2025.10.20
A.
每次有效的操作大概只有两种
-
0\(\to\)010 -
101\(\to\)1
发现颜色段的奇偶性是不变的,特殊的在于边界上。
所以对于同一种奇偶性来说,可以达到的一定是一段区间。
所以我们可以倒着处理 \(L/R[0/1, 0/1, i]\) 表示 \(i\) 这个位置上为 \(1\) ,奇/偶的下界/上界。
然后从前往后贪心即可。
点击查看
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i <= ed##i; ++i)
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i >= ed##i; --i)
#define il inline
#define arr(ty, tn) std::array<ty, tn>
#define gmx(a, b) a = std::max(a, b)
#define gmn(a, b) a = std::min(a, b)
template <typename T>
void _debug(const T& t) { std::cerr << t << '\n'; }
template <typename T, typename... Args>
void _debug(const T& t, const Args&...res) { std::cerr << t << ' '; _debug(res...); }
#define debug(...) _debug(#__VA_ARGS__ " =", __VA_ARGS__)
const int LN = 2e6 + 7;
const int inf = 1e9;
typedef long long ll;
typedef std::pair<int, int> PII;
bool FIRPOS;
int n, m, L[2][2][LN], R[2][2][LN]; std::string s;
char t[LN];
bool ENDPOS;
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),
std::cin.tie(nullptr), std::cout.tie(nullptr);
int c1 = clock();
std::cin >> n >> m >> s; ++m, s = " " + s;
L[0][0][n] = L[1][0][n] = inf, R[0][0][n] = R[1][0][n] = -inf;
if (s[n] == '0') L[1][1][n] = inf, R[1][1][n] = -inf;
else L[1][1][n] = R[1][1][n] = 1;
if (s[n] == '1') L[0][1][n] = inf, R[0][1][n] = -inf;
else L[0][1][n] = R[0][1][n] = 1;
rep(i, n - 1, 1) {
L[0][0][i] = L[1][0][i] = L[0][1][i] = L[1][1][i] = inf,
R[0][0][i] = R[1][0][i] = R[0][1][i] = R[1][1][i] = -inf;
if (s[i] != '1') gmn(L[0][0][i], std::min(L[0][0][i + 1], L[1][1][i + 1] + 1)),
gmn(L[0][1][i], std::min(L[0][1][i + 1], L[1][0][i + 1] + 1)),
gmx(R[0][0][i], std::max(R[0][0][i + 1], R[1][1][i + 1] + 1)),
gmx(R[0][1][i], std::max(R[0][1][i + 1], R[1][0][i + 1] + 1));
if (s[i] != '0') gmn(L[1][0][i], std::min(L[1][0][i + 1], L[0][1][i + 1] + 1)),
gmn(L[1][1][i], std::min(L[1][1][i + 1], L[0][0][i + 1] + 1)),
gmx(R[1][0][i], std::max(R[1][0][i + 1], R[0][1][i + 1] + 1)),
gmx(R[1][1][i], std::max(R[1][1][i + 1], R[0][0][i + 1] + 1));
}
t[0] = '2';
lep(i, 1, n) {
if ((m - (t[i - 1] == '1')) & 1 and L[0][1][i] + (t[i - 1] == '1') <= m and m <= R[0][1][i] + (t[i - 1] == '1'))
t[i] = '0', m -= (t[i - 1] == '1');
else if ((m - (t[i - 1] == '1')) & 1 ^ 1 and L[0][0][i] + (t[i - 1] == '1') <= m and m <= R[0][0][i] + (t[i - 1] == '1'))
t[i] = '0', m -= (t[i - 1] == '1');
else if ((m - (t[i - 1] == '0')) & 1 and L[1][1][i] + (t[i - 1] == '0') <= m and m <= R[1][1][i] + (t[i - 1] == '0'))
t[i] = '1', m -= (t[i - 1] == '0');
else if ((m - (t[i - 1] == '0')) & 1 ^ 1 and L[1][0][i] + (t[i - 1] == '0') <= m and m <= R[1][0][i] + (t[i - 1] == '0'))
t[i] = '1', m -= (t[i - 1] == '0');
else std::cout << "-1\n", exit(0);
}
lep(i, 1, n) std::cout << t[i]; std::cout << '\n';
std::cerr << clock() - c1 << " ms " << fabs(&ENDPOS - &FIRPOS) / 1024 / 1024 << " MB\n";
return 0;
}
B
发现直接做的话限制太多,改成钦定 \(i\) 个点,权值变为 \((m-1)^i\)。
