Vue2 --- 脚手架编程 -- 基础语法
0. ref 属性
1. 普通标签绑定ref属性,用来获取Dom元素
<template>
<div class="hello">
<!-- 1. 使用 ref 绑定标签 -->
<h1 ref="title">{{ msg }}</h1>
<button @click="showDom">点我输出上面的Dom元素</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'school-info',
data() {
return {
msg: "你好"
}
},
methods: {
showDom() {
// 2. 所有被ref绑定Dom元素都被存储在了$refs里
console.log(this.$refs.title);
}
}
}
</script>
1. 父向子传递数据
1. 子组件接收数据
1. 简单声明接收数据
R
StudentInfo.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生性别: {{sex}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data(){
return {
title: "这是学生信息页面"
}
},
// 声明这个页面需要向外部接收的数据
props:["name","sex","age"]
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2. 对参数做限制
1. 可以限制传递的参数类型
如果接收的数据类型错误,会在控制台报错,需要的是什么类型,传过来的是什么类型
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生性别: {{sex}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age+1}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
title: "这是学生信息页面"
}
},
// 声明这个页面需要向外部接收的数据,并限制传进来的类型
props: {
name:String,
age:Number,
sex:String
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2. 更多限制条件
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生性别: {{sex}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age+1}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
title: "这是学生信息页面"
}
},
// 声明这个页面需要向外部接收的数据,并限制传进来的类型
props: {
name: {
type: String, // 声明参数类型
require: true, // 声明此参数为必传参数
},
age: {
type: Number,
default: 99, // 设置如果没有传此参数的默认值
},
sex: {
type: String,
require: true,
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
3. 修改接收的参数
默认情况下子组件内接收到的参数是不允许修改的,但是有的时候可能需要对这个参数进行修改,prop的优先级比data中的参数高,如果data中定义的参数和prop冲突,那么优先使用prop中的参数
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生性别: {{sex}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{myAge}}</h2> <!-- 2.读数据为 data 中定义的 -->
<button @click="updateAge">修改学生年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
title: "这是学生信息页面",
myAge: this.age // 1. 定义要修改的数据,数据来源于prop中的age
}
},
methods:{
updateAge(){
this.myAge++ // 3. 调用方法修改data中的数据
}
},
props: {
name: {
type: String,
require: true,
},
age: {
type: Number,
default: 99,
},
sex: {
type: String,
require: true,
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2. 父组件传递数据
SchoolInfo.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 使用自定义属性向子组件传递 name,sex,age 参数,不允许自定义Vue内置的一些属性 -->
<student-info name="小明" sex="男" age="18"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: "schoolInfo",
components: {StudentInfo},
comments:{
StudentInfo
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
3. 参数的类型
1. 传递字符串类型
<template>
<div>
<!-- age="18" 传的是字符串类型 -->
<student-info name="小明" sex="男" age="18"/>
</div>
</template>
2. 传递数值类型
<template>
<div>
<!-- :age="18" 前面加了冒号: ,传的是数值类型 -->
<student-info name="小明" sex="男" :age="18"/>
</div>
</template>
2. 子向父传递数据
1. 自定义函数携带数据
1. 父组件中定义一个函数,并将此函数传递到子组件中
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<div class="todo-container">
<div class="todo-warp">
<Header :receiveTodos="receiveTodos"/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Header from "@/components/TodoHeader";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Header
},
data() {
return {
// 1. 定义事件列表
todos: [
{id: "1", title: "吃饭", done: false},
{id: "2", title: "睡觉", done: true},
{id: "3", title: "打豆豆", done: false},
]
}
},
methods:{
receiveTodos(todoObj){
console.log("我是App组件,我接受到了来自子组件的参数: ",todoObj)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
Header.vue
<template>
<div class="todo-header">
<!-- 1. 绑定回车键按下再抬起的事件,并将input中输入的值和title双向绑定 -->
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入你的任务名称,按回车确认" v-model="title" @keyup.enter="addTodo">
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 3.2 导入nanoid包,用来生成唯一随机字符串
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name: "HeaderInfo",
props:["receiveTodos"], // 1. 声明接收来自App组件的参数名
data() {
return {
title: ""
}
},
methods: {
addTodo() {
console.log(this.title)
const todoObj = {id: nanoid(), title: this.title, done: false}
// 2. 调用receiveTodos(todObj), 并将用户生成的todo对象传到receiveTodos(todObj)函数中
// 控制台可以看到父组件App接收到了子组件传递过来的参数
this.receiveTodos(todoObj)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2. 自定义事件传递参数
自定义事件是只给组件来使用的
1. 定义自定义事件
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP: </h1>
<!-- 1. 用 v-on:事件名="函数名" / @事件名="函数名" 定义一个自定义事件,如果时间被触发了就调用 getStudentName()函数-->
