IO流
File
File是Java.io.包下的类,File类的对象用于代表当前操作系统的文件/文件夹。File类只能对文件本身进行操作,不能读写文件里面存储的数据。
- 递归
/**
* @author Pickle
* @version V1.0
* @date 2024/3/11 9:22
*/
public class demo {
private static int lastBottleNumber;
private static int totalNumber;
private static int lastCoverNumber;
public static void main(String[] args) {
buy(10);
System.out.println("可购买总数:"+totalNumber);
System.out.println("剩余瓶子数量"+lastBottleNumber);
System.out.println("剩余瓶盖数量"+lastCoverNumber);
}
public static void buy(int money){
//先买了再说
int buyNumber = money / 2;
totalNumber += buyNumber;
money %= 2;
//增加了多少瓶盖和瓶子
lastBottleNumber += buyNumber;
lastCoverNumber += buyNumber;
//瓶子换钱
money += (lastBottleNumber / 2) * 2;
lastBottleNumber %= 2;
//瓶盖换钱
money += (lastCoverNumber / 4) * 2;
lastCoverNumber %= 4;
if (money >= 2) buy(money);
}
}
- 案例
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Pickle
* @version V1.0
* @date 2024/3/11 8:58
*/
public class FileSearchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
searchFile(new File("D:/QQ"), "QQ.exe");
}
/**
* 查找指定文件
* @param dir 目录
* @param fileName 文件名字
*/
public static void searchFile(File dir, String fileName) throws IOException {
if (dir == null || !dir.exists() || dir.isFile()){
return;
}
//获取目录下的一级文件对象
final File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files != null && files.length > 0){
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()){
if (file.getName().contains(fileName)){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
final Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.exec(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}else {
searchFile(file, fileName);
}
}
}
}
}
字符集
Java的编码和解码

import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author Pickle
* @version V1.0
* @date 2024/3/11 9:52
*/
public class CodeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String data = "a我b";
//默认是按照平台字符集(UTF-8)进行编码的
final byte[] bytes = data.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
//解码
String str = new String(bytes,"GBK");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
IO流
IO总体四大流
- 字节输出流
- 字节输入流
- 字符输出流
- 字符输入流
字节流
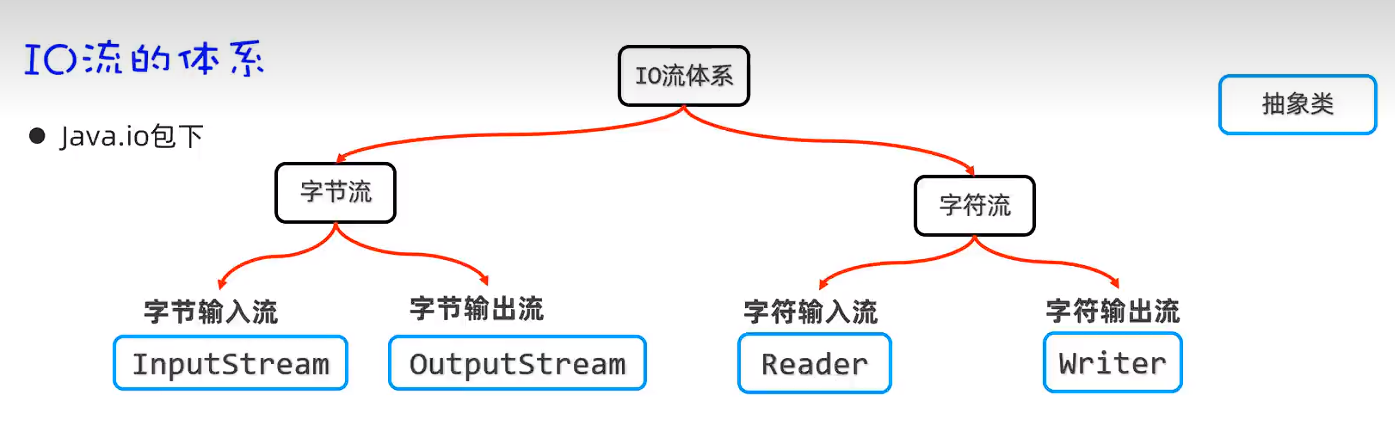
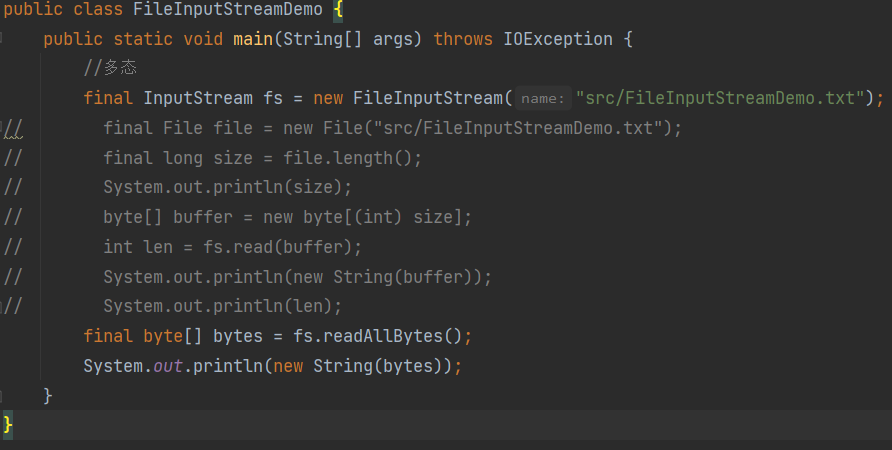
FileInputStream
文件字节输入流



