第二次blog作业
第二次blog作业
一.前言
第八次题目集和第九次题目集都只有三个题目,其中在第九次题目集中,有一道对第八次题目集中点面线的重构(容器),有一道题为对第八次题目集中航空货运管理系统的继承与多态,总体来说题量小,第八次题目集简单,只有简单的类的设计和抽象方法的使用,对于第九次题目集,如果熟练掌握了继承与多态,第九次题目集也是车到山前必有路,船到桥头自然直。
二.对于航空货物管理系统的设计与分析
代码展示:
题目集8
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String b = sc.nextLine();
String c = sc.nextLine();
String d = sc.nextLine();
k ke = new k(a, b, c, d);
int e = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
List<h> gL = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
int hId = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String j = sc.nextLine();
double k = sc.nextDouble();
double length = sc.nextDouble();
double height = sc.nextDouble();
double weight = sc.nextDouble();
sc.nextLine();
gL.add(new h(hId, j, k, length, height, weight));
}
String l = sc.nextLine();
String m = sc.nextLine();
String n = sc.nextLine();
String o = sc.nextLine();
int p = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
a ai = new a(l, m, n, o, p);
int q = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String r = sc.nextLine();
d order = new d(q, r);
String s = sc.nextLine();
String t = sc.nextLine();
String u = sc.nextLine();
f fa = new f(t, u, s);
String v = sc.nextLine();
String w = sc.nextLine();
String x = sc.nextLine();
s sh = new s(w, x, v);
show show1=new show(ke, ai, order, fa, sh, gL);
show1.showz();
}
}
interface K {}
interface F {}
interface S {}
class C {
private final String name;
private final String phone;
private final String add;
public C(String name, String phone, String add) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.add = add;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public String getPhone() { return phone; }
public String getAdd() { return add; }
}
class k implements K {
private final int id;
private C a;
public k(int id, String name, String phone, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.a = new C(name, phone, address);
}
public String getName() { return a.getName(); }
public String getPhone() { return a.getPhone(); }
}
class f implements F {
private final String name;
private final String phone;
private final String add;
public f(String name, String phone, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.add = address;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public String getPhone() { return phone; }
public String getAdd() { return add; }
}
class s implements S {
private final String name;
private String phone;
private String add;
public s(String name, String phone, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.add = address;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public String getPhone() { return phone; }
public String getAdd() { return add; }
}
class h {