<student-info @getName="getStudentName"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SchoolInfo from "@/components/SchoolInfo";
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
SchoolInfo,
StudentInfo
},
methods:{
// ...options 接收其他参数,是个数组
getStudentName(name,...options){
console.log("App 组件的getStudentName被调用了",name)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
2. 触发自定义事件
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentName">点击发送学生姓名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
name: "小明",
age: 18
}
},
methods:{
sendStudentName(){
// 使用this.$emit(事件名,参数)触发Student组件实例对象上的getName事件,并传递学生姓名参数
this.$emit("getName",this.name)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.student{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
3. ref 标识子组件,并绑定自定义事件
子组件标签绑定 ref 属性,用来获取子组件实例对象,是组件间通信的基础
用 id 绑定组件标签只会获得组件的Dom结构,无法获得组件实例对象
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP: </h1>
<!-- 1. 使用ref 获取子组件实例对象的名称-->
<student-info ref="student"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
// 2. 声明 mouted() 函数给子组件绑定自定义事件
mounted() {
// this.$refs.student,获取到子组件实例对象
// .$on("getName",this.getStudentName) 给子组件实例对象绑定 getName事件,当这个getName事件被触发的时候执行回调函数getStudentName()
this.$refs.student.$on("getName",this.getStudentName)
},
methods: {
getStudentName(name,...options) {
console.log("App 组件的getStudentName被调用了", name)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentName">点击发送学生姓名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
name: "小明",
age: 18
}
},
methods:{
sendStudentName(){
// 1. 触发Student组件实例对象上的getName事件,并传递学生姓名参数
this.$emit("getName",this.name)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.student{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
4. ref 的优势
这种方法更灵活,比如我要在App挂载后等ajax请求发送得到结果后,再给Student组件实例对象绑定自定义事件
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP: </h1>
<!-- 1. 使用ref 获取子组件实例对象的名称-->
<student-info ref="student"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
mounted() {
// 3秒后再绑定点击事件,这里模拟ajax请求的网络延迟
setTimeout(() => {
this.$refs.student.$on("getName", this.getStudentName)
}, 3000)
},
methods: {
getStudentName(name,...options) {
console.log("App 组件的getStudentName被调用了", name)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
5. 自定义事件也可以用事件修饰符
设置自定义事件只触发一次
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP,学生姓名是: {{studentName}} </h1>
<student-info ref="student"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
mounted() {
// 1. 使用$once() 控制只触发一次
this.$refs.student.$once("getName", this.getStudentName)
},
methods: {
getStudentName(name,...options) {
console.log("App 组件的getStudentName被调用了", name)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
6. 解绑自定义事件
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentInfo">点击发送学生信息</button>
<button @click="unbind">解绑一个自定义事件</button>
<button @click="unbinds">解绑多个自定义事件</button>
<button @click="unbindAll">解绑所有自定义事件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
name: "小明",
age: 18
}
},
methods: {
sendStudentInfo() {
this.$emit("getName", this.name)
this.$emit("getAge", this.age)
},
unbind() {
// 解绑一个自定义事件
this.$off("getName")
},
unbinds() {
// 解绑多个自定义事件
this.$off(["getName","getAge"])
},
unbindAll(){
// 解绑所有的自定义事件
this.$off()
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.student {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
如果当前组件或者Vue实例对象被销毁了,其所绑定的自定义事件也会被销毁
7. 自定义事件的回调
谁触发的这个自定义事件,自定义事件中的回调就是谁,methods中定义的函数中的this永远是当前组件的实例对象
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP,学生姓名是 {{studentName}}</h1>
<student-info ref="student"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
data() {
return {
studentName: ""
}
},
mounted() {
// 1. 正常使用回调,在getStudentName中赋值this.studentName(可以)
// this.$refs.student.$on("getName", this.getStudentName)
// 2.直接在这里赋值,这里的this是触发getName这个自定义事件的实例对象(不可以)
// this.$refs.student.$on("getName", function (name) {
// console.log(this)
// this.studentName = name
// })
// 3. 修改上面的问题,将函数改为剪头函数,箭头函数是没有自己的this,会找外部的mouted()的this
// 这个this就是app组件实例对象,即可赋值他的studentName
this.$refs.student.$on("getName", name =>{
console.log(this)
this.studentName = name
})
},
methods: {
getStudentName(name) {
console.log("App 组件的getStudentName被调用了", name)
this.studentName = name
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
8. 组件绑定原生 DOM 事件
方法一: 子组件内触发原生DOM事件
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP</h1>
