C# 新教程
C#基础
- 参考网址
- https://c.biancheng.net/csharp/data-type-conversion.html
- Hello World程序
- 新建控制台应用程序
- 输入代码:
using System;
namespace demo_gram // 命名空间声明
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
Console.ReadKey(); // 不再输出调试信息
}
}
}
-
静态static与非static- static: 类的成员 - 非static: 实例的成员 -
形参和实参在英语里面的含义
- 形参: parameter
- 实参: argument
- 再来一个实例
我们创建了一个 Rectangle 对象,用它来表示长方形,Rectangle 对象中具有 length(长)和 width(宽)两个属性。如果我们要计算长方形面积的话,则可以使用一个方法来接收 length 和 width 这两个属性的值,以此来计算这个长方形的面积
using System;
namespace c.biancheng.net {
class Rectangle { // 创建长方形类
// 成员变量
double length;
double width;
// 成员函数
public void Acceptdetails() {
length = 4.5;
width = 3.5;
}
public double GetArea() {
return length * width;
}
public void Display() {
Console.WriteLine("Length: {0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("Width: {0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("Area: {0}", GetArea());
}
}
class ExecuteRectangle { // 调用长方形类,计算最终结果
static void Main(string[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(); // 先实例化对象,然后掉用并计算结果
r.Acceptdetails();
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
- 常用快捷键
批量注释/取消注释:
- ctrl+k
- ctrl + c
- ctrl + u
- 敲for的时候, 连按两次tab键,for的循环主体就写好了
- 快速声明构造函数: ctor+tab
递归经典示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Form form = new Form();
//form.ShowDialog();
Program p = new Program();
p.PrintToX(10);
}
public void PrintToX(int x)
{
if (x == 1)
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
PrintToX(x - 1); // 不断调用自身
}
}
}
}
-
三大数据类型
-
值类型(Value types)
- 从
System.ValueType类中派生出来,例如bool,byte,char,double...... - 实例如下
namespace my_demo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("int类型的大小为{0}", sizeof(int)); // int 类型的大小为: 4 Console.ReadLine(); } } } - 从
-
引用类型(Reference types): 并不存储实际的数据值,而是存储的对数据(对象)的引用(存储的是数据在内存中的位置)
- 当多个变量都引用同一个内存地址时,如果其中一个变量改变了内存中数据的值,那么所有引用这个内存地址的变量的值都会改变- 对象类型(Object)
- 动态类型(Dynamic)
dynamic <variable_name> = value; dynamic d = 20;-
字符串类型(String)
- 两种声明方式:
""和@""
String message = "king"; @"king"; // 相当于python忠的 message = r"..." - 注意事项: 使用@""声明方式时,换行符及缩进空格等都会计算在字符串的长度之中 - 两种声明方式:
-
指针类型(Pointer types): 指针是一个变量,也称为定位器或指示符,其中可以存储另一种类型的内存地址
type* identifier; char* cptr; int* iptr;- 变量的声明
int i, j, k; double a; char b, c; float d; char d = ''; float e = 3.14, f = 1.23;namespace my_demo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //Console.WriteLine("int类型的大小为{0}", sizeof(int)); //Console.ReadLine(); short a; int b; double c; a = 10; b = 20; c = a + b; Console.WriteLine("a={0},b={1},c={2}",a,b,c); Console.ReadLine(); } } }- 接收用户输入的值--
ReadLine()函数
- 数据类型的转换
-
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double d = 5673.74;
int i;
// i = Convert.ToInt32(d); // 用这句也可以
i = (int)d;
Console.WriteLine("转换前{0},转换后{1}",d,i); // 转换前5673.74,转换后5673
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
int i = 75;
float f = 53.005f; // 声明float类型要加'f'后缀
double d = 2345.7652;
bool b = true;
Console.WriteLine(i.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(f.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(d.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(b.ToString());
- 自增运算符
i++和++i
int a = 10;
Console.WriteLine("a++的值为{0}",a++); // 10
Console.WriteLine("++a的值为{0}",++a) // 12
第一次输出 (a++) 使用的是 a 的原始值 10,然后将 a 增加到 11。
第二次输出 (++a) 先将 a 增加到 12,然后使用这个新值进行输出。
goto语句: 跳到哪个代码块,需给该代码块先取一个名称,示例(登录demo)如下
int count = 1;
login: // 代码块名称
Console.WriteLine("请输入用户名");
string username = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("请输入密码");
string password = Console.ReadLine();
if (username == "admin" && password == "123456") {
Console.WriteLine("登录成功");
} else {
count++;
if (count > 3)
{
Console.WriteLine("错误次数太多");
} else {
Console.WriteLine("用户名或密码错误");
goto login; // 跳到代码块
}
}
函数篇
void关键字: 声明该函数没有返回值
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 在主程序里面实例化并调用output函数
Program p = new Program();
p.output();
}
public void output() {
Console.WriteLine("测试,测试,测试");
}
}
}
- 传参示例,把上面的实例修改一下
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
// 传实参
p.output("测试,测试,测试");
}
// 传形参
public void output(string message) {
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
}
- 有返回值示例
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
string res = p.output("测试,测试,测试"); // 接收并打印出来
Console.WriteLine(res);
}
public string output(string message) {
return message; // 返回message
}
}
}
static关键字,声明静态方法,调用方式更加简单,不必再实例化类对象,可以直接调用
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 无需实例化,直接调用
string res = output("测试,测试,测试");
Console.WriteLine(res);
}
// 声明静态方法
static string output(string message) {
return message;
}
}
}
- 传入不定参数(数组),例如
getSum(params int[] arr)
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
string str1 = p.getSum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); // 这么传也可以
Console.WriteLine(str1);
int[] arr1 = { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 };
string str2 = p.getSum(arr1); // 传入数组
Console.WriteLine(str2);
}
public string getSum(params int[] arr) // 传入不定参数
{
int sum = 0;
string str = "";
foreach (int i in arr)
{
sum += i;
str += "+ " + i + " ";
}
str = str.Trim('+');
str += "= " + sum;
return str;
}
}
}
- 函数声明的关键字
- public
- private: 只能在类的内部,才能访问
- internal: 只要在同一"namespace"底下,就可以访问
- protected
- protected internal
public关键字实例演示
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.width = 2;
r.length = 6;
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Rectangle
{
public double width, length;
public double GetArea()
{
return width * length;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("长为{0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("宽为{0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("面积为为{0}", GetArea());
}
}
}
Private关键字演示
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
// 在Program类里面,是无法访问width和length的,因为它们是private声明的
//r.width = 2;
//r.length = 6;
r.AcceptDetails(); // 可以调用public方法
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
static string output(string message) {
return message;
}
}
class Rectangle
{
private double width, length;
public void AcceptDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入长方形的长度: ");
length = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("请输入长方形的宽度: ");
width = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
}
public double GetArea()
{
return width * length;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("长方形的长:{0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("长方形的宽:{0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("长方形的面积:{0}", GetArea());
}
}
}
internal关键字演示
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
// 可以访问
r.width = 2;
r.length = 6;
r.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Rectangle
{
// 用internal声明
internal double width, length;
double GetArea()
{
return width * length;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("长方形的长:{0}", length);
Console.WriteLine("长方形的宽:{0}", width);
Console.WriteLine("长方形的面积:{0}", GetArea());
}
}
}
ref关键字:引用传递
- 正常而言,函数中的形参和实参(命名一样)是不会相互影响的,现在如果想通过形参去改变实参,就可以通过ref标识来实现
- 这种实现方式,就称为'引用传递'
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int val = 10;
Program p = new Program();
Console.WriteLine("val的原始值为: {0}",val); // 10
p.Func(ref val); // 20 // 该函数改变了val的值,上面的实参val也会受到影响(ref的效果)
Console.WriteLine("val现在的值为: {0}", val); // 20
}
public void Func(ref int val) // 声明ref标识
{
val += val;
Console.WriteLine("函数内部的值为: {0}",val);
}
}
}
out关键字:输出传递,用法类似于ref,不同之处在于
- ref 负责函数的输入部分
- out 负责函数的输出部分
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int val = 10;
Program p = new Program();
Console.WriteLine("val的原始值为: {0}",val);
p.Func(out val); // 调用
Console.WriteLine("val现在的值为: {0}", val);
}
public void Func(out int x) // out声明
{
int temp = 11;
x = temp;
x += x;
}
}
}
- 关于
null,不能直接赋值,要加上?,示例如下
// int val = null; // 这种写法是错误的,不能直接赋值
int? val = null;
bool? val2 = null;
Console.WriteLine(val);
Console.WriteLine(val2);
Console.ReadLine();
a??b表达式解析: 如果a为null则返回b,如果a不为null则返回a
int? val = null;
int? val2 = 123;
int? val3;
val3 = val ?? val2;
Console.WriteLine(val3); // 结果为 123
