优化器
1、tensorflow2-API,可以看出tensorflow2预制4个衰减接口;另外LearningRateSchedule可用来自定义衰减方法
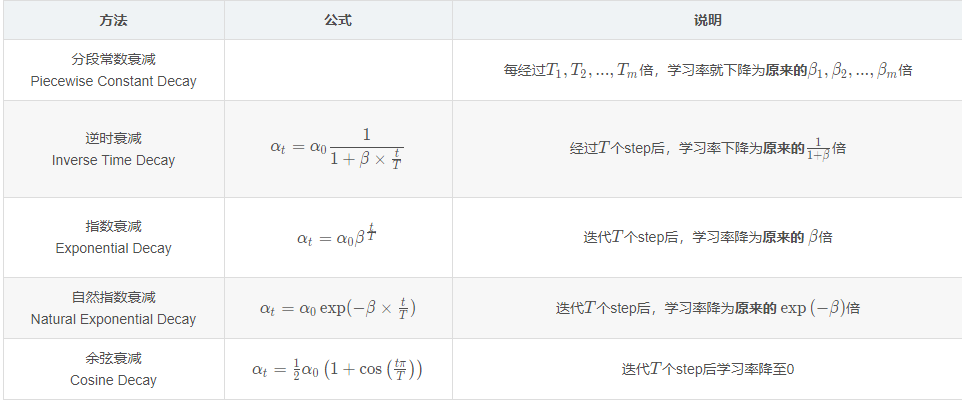
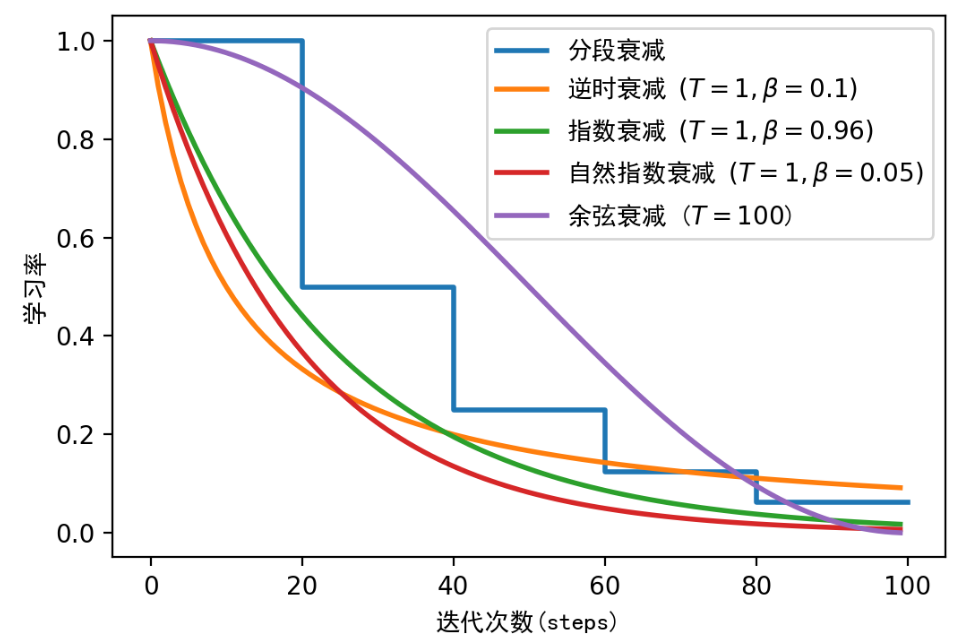
2、衰减方法
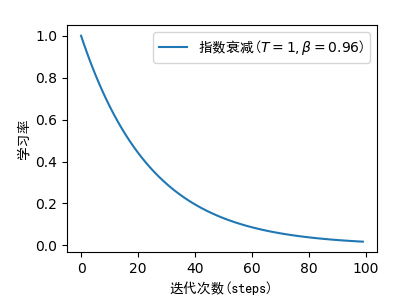
3、ExponentialDecay 指数衰减
3.1 API
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(
initial_learning_rate, decay_steps, decay_rate, staircase=False, name=None
)
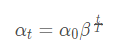
Args | |
|---|---|
initial_learning_rate |
A scalar 对应公式a0 |
decay_steps |
A scalar 对应公式T |
decay_rate |
A scalar 对应公式 |
staircase |
Boolean. If 是否使用阶梯 |
name |
String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to 'ExponentialDecay'. |
4、InverseTimeDecay逆时衰减
4.1 API
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.InverseTimeDecay(
initial_learning_rate, decay_steps, decay_rate, staircase=False, name=None
)
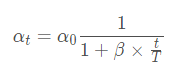

Args | |
|---|---|
initial_learning_rate |
A scalar 对应公式a0 |
decay_steps |
How often to apply decay. 对应公式T |
decay_rate |
A Python number. The decay rate. 对应公式 |
staircase |
Whether to apply decay in a discrete staircase, as opposed to continuous, fashion. |
name |
String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to 'InverseTimeDecay'. |
5、PiecewiseConstantDecay分段常数衰减
5.1 API
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay(
boundaries, values, name=None
)
Args | |
|---|---|
boundaries |
A list of 分段的各段边界值 |
values |
A list of 对应boundaries各段的衰减常量 |
name |
A string. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to 'PiecewiseConstant'. |
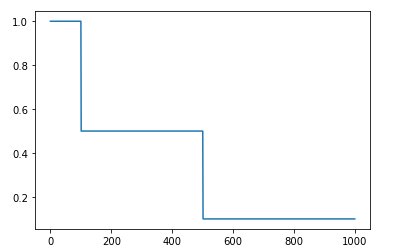
5.2 示例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
boundaries = [100, 500]
values = [1.0, 0.5, 0.1]
learning_rate_fn = tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay(
boundaries, values)