<!-- 绑定原生click 原生Dom事件 -->
<student-info @click="show"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
methods: {
show(){
alert(12345)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentInfo">点击发送学生信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
name: "小明",
age: 18
}
},
methods: {
sendStudentInfo() {
// 必须在子组件中触发这个原生DOM事件
this.$emit("click")
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.student {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
方法二: 用修饰符指定组件绑定的事件为原生事件
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP</h1>
<!-- 使用native事件修饰符来表明当前事件为原生DOM事件,事件绑定在子组件的最外层div标签上 -->
<student-info @click.native="show"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
methods: {
show(){
alert(12345)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
Student.vue 中不用再触发DOM事件
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentInfo">点击发送学生信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
name: "小明",
age: 18
}
},
methods: {
sendStudentInfo() {
console.log(this.name)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.student {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
3. 全局事件总线(任意组件传递)
任意组件之间的通信,更适用于爷爷和孙子之间传递数据
1. 实现思路
**流程: **
在A组件中给X绑定一个自定义事件demo,并将回调函数定义在A组件中,B组件想给A组件传数据,B组件触发X上的自定义事件demo,并将数据传到X,X所对应的回调就要执行,就将数据以参数的形式传给A组件中定义的回调函数参数中

**思路: **
- 必须要求X被所有的组件看到: Vue的原型对象上
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.prototype.x = {a:1,b:2}
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
- 必须能调用到
$on $off $emit函数: Vue的实例对象(vm)或VueComponent的实例对象(vc)
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this; // 安装全局事件总线,$bus就是当前应用的vm
}
}).$mount('#app')
2. 案例
main.js 安装全局事件总线
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this // 安装全局事件总线,$bus就是当前应用的vm
}
}).$mount('#app')
App.vue 接收数据方绑定自定义事件和回调函数
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP,接收到来自Student组件的学生姓名: {{studentName}}</h1>
<student-info/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
data() {
return {
studentName: ""
}
},
mounted() {
// 1. 给全局事件总线绑定 getName自定义事件,并指定回调函数,如果是直接写在绑定自定义事件的$on()里,必须用剪头函数 =>
this.$bus.$on("getName", (name) => this.studentName = name)
},
beforeDestroy() {
this.$bus.off("getName") // 2. 记得解绑自定义事件,事件总线上的自定义事件越来越多
}
}
</script>
<style>
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
Student.vue 发送数据方触发自定义事件并传递参数
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentInfo">点击发送学生信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
name: "小明",
age: 18
}
},
methods:{
sendStudentInfo(){
// 触发全局事件总线上绑定的getName,并执行对其绑定getName自定义事件的回调函数
this.$bus.$emit("getName",this.name)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.student {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
4. 消息订阅与发布
任意组件之间通信,推荐使用事件总线
1. 实现思路
- 需要数据的组件订阅消息(定义回调函数)
- 传递数据的组件发布消息(执行函数)
2. 下载三方库
npm i pubsub-js
3. 使用
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是APP,接收到来自Student组件的学生姓名: {{studentName}}</h1>
<student-info/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import StudentInfo from "@/components/StudentInfo";
// 1. 引入pubsubjs
import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
StudentInfo
},
data() {
return {
studentName: ""
}
},
// 2. 在mounted中订阅消息,消息名为:getName
mounted() {
// msgName为消息名,如果msgName不需要用到,可以用_占位,data是携带的数据,并将返回的消息ID设置在vm身上,将来要取消订阅
// 2.1 这里的函数如果是自定义函数,this是undefind,要改成箭头函数
this.pubID = pubsub.subscribe("getName", (msgName, data) => {
this.studentName = data
})
// 2.2 或者将回调函数体写在methods中
this.pubID = pubsub.subscribe("getName", this.getStudentName)
},
// 3. 在 beforeDestroy 中取消订阅
beforeDestroy() {
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.pubID)
},
methods:{
// 如果msgName不需要用到,可以用_占位
getStudentName(msgName, name){
this.studentName = name
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
h1 {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>学生姓名: {{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄: {{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentInfo">点击发送学生信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1. 引入pubsubjs
import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
export default {
name: "Student-info",
data() {
return {
name: "小明",
age: 18
}
},
methods:{
// 2. 在点击事件的回调函数中发布消息
sendStudentInfo(){
pubsub.publish("getName",this.name)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.student {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
5. slot 插槽