Console.ReadLine();
- 上述示例修改一下,变成以下样子
int? val = 456; // 修改值
int? val2 = 123;
int? val3;
val3 = val ?? val2;
Console.WriteLine(val3); // 结果为 456
Console.ReadLine();
- 小结 a ?? b 的含义
- 若a为true,则直接返回a,无需理会b;
- 若a为false,则返回b;
数组
- 声明并赋值
int[] arr1;
double[] arr2;
arr1 = new int[10];
arr2 = new double[10];
string[] arr3 = new string[10];
arr3[0] = "a";
arr3[1] = "b";
Console.WriteLine("arr3的前两个元素值为{0}-{1}",arr3[0], arr3[1]);
Console.ReadLine();
- 最直接的声明赋值方式: int[] arr4 = {1,2,3,4,5};
- 指明数组长度: int[] arr2 = new int[10]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
- 数组长度可以省略: int[] arr2 = new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
- 注意事项:当我们创建一个数组时,C# 的编译器会根据数组类型隐式的为数组中的每个元素初始化一个默认值。例如 int 类型的数组中所有元素都会被初始化为 0。
- 实例: 遍历数组并输入每一个元素
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr1 = new int[10] { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++) {
Console.WriteLine("arr1[{0}]的值为{1}",i,arr1[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
- foreach示例
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr1 = new int[10] { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
//for (int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++) {
// Console.WriteLine("arr1[{0}]的值为{1}",i,arr1[i]);
//}
foreach (int i in arr1) {
Console.WriteLine("arr1[{0}]的值为{1}", i, arr1[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
数组常用方式演示实例
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
int[] arr1 = { 15, 33, 29, 55, 10, 11 };
int[] arr2 = new int[6];
// 数组的长度为: 6
Console.WriteLine("数组的长度为: {0}",arr1.Length);
// 排序后的数组为: 10,11,15,29,33,55
Array.Sort(arr1);
Console.WriteLine("排序后的数组为: {0}", string.Join(",",arr1));
// 值29的索引为: 3
Console.WriteLine("值29的索引为: {0}", Array.IndexOf(arr1,29));
// 拷贝以后,arr2数组为10,11,15,29,33,55
Array.Copy(arr1, arr2, arr1.Length);
Console.WriteLine("拷贝以后,arr2数组为{0}", string.Join(",",arr2));
// 反排序后的数组为: 55,33,29,15,11,10
Array.Reverse(arr1);
Console.WriteLine("反排序后的数组为: {0}", string.Join(",", arr1));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
字符串
- 声明
字符串的几种方式
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
// 显示声明
string str1 = System.String.Empty;
Console.WriteLine("str1的值为:{0}",str1);
// 隐式声明
var str2 = "测试文字";
Console.WriteLine("str2的值为:{0}", str2);
// 常量声明
const string str3 = "第三次测试文字";
Console.WriteLine("str32的值为:{0}", str3);
// 使用字符串构造函数定义字符串
char[] letters = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' };
// string[] letters = { "C","语","言"};
string message = new string(letters);
// message 的值为:Hello
Console.WriteLine("message 的值为:" + message);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
- 字符串常用方法
- 比较两个字符串是否相同
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str1 = "www.bing.com";
// string str2 = "www.bing.cn";
string str2 = "www.bing.com";
if (String.Compare(str1, str2) == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("两个值相同");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("两个值不同");
}
}
}
}
- 确认字符串1是否包含在字符串2里面
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str1 = "www.bing.com";
// string str2 = "bing";
string str2 = "binging";
if (str1.Contains(str2))
{
Console.WriteLine("str1包含str2");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("str1没有包含str2");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
- 截图特定长度的字符串
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str1 = "http://www.bing.com";
// http://www.bing.com
Console.WriteLine("原始字符串为: {0}",str1);
string str2 = str1.Substring(7);
Console.WriteLine("截取后字符串为: {0}", str2);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
- 把数组中的字符串元素,拼接成一个字符串
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] str_arr = {
"C语言中文网",
"http://c.biancheng.net/",
"C# 教程"
};
string str1 = String.Join("-", str_arr);
Console.WriteLine(str1); // C语言中文网-http://c.biancheng.net/-C# 教程
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
结构体
- 理解: 和
类很像,示例如下
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
struct Book
{
public string author;
public string title;
public string description;
public int page;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Book book1 = new Book();
Book book2 = new Book();
book1.author = "Jim Green";
book1.title = "DemoTitle";
book1.description = "DemoDescription";
book1.page = 100;
Console.WriteLine("书名为: {0}",book1.title);
Console.WriteLine("作者为: {0}",book1.author);
Console.WriteLine("描述为: {0}",book1.description);
Console.WriteLine("页数为: {0}",book1.page);
book2.author = "Kate Green";
book2.title = "DemoTitle2";
book2.description = "DemoDescription2";
book2.page = 200;
Console.WriteLine("书名为: {0}", book2.title);
Console.WriteLine("作者为: {0}", book2.author);
Console.WriteLine("描述为: {0}", book2.description);
Console.WriteLine("页数为: {0}", book2.page);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
'''
书名为: DemoTitle
作者为: Jim Green
描述为: DemoDescription
页数为: 100
书名为: DemoTitle2
作者为: Kate Green
描述为: DemoDescription2
页数为: 200
'''
- 和
类的一个重要区别:结构体是不能被继承的,但结构体可以实现接口结构体也不能实现构造方法类和结构体区别的实例如下
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
struct Book
{
public string author;
public string title;
public string description;
public int page;
// 赋值
public void getValue(string t,string a,string d,int p)
{
title = t;
author = a;
description = d;
page = p;
}
// 展示
public void display()
{
Console.WriteLine("Title:{0}", title);
Console.WriteLine("Author:{0}", author);
Console.WriteLine("description:{0}", description);
Console.WriteLine("page:{0}", page);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 实例化以后调用
Book book1 = new Book();
Book book2 = new Book();
book1.getValue("DemoTitle1","Jim Green","DemoDescription1",100);
book1.display();
book2.getValue("DemoTitle2", "Kate Green", "DemoDescription2", 200);
book2.display();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
枚举类型---enum
- 由一组具有独立标识符(名称)的整数类型常量构成,默认值从
0开始,逐一递增
using System;
namespace my_demo
{
class Program
{
enum Day { Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat };
static void Main(string[] args)
{ // 使用 Enum.GetValues 方法获取枚举类型的所有值
foreach (var day in Enum.GetValues(typeof(Day))) {
Console.WriteLine("该元素为{0},它的整数值为{1}",day,(int)day);
}
}
}
}
'''
该元素为Sun,它的整数值为0
该元素为Mon,它的整数值为1
该元素为Tue,它的整数值为2
该元素为Wed,它的整数值为3
该元素为Thu,它的整数值为4
该元素为Fri,它的整数值为5
该元素为Sat,它的整数值为6
'''
类
-
构造函数: 实例化类的时候,自动调用的方法,称为构造函数-
实例构造函数
using System; namespace my_demo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 实例化时,自动调用"实例构造函数" Person p = new Person("Jim Green", 20); Console.WriteLine(p); } } public class Person { // 声明两个类属性 private string name; private int age; // 声明实例构造函数 public Person(string n,int a) { name = n; age = a; } } } -
静态构造函数
-
用于初始化类中的静态数据
-
用于仅需执行一次的特定操作
-
调用方式:自动调用
- 创建第一个实例之前
- 引用类中的静态成员之前
-
特性
- 不使用访问权限修饰符修饰或不具有参数;
- 类或结构体中只能具有一个静态构造函数;
- 静态构造函数不能继承或重载;
- 静态构造函数不能直接调用,仅可以由公共语言运行时 (CLR) 调用;
- 用户无法控制程序中静态构造函数的执行时间;
- 在创建第一个实例或引用任何静态成员之前,将自动调用静态构造函数以初始化类;
- 静态构造函数会在实例构造函数之前运行。
using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { public static int num = 0; // 构造函数 Demo() { num = 1; } // 静态构造函数 static Demo() { num = 2; } static void Main(string[] args) { // 未实例化之前,先调用static构造函数 Console.WriteLine("num = {0}", num); // 实例化以后,调用实例构造函数 Demo Obj = new Demo(); Console.WriteLine("num = {0}", num); Console.Read(); } } } ''' num = 2 num = 1 '''
-
-
私有构造函数
- 是一种特殊的
实例构造函数,通常用在只包含静态成员的类中 - 注意事项:
- 如果一个类中具有一个或多个"私有构造函数"而没有"公共构造函数"的话,那么其他类(除嵌套类外)则无法创建该类的实例using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { static void Main(string[] args) { // 这里不能再实例化了,因为Student类只有"私有构造函数",因此其他类无法再创建Student实例 // Student stu = new Student(); Student.id = 101; Student.name = "张三"; Student.Display(); Console.Read(); } } public class Student { private Student() { } public static int id; public static string name; public static void Display() { Console.WriteLine("姓名:" + name + " 编号:" + id); } } } - 是一种特殊的
-
析构函数: 主要用于在垃圾回收器回收类实例时执行一些必要的清理操作.-
我的理解: 就是
自动删除函数,由系统的适当的时候调用,删除实例的时候可以实现自定义的逻辑- 注意事项: 该函数何时被调用,是由系统决定的!程序员无法做决定么?
-
特点
- 只能在类中定义,不能用于结构体;
- 一个类中只能定义一个析构函数;
- 析构函数不能继承或重载;它没有返回值;
- 是自动调用的,不能手动调用;
- 不能使用访问权限修饰符修饰,也不能包含参数.