对于一个实际有 \(k\) 个合法点的方案,总权值为 \(\sum_{i=0}^k {k\choose i}(m-1)^i=m^k\) 。
然后我们就记录 \(f[u, k]\) 表示 \(u\) 子树内限制为 \(k\) 的权值和,限制指的是其祖先排列应该全部大于它。
先枚举限制的位置合并子树,然后再钦定即可。
观察上面的式子,发现只有当 \(sz_v+x\ge k\) 时左侧系数不为 \(0\) ,所以 \(sz_u\le k \le sz_u+sz_v\) 。(右侧系数同理)
使用前缀和优化转移,由树上背包的分析可知复杂度为 \(\mathcal O(n^2)\) 。
点击查看
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i <= ed##i; ++i)
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i >= ed##i; --i)
#define il inline
#define arr(ty, tn) std::array<ty, tn>
#define gmx(a, b) a = std::max(a, b)
#define gmn(a, b) a = std::min(a, b)
template <typename T>
void _debug(const T& t) { std::cerr << t << '\n'; }
template <typename T, typename... Args>
void _debug(const T& t, const Args&...res) { std::cerr << t << ' '; _debug(res...); }
#define debug(...) _debug(#__VA_ARGS__ " =", __VA_ARGS__)
const int LN = 6e3 + 7;
const int mod = 998244353;
typedef long long ll;
typedef std::pair<int, int> PII;
bool FIRPOS;
int n, m, f[LN][LN], fa[LN], sz[LN], g[LN];
int fac[LN], inv[LN];
std::vector <int> e[LN];
bool ENDPOS;
il int add(int u, int v) { return u + v >= mod ? u + v - mod : u + v; }
il void upa(int&u, int v) { u = add(u, v); }
il int mul(ll u, ll v) { return u * v >= mod ? u * v % mod : u * v; }
il void upm(int&u, int v) { u = mul(u, v); }
il int MyPow(int a, int b) { int ans = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, upm(a, a)) if (b & 1) upm(ans, a); return ans; }
il int C(int n, int m) { if (n < 0 or m < 0 or n < m) return 0; return mul(mul(fac[n], inv[m]), inv[n - m]); }
void dfs(int u) {
f[u][0] = 1;
for (int v : e[u]) {
dfs(v); std::memset(g, 0, sizeof(g));
g[0] = mul(mul(f[u][0], f[v][0]), C(sz[u] + sz[v], sz[u]));
lep(x, 1, sz[u]) upa(f[u][x], f[u][x - 1]);
lep(y, 1, sz[v]) upa(f[v][y], f[v][y - 1]);
lep(x, 1, sz[u]) lep(k, x, sz[v] + x)
upa(g[k], mul(mul(C(k - 1, x - 1), C(sz[u] + sz[v] - k, sz[u] - x)), mul(add(f[u][x], mod - f[u][x - 1]), f[v][k - x])));
lep(y, 1, sz[v]) lep(k, y, sz[u] + y)
upa(g[k], mul(mul(C(k - 1, y - 1), C(sz[u] + sz[v] - k, sz[v] - y)), mul(add(f[v][y], mod - f[v][y - 1]), f[u][k - y])));
sz[u] += sz[v];
lep(x, 0, sz[u]) f[u][x] = g[x];
} std::memset(g, 0, sizeof(g));
++sz[u];
g[0] = mul(sz[u], f[u][0]);
lep(x, 1, sz[u]) upa(f[u][x], f[u][x - 1]);
lep(x, 1, sz[u]) {
upa(g[x], mul(sz[u] - x, add(f[u][x], mod - f[u][x - 1])));
upa(g[x], mul(m - 1, f[u][x - 1]));
}
lep(x, 0, sz[u]) f[u][x] = g[x];
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),
std::cin.tie(nullptr), std::cout.tie(nullptr);
int c1 = clock();
fac[0] = 1; lep(i, 1, LN - 1) fac[i] = mul(fac[i - 1], i);
inv[LN - 1] = MyPow(fac[LN - 1], mod - 2);
rep(i, LN - 1, 1) inv[i - 1] = mul(inv[i], i);
std::cin >> n >> m;
lep(i, 2, n) std::cin >> fa[i], e[fa[i]].push_back(i);
dfs(1);
int ans = 0;
lep(i, 0, n) upa(ans, f[1][i]);
std::cout << ans << '\n';
std::cerr << clock() - c1 << " ms " << fabs(&ENDPOS - &FIRPOS) / 1024 / 1024 << " MB\n";
return 0;
}
C.