# Later, whenever we perform an optimization step, we pass in the step.
y = []
x = []
for i in range(1000):
learning_rate = learning_rate_fn(i)
x.append(i)
y.append(learning_rate.numpy())
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()
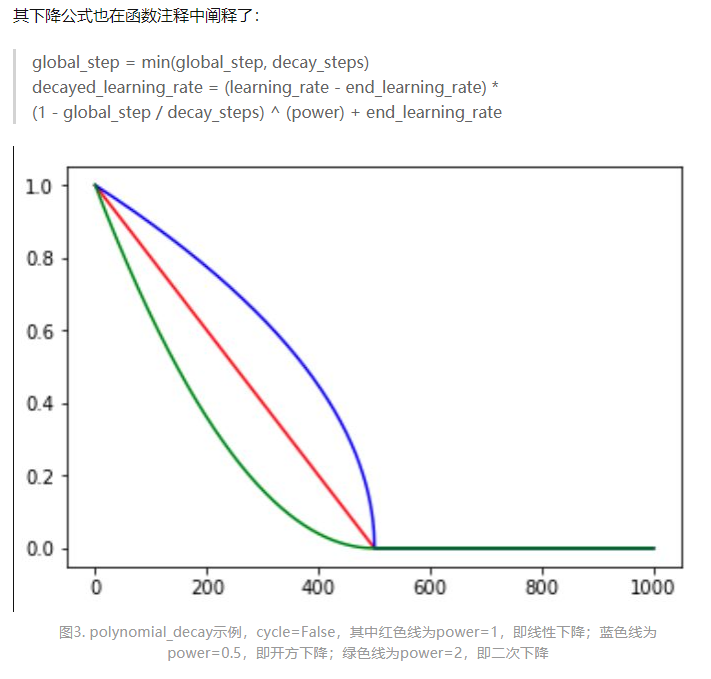
6、PolynomialDecay 多项式衰减
6.1 API
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PolynomialDecay(
initial_learning_rate, decay_steps, end_learning_rate=0.0001, power=1.0,
cycle=False, name=None
)
Args | |
|---|---|
initial_learning_rate |
A scalar float32 or float64 Tensor or a Python number. The initial learning rate. |
decay_steps |
A scalar int32 or int64 Tensor or a Python number. Must be positive. See the decay computation above. |
end_learning_rate |
A scalar float32 or float64 Tensor or a Python number. The minimal end learning rate. |
power |
A scalar float32 or float64 Tensor or a Python number. The power of the polynomial. Defaults to linear, 1.0. |
cycle |
A boolean, whether or not it should cycle beyond decay_steps. |
name |
String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to 'PolynomialDecay'. |
7、使用方法
学习率衰减调度器的使用方法非常简单,以指数衰减为例。
- 先创建一个学习率衰减调度器
- 把它传入你选择的优化器(这里选择Adam优化器)
initial_learning_rate = 0.1
lr_schedule = tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(
initial_learning_rate,
decay_steps=100000,
decay_rate=0.96,
staircase=True)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=lr_schedule),
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(data, labels, epochs=5)
8、自定义学习率衰减
import tensorflow as tf
class PiecewiseConstantDecay(tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule):
def __init__(self, boundaries, values):
super().__init__()
self.boundaries = tf.cast(boundaries, dtype=tf.float32)
self.values = tf.cast(values, dtype=tf.float32)
def __call__(self, step):
for i in range(len(self.boundaries)):
if self.boundaries[i] >= step:
return self.values[i]
else:
return self.values[-1]





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号