- 语法: 类似
实例构造函数,使用~符号
class Car { ~Car() // 析构函数 { } }using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { static void Main(string[] args) { var stu1 = new Student(); var stu2 = new Student(); } } public class Student { public Student() { Console.WriteLine("我是实例构造函数的内容"); } ~Student() { Console.WriteLine("我是析构函数的内容"); } } } - 执行结果: ''' // 正常只会输出这两行 类中的构造函数 类中的构造函数 // 以下输入结果的时间点不确定,由系统决定 类中的析构函数 类中的析构函数 '''
this关键字: 代指当前对象- 类对象实例1: 用
this来代指类对象
using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { static void Main(string[] args) { var stu1 = new Student("Jim Green",20); stu1.display(); } } public class Student { private string name; private int age; public Student(string name,int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public void display() { Console.WriteLine("该学生姓名为:{0},年龄为:{1}",this.name,this.age); } } } - 运行结果: ''' 该学生姓名为:Jim Green,年龄为:20 '''- 类对象实例2: 用
this来代指类对象
using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { static void Main(string[] args) { // 带参数实例化 var stu1 = new Student("Jim Green"); } } public class Student { // 无参数的实例构造函数 public Student() { Console.WriteLine("我在无参数的构造函数里面!"); } // 有参数的实例构造函数 public Student(string name) { Console.WriteLine("我在有参数的构造函数里面!"); Console.WriteLine("我的值是: {0}",name); } } } - 输出结果: "无参数的实例构造函数"并不会被执行 ''' 我在有参数的构造函数里面! 我的值是: Jim Green '''using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { static void Main(string[] args) { // var stu1 = new Student("Jim Green"); // 不带参数实例化 var stu1 = new Student(); } } public class Student { public Student() { Console.WriteLine("我在无参数的构造函数里面!"); } public Student(string name) { Console.WriteLine("我在有参数的构造函数里面!"); Console.WriteLine("我的值是: {0}",name); } } } - 输出结果: "有参数的实例构造函数"并不会被执行 ''' 我在无参数的构造函数里面! '''- 如果想同时执行两个构造函数,最直接的办法,可以这么干: static void Main(string[] args) { // 分别调用这两个构造方法 var stu1 = new Student(); var stu2 = new Student("Jim Green"); } - 还可以用this using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { static void Main(string[] args) { var stu1 = new Student("Jim Green"); } } public class Student { public Student() { Console.WriteLine("我在无参数的构造函数里面!"); } // 先执行一次Student(),再执行传参的,this代指Student public Student(string name) :this() { Console.WriteLine("我在有参数的构造函数里面!"); Console.WriteLine("我的值是: {0}",name); } } } -
-
static静态 修饰符,声明静态方法 || 静态属性,这个静态成员会被所有对象共享
- 共享实例如下
using System;
namespace c.biancheng.net
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student.name = "Jim Green";
// Jim Green
Console.WriteLine(Student.name);
var stu1 = new Student();
// 该学生的姓名为:Jim Green
stu1.GetAttr();
var stu2 = new Student();
// 对静态变量重新赋值(刷新操作)
stu2.SetAttr("Kate Green");
// 该学生的姓名为:Kate Green
stu2.GetAttr();
}
}
public class Student
{
public static string name;
public void SetAttr(string StrName) {
name = StrName;
}
public void GetAttr() {
Console.WriteLine("该学生的姓名为:{0}", Student.name);
}
}
}
- 静态函数: 只能通过
类来调用,而不能通过类实例调用(在Python中,都支持)
using System;
namespace c.biancheng.net
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student.name = "Jim Green";
Console.WriteLine(Student.name);
var stu1 = new Student();
// stu1.GetAttr(); // 这种调用方式会报错
Student.GetAttr();
var stu2 = new Student();
stu2.SetAttr("Kate Green");
// stu2.GetAttr(); // 这种调用方式会报错
Student.GetAttr();
}
}
public class Student
{
public static string name;
public void SetAttr(string StrName) {
name = StrName;
}
public static void GetAttr() {
Console.WriteLine("该学生的姓名为:{0}", Student.name);
}
}
}
继承
- 在
C#中,只能单继承,只能继承一个类(Python支持多继承)
using System;
namespace c.biancheng.net
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var MyShapeObj = new MyShape();
MyShapeObj.setValue(20,10);
var res = MyShapeObj.CountArea();
Console.WriteLine(res);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class BaseShape
{
protected int width, height;
public void setValue(int w,int h) {
width= w;
height = h;
}
}
public class MyShape : BaseShape { // 继承BaseShape
public int CountArea() { // 新增计算面积的方法
int area = width*height;
return area;
}
}
}
多重继承: 可以通过基类和接口的方式,实现多重继承
using System;
namespace c.biancheng.net
{
class Demo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var MyShapeObj = new MyShape();
MyShapeObj.setValue(20,10);
var res = MyShapeObj.CountArea();
var res2 = MyShapeObj.CountDoubleArea();
Console.WriteLine("面积为: {0}",res); // 面积为: 200
Console.WriteLine("双倍面积为: {0}",res2); // 双倍面积为: 400
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class BaseShape
{
protected int width, height;
public void setValue(int w,int h) {
width= w;
height = h;
}
}
public interface DoubleArea // 定义接口
{
int CountDoubleArea(); // 预留方法(继承以后重写)
}
public class MyShape : BaseShape,DoubleArea {
public int CountArea() {
int area = width*height;
return area;
}
public int CountDoubleArea() { // 重写该方法
int area = width * height*2;
return area;
}
}
}
接口(Interface)
- 理解: 所谓
接口,即需求,定义接口,就是定义需求,类继承接口的时候,必须实现接口预埋的方法
using System;
namespace Demo
{
public interface Iwebsite
{
// 预定义两个方法
void setValue(string str1,string str2);
void display();
}
// 继承接口
public class MyWebsite : Iwebsite {
public string name, url;
// 实现接口预埋的方法
public void setValue(string n, string u)
{
name = n;
url = u;
}
// 实现接口预埋的方法
public void display() {
Console.WriteLine("名称为{0},网址为{1}",name,url);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args) {
MyWebsite MyWebsiteObj = new MyWebsite();
MyWebsiteObj.setValue("sina", "www.sina.com");
MyWebsiteObj.display();
}
}
}
- 注意事项
- 不能直接对接口进行实例化;
- 接口名称一般习惯使用字母“I”作为开头(不是必须的,不这样声明也可以);
- 接口中成员的访问权限默认为
public,所以我们在定义接口时不用再为接口成员指定任何访问权限修饰符,否则编译器会报错; - 在声明接口成员的时候,不能为接口成员编写具体的可执行代码,也就是说,只要在定义成员时指明成员的名称和参数就可以了(定义一个壳,不能定义具体的逻辑);
- 接口一旦被实现(被一个类继承),派生类就必须实现接口中的所有成员,除非派生类本身也是抽象类
多态
- 可以定义相同的函数名称,但传入不同类型的参数,实现
多态
using System;
namespace c.biancheng.net
{
class Demo
{
void print(int i){
Console.WriteLine("打印 int 类型的数据:{0}", i);
}
void print(double d){
Console.WriteLine("打印 double 类型的数据:{0}", d);
}
void print(string s){
Console.WriteLine("打印 string 类型的数据:{0}", s);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Demo p = new Demo();
p.print(123); // 调用int函数
p.print("C语言中文网"); // 调用string函数
p.print(3.1415926); // 调用 double函数
}
}
}
抽象类
-
使用
abstract关键字来创建抽象类,抽象类用于实现部分接口- 不能创建一个抽象类的实例;
- 不能在一个抽象类外部声明抽象方法;
- 通过在类定义时使用 sealed 关键字,可以将类声明为密封类,密封类不能被继承,因此抽象类中不能声明密封类(暂时看不懂)
using System; namespace c.biancheng.net { class Demo { static void Main(string[] args) { var BaseShapeObj = new MyShape(); BaseShapeObj.SetValue(20, 10); var res = BaseShapeObj.GetArea(); Console.WriteLine(res); // 200 Console.ReadLine(); } } abstract class BaseShape // 声明一个抽象类 { public abstract int GetArea(); // 等待被继承 } class MyShape : BaseShape { public int width; public int height; public void SetValue(int w,int h) { width = w; height = h; } public override int GetArea() // 覆盖基类的方法,重写 { int area = width * height; return area; } } } -
方法的重载: 本质就是同一个方法可以接收不同的参数,方便开发者调用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator c = new Calculator();
Console.WriteLine(c.Add(1,2));
Console.WriteLine(c.Add(1.0,2.0));
Console.WriteLine(c.Add(1,2,3));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Calculator
{
public int Add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
public int Add(int x, int y, int z)
{
return x + y + z;
}
public double Add(double x, double y)
{
return x + y;
}
}
}
委托: 就是类实例把方法委托给别人(Action)去调用(自己不去调用)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Message m = new Message();
// 把PrintText方法委托给myAction对象
Action myAction = new Action(m.PrintText);
// 加括号就是调用
myAction();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Message
{
public void PrintText() {
Console.WriteLine("Hello!");
}
}
}
- 实例: 把
类和类属性打包成Dict示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个空dict对象
Dictionary<string,Student> stuDict = new Dictionary<string,Student>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Student student = new Student();
student.name = "student_" + i.ToString();
student.score = 60 + i;
// 往dict插入key和value
stuDict.Add(student.name, student);
}
// 输出其中一个结果
Student student6 = stuDict["student_6"];
Console.WriteLine(student6.score);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Student
{
public string name;
public int score;
}
}
typeof应用示例: 查看int类型所有的方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type i = typeof(int);
Console.WriteLine(i.FullName);
Console.WriteLine(i.Name);
Console.WriteLine(i.Namespace);
foreach (var method in i.GetMethods()) {
Console.WriteLine(method.Name);
}
Console.WriteLine(i.GetMethods().Length);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
default关键字的作用: 设置默认值
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// int默认值为0
int i = default(int);
Console.WriteLine(i);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
- 注意事项: 使用default去操作"枚举类型"的时候,有坑,结果可能和你想的不一样,需预先验证一下
new关键字
- 作用: 声明实例对象,如果想声明实例对象的时候,同时初始化部分对象的属性值,可以添加"{}",在这里初始化值
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明实例对象的同时,初始化text属性值(这里就是窗体标题)
Form myForm = new Form() {Text="Hello" };
myForm.ShowDialog();
}
}
}
- 注意事项: 创建实例对象的时候,一定要使用new关键字吗?
- 不是的,有语法糖,例如 int x = 123;
var配合new实现声明匿名类型
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明匿名类型
var person = new {name="Jim Green",age=20 };
Console.WriteLine(person.name);
Console.WriteLine(person.age);
// <>f__AnonymousType0`2 // 后缀的'2'表示该'匿名类型'由2种数据类型构成
Console.WriteLine(person.GetType().Name);
}
}
}
- 还可以实现
子类重写父类的方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
NewStudent newStudent = new NewStudent();
student.PrintText();
newStudent.PrintText();
}
}
class Student
{
public void PrintText()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm a student!");
}
}
class NewStudent : Student {
// 重写父类的方法
new public void PrintText() {
Console.WriteLine("I'm a newStudent!");
}
}
}
checked和unchecked操作符
- 作用: 检查变量在内存中,有没有
溢出
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// uint类型为'正整型'类型
uint myUint = uint.MaxValue;
Console.WriteLine(myUint);
// 转换成二进制类型数据
string binStr = Convert.ToString(myUint,2);
Console.WriteLine(binStr);
uint overUint = checked(myUint+1);
Console.WriteLine(overUint);
}
}
}
- 返回结果
'''
4294967295
11111111111111111111111111111111
未经处理的异常: System.OverflowException: 算术运算导致溢出。
'''
- 修改一下上面的示例,添加
异常处理机制
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
uint myUint = uint.MaxValue;
Console.WriteLine(myUint);
string binStr = Convert.ToString(myUint,2);
Console.WriteLine(binStr);
try
{
uint overUint = checked(myUint + 1);
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{
// 算术运算导致溢出
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
数据类型转换
显示转换,实例如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
uint x = uint.MaxValue;
Console.WriteLine(x);
ushort y = x; // 这里会报错
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
}
- 该实例纠正如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
uint x = uint.MaxValue;
// 4294967295
Console.WriteLine(x);
// 这里进行显示转换,就不会报错了,但是数据的精度会丢失
ushort y = (ushort)x;
// 65535
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
}
自定义类型转换: 通过自定义显式转换操作符实现石头变猴子的类型转换实例
Nullableusing System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stone stone = new Stone();
stone.age = 5000;
// 使用Monkey运算符,实现由stone类型向monkey类型的转换
Monkey WuKong = (Monkey)stone;
Console.WriteLine(WuKong.age);
}
}
class Stone
{
public int age;
// 自定义显式转换运算符Monkey
public static explicit operator Monkey(Stone stone)
{
Monkey m = new Monkey();
m.age = stone.age/500;
return m;
}
}
class Monkey
{
public int age;
}
}
- 这个例子修改一下,变成"隐式转换"
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stone stone = new Stone();
stone.age = 5000;
// (Monkey)不用再写
Monkey WuKong = stone;
Console.WriteLine(WuKong.age);
}
}
class Stone
{
public int age;
// 只修改关键字,其他不变
public static implicit operator Monkey(Stone stone)
{
Monkey m = new Monkey();
m.age = stone.age/500;
return m;
}
}
class Monkey
{
public int age;
}
}
可空类型-Nullable
- 作用: 让"数据类型"具有存储"Null"的能力
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明int类型数据,具有存储null的能力
// 语法糖简写: int? x = null;
Nullable<int> x = null;
// 输出为空
Console.WriteLine(x);
x = 1;
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
}
}
三元操作符和python一样
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 100;
// 三元表达式
int y = x==100 ? 200 : 300;
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
}
- 快捷键
- F12 追踪源码
空合并操作符??:??的左边操作数为null时,返回右边的操作数(若左边不为null,则取左边的值)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// x 复制为 null
int? x = null;
// x为null,所以y=100
var y = x ?? 100;
Console.WriteLine(y);
Console.WriteLine(y.GetType().FullName);
}
}
}
委托Action实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// delegate 表示匿名函数
Action myAction = delegate() { Console.WriteLine("Hello"); };
myAction();
}
}
}
- 上述实例修改一下,使用lambda表达式实现一样的效果
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 匿名函数表达方式,跟js语法一样
Action myAction = ()=> { Console.WriteLine("Hello"); };
myAction();
}
}
}
方法的单一职责
- 一个方法只对应一个功能,避免有两个或者以上功能
- 多个功能以后改起来,可能引入隐性的bug!