将序列下标变为 \([0, n-1]\) ,称 \(v-u=c_1\) 的为一类边,\(v-u=c_2\) 的为二类边。
将序列按照 \(\bmod c_2\) 划分等价类,二类边一定在同一个等价类中。
左端点在一个等价类中的一类边,右端点也一定在一个等价类中。
而可能存在一类边的等价类之间一定会形成若干个环,对每个环单独处理。
具体的,枚举第一行的状态,然后做轮廓线 DP 即可。
注意要根据相邻等价类 \(\bmod c_2\) 的值相对大小做一定的偏移,至多一位。
因为枚举首行,复杂度 \(\mathcal O(n2^{\frac{2n}{c_2}})\) 。
同时我们容易有一个记录前 \(c_2\) 个位的 \(\mathcal O(n2^{c_2})\) 状压 DP 。
设阈值 \(B=\sqrt {2n}\) 来平衡复杂度做到 \(\mathcal O(n2^{\sqrt{2n}})\) 。
点击查看
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i <= ed##i; ++i)
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i >= ed##i; --i)
#define il inline
#define pb push_back
#define arr(ty, tn) std::array<ty, tn>
#define gmx(a, b) a = std::max(a, b)
#define gmn(a, b) a = std::min(a, b)
template <typename T>
void _debug(const T& t) { std::cerr << t << '\n'; }
template <typename T, typename... Args>
void _debug(const T& t, const Args&...res) { std::cerr << t << ' '; _debug(res...); }
#define debug(...) _debug(#__VA_ARGS__ " =", __VA_ARGS__)
const int LN = 200 + 7;
const int LS = 1e4;
const int mod = 998244353;
typedef long long ll;
typedef std::vector <int> vec;
typedef std::pair<int, int> PII;
bool FIRPOS;
int n, m, c1, c2, f[2][1207], g[2][1200007], up, U, ans, res, len;
bool E[LN][LN], vis[LN]; vec c;
bool ENDPOS;
il int add(int u, int v) { return u + v >= mod ? u + v - mod : u + v; }
il void upa(int&u, int v) { u = add(u, v); }
il int mul(ll u, ll v) { return u * v >= mod ? u * v % mod : u * v; }
il void upm(int&u, int v) { u = mul(u, v); }
il int sel(int S, int k) { return S | (1 << k); }
il int ret(int S, int k) { return S & (U ^ (1 << k)); }
il bool ck(int S, int k) { return (S >> k) & 1; }
void dfs(int u, int T, int Q) {
if (c[0] + u * c2 >= n) {
int op = 0; std::memset(f[op], 0, sizeof(f[op])); f[op][T] = 1;
lep(k, 1, len - 1) {
if (c[k] > c[k - 1]) {
lep(i, 0, up - 1) { op ^= 1, std::memset(f[op], 0, sizeof(f[op]));
lep(S, 0, U) {
if (k == len - 1 and ck(Q, i)) upa(f[op][sel(S, i)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
else {
upa(f[op][ret(S, i)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
if (E[c[k] + i * c2][c[k - 1] + i * c2] and !ck(S, i)) upa(f[op][sel(S, i)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