也是一种组件间通信的方式,只不过父组件向子组件传递的不是数据,而是html结构,而子组件向父组件传递的是数据,不能单独使用,必须搭配使用,不能向之前的那些一样值传递数据
1. 不使用插槽

App.vue
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<Category :title="'美食'" :listData="foods"/>
<Category :title="'游戏'" :listData="games"/>
<Category :title="'电影'" :listData="films"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "@/components/Category.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Category
},
data() {
return {
foods:["火锅","烧烤","小龙虾","牛排"],
games:["红色警戒","穿越火线","劲舞团","超级玛丽"],
films:["<<教父>>","<<拆弹专家>>","你好,李焕英","天下无贼"],
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
Category.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in listData" :key="index">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// eslint-disable-next-line vue/multi-word-component-names
name: "Category",
props:["listData","title"]
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.category {
background-color: aqua;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
2. 需求
只在其中一个或两个组件中展示一张图片
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in listData" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<img v-show="title === '美食'" src="https://q5.itc.cn/q_70/images03/20240313/135f344687dd4387a15fe35dc5a3bfae.jpeg" alt="">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// eslint-disable-next-line vue/multi-word-component-names
name: "Category",
props: ["listData", "title"]
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.category {
background-color: aqua;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: orange;
}
img {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
假如将来不同的不见不同的需求,那么要判断的条件就越来越多,比较混乱
3. 默认插槽

App.vue 将想向子组件中放的标签,放在父组件的子组件标签体中,在App组件中完成解析后再塞入Category组件中,如果样式写在App组件中,就是解析完后带着样式塞进Category,如果样式写在Category中,就是解析完后,再Category中控制样式
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<Category :title="'美食'">
<!-- 声明向这个子组件中放的标签 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in foods" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<img src="https://q5.itc.cn/q_70/images03/20240313/135f344687dd4387a15fe35dc5a3bfae.jpeg" alt="">
</Category>>
<Category :title="'游戏'">
<!-- 声明向这个子组件中放的标签 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</Category>>
<Category :title="'电影'">
<!-- 声明向这个子组件中放的标签 -->
<!-- 加controls属性才能有点击播放的按钮 -->
<video controls src="https://ksv-video-picture.cdn.bcebos.com/f0dbb327492e5a72a2862105d86ca8b5c0b016da.jpg?x-bce-process=image%2Fquality%2Cq_80""></video>
</Category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "@/components/Category.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Category
},
data() {
return {
foods:["火锅","烧烤","小龙虾","牛排"],
games:["红色警戒","穿越火线","劲舞团","超级玛丽"],
films:["<<教父>>","<<拆弹专家>>","你好,李焕英","天下无贼"],
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
Category.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<!-- 使用slot标签占位,vue渲染的时候会将父组件中在子组件标签体中定义好的标签放在这里,可以设置默认值 -->
<slot>我是默认值,当父组件没有传递标签结构时,我会出现</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Category",
props: ["title"]
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.category {
background-color: aqua;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: orange;
}
video{
width: 100%;
}
img {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
4. 具名插槽
具有名字的插槽,当Category组件中出现多个插槽,并且位置有序,就需要有名字了
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<Category :title="'美食'">
<!-- 声明这个标签放在 slotHeader 插槽的位置 -->
<ul slot="slotHeader">
<li v-for="(item,index) in foods" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<!-- 声明这个标签放在 slotFooter 插槽的位置 -->
<img slot="slotFooter" src="https://q5.itc.cn/q_70/images03/20240313/135f344687dd4387a15fe35dc5a3bfae.jpeg" alt="">
</Category>>
<Category :title="'游戏'">
<!-- 声明这个标签放在 slotHeader 插槽的位置 -->
<ul slot="slotHeader">
<li v-for="(item,index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</Category>>
<Category :title="'电影'">
<!-- 声明这个标签放在 slotFooter 插槽的位置 -->
<video slot="slotFooter" controls src="https://ksv-video-picture.cdn.bcebos.com/f0dbb327492e5a72a2862105d86ca8b5c0b016da.jpg?x-bce-process=image%2Fquality%2Cq_80""></video>
</Category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "@/components/Category.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Category
},
data() {
return {
foods:["火锅","烧烤","小龙虾","牛排"],
games:["红色警戒","穿越火线","劲舞团","超级玛丽"],