switch语句实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Level myLevel = Level.High;
switch (myLevel)
{
case Level.High:
Console.WriteLine("High Level");
break;
case Level.Middle:
Console.WriteLine("Middle Level");
break;
case Level.Low:
Console.WriteLine("Low Level");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("No Level...");
break;
}
}
}
// 声明枚举类型(所谓'枚举',即'常量'集)
enum Level
{
High,
Middle,
Low
}
}
循环介绍
- 在
c#中一共有四种循环体,互通,只不过侧重点不一样,哪种应景就用哪种whiledo...whileforforeach
while示例如下: 计算和为100,若不为100则退出并返回用户得分~~~
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 0;
bool canContinue = true;
while (canContinue) {
Console.WriteLine("Please enter the first number: ");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
int firstNumber = int.Parse(str1);
Console.WriteLine("Please enter the second number: ");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
int secondNumber = int.Parse(str2);
int sum = firstNumber + secondNumber;
if (sum == 100)
{
score++;
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}", firstNumber, secondNumber, sum);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("Error,{0}+{1}={2}", firstNumber, secondNumber, sum);
canContinue = false;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Game Over!!!");
Console.WriteLine("Your score is {0}",score);
}
}
}
-
迭代器- 通俗理解: 就是
指月,用手指指向月亮,假设有10个月亮,手指指向哪个月亮,我们就看那个月亮 - 使用
迭代器来遍历循环数组示例
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Collections; namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 声明数组 int[] intArray = new int[] { 1,2,3,4,5 }; // 为数组 IEnumerator enumerator = intArray.GetEnumerator(); while (enumerator.MoveNext()) { Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current); } } } } - 升级示例 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Collections; namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] intArray = new int[] { 1,2,3,4,5 }; IEnumerator enumerator = intArray.GetEnumerator(); while (enumerator.MoveNext()) { Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current); } // 不会被执行,因为迭代器已经指向最后一个元素了 // 解决办法,刷新迭代器即可 // enumerator.Reset(); while (enumerator.MoveNext()) { Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current); } } } }静态构造函数只执行一次
- 通俗理解: 就是
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 静态构造器执行一次
Student stu1 = new Student();
// 静态构造器不会再执行
Student stu2 = new Student();
}
}
class Student
{
public string name;
public int age = 18;
static Student() {
Console.WriteLine("我是静态构造器的内容");
}
}
}
实例构造函数: 每创建一次实例,就执行一次该函数
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建两个实例,所以执行两次
Student stu1 = new Student();
Student stu2 = new Student();
}
}
class Student
{
public string name;
public int age = 18;
public Student()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是实例构造器的内容");
}
}
}
readonly关键字
- 作用: 声明
只读字段,初始化的时候赋值一次,接下来不可修改
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int studentID = 1;
Student stu1 = new Student(studentID);
Console.WriteLine("学生的ID是:{0}",studentID);
// 想修改的时候,就报错了
// stu1.Id = 2;
}
}
class Student
{
// 声明只读字段ID
public readonly int Id;
public Student(int id)
{
// 创建实例的时候,赋值(赋值的唯一机会)
this.Id = id;
}
}
}
- 声明
自定义静态字段实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(Brush.originalColor.red);
Console.WriteLine(Brush.originalColor.green);
Console.WriteLine(Brush.originalColor.blue);
}
}
class Color
{
public int red;
public int green;
public int blue;
}
class Brush
{
// 声明自定义静态字段
public static Color originalColor = new Color() { red = 0, green = 0, blue = 0 };
}
}
private关键字
- 声明
私有字段,不能通过类实例访问(例如object.XXfield),而是通过方法去访问 - 作用: 起到·保护字段·的作用(对·字段·的限制逻辑可以在·方法·中实现)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.SetAge(20);
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.SetAge(200);
Student stu3 = new Student();
stu3.SetAge(20);
Console.WriteLine((stu1.GetAge()+stu2.GetAge()+stu3.GetAge())/3);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int GetAge() { return this.age; }
// 通过SetAge()d对age字段的赋值进行限制
public void SetAge(int value)
{
if (value < 0 || value > 120) {
throw new Exception("输入年龄值异常");
}
else
{
this.age = value;
}
}
}
}
语法糖
- 定义:一段看似简单的逻辑背后,隐藏着一段复杂的逻辑,方便程序员调用!
- 把上述实例修改一下,通过
自定义公共属性对私有属性进行访问和限制
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
// 给公共属性赋值,从而影响私有属性的值
stu1.Age = 20;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 20;
Student stu3 = new Student();
stu3.Age = 20;
Console.WriteLine((stu1.Age + stu2.Age + stu3.Age) / 3);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
// 自定义公共属性
public int Age{
get{
return this.age;
}
set
{
if (value < 0 || value > 120)
{
throw new Exception("输入年龄值异常");
}
else
{
this.age = value;
}
}
}
}
}
- 自定义属性声明
- 自定义属性: propfull,再tab两次,生成格式如下
private int myVar;
public int MyProperty
{
get { return myVar; }
set { myVar = value; }
}
- 自定义简略属性: 用于传递数据
- 输入 prop 再tab两次,自动生成结构,实例如下
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Age = 1;
}
}
class Student
{
// 简略声明
public int Age { get; set; }
}
}
- 也可以利用编辑器的"重构"功能,快速声明自定义字段
- 光标停在字段处,右键,重构-封装...
- 进阶实例: 区分readonly field(只读属性)和 private属性(只能从类的内部去访问)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
// 这种访问方式会报错
// student.Age = 123;
// 通过内部访问方式来设置值
student.setMethod(1);
Console.WriteLine(student.Age);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
// 这里的private表示,只能从内部设置age属性,外部无法访问它
public int Age { get => age; private set => age = value; }
// 自定义内部访问方式
public void setMethod(int myAge)
{
this.Age = myAge;
}
}
}
- 两个实例对比一下,适用的场景不同
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Age = 10;
Console.WriteLine(student.canWork);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age { get => age; set => age = value; }
public bool canWork
{
get
{
if (this.age < 16)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Age = 16;
Console.WriteLine(student.CanWork);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age {
get => age;
set
{
this.age = value;
this.CaculatorCanWork();
}
}
private bool canWork;
public bool CanWork { get => canWork;}
private void CaculatorCanWork()
{
if (this.age >= 16)
{
this.canWork = true;
}
else {
this.canWork = false;
}
}
}
}
总结
对比项 第一段代码 第二段代码
canWork 实现 动态计算 预计算存储
性能 高频访问时较差 高频访问时更优
设计复杂度 简单 略复杂(需维护额外字段和方法)
适用场景 逻辑简单、访问频率低 逻辑复杂或访问频率高
索引器声明示例: 以下示例是错的,末尾的value值提示错误- 注意事项:
非集合类型的自定义索引器,实际应用中,很少见,以下例子只是为了演示 scoreDictionary值为int- 而
索引器值为int?,二者发生了冲突,所以导致value值报错
- 注意事项:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary<string,int> scoreDictionary = new Dictionary<string,int>();
public int? this[string subject]
{
get {
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject)) return this.scoreDictionary[subject]; else return null;
}
set {
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
this.scoreDictionary[subject] = value;
}
else
{
this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject, value);
}
}
}
}
}
- 解决办法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
// var mathSubject = student["Math"];
// Console.WriteLine(mathSubject == null); // true
student["Math"] = 95;
Console.WriteLine(student["Math"]);
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary<string,int> scoreDictionary = new Dictionary<string,int>();
public int? this[string subject]
{
get {
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject)) return this.scoreDictionary[subject]; else return null;
}
set {
// null值处理
if(value.HasValue == false)
{
throw new Exception("值不能为null");
}
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
// 类型转换:value 是 int? 类型,通过 value.Value 提取实际的 int 值存入字典
this.scoreDictionary[subject] = value.Value;
}
else
{
this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject, value.Value);
}
}
}
}
}
属性和字段
- 在
C#中,属性和``字段是不一样的- 当你想对外暴露数据的时候,定义
属性是更好的选择
- 当你想对外暴露数据的时候,定义
引用类型
- 先来一个实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Name = "Kate Green";
Program.SomeMethod(student); // Jim Green
Console.WriteLine(student.Name); // Kate Green
}
// 重新实例化并赋值
public static void SomeMethod(Student stu)
{
stu = new Student() { Name="Jim Green" };
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
// 声明一个公共属性Name
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
- 解释: SomeMethod方法
- 当传入实例的时候,SomeMethod内部逻辑重新实例化了"对象实例",所以,原实例对象的属性是不会变化的
- 小改一下 SomeMethod 逻辑: stu.Name = "Jim Green"; // 原对象的属性就会被修改了
- 小技巧: 判断两个对象是不是同一个对象,可以通过"object.GetHashCode()"进行判断
- 例如上述示例可以这么写: Console.WriteLine(student.GetHashCode()); // 12289376
- 实际应用:
- 实际开发中,重新实例化的现象非常少见,这种就是面试题...
- 方法的作用主要是返回值,比如这个方法中,实际还修改了对象的属性值,这种成为'方法的副作用(非主要功能)',尽量避免这么做!