private int id;
private String name;
private double width;
private double length;
private double height;
private double weight;
public h(int id, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public boolean isW() { return weight >= (width * length * height) / 6000; }
public double getCW() { return isW() ? weight : (width * length * height) / 6000; }
public int getId() { return id; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public double getWidth() { return width; }
public double getLength() { return length; }
public double getHeight() { return height; }
public double getWeight() { return weight; }
}
class a {
private String id;
private int max;
public a(String id, String departure, String arrival, String date, int max) {
this.id = id;
this.max = max;
}
public String getId() { return id; }
public int getMax() { return max; }
}
class d {
private int id;
private String date;
public d(int id, String date) {
this.id = id;
this.date = date;
}
public int getId() { return id; }
public String getT() { return date; }
}
class mo {
h hu;
public mo(h hu) {
this.hu = hu;
}
public double money() {
double isW = getW();
double fe = getR();
return isW * fe;
}
public double getW() { return hu.isW() ? hu.getWeight() : (hu.getWidth() * hu.getLength() * hu.getHeight()) / 6000; }
public double getR() {
if (getW() < 20) return 35;
else if (getW() >= 20 && getW() < 50) return 30;
else if (getW() >= 50 && getW() < 100) return 25;
else return 15;
}
}
class all {
public static double all(List<h> gL) {
double totalWeight = 0;
for (h goods : gL) {
totalWeight += goods.getCW();
}
return totalWeight;
}
}
class ch {
public static boolean ch(a ai, double totalWeight) {
if (totalWeight > ai.getMax()) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.", ai.getId());
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
class Fee {
public static double fe(List<h> gL) {
double totalFee = 0;
for (h goods : gL) {
mo m1 = new mo(goods);
totalFee += m1.money();
}
return totalFee;
}
}
class show {
k ke;
a ai;
d order;
f fa;
s sh;
List<h> gL;
public show(k ke, a ai, d order, f fa, s sh, List<h> gL) {
this.ke = ke;
this.ai = ai;
this.order = order;
this.fa = fa;
this.sh = sh;
this.gL = gL;
}
public void showz() {
double totalWeight = all.all(gL);
if (!ch.ch(ai, totalWeight)) return;
System.out.println("客户:" + ke.getName() + "(" + ke.getPhone() + ")订单信息如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("航班号:" + ai.getId());
System.out.println("订单号:" + order.getId());
System.out.println("订单日期:" + order.getT());
System.out.println("发件人姓名:" + fa.getName());
System.out.println("发件人电话:" + fa.getPhone());
System.out.println("发件人地址:" + fa.getAdd());
System.out.println("收件人姓名:" + sh.getName());