films:["<<教父>>","<<拆弹专家>>","你好,李焕英","天下无贼"],
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
video{
width: 100%;
}
</style>
Category.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<!-- 定义两个具名插槽 -->
<slot name="slotHeader">我是默认值,当父组件没有传递标签结构时,我会出现</slot>
<slot name="slotFooter">我是默认值,当父组件没有传递标签结构时,我会出现</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Category",
props: ["title"]
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.category {
background-color: aqua;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: orange;
}
video{
width: 100%;
}
img {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
根据声明的标签,和插槽的位置匹配插入结构,没有插入结构的出现默认值

如果外层是用template标签包裹的,可以有第二种写法
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<Category :title="'美食'">
<ul slot="slotHeader">
<li v-for="(item,index) in foods" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<img slot="slotFooter" src="https://q5.itc.cn/q_70/images03/20240313/135f344687dd4387a15fe35dc5a3bfae.jpeg"
alt="">
</Category>
<Category :title="'游戏'">
<ul slot="slotHeader">
<li v-for="(item,index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</Category>
<Category :title="'电影'">
<video slot="slotHeader" controls
src="https://ksv-video-picture.cdn.bcebos.com/f0dbb327492e5a72a2862105d86ca8b5c0b016da.jpg?x-bce-process=image%2Fquality%2Cq_80""></video>
<!-- 只有 template 标签包裹的标签,可以使用 v-slot:插槽名 指定插槽 -->
<template v-slot:slotFooter>
<div class="foot">
<a href="">推荐</a>
<a href="">经典</a>
<a href="">热门</a>
</div>
<h4> 欢迎观影! </h4>
</template>
</Category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "@/components/Category.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Category
},
data() {
return {
foods: ["火锅", "烧烤", "小龙虾", "牛排"],
games: ["红色警戒", "穿越火线", "劲舞团", "超级玛丽"],
films: ["<<教父>>", "<<拆弹专家>>", "你好,李焕英", "天下无贼"],
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
video {
width: 100%;
}
.foot{
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
5. 作用域插槽
需求: 页面中有三个游戏分类,数据也是一样的,但是要生成里面结构的时候,一个是无需列表,一个是有序列表,一个全是h4 标题
App.vue 使用Category组件,App组件中定义Category组件中的结构
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<Category :title="'游戏'">
<!-- 1. 外侧必须包裹 template 标签,用scope属性起个名字 -->
<template scope="name1">
<ul>
<!-- 取数据时,使用上面scope定义的名字.games.即name1.games -->
<li v-for="(item,index) in name1.games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</template>
</Category>
<Category :title="'游戏'">
<!-- 可以不起名字,使用解构赋值语法 -->
<template scope="{games}">
<ol>
<li v-for="(item,index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ol>
</template>
</Category>
<Category :title="'游戏'">
<!-- 可以使用 slot-scope 属性,跟scope是一样的 -->
<template slot-scope="name3">
<h4 v-for="(item,index) in name3.games" :key="index">{{ item }}</h4>
</template>
</Category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "@/components/Category.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Category
},
}
</script>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
video {
width: 100%;
}
.foot {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
Category.vue 将数据传给插槽的使用者App组件
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<!-- 将 Category 组件中的数据传递给插槽的使用者 App 组件,让其可以循环这个games,可以传多个,用名字.msg即可取到 -->
<slot :games="games" msg="hello">我是默认值,当父组件没有传递标签结构时,我会出现</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Category",
props: ["title"],
data() {
return {
games: ["红色警戒", "穿越火线", "劲舞团", "超级玛丽"],
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.category {
background-color: aqua;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: orange;
}
video{
width: 100%;
}
img {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
6. Vuex
1. 是什么
专门在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写).也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任何组件间通信
2. 什么时候使用Vuex
- 多个组件依赖于同一个状态(数据)
- 来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态(数据)
3. 对比
1. 全局事件总线

2. Vuex
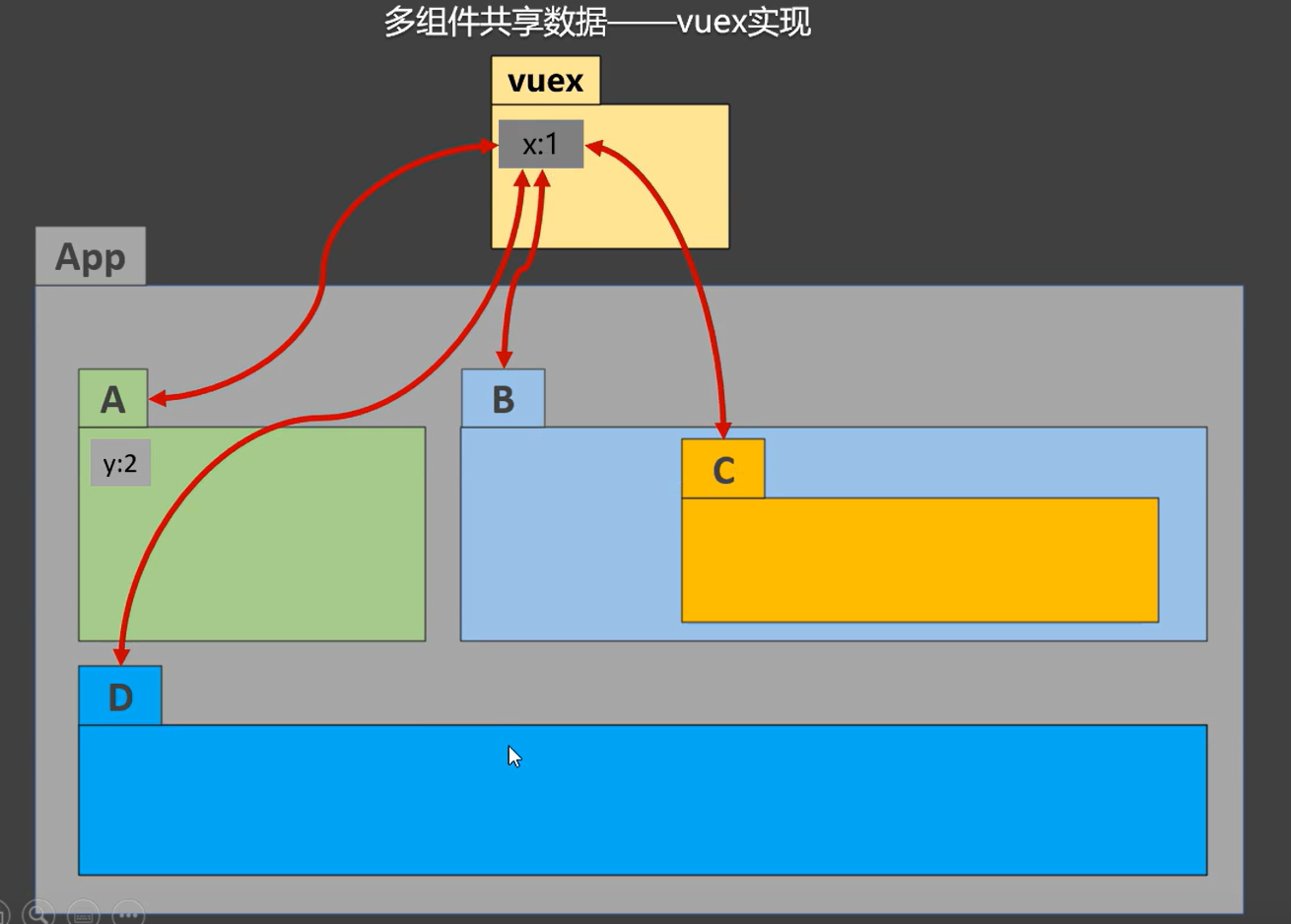
4. 工作原理图

Actions --- 存储数据操作函数的一个对象,同时可以发送ajax请求到其他的后端服务器,得到一些数据然后将函数和数据commit给Mutations进行加工,如果不发送ajax请求,可以省略这一步,直接commit给Mutations
Mutations --- 存储着数据操作函数和存储数据的State的一个对象
State --- vuex用来存储数据的一个对象
Store --- 管理所有的vuex组件
Dispatch --- store提供的方法,用来提交数据操作函数和参数
Commit ---store提供的方法,用来将数据操作函数和参数,提交给Mutations
5. 环境搭建
1. 安装Vuex
# vue2必须指定vuex的3版本
npm install vuex@3
2. 引入Vuex