if (i and E[c[k] + i * c2][c[k] + (i - 1) * c2] and !ck(S, i - 1))
upa(f[op][sel(sel(S, i), i - 1)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
}
}
}
} else {
op ^= 1, std::memset(f[op], 0, sizeof(f[op]));
lep(S, 0, U) upa(f[op][((S << 1) & U) | (Q & (k == len - 1))], f[op ^ 1][S]);
lep(i, 1, up - 1) { op ^= 1, std::memset(f[op], 0, sizeof(f[op]));
lep(S, 0, U) {
if (k == len - 1 and ck(Q, i)) upa(f[op][sel(S, i)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
else {
upa(f[op][ret(S, i)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
if (E[c[k] + i * c2][c[k - 1] + (i - 1) * c2] and !ck(S, i)) upa(f[op][sel(S, i)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
if (E[c[k] + i * c2][c[k] + (i - 1) * c2] and !ck(S, i - 1))
upa(f[op][sel(sel(S, i), i - 1)], f[op ^ 1][S]);
}
}
}
}
}
lep(S, 0, U) upa(res, f[op][S]);
return;
} dfs(u + 1, T, Q);
if (c[0] > c[len - 1] and E[c[0] + u * c2][c[len - 1] + u * c2]) dfs(u + 1, sel(T, u), sel(Q, u));
if (u and c[0] < c[len - 1] and E[c[0] + u * c2][c[len - 1] + (u - 1) * c2]) dfs(u + 1, sel(T, u), sel(Q, u - 1));
if (u and E[c[0] + (u - 1) * c2][c[0] + u * c2] and !ck(T, u - 1)) dfs(u + 1, sel(sel(T, u - 1), u), Q);
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),
std::cin.tie(nullptr), std::cout.tie(nullptr);
int c1 = clock(), u, v;
std::cin >> n >> m >> c1 >> c2;
lep(i, 1, m) std::cin >> u >> v, --u, --v, E[u][v] = E[v][u] = true;
if (c2 > std::sqrt(2 * n)) {
ans = 1;
up = (n - 1) / c2 + 2, U = (1 << up) - 1;
int nw;
lep(k, 0, c2 - 1) if (!vis[k]) { c.clear();
nw = k; while (!vis[nw]) c.pb(nw),
vis[nw] = true, nw = (nw + c1) % c2;
res = 0, len = c.size(), dfs(0, 0, 0), upm(ans, res);
}
} else { ans = 0;
U = (1 << c2) - 1; int op = 0; g[op][0] = 1;
lep(i, 0, n - 1) { op ^= 1, std::memset(g[op], 0, sizeof(g[op]));
lep(S, 0, U) {
upa(g[op][(S << 1) & U], g[op ^ 1][S]);
if (i >= c1 and E[i - c1][i] and !ck(S, c1 - 1)) upa(g[op][sel((S << 1) & U, c1) | 1], g[op ^ 1][S]);
if (i >= c2 and E[i - c2][i] and !ck(S, c2 - 1)) upa(g[op][((S << 1) & U) | 1], g[op ^ 1][S]);
}
}
lep(S, 0, U) upa(ans, g[op][S]);
}
std::cout << ans << '\n';
std::cerr << clock() - c1 << " ms " << std::fabs(&ENDPOS - &FIRPOS) / 1024 / 1024 << " MB\n";
return 0;
}
D.