- 快捷键
Ctrl+.或者Alt+Enter,弹出的小菜单中,可以快速弹出修补程序 引用类型关键字ref- 作用: 修改
原始变量的值,实例如下
- 作用: 修改
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int y = 1;
// 传参,ref不能省略
Program.SomeMethod(ref y);
// 101
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
// 声明引用类型变量x
public static void SomeMethod(ref int x)
{
x += 100;
}
}
}
- 用
类实例演示如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Name = "Kate Green";
// Jim Green
Program.SomeMethod(ref student);
Console.WriteLine("--------");
// Jim Green
Console.WriteLine(student.Name);
}
public static void SomeMethod(ref Student stu)
{
// student指向新的对象(变成新的对象了)
stu = new Student() { Name="Jim Green" };
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
- 把这个例子修改一下,结果是相同的
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Name = "Kate Green";
Program.SomeMethod(ref student);
Console.WriteLine("--------");
Console.WriteLine(student.Name);
}
public static void SomeMethod(ref Student stu)
{
// stu = new Student() { Name="Jim Green" };
stu.Name = "Jim Green";
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
- 再修改一下,结果一样,但是
内存原理不同
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Name = "Kate Green";
// 去掉ref
Program.SomeMethod(student);
Console.WriteLine("--------");
Console.WriteLine(student.Name);
}
// 去掉ref
public static void SomeMethod(Student stu)
{
stu.Name = "Jim Green";
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
输出参数out示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string arg1 = Console.ReadLine(); // 10
double x = 0;
// out接收TryParse的返回结果并赋值给x(若转换不成功则默认为0)
bool b1 = double.TryParse(arg1, out x);
if (b1 == false)
{
Console.WriteLine("输入错误!");
return;
}
string arg2 = Console.ReadLine(); // 20
double y = 0;
bool b2 = double.TryParse(arg2, out y);
if (b2 == false)
{
Console.WriteLine("输入错误!");
return;
}
double z = x + y;
Console.WriteLine(z);
}
}
}
- 自定义方法
out示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 0;
// TryParse("kkk", out x);
bool b = DoubleParser.TryParse("789", out x);
if (b == true)
{
Console.WriteLine(x + 1);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine("解析错误");
}
}
class DoubleParser
{
public static bool TryParse(string input, out double result)
{
try
{
result = double.Parse(input);
return true;
}
catch
{
result=0;
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
- 传入
类实例示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 初始化值
Student student = null;
// Student student = new Student(); // 一样的效果
bool res = StudentFactory.Create("Jim Green", 22,out student);
if (res == true) {
Console.WriteLine("student' name is {0} and age is {1}",student.Name,student.Age);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class StudentFactory
{
public static bool Create(string name, int age, out Student result)
{
result = null;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
return false;
}
if(age < 20 || age > 80)
{
return false;
}
result = new Student() { Name=name,Age=age };
return true;
}
}
}
语法糖--params关键字,让代码更加简洁- 原求和实例如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 需提前声明数组
int[] sumArray = { 1, 2, 3 };
// Console.WriteLine(Program.CalculatorSum(sumArray));
Console.WriteLine(CalculatorSum(sumArray)); // 调用静态方法,省略Program类对象
}
static int CalculatorSum(int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
foreach (int i in nums) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
}
- 使用
params关键字如下,一模一样的效果,代码更加简洁
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// int[] sumArray = { 1, 2, 3 };
Console.WriteLine(CalculatorSum(1,2,3));
}
static int CalculatorSum(params int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
foreach (int i in nums) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
}
- 注意事项
- params参数只能有一个,而且必须是最后一个参数
具名参数实例调用
不具名参数(位置参数)实例调用如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintMsg("Jim Green", 20);
}
static void PrintMsg(string name,int age)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}---{1}", name, age);
}
}
}
具名参数实例调用如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 格式如下
PrintMsg(age:20,name:"Jim Green");
}
static void PrintMsg(string name,int age)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}---{1}", name, age);
}
}
}
可选参数
- 示例如下(不传参)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 不传参,没有问题
PrintMsg();
}
static void PrintMsg(string name="Jim Green",int age=20)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}---{1}", name, age);
}
}
}
- 传参示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 传参
PrintMsg(age:18,name:"Kate Green");
}
static void PrintMsg(string name="Jim Green",int age=20)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}---{1}", name, age);
}
}
}
this关键字实例: 为double类型添加Round方法- 注意事项: 这里的
this的作用是为double类型添加拓展方法(从源码去添加不太实际)- 这类
拓展方法的书写格式有规定,要按照格式写
- 这类
- 注意事项: 这里的
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 3.141592;
// 等效 double y = DoubleExtension.Round(x,4);
double y = x.Round(4); // 关键点:扩展方法调用
Console.WriteLine(y); // 输出结果:3.1416
}
}
static class DoubleExtension // 扩展方法必须定义在静态类中
{
// 扩展方法定义(为double类型添加新功能)
// this后面跟的参数是谁,就是为谁添加功能
public static double Round(this double input, int digits)
{
return Math.Round(input, digits);
}
}
}
demo实例如下: 判断数组里面的每一个数是否大于10
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> intArray = new List<int>() { 10,12,13,14 };
Console.WriteLine(CaculatorNumThanTen(intArray));
}
public static bool CaculatorNumThanTen(List<int> intArray)
{
foreach (int i in intArray) {
if(i < 10)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
-
使用
linq实现方式- 所谓
linq是C#一个工具集,集成各种便捷方法,让开发者更方便的调用- 实例的All():LINQ 方法,检查集合中所有元素是否满足条
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; // 引入linq using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Collections; namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> intArray = new List<int>() { 11, 12, 13, 14 }; // 调用All()方法并传入lambda表达式,更简便实现需求 Console.WriteLine(intArray.All(i=>i>10)); } } } - 所谓
Action委托
- 所谓
委托,就是把事情委托给别人,别人代我做这件事情Action关键字Func关键字
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Caculatror caculatror = new Caculatror();
// 直接调用
caculatror.Report();
// 委托调用
Action myAction = new Action(caculatror.Report);
myAction.Invoke();
// 更简便的调用方式
myAction();
// 带参数的委托
Func<int, int, int> fun1 = new Func<int, int, int>(caculatror.Add);
Func<int, int, int> fun2 = new Func<int, int, int>(caculatror.sub);
int x = 200;
int y = 100;
Console.WriteLine(fun1.Invoke(x, y));
Console.WriteLine(fun2.Invoke(x, y));
// 更便捷的调用
Console.WriteLine(fun1(x, y));
Console.WriteLine(fun2(x, y));
}
}
class Caculatror
{
public void Report()
{
Console.WriteLine("I have 3 methods.");
}
public int Add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
public int sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
}
}
自定义委托delegate实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
// delegate声明自定义委托类Calc
public delegate double Calc(double x,double y);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
Calc calc1 = new Calc(calculator.Add);
Calc calc2 = new Calc(calculator.Sub);
Calc calc3 = new Calc(calculator.Mul);
Calc calc4 = new Calc(calculator.Div);
Console.WriteLine(calc1(100, 200));
Console.WriteLine(calc2(100, 200));
Console.WriteLine(calc3(100, 200));
Console.WriteLine(calc4(100, 200));
}
}
class Calculator
{
public double Add(double x, double y) { return x + y; }
public double Sub(double x, double y) { return x - y; }
public double Mul(double x, double y) { return x * y; }
public double Div(double x, double y) { return x / y; }
}
}
自定义模版方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
// 生成委托函数对象并传入WrapProduct
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToCar);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
// 传入一个委托类型的函数对象
public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct) {
Box box = new Box();
Product product = getProduct.Invoke();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeToCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Car";
return product;
}
}
}
- 修改这个
模板方法新增log功能
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToCar);
// 新增部分
Logger logger = new Logger();
Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1,log);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2,log);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
class Logger
{
public void Log(Product product)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1}-{2}",product.Name,product.Price,DateTime.UtcNow);
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
// 新增logCallback委托
public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct,Action<Product>logCallback) {
Box box = new Box();
Product product = getProduct.Invoke();
// 如果产品价格大于50,则log记录一下
if(product.Price > 50)
{
logCallback(product);
}
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
product.Price = 12;
return product;
}
public Product MakeToCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Car";
product.Price = 100;
return product;
}
}
}
- 特别提醒: 实际开发中,使用
委托要慎之又慎,避免滥用,出现的bug很难调试...- 难精通,易用,又功能强大(这种东东往往很难控制...)