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1. 导入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 2. 使用Vuex插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
3. 创建store
src目录下创建store/index.js
src/store/index.js
// 该文件用于创建Vuex中最为核心的store
// 1. 导入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 2. 导入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 3. 应用Vuex插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 准备actions对象,用于响应组件中的动作
const actions = {}
// 准备mutations对象,用于操作数据
const mutations = {}
// 准备state对象,用于存储数据
const state = {}
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
// 配置项
actions,
mutations,
state,
})
4. 配置store
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1. 引入store,默认引入index.js 可以省略
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 2. 配置store,Vux在store中引入及使用了
store: store
}).$mount('#app')
6. 案例
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const actions = {
// 2. 定义操作sum的方法,context为上下文对象,其中保存着所有的数据及操作函数
add: function (context, value) {
// 2. 提交给mutations操作数据
context.commit("ADD", value)
},
sub: function (context, value) {
context.commit("SUB", value)
},
// 当sum值为奇数时再加
addOdd:function (context,value){
if (context.state.sum % 2){
context.commit("ADD",value)
}
},
// 在actions中调用ajax请求,这里使用定时器模拟
addWait:function (context,value){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('ADD',value)
},500)
}
}
// 一般mutations中的函数大写,用来区分和actions中的函数
// 只定义真实操作数据的逻辑,没有业务逻辑
const mutations = {
ADD: function (state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
SUB: function (state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
}
const state = {
// 1. 定义数据
sum: 0
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
})
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<h3>求和结果为:{{ sum }}</h3>
<h3>放大十倍结果为:{{ bigSum }}</h3>
<div class="warpper">
<Add/>
<Sub/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Add from "@/components/Add.vue";
import Sub from "@/components/Sub.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Add,
Sub
},
computed: {
sum() {
// 1. 展示数据,数据是存在Vuex中的state中的,使用$store.state调用
return this.$store.state.sum
},
bigSum() {
return this.$store.getters.bigSum
},
}
}
</script>
<style>
.warpper {
display: flex;
}
</style>
Add.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">延时+</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">奇数+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Add",
methods:{
increment(){
// 1. 提交sum的操作函数名
// this.$store.dispatch('add',1)
// 如果没有复杂的业务逻辑,很直接的操作数据,也可以直接调用mutations中定义的ADD
this.$store.commit("ADD",1)
},
// 模拟网络请求后得到数据后再具体操作
incrementWait(){
this.$store.dispatch('addWait',1)
},
incrementOdd(){
this.$store.dispatch("addOdd",1)
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button{
margin-left: 30px;
}
</style>
Sub.vue
<template>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// eslint-disable-next-line vue/multi-word-component-names
name: "Sub",
methods:{
decrement(){
// 1. 提交sum的操作函数名
// this.$store.dispatch("sub",1)
// 2. 如果没有复杂的业务逻辑,很直接的操作数据,也可以直接调用mutations中定义的SUB
this.$store.commit("SUB",1)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button{
margin-left: 20px;
}
</style>
7. getters
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const actions = {
add: function (context, value) {
context.commit("ADD", value)
},
sub: function (context, value) {
context.commit("SUB", value)
},
addOdd:function (context,value){
if (context.state.sum % 2){
context.commit("ADD",value)
}
},
addWait:function (context,value){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('ADD',value)
},500)
}
}
const mutations = {
ADD: function (state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
SUB: function (state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
}
const state = {
sum: 0
}
// 选用:对数据的进一步加工
const getters = {
// 用于将state中的数据加工
bigSum(state){
return state.sum * 10
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
getters // 配置getters
})
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<h3>求和结果为:{{ sum }}</h3>
<!-- 使用计算属性获得bigSum的值 -->
<h3>放大十倍结果为:{{ bigSum }}</h3>
<div class="warpper">
<Add/>
<Sub/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Add from "@/components/Add.vue";
import Sub from "@/components/Sub.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Add,
Sub
},
computed: {
sum() {
return this.$store.state.sum
},
// 取getters中对数据进一步加工后的值
bigSum() {
return this.$store.getters.bigSum