将 \(w\) 向 \((u, v)\) 路径做投影交于点 \(x\) ,\(u, v, w\) 一定位于 \(x\) 的不同子树内且距离 \(x\) 的距离相等。
对于结构
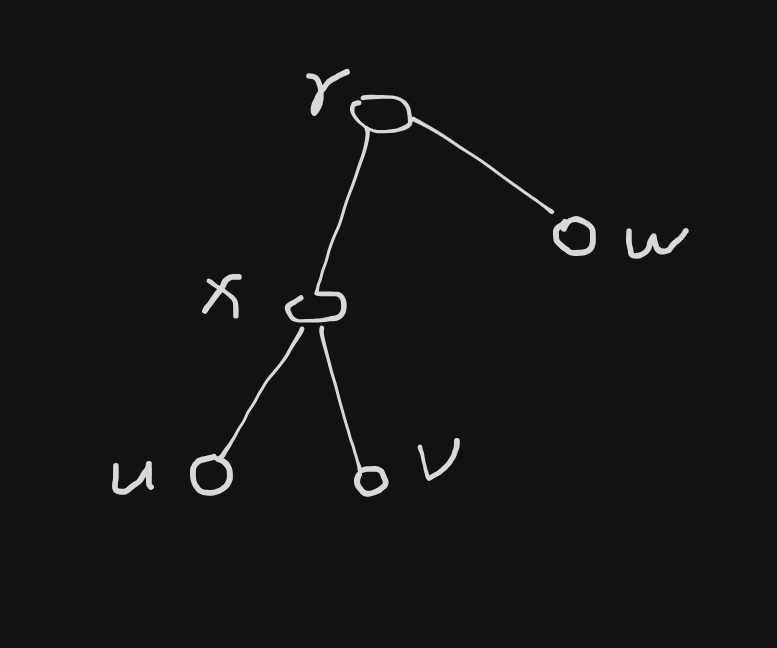
(全部在 \(x\) 子树内的情况可以看作 \(r,x\) 重合)
有 \(dep_u-dep_x=dep_x-dep_r+dep_w-dep_r\) ,移项得 \(dep_w-dep_r=dep_r-2dep_x+dep_u\) 。
有了长链剖分的形式,维护 \(g[r, k]\) 表示 \(r\) 子树内 \(dep_r-2dep_x+dep_u\) 的 \((u, v)\) 对数量。
\(g\) 在 \((u, v)\) 的 LCA \(x\) 处统计。
注意这里合并轻儿子时下标会 \(-1\) ,所以预留空间要前面一份,后面一份(留给重儿子便于继承)。
点击查看
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i <= ed##i; ++i)
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a), ed##i = (b); i >= ed##i; --i)
#define il inline
#define arr(ty, tn) std::array<ty, tn>
#define gmx(a, b) a = std::max(a, b)
#define gmn(a, b) a = std::min(a, b)
template <typename T>
void _debug(const T& t) { std::cerr << t << '\n'; }
template <typename T, typename... Args>
void _debug(const T& t, const Args&...res) { std::cerr << t << ' '; _debug(res...); }
#define debug(...) _debug(#__VA_ARGS__ " =", __VA_ARGS__)
const int LN = 4e6 + 7;
typedef long long ll;
typedef std::pair<int, int> PII;
bool FIRPOS;
int n, fa[LN], h[LN], son[LN]; ll tf[LN], *f[LN], *nf, ans, tg[LN], *g[LN], *ng;
std::vector <int> e[LN];
bool ENDPOS;
void init(int u) {
for (int v : e[u]) init(v), son[u] = h[v] > h[son[u]] ? v : son[u];
h[u] = h[son[u]] + 1;
}
void dfs(int u) {
f[u][0] = 1; if (!son[u]) return;
f[son[u]] = f[u] + 1, g[son[u]] = g[u] - 1;
dfs(son[u]);
for (int v : e[u]) if (v != son[u]) {
f[v] = nf, nf += h[v], ng += h[v], g[v] = ng, ng += h[v] + 1, dfs(v);
lep(i, 1, h[v]) ans += f[v][i - 1] * g[u][i] + f[u][i] * g[v][i + 1],
g[u][i] += f[u][i] * f[v][i - 1], f[u][i] += f[v][i - 1];
lep(i, 0, h[v]) g[u][i - 1] += g[v][i];
}
ans += g[u][0];
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),
std::cin.tie(nullptr), std::cout.tie(nullptr);
int c1 = clock(); nf = tf, ng = tg;
std::cin >> n;
lep(i, 2, n) std::cin >> fa[i], e[fa[i]].push_back(i);
init(1);
f[1] = nf, nf += h[1], ng += h[1], g[1] = ng, ng += h[1] + 1;
dfs(1);
std::cout << ans << '\n';
std::cerr << clock() - c1 << " ms " << fabs(&ENDPOS - &FIRPOS) / 1024 / 1024 << " MB\n";
return 0;
}
时间仓促,如有错误欢迎指出,欢迎在评论区讨论,如对您有帮助还请点个推荐、关注支持一下
 贪心+容斥+根号分治/轮廓线+长链剖分
贪心+容斥+根号分治/轮廓线+长链剖分

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号