Pytorch 多项式回归
一、一般的多项式回归模型:
$y=\beta_{0}+\beta_{1} x+\beta_{2} x^{2}+\beta_{3} x^{3}+\cdots+\beta_{n} x^{n}+\varepsilon$
$\left[\begin{array}{c}y_{1} \\ y_{2} \\ y_{3} \\ \vdots \\ y_{n}\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1 & x_{1} & x_{1}^{2} & \ldots & x_{1}^{m} \\ 1 & x_{2} & x_{2}^{2} & \ldots & x_{2}^{m} \\ 1 & x_{3} & x_{3}^{2} & \ldots & x_{3}^{m} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ 1 & x_{n} & x_{n}^{2} & \ldots & x_{n}^{m}\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{c}\beta_{0} \\ \beta_{1} \\ \beta_{2} \\ \vdots \\ \beta_{m}\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c}\varepsilon_{1} \\ \varepsilon_{2} \\ \varepsilon_{3} \\ \vdots \\ \varepsilon_{n}\end{array}\right]$
二、步骤及代码
因此,首先我们需要将输入 [x1, x2, ..., xn] 转变成矩阵 $\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1 & x_{1} & x_{1}^{2} & \ldots & x_{1}^{m} \\ 1 & x_{2} & x_{2}^{2} & \ldots & x_{2}^{m} \\ 1 & x_{3} & x_{3}^{2} & \ldots & x_{3}^{m} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ 1 & x_{n} & x_{n}^{2} & \ldots & x_{n}^{m}\end{array}\right]$,构造如下函数:
def make_features(x):
x = x.unsqueeze(1)
return torch.cat([x**i for i in range(0,4)],1)传入参数x是n维向量tensor([x1,x2,...,xn]),
x.unsqueeze(1):返回一个新的张量,对输入的既定位置插入一个新维度, 既定位置通过传入参数dim = n (0,1,2,...)指定。
传入参数1代表的是参数dim=1,按行unsqueeze;dim=0是按列unsqueeze
1. 当x是一个向量:
dim = 1: 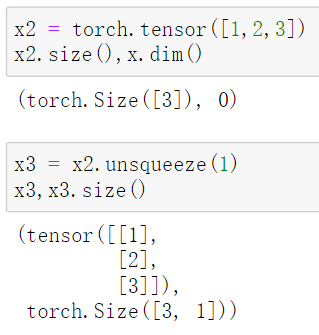 dim = 0:
dim = 0: 
dim = 2: 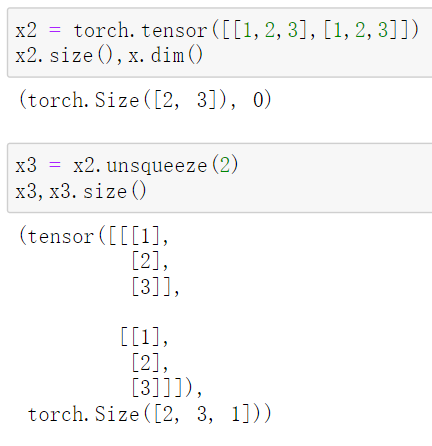
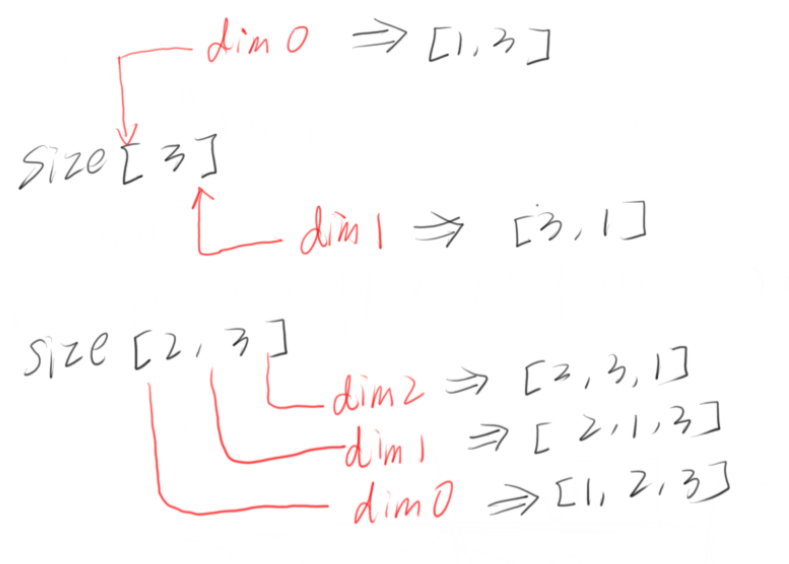
因此这个程序,就是把size[n]的tensor变成size[n,1]的tensor,之后再用torch.cat()按列连接起来。
torch.cat([x**i for i in range(0,4)],1):
x是一个tensor, x**i运算是把x里每一个数都执行**i运算。1指的是dim=1,把x**i放在列上。

定义真实的函数:
def f(x):
w_target = torch.FloatTensor([0.9,0.5,3,2.4]).unsqueeze(1)
return x.mm(w_target)其中:0.9-ε, 0.5-β1, 03-β2, 2.4-β3
x.mm(w_target) 和 x@w_target 一样,都是矩阵乘法
随机生成一些独立同分布的点:
def get_batch(batch_size=32):
random = torch.randn(batch_size)
x = make_feature(random)
y = f(x)
return x,ytorch.randn(*size, out=None):返回一个张量,包含了从标准正态分布(均值为0,方差为1,即高斯白噪声)中抽取的一组随机数。张量的形状由参数sizes定义。size是整数序列,例如torch.randn(32)就是返回size[32]的32维向量;torch.randn(2,3)返回size[2,3]的矩阵。
构建模型:
class Poly_Regression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.poly = nn.Linear(4,1)
def forward(self,x):
out = self.poly(x)
return out
实例化模型:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = Poly_Regression().cuda()
else:
model = Poly_Regression()
选择损失函数,优化器:
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.001)
训练模型:
epoch = 0
loss_val = 1
while loss_val>0.001:
batch_x, batch_y = get_batch()
pred = model(batch_x)
loss = loss_fn(pred,batch_y)
loss_val = loss.item()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch%100 == 0:
print(f'Loss: {loss_val} after {epoch} batches.')
epoch += 1
print(f'Loss: {loss_val} after {epoch} batches.')



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号