System.out.println("收件人电话:" + sh.getPhone());
System.out.println("收件人地址:" + sh.getAdd());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n", totalWeight);
double totalFee = Fee.fe(gL);
System.out.printf("微信支付金额:%.1f\n", totalFee);
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
for (int i = 0; i < gL.size(); i++) {
h hu = gL.get(i);
mo m1 = new mo(hu);
double mone = m1.getW();
double rate = m1.getR();
double fee = m1.money();
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n", i + 1, hu.getName(), mone, rate, fee);
}
}
}
题目集9
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String typek = sc.nextLine();
int a = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String b = sc.nextLine();
String c = sc.nextLine();
String d = sc.nextLine();
k ke = new k(typek, a, b, c, d);
String typeh = sc.nextLine();
int e = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
List<h> gL = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
int hId = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String j = sc.nextLine();
double k = sc.nextDouble();
double length = sc.nextDouble();
double height = sc.nextDouble();
double weight = sc.nextDouble();
sc.nextLine();
gL.add(new h(typeh, hId, j, k, length, height, weight));
}
String l = sc.nextLine();
String m = sc.nextLine();
String n = sc.nextLine();
String o = sc.nextLine();
int p = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
a ai = new a(l, m, n, o, p);
int q = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String r = sc.nextLine();
d order = new d(q, r);
String s = sc.nextLine();
String t = sc.nextLine();
String u = sc.nextLine();
f fa = new f(t, u, s);
String v = sc.nextLine();
String w = sc.nextLine();
String x = sc.nextLine();
s sh = new s(w, x, v);
String zhifu = sc.nextLine();
zhi zh = new zhi(zhifu);
show show1 = new show(ke, ai, order, fa, sh, gL, zh);
show1.showz();
}
}
abstract class C {
String name;
String phone;
String add;
public C(String name, String phone, String add) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.add = add;
}
public abstract String getName();
public abstract String getPhone();
public abstract String getAdd();
}
class k extends C {
int id;
String type;
public k(String type, int id, String name, String phone, String add) {
super(name, phone, add);
this.id = id;
this.type = type;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public String getPhone() {
return this.phone;
}
@Override
public String getAdd() {
return this.add;
}
}
class f extends C {
public f(String name, String phone, String add) {
super(name, phone, add);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public String getPhone() {
return this.phone;
}
@Override
public String getAdd() {
return this.add;