},
}
}
</script>
<style>
.warpper {
display: flex;
}
</style>
8. mapState
如果有多个state中定义的数据,使用mapState可以很简单的生成多个计算属性的函数
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<!-- 1. 展示数据,数据是存在Vuex中的state中的,使用$store.state调用 -->
<h3>求和结果为:{{ he }}</h3>
<h3>放大十倍结果为:{{ bigSum }}</h3>
<h3>学校:{{ xuexiao }}</h3>
<h3>地址:{{ dizhi }}</h3>
<div class="warpper">
<Add/>
<Sub/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Add from "@/components/Add.vue";
import Sub from "@/components/Sub.vue";
// 1. 导入mapState
import {mapState} from "vuex";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Add,
Sub
},
computed: {
// 原生写法
sum() {
return this.$store.state.sum
},
school(){
return this.$store.state.school
},
address(){
return this.$store.state.address
},
// 两种写法
// 借助 mapState 生成多个计算属性,从state中获取数据
// 对象写法,生成的计算属性的函数名和$state.state中定义的变量名根据对象中的key-value生成
...mapState({he:"sum",xuexiao:"school",dizhi:"address"}),
// 借助 mapState 生成多个计算属性,从state中获取数据
// 数组简写方法,生成的计算属性的函数名和变量名根据数组中的元素生成,函数名和$state.state中定义的变量名相同
...mapState(["sum","school","address"]),
}
}
</script>
<style>
.warpper {
display: flex;
}
</style>
9. mapGetters
<template>
<div id="app" class="container">
<!-- 1. 展示数据,数据是存在Vuex中的state中的,使用$store.state调用 -->
<h3>求和结果为:{{ he }}</h3>
<h3>放大十倍结果为:{{ bigSum }}</h3>
<h3>学校:{{ xuexiao }}</h3>
<h3>地址:{{ dizhi }}</h3>
<div class="warpper">
<Add/>
<Sub/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Add from "@/components/Add.vue";
import Sub from "@/components/Sub.vue";
// 1. 导入mapGetters
import {mapState,mapGetters} from "vuex";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Add,
Sub
},
computed: {
...mapState(["sum","school","address"]),
// 两种写法
// 借助 mapState 生成多个计算属性,从getters中获取数据
// 对象写法,生成的计算属性的函数名和$state.getters中定义的变量名根据对象中的key-value生成
...mapGetters({bigSum:"bigSum"})
// 借助 mapState 生成多个计算属性,从getters中获取数据
// 数组简写方法,生成的计算属性的函数名和变量名根据数组中的元素生成,函数名和$state.getters中定义的变量名相同
...mapGetters(["bigSum"])
}
}
</script>
<style>
.warpper {
display: flex;
}
</style>
10. mapActions
Add.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<button @click="increment(1)">+</button>
<!-- 2. 手动将想要Add的value参数传到incrementWait中 -->
<button @click="incrementWait(1)">延时+</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(1)">奇数+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1. 导入mapActions
import {mapActions,mapMutations} from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Add",
methods:{
// mapMutations的原生写法
increment(){
this.$store.commit("ADD",1)
},
...mapMutations({increment:"increment"})
...mapMutations(["increment"])
// mapActions的原生写法
incrementWait(){
this.$store.dispatch('addWait',1)
},
incrementOdd(){
this.$store.dispatch("addOdd",1)
}
// 两种写法
// 3. 借助 mapState 生成多个方式,调用$store.dispatch(),对象写法
...mapActions({incrementWait:"incrementWait",incrementOdd:"incrementOdd"})
// 3. 借助 mapState 生成多个方式,调用$store.dispatch(),如果事件回调函数和actions中定义的方法名相同,数组写法
...mapActions(["increment",incrementOdd])
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button{
margin-left: 30px;
}
</style>
11. mapMutations
Add.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<!-- 2. 手动将想要Add的value参数传到increment中 -->
<button @click="increment(1)">+</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">延时+</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">奇数+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1. 导入mapMutations
import {mapMutations} from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Add",
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit("ADD",1)
},
// 两种写法
// 3. 借助 mapState 生成多个方式,调用$store.commit(),对象写法
...mapMutations({increment:"increment"})
// 3. 借助 mapState 生成多个方式,调用$store.commit(),如果事件回调函数和mutations中定义的方法名相同,数组写法
...mapMutations(["increment"])
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button{
margin-left: 30px;
}
</style>
或者手动调用函数传参数
<template>
<div class="category">
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">延时+</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">奇数+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Add",
methods:{
// 1. 手动调用函数传递参数
increment(){
this.incrementFunc(1)
},
// 借助 mapState 生成多个方式,调用$store.commit()
...mapMutations({incrementFunc:"increment"})
incrementWait(){
this.$store.dispatch('addWait',1)
},
incrementOdd(){
this.$store.dispatch("addOdd",1)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button{
margin-left: 30px;