单波委托:以下实例和之前一样,没什么不同
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID = 1,PenColor=ConsoleColor.Red };
Student student2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student student3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Blue };
Action action1 = new Action(student1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(student2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(student3.DoHomework);
action1();
action2();
action3();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1}", ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
- 变成
多波委托,可以这么处理
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID = 1,PenColor=ConsoleColor.Red };
Student student2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student student3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Blue };
Action action1 = new Action(student1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(student2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(student3.DoHomework);
// 委托合并,执行action1,action2和action3也得到执行
// 同步调用
action1 += action2;
action1 += action3;
action1();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1}", ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
异步调用示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID = 1,PenColor=ConsoleColor.Red };
Student student2 = new Student() { ID = 2, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
Student student3 = new Student() { ID = 3, PenColor = ConsoleColor.Blue };
Action action1 = new Action(student1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(student2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(student3.DoHomework);
// 异步调用
action1.BeginInvoke(null,null);
action2.BeginInvoke(null,null);
action3.BeginInvoke(null,null);
Console.WriteLine("主程序执行完成!");
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public ConsoleColor PenColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomework()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1}", ID, i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
- 注意事项: 可以用
接口来代替委托的功能
事件
-
作用: 使
成员具有提供通知的能力,简而言之,事件就是通知别人的工具手机响铃,响铃这个事件,使手机有了通知别人的能力!事件参数: 顺着通知这个事情,携带过来的消息- 比如说是QQ提示音,我们就知道是QQ来消息了,是微信提示音,我们就知道微信来消息了
订阅,谁订阅了这个事件(谁关心这个事件)
-
5个要素
- 事件的拥有者
- 事件成员
- 事件的响应者
- 事件处理器
- 事件订阅
-
快捷键
- 小方块: 指的是'方法'
- 小扳手: 指的是'属性'
- 小闪电: 指的是'事件'
- 订阅事件的时候,当出现"+="时,连续tab两次,可以自动生成事件处理器
- 选中一个方法,右键,选择"查看所有引用"
- F4键,可以出现属性窗口
- 基于
事件的第一个实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// 以下两个类库,也有Timer,避免混淆
// using System.Threading;
// using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer(); // 事件拥有者timer
timer.Interval = 1000;
Boy boy = new Boy(); // 事件的响应者
timer.Elapsed += boy.Action; // 订阅事件(用"+="来订阅事件)
timer.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Boy
{
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Jump!"); // 触发事件以后,需要做的事情
}
}
}
- 基于
事件的第二个实例,窗体的点击事件
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form form = new Form(); // 事件拥有者
Controller controller = new Controller(form); // 响应者
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class Controller
{
private Form form;
public Controller(Form form)
{
if (form != null) {
this.form = form;
this.form.Click += this.FormClick; // 订阅
}
}
private void FormClick(object sender, EventArgs e) // 事件处理器
{
this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
- 基于
事件的第三个实例,窗体的点击事件,当前对象即是事件拥有者,又是事件响应者
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm(); // 拥有者,响应者
form.Click += form.FormClicked;
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form // 派生子类
{
internal void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
- 实际开发中的实例: 点击按钮的时候,文本框展示相应的内容
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form
{
private TextBox textBox;
private Button button;
public MyForm() {
this.button = new Button();
this.textBox = new TextBox();
this.Controls.Add(this.button);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);
this.button.Click += this.ButtonClicked;
this.button.Text = "点击我";
this.button.Top = 20;
}
private void ButtonClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.textBox.Text = "Hello World!";
}
}
}
点击事件又一个示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApp1
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 传统的委托书写方式
// this.button3.Click += this.button1_Click;
// 新的委托书写方式
// this.button3.Click += new EventHandler(this.button1_Click);
// 已经被抛弃的写法
// this.button3.Click += delegate(object sender, EventArgs e) {
// this.textBox1.Text = "Demo";
// };
// 流行的写法,拉姆匿名表达式
// this.button3.Click += (object sender, EventArgs e) =>
// {
// this.textBox1.Text = "666";
// };
// 更简便的拉姆匿名表达式写法
// 编译器会自动推断传入的数据类型
this.button3.Click += (sender, e) =>
{
this.textBox1.Text = "666";
};
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(sender == this.button1)
{
this.textBox1.Text = "Hello";
}
if (sender == this.button2)
{
this.textBox1.Text = "World";
}
if (sender == this.button3)
{
this.textBox1.Text = "OK";
}
}
}
}
自定义触发事件实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
// 订阅事件
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
// 开始执行一系列动作
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
}
}
// 自定义事件参数
public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
// 自定义委托类型(自定义委托类型的事件处理器)
public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
public class Customer
{
public double Bill { get; set; }
private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;
// 自定义事件
public event OrderEventHandler Order
{
add
{
this.orderEventHandler += value;
}
remove
{
this.orderEventHandler -= value;
}
}
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("The bill is {0}", this.Bill);
}
public void Walk()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walking in the restaurant");
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit down!");
}
public void Think()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm thinking!");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
if (orderEventHandler != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";
e.Size = "Large";
// 触发自定义事件
this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadLine();
this.Walk();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
public class Waiter
{
internal void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("I will service you {0}", e.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch(e.Size){
case "Small":
price = price * 0.5;
break;
case "Large":
price = price * 1.5;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}
- 运行结果
'''
Walking in the restaurant
Sit down!
I'm thinking!
I'm thinking!
I'm thinking!
I'm thinking!
I'm thinking!
I will service you Kongpao Chicken
The bill is 15
'''
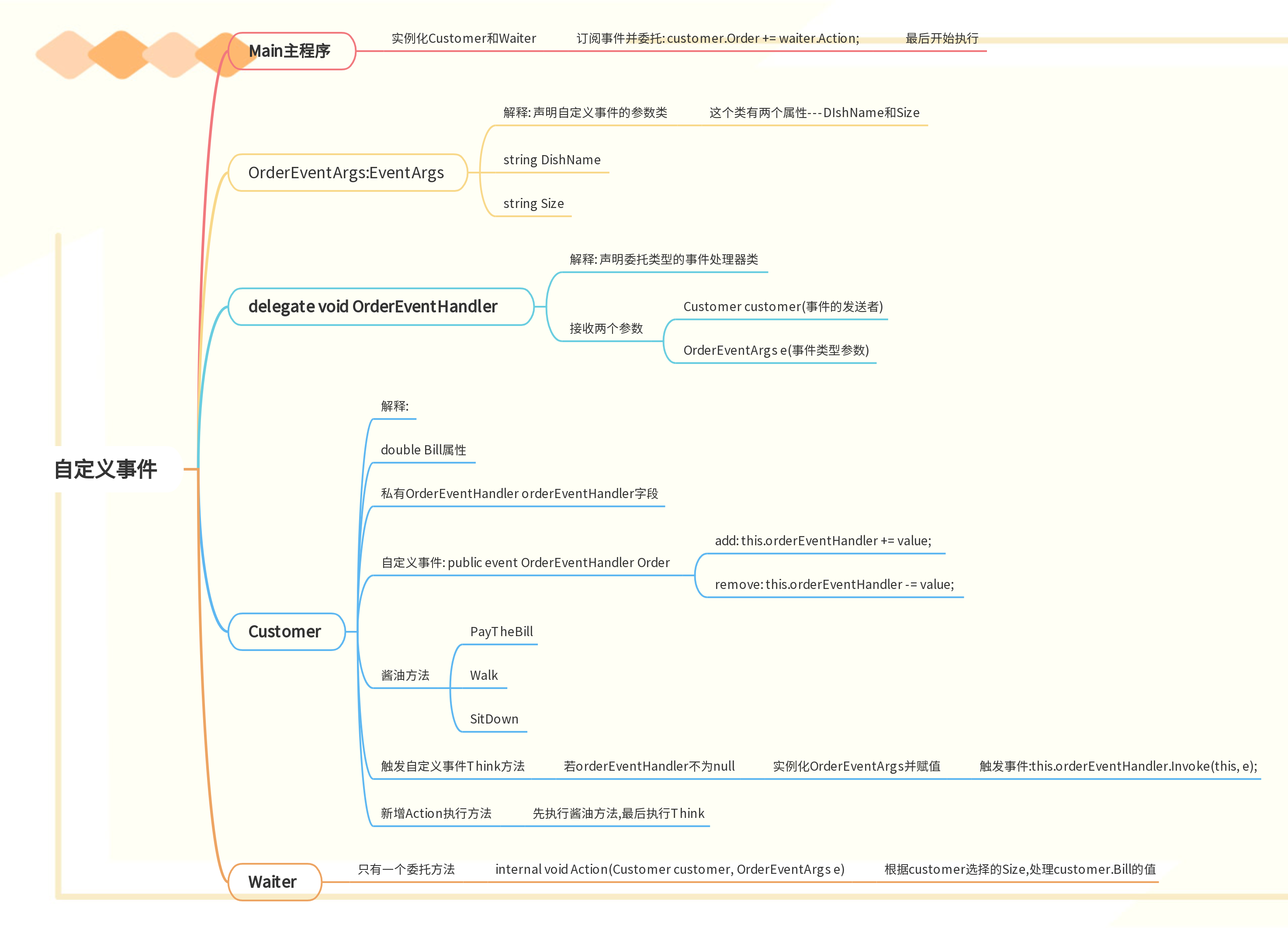
- 简化
自定义事件声明实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
// customer.Order += waiter.Action;
customer.Order += new OrderEventHandler(waiter.Action);
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
}
}
public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
public class Customer
{
public double Bill { get; set; }
private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;
// 化简
public event OrderEventHandler Order;
//public event OrderEventHandler Order
//{
// add
// {
// this.orderEventHandler += value;
// }
// remove
// {
// this.orderEventHandler -= value;
// }
//}
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("The bill is {0}", this.Bill);
}
public void Walk()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walking in the restaurant");
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit down!");
}
public void Think()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm thinking!");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
// if (orderEventHandler != null)
if (this.Order != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "Kongpao Chicken";
e.Size = "Large";
// this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);
this.Order.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadLine();
this.Walk();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
public class Waiter
{
internal void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("I will service you {0}", e.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch(e.Size){
case "Small":
price = price * 0.5;
break;
case "Large":
price = price * 1.5;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}
析构器
- 作用: 当
对象在内存中被垃圾回收的时候,做一些事情- 通俗理解: 是一个钩子,当对象被当垃圾回收的时候,做一些事情
- 语法和
构造器的写法很像,只不过把public换成了~线
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student(1,"Jim Green");
Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1}",student.Id,student.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Student(int id,string name)
{
Name = name;
Id = id;
}
// 析构器
~Student() {
Console.WriteLine("内存资源被释放了!");
}
}
}
- 运行结果:
1-Jim Green
内存资源被释放了!
-
初识
反射- 作用一: 根据
类型来动态创建实例
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Threading; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Collections; using System.Timers; namespace EventExample { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 获取Student类型 Type t = typeof(Student); // 动态创建实例对象 object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t,20,"Jim Green"); // 类型转换 Student student = (Student)o; Console.WriteLine(student.Name); } } class Student { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public Student(int id,string name) { Name = name; Id = id; } } }- 使用
dynamic来写,会更简便
...... namespace EventExample { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Type t = typeof(Student); //object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t,20,"Jim Green"); //Student student = (Student)o; // 省掉了类型转换那步 dynamic student = Activator.CreateInstance(t, 20, "Jim Green"); Console.WriteLine(student.Name); } } class Student { ...... } } - 作用一: 根据
类的修复访问符
-
对于同一个
名称空间来说public class: 别人(别的类库)可以访问internal class: 别人(别的类库)无法访问,但是类库内部之间,可以互相访问- 同一个项目中,可以互相访问,英文名称为
assembly
- 同一个项目中,可以互相访问,英文名称为
// 自定义类库如下: ClassLibrary类库地下,新建目录 MyNameSpace(目录即"名称空间") using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ClassLibrary1.MyNameSpace { // internal 是默认的行为,表示只在"名称空间"内部使用 // 换成这句的话,外部就无法访问Calculator类了 // internal class Calculator // public对外暴露 public class Calculator { public double Add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } } } // 引用该类库 ...... // 导入该类库(需先添加引用) using ClassLibrary1.MyNameSpace; namespace EventExample { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Calculator calculator = new Calculator(); var res = calculator.Add(1, 1); Console.WriteLine(res); } } } -
快捷键
- 所谓的"目录",就是"名称空间"
- 同一
类库底下,两个名称空间之间使用internal,可以互相访问(单向引用,循环引用会报错)
// ClassLibrary.MyNameSpace.Calculator.cs
......
namespace ClassLibrary1.MyNameSpace
{
internal class Calculator
{
public double Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
}
// ClassLibrary.MyNameSpace2.Student.cs
......