}
}
class s extends C {
public s(String name, String phone, String add) {
super(name, phone, add);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public String getPhone() {
return this.phone;
}
@Override
public String getAdd() {
return this.add;
}
}
class h {
private int id;
private String name;
private double width;
private double length;
private double height;
private double weight;
private String type;
public h(String type, int id, String name, double width, double length, double height, double weight) {
this.type = type;
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public boolean isW() {
return weight >= (width * length * height) / 6000;
}
public double getCW() {
return isW() ? weight : (width * length * height) / 6000;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
}
class a {
private String id;
private int max;
public a(String id, String departure, String arrival, String date, int max) {
this.id = id;
this.max = max;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public int getMax() {
return max;
}
}
class d {
private int id;
private String date;
public d(int id, String date) {
this.id = id;
this.date = date;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getT() {
return date;
}
}
class mo {
h hu;
W w;
R r;
public mo(h hu, R r, W w) {
this.hu = hu;
this.r = r;
this.w = w;
}
public double money() {
double isW = w.getW();
double fe = r.RRR();
return isW * fe;
}
}
class W {
h hu;
public W(h hu) {
this.hu = hu;
}
public double getW() {
return hu.isW() ? hu.getWeight() : (hu.getWidth() * hu.getLength() * hu.getHeight()) / 6000;
}
}
abstract class RR {
W w;
public RR(W w) {
this.w = w;
}
public abstract double getR();
}
class R1 extends RR {
public R1(W w) {
super(w);
}
@Override
public double getR() {
if (w.getW() < 20) return 35;
else if (w.getW() >= 20 && w.getW() < 50) return 30;
else if (w.getW() >= 50 && w.getW() < 100) return 25;
else return 15;
}
}
class R2 extends RR {
public R2(W w) {
super(w);
}
@Override
public double getR() {
if (w.getW() < 20) return 80;
else if (w.getW() >= 20 && w.getW() < 50) return 50;
else if (w.getW() >= 50 && w.getW() < 100) return 30;
else return 20;
}
}
class R3 extends RR {
public R3(W w) {
super(w);
}
@Override
public double getR() {
if (w.getW() < 20) return 60;
else if (w.getW() >= 20 && w.getW() < 50) return 50;
else if (w.getW() >= 50 && w.getW() < 100) return 40;
else return 30;
}
}
class R {
private h hu;
private W w;
public R(h hu, W w) {
this.hu = hu;
this.w = w;
}
public double RRR() {
RR rr;
if ("Normal".equals(hu.getType())) {
rr = new R1(w);
} else if ("Expedite".equals(hu.getType())) {
rr = new R3(w);
} else {
rr = new R2(w);
}
return rr.getR();
}
}
class all {
public static double all(List<h> gL) {