}
</style>
12. 模块化拆分
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 求和相关的配置
const countOptions = {
namespaced:true, // 加命名空间
actions: {
add: function (context, value) {
context.commit("ADD", value)
},
sub: function (context, value) {
context.commit("SUB", value)
},
addOdd: function (context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit("ADD", value)
}
},
addWait: function (context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('ADD', value)
}, 500)
}
},
mutations: {
ADD: function (state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
SUB: function (state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
},
state: {
sum: 0,
school: "一中",
address: "北京"
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}
// 人员相关的配置
const personOptions = {
namespaced:true, // 加命名空间
actions: {
add: function (context, value) {
context.commit("ADD", value)
},
sub: function (context, value) {
context.commit("SUB", value)
},
addOdd: function (context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit("ADD", value)
}
},
addWait: function (context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('ADD', value)
}, 500)
}
},
mutations: {
ADD: function (state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
SUB: function (state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
},
state: {
sum: 0,
school: "一中",
address: "北京"
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
countOptions, // 求和相关的配置
personOptions // 人员相关的配置
}
})
调用
// 原生调用
this.$store.state.countOptions.sum // 读取countOptions中的state数据
this.$store.getters["countOptions/bigSum"] // 读取countOptions中的getters数据
this.$store.dispath("countOptions/incrementWait",1)
this.$store.commit("countOptions/incrementWait",1)
// 借助map
...mapState("countOptions",["sum","school","address"]), // 读取 countOptions中state中的sum school address
...mapState("personOptions",["personList"]), // 读取 personOptions
...mapGetters("countOptions",["bigSum"]), // 读取 countOptions中getters中的bigSum
...mapGetters("personOptions",["personName"]), // personOptions的
...mapActions("countOptions",["incrementWait","incrementOdd"]), // 调用 countOptions的actions中的incrementWait
...mapActions("personOptions",["personNameAdd"]), // 调用 personOptions的
...mapMutations("countOptions",["increment"]), // 调用 countOptions的mutations中的incrementWait
...mapMutations("personOptions",["personList"]), // 调用 personOptions的
13. 文件拆分
src/store/count.js
// 求和相关的配置
export default {
actions: {
// 2. 定义操作sum的方法,context为上下文对象,其中保存着所有的数据及操作函数
add: function (context, value) {
// 2. 提交给mutations操作数据
context.commit("ADD", value)
},
sub: function (context, value) {
context.commit("SUB", value)
},
// 当sum值为奇数时再加
addOdd: function (context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit("ADD", value)
}
},
// 在actions中调用ajax请求,这里使用定时器模拟
addWait: function (context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('ADD', value)
}, 500)
}
},
// 一般mutations中的函数大写,用来区分和actions中的函数
mutations: {
// 3. 定义真正操作sum的方法
ADD: function (state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
SUB: function (state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
},
state: {
// 1. 定义数据
sum: 0,
school: "一中",
address: "北京"
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}
src/store/person.js
// 人员相关的配置
export default {
actions: {
// 2. 定义操作sum的方法,context为上下文对象,其中保存着所有的数据及操作函数
add: function (context, value) {
// 2. 提交给mutations操作数据
context.commit("ADD", value)
},
sub: function (context, value) {
context.commit("SUB", value)
},
// 当sum值为奇数时再加
addOdd: function (context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit("ADD", value)
}
},
// 在actions中调用ajax请求,这里使用定时器模拟
addWait: function (context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('ADD', value)
}, 500)
}
},
// 一般mutations中的函数大写,用来区分和actions中的函数
mutations: {
// 3. 定义真正操作sum的方法
ADD: function (state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
SUB: function (state, value) {
state.sum -= value
}
},
state: {
// 1. 定义数据
sum: 0,
school: "一中",
address: "北京"
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10
}
}
}
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
import countOptions from "@/store/count";
import personOptions from "@/store/person";
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
countOptions, // 求和相关的配置
personOptions // 人员相关的配置
}
})


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号