// 引入同一类库下面的名称空间
using ClassLibrary1.MyNameSpace;
namespace ClassLibrary1.MyNameSpace2
{
class Student
{
// 声明属性
public Calculator Calculator { get; set; }
}
}
继承
父类可以引用子类的实例对象
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
- 使用
sealed关键字修饰的类,不能被继承 C#是单继承的模式,一次只能继承一个类,不能一次性继承多个类(可以继承多个接口)子类的访问权限不能超过父类
- 举例: 若父类的访问权限是默认的 internal声明(即隐藏声明),子类此时声明为public 就会报错
继承的过程中,当引入新的类成员时,只能实现拓展的功能,而不能去削减,这是静态语言的特征
- 提示点: 所以,引入新的类成员要谨慎,避免污染现有的成员或者api
- 举例说明,Vehicle有一个属性叫Owner,Car子类继承Owner,在Car类中,可以删除Owner属性吗?目前木办法做到!
- 动态语言可以实现自由分配,需要的时候加进来,不需要的时候可以移除(Python,js)
- 快捷键
- F12可以查看源码,再按"Ctrl+-"可以迅速跳转回来
base作用: 访问父类的成员- 注意点:
base只能向上访问一层,无法再访问更进一层的类
- 注意点:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
// using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
// using ClassLibrary.MyNameSpace;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Car car = new Car();
Console.WriteLine(car.Owner); // Son
car.GetOwner(); // Son
Vehicle vehicle = new Vehicle();
Console.WriteLine(vehicle.Owner); // Parent
}
}
class Vehicle
{
public string Owner { get; set; }
public Vehicle()
{
this.Owner = "Parent";
}
}
class Car : Vehicle
{
public Car()
{
this.Owner = "Son";
}
public void GetOwner()
{
// 访问父类的成员
Console.WriteLine(base.Owner);
}
}
}
"""
base关键字的作用:
GetOwner方法中通过base.Owner访问基类的属性。
由于未使用new或virtual/override,子类直接修改了基类的Owner属性。此时,无论是this.Owner还是base.Owner,访问的是同一个属性,最终值为"Son"。
"""
- base基础实例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
// using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
// using ClassLibrary.MyNameSpace;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Car car = new Car();
car.GetOwner();
}
}
class Vehicle
{
public string Owner { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Vehicle()
{
this.Owner = "Parent";
this.Name = "Jim Green";
}
}
class Car : Vehicle
{
public Car()
{
this.Owner = "Son";
}
public void GetOwner()
{
Console.WriteLine(base.Owner); // Son
Console.WriteLine(base.Name); // Jim Green
}
}
}
- 使用
base继承父类的构造方法实例- 提示点: 父类的
构造器是不能被子类所继承的,若可以继承,就没有下面这种啰嗦的写法
- 提示点: 父类的
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
// using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Collections;
using System.Timers;
// using ClassLibrary.MyNameSpace;
namespace EventExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Car car = new Car("Jim Green");
Console.WriteLine(car.Owner); // Jim Green
}
}
class Vehicle
{
public string Owner { get; set; }
public Vehicle(string owner)
{
this.Owner = owner;
}
}
class Car : Vehicle
{
// public Car(string owner) // 这种写法会报错
// base(owner)显式调用了基类Vehicle的构造函数,并将参数owner传递给它。这是必须的,因为基类Vehicle没有无参构造函数(默认无参构造已被覆盖)
public Car(string owner):base(owner)
{
this.Owner = owner;
}
}-
}
-
访问级别说明-
类成员的访问级别,最高不能超过类对象本身- 假如
类对象的访问级别为默认的internal,即使类成员的访问级别为public,外界也是无法访问的 类成员之间的访问级别:public>internal>private
- public: 没有限制 - internal: 只要在同一个项目里面,都可以访问 - private(声明类成员的默认级别是private,声明类的默认级别是internal): 同一个类的内部,才能访问(名称空间里面的其他类无法访问) - protected: 只有继承链上面的成员可以访问该属性,不在链上面的,就无法访问(跨项目继承以后,也可以访问) - 注意点: 除了"private",其他三个关键字,子类都可以访问父类的成员 - internal+protected: 既能被继承类访问,也能被同项目的其他类访问,是"或"的关系 - 注意点: 声明方式上,位置可以互换,不影响功能(因为是"或"的关系,谁前谁后无所谓)快捷键
- 变量名为"_xxx"的,约定是属于'实例字段': public string _name - 假如
重写 -
-
重写的关键字virtual和override
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp9
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Car car = new Car();
car.Run();
}
}
class Vehicle
{
// 父类方法的虚拟方法,允许子类重写
public virtual void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm running");
}
}
class Car : Vehicle {
// 重写
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
}
子类对父类的方法隐藏
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp9
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 编译器会以"声明类型为准",调用"声明类型"的方法
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
vehicle.Run(); // I'm running
}
}
class Vehicle
{
// 没有virtual关键字
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm running");
}
}
class Car : Vehicle {
// 没有override关键字
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp9
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 调用重写的最新版本,也就是Car里面的Run方法
Vehicle vehicle = new RaseCar();
vehicle.Run(); // Car is running
}
}
class Vehicle
{
public virtual void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm running");
}
}
class Car : Vehicle {
// 重写一次
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
class RaseCar:Car
{
// 这里并没有重写
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
}
- 重写
属性示例
using System;
namespace PropertyOverrideExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 通过基类引用指向子类对象
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
Console.WriteLine($"当前速度:{vehicle.Speed}"); // 输出子类重写后的逻辑
// 直接使用子类引用
Car car = new Car();
Console.WriteLine($"当前速度:{car.Speed}");
}
}
class Vehicle
{
private int _speed = 50;
// 标记为 virtual 的基类属性
public virtual int Speed
{
get { return _speed; }
set { _speed = value; }
}
}
class Car : Vehicle
{
private int _boost = 20;
// 重写基类属性,添加额外逻辑
public override int Speed
{
get
{
// 子类在基类速度基础上增加 boost
return base.Speed + _boost;
}
set
{
// 子类可以修改赋值逻辑
base.Speed = value > 200 ? 200 : value;
}
}
}
}
抽象类
- 通俗理解: 就是
残缺类,具有部分类的功能- 就是一个
空壳,一个空的模板
- 就是一个
- 作用
- 作为
基类,定义一些函数成员让子类去实现(为复用而生) - 声明变量,引用
子类实例对象,调用子类的成员 - 以之前
重写的例子举例
- 作为
- 好处
- 作为
基类模板,几乎不用去动到,要实现功能,继承它并在子类中进行- 出了啥问题,我们直接在
子类中进行修改
- 出了啥问题,我们直接在
- 作为
- 注意点
抽象类不能创建实例对象
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
vehicle.Run(); // Car is running!
}
}
class Vehicle
{
public virtual void Run() {
Console.WriteLine("Vehicle is running!");
}
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("stopped!");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running!");
}
}
class Truck : Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running!");
}
}
}
- 把
Vehicle类改造成抽象类,实例如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
vehicle.Run();
}
}
// abstract 声明抽象类
abstract class Vehicle
{
// 声明抽象方法
public abstract void Run();
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("stopped!");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running!");
}
}
class Truck : Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running!");
}
}
}
接口(Interface)
- 定义: 完全未实现的
类- 区别于
抽象类: 未完全实现的类 接口的所有成员都是默认的public和abstract,所以这两个关键字都强制不用写
- 区别于
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vehicle vehicle = new RaseCar();
vehicle.Run(); // RaseCar is running!
}
}
// 特别抽象的类,完全的一个壳,啥都没有
abstract class VehicleBase
{
public abstract void Run();
public abstract void Stop();
}
// 继承
abstract class Vehicle:VehicleBase
{
public override void Run() {
Console.WriteLine("Vehicle is running!");
}
public override void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("stopped!");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running!");
}
}
class Truck : Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running!");
}
}
class RaseCar : Vehicle
{
public override void Run() {
Console.WriteLine("RaseCar is running!");
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vehicle vehicle = new RaseCar();
vehicle.Run(); // RaseCar is running!