double totalWeight = 0;
for (h goods : gL) {
totalWeight += goods.getCW();
}
return totalWeight;
}
}
class ch {
public static boolean ch(a ai, double totalWeight) {
if (totalWeight > ai.getMax()) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.", ai.getId());
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
class Fee {
public static double fe(List<h> gL, k ke) {
double totalFee = 0;
for (h goods : gL) {
W w = new W(goods);
R r = new R(goods, w);
mo m1 = new mo(goods, r, w);
totalFee += m1.money();
}
if ("Individual".equals(ke.getType())) {
return totalFee * 0.9;
} else if ("Corporate".equals(ke.getType())) {
return totalFee * 0.8;
}
return totalFee;
}
}
class zhi {
String fa;
public zhi(String fa) {
this.fa = fa;
}
public String getFa() {
return fa;
}
public void setFa(String fa) {
this.fa = fa;
}
public void s() {
if ("ALiPay".equals(this.fa))
System.out.printf("支付宝支付金额:");
if ("Wechat".equals(this.fa))
System.out.printf("微信支付金额:");
if ("Cash".equals(this.fa))
System.out.printf("现金支付金额:");
}
}
class show {
k ke;
a ai;
d order;
f fa;
s sh;
List<h> gL;
zhi zh;
public show(k ke, a ai, d order, f fa, s sh, List<h> gL, zhi zh) {
this.ke = ke;
this.ai = ai;
this.order = order;
this.fa = fa;
this.sh = sh;
this.gL = gL;
this.zh = zh;
}
public void showz() {
double totalWeight = all.all(gL);
if (!ch.ch(ai, totalWeight)) return;
System.out.println("客户:" + ke.getName() + "(" + ke.getPhone() + ")订单信息如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("航班号:" + ai.getId());
System.out.println("订单号:" + order.getId());
System.out.println("订单日期:" + order.getT());
System.out.println("发件人姓名:" + fa.getName());
System.out.println("发件人电话:" + fa.getPhone());
System.out.println("发件人地址:" + fa.getAdd());
System.out.println("收件人姓名:" + sh.getName());
System.out.println("收件人电话:" + sh.getPhone());
System.out.println("收件人地址:" + sh.getAdd());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n", totalWeight);
double totalFee = Fee.fe(gL, ke);
zh.s();
System.out.printf("%.1f\n", totalFee);
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
for (int i = 0; i < gL.size(); i++) {
h hu = gL.get(i);
W w1 = new W(hu);
R r = new R(hu, w1);
mo m1 = new mo(hu, r, w1);
double mone = w1.getW();
double rate = r.RRR();
double fee = m1.money();
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n", i + 1, hu.getName(), mone, rate, fee);
}
}
}
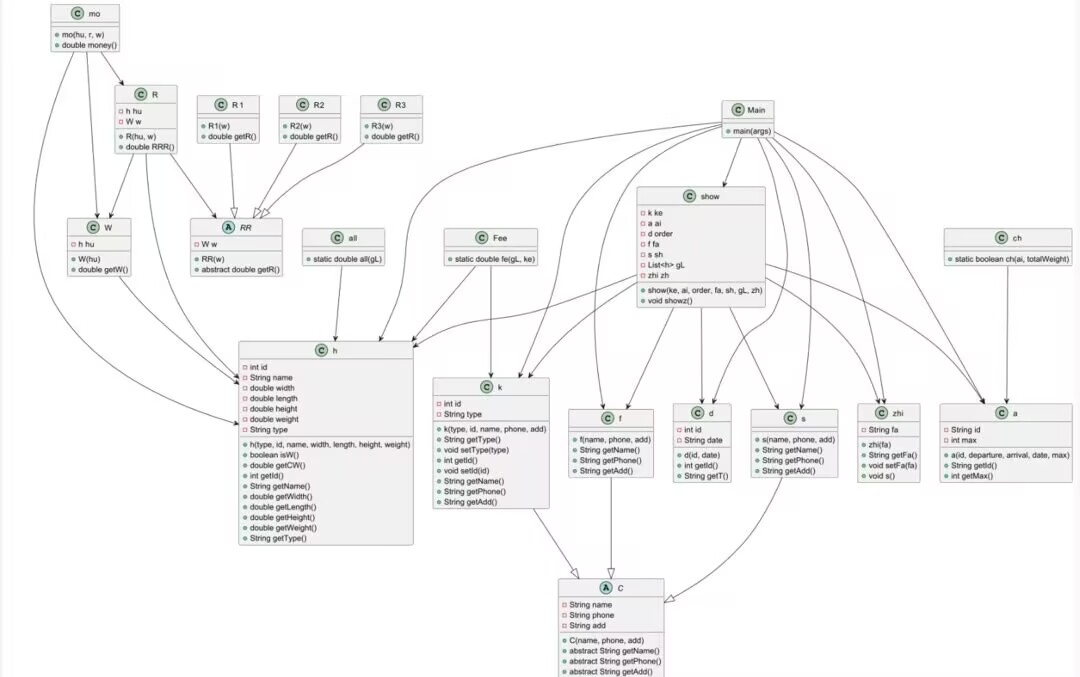
类图设计:
题目集8:

题目集9:
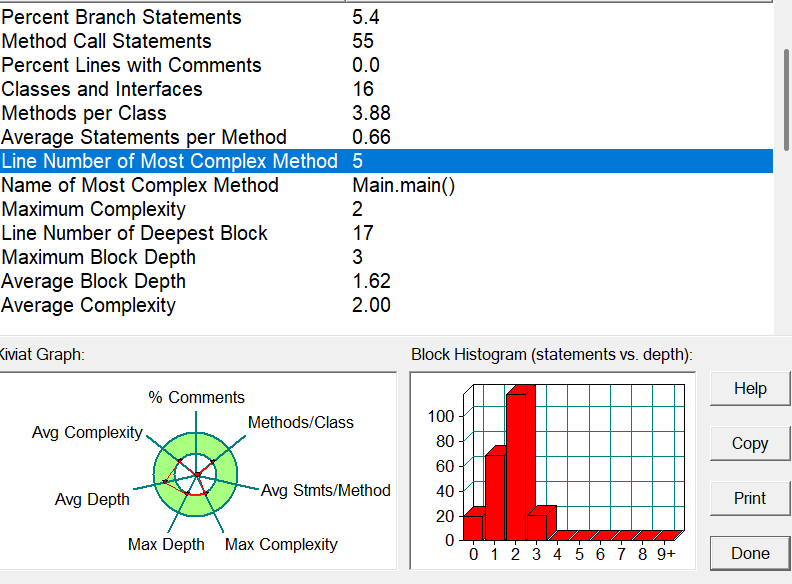
sourcemonitor分析:
题目集8:
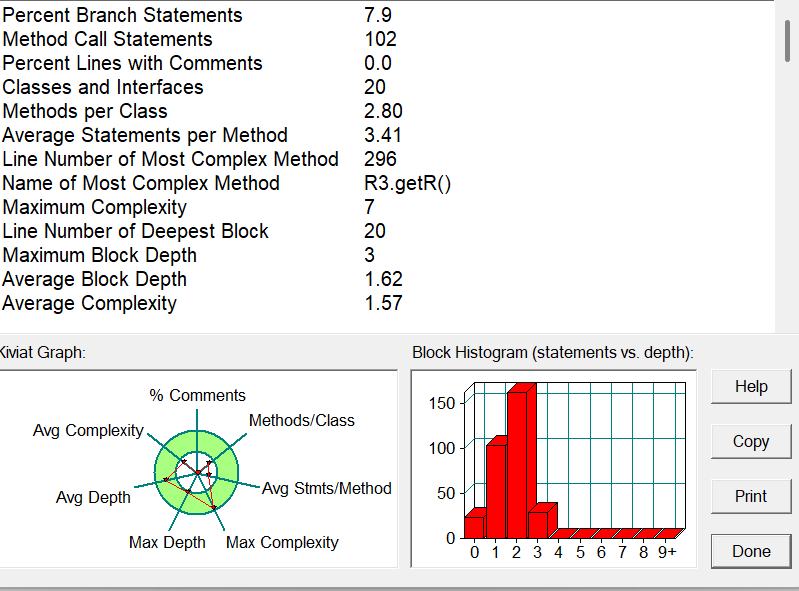
题目集9:
对设计的内容进行总结:
1.从代码数量上来看,第九次比第八次多了几十行,因为在第八次只对人进行拓展的基础上,对货物费率的计算,和支付方式进行了拓展。
2.在类图设计上我们可以直观的感受到在第八次题目集我对于单一职责的把控不得当,在show函数中,既完成了show的内容,而且对计费金额的计算也是在这里完成的,这也导致了代码复杂性的提高。但是可惜的是,我再设计第九题是也忘记把它移出去了。
