代码集合
1. embedding层
输入的:batch_size*seq_len 经过embedding层后的输出:batch_size*seq_len*dim(embedding后的dim维度)

2. attention
import numpy as np
def self_attention(X):
"""
Simple self-attention mechanism.
X: Input sequence (2D array of shape [seq_len, features])
"""
# Compute query, key, and value matrices
Q = X
K = X.T
V = X
# Compute attention scores
scores = np.dot(Q, K) / np.sqrt(K.shape[0])
# Apply softmax to get attention weights
attention_weights = np.exp(scores) / np.sum(np.exp(scores), axis=1, keepdims=True)
# Compute the output
output = np.dot(attention_weights, V)
return output
# Example input
X = np.array([[1, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1]])
output = self_attention(X)
print("Self-Attention Output:\n", output)
def target_attention(source, target):
"""
Simple target attention mechanism.
source: Source sequence (2D array of shape [source_len, features])
target: Target sequence (2D array of shape [target_len, features])
"""
# Compute query, key, and value matrices
Q = target
K = source.T
V = source
# Compute attention scores
scores = np.dot(Q, K) / np.sqrt(K.shape[0])
# Apply softmax to get attention weights
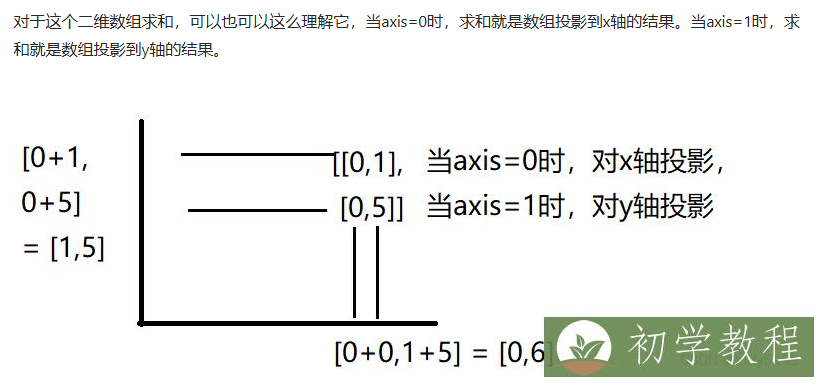
attention_weights = np.exp(scores) / np.sum(np.exp(scores), axis=1, keepdims=True) -- 1表示投影到y轴
# Compute the output
output = np.dot(attention_weights, V)
return output
# Example input
source = np.array([[1, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1]])
target = np.array([[1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1]])
output_target = target_attention(source, target)
print("Target Attention Output:\n", output_target)
Q是deconder层,K,V来自enconder层,Q是生成的目标序列
Q, K, V 的关系
- Query (Q): 查询向量,用于对输入信息进行查询,以决定关注哪些部分。
- Key (K): 键向量,表示输入信息的特征,用于与查询向量进行匹配。
- Value (V): 值向量,表示输入信息的实际内容,用于生成加权输出。
为什么在 Target Attention 中 Q 是 Target
在目标注意力(Target Attention)中,Query (Q) 通常来源于目标序列(Target),而 Key (K) 和 Value (V) 通常来源于源序列(Source)。这是因为:
-
目标序列(Target): 在解码阶段,模型需要生成目标序列的每个元素。为了生成这些元素,模型需要根据目标序列的当前状态(即当前生成的部分)来决定应该关注源序列的哪些部分。因此,目标序列的当前状态作为查询向量(Q)。
-
源序列(Source): 源序列提供了需要被关注的上下文信息,因此它们的特征作为键(K)和值(V)。
计算过程
- 匹配: 使用目标序列中的每个元素(作为查询Q)与源序列中的元素(作为键K)进行匹配,计算注意力分数。
- 加权求和: 使用注意力分数对源序列的值向量(V)进行加权求和,得到最终的输出
计算auc
##给定的真实y 和 预测pred
y_true = np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ])
y_pred = np.array([0.9, 0.4, 0.3, 0.1, 0.35, 0.6, 0.65, 0.32, 0.8, 0.7])
def cal_auc(y_pred,y_true):
fz = 0 #分子
fm = 0 #分母
for i in range(0,len(y_true)-1):
for j in range(i+1,len(y_true)):
if y_true[i]!=y_true[j]:
fm += 1
# 统计所有正负样本对中,模型把相对位置排序正确的数量
if y_true[i]>y_true[j] and y_pred[i]>y_pred[j] or y_true[i]<y_true[j] and y_pred[i]<y_pred[j]:
fz+=1
return fz/fm
print("AUC =" , cal_auc(y_pred,y_true))




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号