}
}
// 使用Interface 关键字声明接口
interface VehicleBase
{
void Run();
void Stop();
}
// 继承
abstract class Vehicle:VehicleBase
{
// 添加virtual关键字,让派生类重写
public virtual void Run() {
Console.WriteLine("Vehicle is running!");
}
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("stopped!");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running!");
}
}
class Truck : Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running!");
}
}
class RaseCar : Vehicle
{
public override void Run() {
Console.WriteLine("RaseCar is running!");
}
}
}
接口的本质就是契约
-
生产者和消费者之间的契约- 既然是
契约,就要求契约是公开并且透明的,所以声明的方式默认并强制是public
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApp1 { internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // PhoneUser phoneUser = new PhoneUser(new NokiaPhone()); PhoneUser phoneUser = new PhoneUser(new SonyPhone()); phoneUser.UserPhone(); } } // 声明接口,预制方法 interface IPhone { void Daily(); void PickUp(); void Send(); void Receive(); } // 调用子类的实例,实现需求 class PhoneUser { private IPhone _phone; public PhoneUser(IPhone phone) { _phone = phone; } public void UserPhone() { _phone.Daily(); _phone.PickUp(); _phone.Send(); _phone.Receive(); } } // 继承接口并实现各自的方法 class NokiaPhone : IPhone { public void Daily() { Console.WriteLine("Nokia daily..."); } public void PickUp() { Console.WriteLine("Nokia pick up..."); } public void Receive() { Console.WriteLine("Nokia pick up..."); } public void Send() { Console.WriteLine("Nokia send..."); } } // 继承接口并实现各自的方法 class SonyPhone : IPhone { public void Daily() { Console.WriteLine("Sony daily..."); } public void PickUp() { Console.WriteLine("Sony pick up..."); } public void Receive() { Console.WriteLine("Sony received..."); } public void Send() { Console.WriteLine("Sony send..."); } } }快捷键
- 既然是
- cw: Console.WriteLine("......");
-
注意事项:
接口允许多继承(类似python类的多重继承) -
隐藏接口: 也可以称为显示调用显示调用: 必须声明更具体的实例,才能调用方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
WarmKiller warmKiller = new WarmKiller();
Killer killer = warmKiller;
killer.Kill();
// 这种实现方式也可以
// Killer killer = new WarmKiller();
// killer.Kill();
}
}
interface Gentleman
{
void Love();
}
interface Killer
{
void Kill();
}
class WarmKiller : Gentleman, Killer
{
// WarmKiller实例就可以调用
public void Love()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'll love u forerver...");
}
// 显示调用: Killer实例指向WarmKiller,才可以调用(演示方法在上面)
void Killer.Kill()
{
Console.WriteLine("a killer...");
}
}
}
- 此时,如果想调用
Love()方法怎木破,可以使用强制类型转换
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Killer killer = new WarmKiller();
killer.Kill();
// 强制类型转换(以下两种写法均可)
// var wk = (Gentleman)killer;
// wk.Love();
var wk = killer as WarmKiller;
wk.Love();
}
}
泛型讲解
泛型: 即通过参数化类型来实现在同一份代码上操作多种数据类型- 作用: 实现代码的复用,不必再单独为多个类创建各自的实例对象.声明泛型即可适配多个类实例
泛型类基础示例: 商店卖东西
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Apple apple = new Apple() { Color="Red" };
Book book = new Book() { Name="Nature" };
Box box1 = new Box() { AppleCargo=apple };
Box box2 = new Box() { BookCargo=book };
Console.WriteLine(box1.AppleCargo.Color);
Console.WriteLine(box2.BookCargo.Name);
}
}
class Apple
{
public string Color { get; set; }
}
class Book
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Apple AppleCargo { get; set; }
public Book BookCargo { get; set; }
}
}
- 随着生意越来越好,卖的东西越来越多,成员越来越膨胀,该如何解决这个问题---使用
泛型类
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Apple apple = new Apple() { Color="Red" };
Book book = new Book() { Name="Nature" };
// 声明Apple类型Box
Box<Apple> box1 = new Box<Apple>() { Cargo=apple };
// 声明Book类型Box
Box<Book> box2 = new Box<Book>() { Cargo=book };
Console.WriteLine(box1.Cargo.Color);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Cargo.Name);
}
}
class Apple
{
public string Color { get; set; }
}
class Book
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
// TCargo表示'泛型': 装Apple类型也可以,装Book类型也可以
class Box<TCargo>
{
public TCargo Cargo { get; set; }
}
}
泛型接口: 以学生为例
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明两个不同类型的实例并输出
Student<int> student = new Student<int>();
student.ID = 1;
student.Name = "Jim Green";
Console.WriteLine($"{student.ID}--{student.Name}");
Student<ulong> student2 = new Student<ulong>();
student2.ID = 100000000000000001;
student2.Name = "Kate Green";
Console.WriteLine($"{student2.ID}--{student2.Name}");
}
}
// 声明泛型接口
interface IUnique<Tid>
{
Tid ID { get; set; }
}
// 继承了泛型接口,那么Student类本身就是泛型类
class Student<Tid> : IUnique<Tid>
{
public Tid ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
- 上面这个例子中,
Student类变成了泛型类,它可以接收多种类型的数据,下面的例子,演示只能接收特定类型的类- 注意事项: 此时的
Student类不再是泛型类,而是具体类了
- 注意事项: 此时的
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
// ID只能是ulong类型的
student.ID = 1000000001;
student.Name = "Jim Green";
Console.WriteLine($"{student.ID}--{student.Name}");
}
}
interface IUnique<Tid>
{
Tid ID { get; set; }
}
// Student类只能实现ulong类型的ID属性
class Student : IUnique<ulong>
{
public ulong ID { get; set; }
// 可以额外添加自己的属性
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
- 使用系统自带的
泛型接口示例
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 调用系统自带的泛型接口
IList<int> list1 = new List<int>();
// 声明具体类型
// List<int> list2 = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list1.Add(i);
}
foreach (int item in list1) {
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
}
- 携带多个参数类型的泛型接口实例
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明key为int类型,value为string类型的字典变量
IDictionary<int,string> dict1 = new Dictionary<int,string>();
dict1[1] = "Jim Green";
dict1[2] = "Kate Green";
Console.WriteLine($"{dict1[1]}");
Console.WriteLine($"{dict1[2]}");
}
}
}
快捷键
- 属性 || 字段膨胀
- 方法膨胀
- 成员膨胀
泛型方法示例: 互换变量a和b的值
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
Console.WriteLine($"交换前:a={a},b={b}");
Swap<int>(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine($"交换后:a={a},b={b}");
}
// 声明泛型方法
static void Swap<T>(ref T a, ref T b)
{
T temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
}
}
泛型委托演示,它就是以前的委托示例如下- 无返回值的函数委托,使用
Action - 无返回值的函数委托,使用
Func
- 无返回值的函数委托,使用
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Action示例
Action<string> a1 = Say;
a1("Jim Green");
Action<int> a2 = Mul;
a2(10);
}
static void Say(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Hello {msg}");
}
static void Mul(int x)
{
Console.WriteLine(x * 100);
}
}
}
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Func示例
Func<int, int, int> func1 = Add;
var res1 = func1(10, 20);
Console.WriteLine(res1);
Func<double, double, double> func2 = Add;
var res2 = func2(10.1, 20.1);
Console.WriteLine(res2);
}
static int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
static double Add(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
}
- 上述示例也可以改造成
匿名表达式
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Func<double, double, double> func2 = (a,b)=>a+b;
var res2 = func2(10.1, 20.1);
Console.WriteLine(res2);
}
}
}
partial类
- 作用: 把
类切割成好几块,各个块之间负责自己的逻辑,又可以重新组合成类- 解释:
partial类允许将一个类的定义分散在多个文件中, 编译器会将它们合并成一个完整的类。
- 解释:
- 注意事项:
partial类必须在同一命名空间和程序集中,并且所有部分都要使用partial关键字 - 基础示例如下
// 文件1: Employee.Generated.cs
public partial class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Employee(int id, string name)
{
Id = id;
Name = name;
}
......
}
// 文件2: Employee.Extensions.cs
public partial class Employee
{
// 添加一个自定义方法
public void DisplayInfo()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Employee ID: {Id}, Name: {Name}");
}
......
}
// 主程序调用各个partial类
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Employee emp = new Employee(1, "John Doe");
emp.DisplayInfo(); // 输出: Employee ID: 1, Name: John Doe
}
}
- 应用场景
- 在 Windows Forms 项目中,你会看到类似这样的结构:
- Form1.cs:包含你的业务逻辑代码。
- Form1.Designer.cs:自动生成的界面布局代码(用 partial 修饰)。
- 好处: 这样设计可以避免手动修改被工具生成的代码覆盖的问题
- 小结: 用法无非就是类声明的时候,加了一个
partial,再加上一些范围限制
枚举
- 定义:
枚举就是常量集 - 作用: 用集合数据类型和
枚举进行关联,实现需求(约束选项值,不被人乱选 || 乱定义) - 基础示例如下
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person1 = new Person();
// 使用枚举
person1.Level = Level.Employee;
Person person2 = new Person();
person2.Level = Level.Boss;
Console.WriteLine(person1.Level);
Console.WriteLine(person2.Level);
// 强制类型转换,输出枚举的整数值
Console.WriteLine((int)person1.Level); // 0
Console.WriteLine((int)person2.Level); // 2
}
}
// 声明枚举
enum Level
{
Employee,
Manager,
Boss
}
class Person
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
// 自定义枚举属性
public Level Level { get; set; }
}
}
- 注意事项:
枚举默认的整数值是可以修改的,上面的示例小改一下
enum Level
{
Employee=100,
Manager=50,
Boss=1
}
......
Console.WriteLine((int)person1.Level); // 100
Console.WriteLine((int)person2.Level); // 1
- 如果出现
前面项有赋值,而后面项没有赋值的情况,那么该后面项编译器会自动加1
enum Level
{
Employee=100,
Manager, // 没有赋值,加1就是101
Boss=1
}
枚举的比特位玩法---同时选择多个(即多选)
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person1 = new Person();
// "|"表示二进制运算: 按位或
// person1.Skill = Skill.Cook & Skill.Drive; 输出结果为0 // "&"表示按位与
person1.Skill = Skill.Cook | Skill.Drive;
Console.WriteLine(person1.Skill); // 输出结果为6,表示同时具备Cook(2)和Drive(4)两种技能
}
}
enum Level
{
Employee=100,
Manager,
Boss=1
}
enum Skill
{
Cook=2,
Drive=4,
Swim=8,
program=16
}
class Person
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Level Level { get; set; }
public Skill Skill { get; set; }
}
}
结构体
- 定义: 和
类非常类似 - 以下实例涉及到
装箱和拆箱的操作
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student() { ID=1,Name="Jim Green" };
Console.WriteLine($"{student.ID}---{student.Name}");
// 装箱
object studentObj = student;
// 拆箱
Student student2 = (Student)studentObj;
Console.WriteLine(student2.Name);
}
}
// 这个例子根本看不出和"类"的区别
struct Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
- 所谓的装箱和拆箱
- 装箱: 将值类型转换为object引用类型
- 拆箱: 从object中提取原始值类型
结构体和类的区别
1. 结构体(struct)的特性
特性 说明
值类型 赋值时复制完整数据(栈内存操作)
独立副本 修改副本不影响原始值
默认无空值 不能为null(除非声明为可空类型 Student?)
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID=1,Name="Jim Green" };
// student2属于完整拷贝
Student student2 = student1;
student2.ID = 2;
student2.Name = "Kate Green";
Console.WriteLine($"{student1.ID}---{student1.Name}"); // 1---Jim Green
Console.WriteLine($"{student2.ID}---{student2.Name}"); // 2---Kate Green
}
}
struct Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID=1,Name="Jim Green" };
// student2是引用类型,共享同一对象
Student student2 = student1;
student2.ID = 2;
student2.Name = "Kate Green";
Console.WriteLine($"{student1.ID}---{student1.Name}"); // 2---Kate Green
Console.WriteLine($"{student2.ID}---{student2.Name}"); // 2---Kate Green
}
}
// struct Student
class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
结构体可以实现接口,但不能被继承,没有神马基类和派生类的说法
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID=1,Name="Jim Green" };
student1.Speek(); // I'm speaking.
}
}
interface ISpeak
{
void Speek();
}
struct Student:ISpeak
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Speek()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm speaking."); ;
}
}
}
结构体的构造函数必须带参数,没带参数会报错,编译不过去
......
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student() { ID=1,Name="Jim Green" };
Console.WriteLine(student.Name); // Jim Green
}
}
interface ISpeak
{
void Speek();
}
struct Student:ISpeak
{
public Student(int ID,string Name)
{
this.ID = ID;
this.Name = Name;
}
// 无参数构造器会报错
//public Student()
//{
// this.ID = 1;
// this.Name = "Jim Green";
//}
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Speek()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm speaking."); ;
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号