3.我认为在第八次题目集中最大的缺陷就是我设置了三个空接口,但实际上的继承与多态是通过抽象父类来实现的,第九次题目集中我把他移出去了。
4.在第八次题目集中设计show时遵循依赖倒置原则,但却是高层模块依赖具体类实现,第九次题目集中设置R类时有一样缺陷,应使R依赖于RR的接口。
5.在两次题目集中计算重量和费率时应遵循合成复用原则,避免重复的代码在多次出现,像我这两个题都是多次出现了计费重量的代码。
两次代码比较:
一、代码复杂度与可维护性
| 指标 | 题目集九 | 题目集八 | 分析 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 最大复杂度方法 | R3.getR()(7) |
Main.main()(2) |
题目集九的 R3.getR() 方法复杂度显著增加,表明条件分支逻辑更复杂,需优化分层或策略模式。 |
| 平均复杂度 | 1.57 | 2.00 | 题目集八的平均复杂度更高,但九的最复杂方法更突出,需警惕局部复杂代码对整体维护性的影响。 |
| 方法调用语句数 | 102 | 55 | 题目集九的模块化程度更高,但可能引入更多耦合,需检查是否存在过度设计。 |
二、代码结构与设计质量
| 指标 | 题目集九 | 题目集八 | 分析 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 类与接口数量 | 20 | 16 | 题目集九通过增加类实现更细粒度的职责分离(如策略模式),但需避免类爆炸问题。 |
| 方法/类 | 2.80 | 3.88 | 题目集八的类方法更密集,可能违反单一职责原则;九的类设计更符合高内聚要求。 |
| 平均语句/方法 | 3.41 | 0.66 | 题目集九的方法长度显著增加(如 showz()),需拆分为更小的功能单元。 |
三、代码可读性与维护性
| 指标 | 题目集九 | 题目集八 | 分析 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 注释覆盖率 | 0.0% | 0.0% | 两者均严重缺乏注释,尤其是策略模式中的 R1/R2/R3 类,需补充关键逻辑说明。 |
| 最深代码块行号 | 296 | 17 | 题目集九的复杂逻辑集中在文件末尾(如 showz()),建议通过提取方法减少嵌套层级。 |
| 块深度分布 | 最大深度3,平均1.62 | 最大深度3,平均1.62 | 两者嵌套深度相似,但九的深层逻辑集中在高复杂度方法中,需优先重构。 |
三.踩坑心得
1.针对第八次作业的第三题,本人一次性顺利完成了提交,并未遭遇任何难题。然而,当我目睹部分同学尽管输出结果与我一致,却未能通过测试点时,我不禁陷入了深思。经过一番缜密的数据对比测试,我们发现了症结所在:在计算总重量这一环节,我采用了计费重量作为标准,而他们则沿用了实际重量。此现象凸显了对题目解读的重要性。虽然从直观感受出发,总重量理应指代实际存在的重量,但在该题目集中,一个亟待澄清的关键问题是:在计算运费的过程中,究竟应当采纳实际重量抑或是体积重量为基准?显而易见地讲,本题所提供的测试数据实际上是以实际重量为基础定义了计费重量,但许多同学对此产生了误解,误认为唯有采用实际重量方能得出正确答案。
2.至于第八次作业的第二题,则让我颇费了一番周折。特别是在面对第一个测试点时——即当输入数据非法且控制杆持续上升导致始终存在非零返回值的情况下——我遇到了不小的挑战。起初,在处理大规模数据时出现了越界问题。为此,我引入了InputMismatchException机制以应对输入异常情况下的错误处理需求。遗憾的是,即便如此调整后依旧无法成功通过该测试点。最终,在不懈的努力下查阅相关资料并进行了多次试验之后终于找到了解决方案:运用try-catch结构不仅能够有效地捕捉并妥善处置程序运行过程中可能出现的各种异常状况。
3.关于第九次作业的第三题,在除去有关计费重量的理解差异之外,并无其他显著难点。其核心价值主要体现在探讨如何更为高效便捷地实现功能拓展以及如何在缩减源码规模的基础上增强系统的长期维护便利性等方面。在此背景下,“推荐采取面向对象编程思想中的接口设计策略”显得尤为恰当合理。
四.改进建议
-
类职责划分:现有继承体系混乱,建议将C类拆分基类,采用组合模式将地址信息嵌入到实体中,消除无效继承关系。
-
命名规范化:将k改为Customer、a改为Flight、h改为Cargo等语义化名称,提升代码可读性。字段命名遵循小驼峰式,如maxWeight替代max。
-
费率计算重构:将R1/R2/R3系列类抽象为接口,使用枚举管理策略类型。创建策略工厂根据货物类型返回对应策略对象,消除条件判断链。
-
重量计算封装:将体积重量计算逻辑封装到工具类,提供静态计算方法,避免业务类中重复实现。
-
输入验证增强:在Scanner读取后添加正则校验,如电话号码格式验证、重量非负检查等。对非法输入抛出定制异常并处理。
-
输入模块解耦:创建InputParser类封装所有输入逻辑,通过方法返回领域对象,降低主函数复杂度。
-
使用BigDecimal替代double进行货币计算,设置精确到小数点后两位,避免浮点运算误差。创建Money工具类封装四则运算。
-
分离业务逻辑:将show类拆分为ReportService和ConsoleRenderer,前者负责数据计算,后者专司显示格式。采用模板方法模式输出统一报表。
-
多态支付处理:建立接口及其实现类,将支付方式判断逻辑内聚到支付对象中,通过工厂模式创建支付实例。
五.总结
在这次作业中,我不仅巩固了基础知识,还掌握了许多实用技能。比如:学会了如何优雅地处理输入异常,确保程序的健壮性;理解并实践了开闭原则在费率计算中的应用,提高了代码的可维护性和扩展性。这些宝贵的经验和知识,无疑为我在编程道路上走得更远、做得更好奠定了坚实的基础。
我们团队中的每一位成员——无论是站在讲台前传道授业解惑的一线教师,还是幕后精心设计考题的命题专家——都以高度的责任感和敬业精神,全身心投入到了各自的工作之中。然而,我认为在教学过程中,我们可以进一步优化课堂结构,给予学生更多亲自动手编码的机会。.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号