--, return value
递归
案例和图解
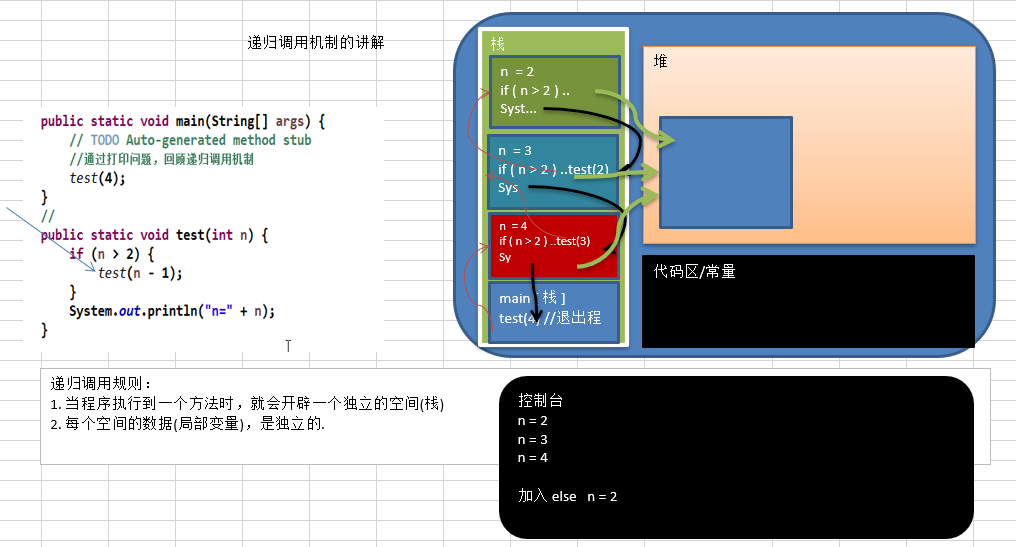
递归要遵守的重要规则
1) 执行一个方法时,就创建一个新的受保护的独立空间(栈空间)
2) 方法的局部变量是独立的,不会相互影响, 比如n变量
3) 如果方法中使用的是引用类型变量(比如数组),就会共享该引用类型的数据.
4) 递归必须向退出递归的条件逼近,否则就是无限递归,出现 StackOverflowError,死龟了:)
5) 当一个方法执行完毕,或者遇到 return,就会返回,遵守谁调用,就将结果返回给谁,同时当方法执行完毕或
者返回时,该方法也就执行完毕



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号