读取所有内容,不需要自己设置buffer大小
FileOutputStream
文件字节输出流

- 案例:文件复制

字节流适合做一切文件的复制工作
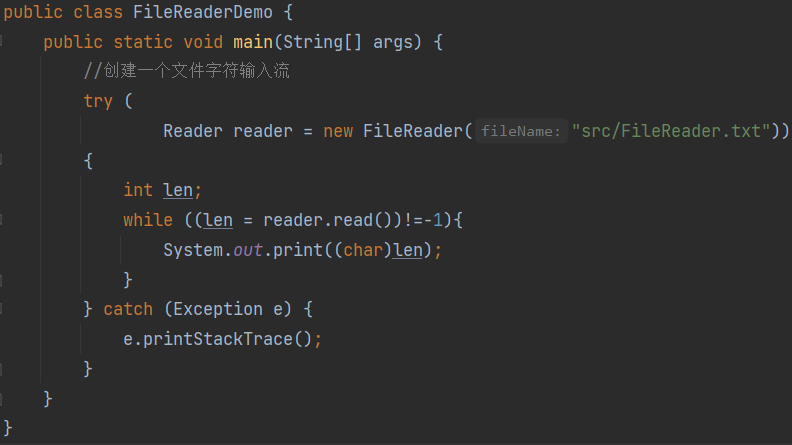
字符流
字符流更是和读取文本
FileReader

FileWriter
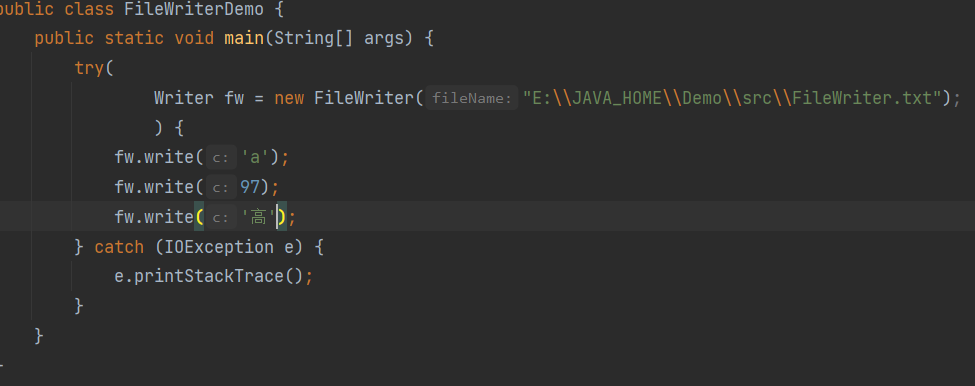
字符输出流写出数据后,必须刷新流,或者关闭流,写出取得数据才能生效,底层原理就是延迟写,减少向硬盘写数据的次数
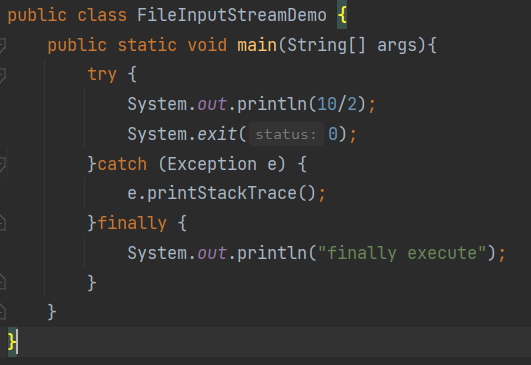
释放资源的两种方式
- try-catch-finally
finally代码区的特点:无论try中的程序是正常执行还是出现异常,最后都一定会执行finally区,除非JVM终止

打印
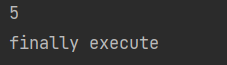
终止虚拟机
打印

在finally中不要使用return语句
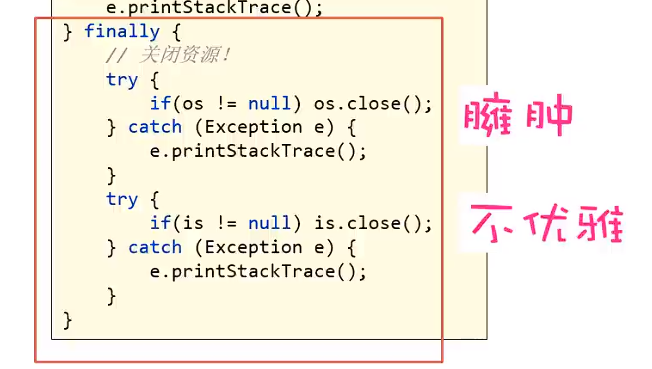
- try-with-resource
始于JDK7,finally释放代码过于臃肿
缓冲流
- 字节缓冲输入流
- 字节缓冲输出流
- 字符缓冲输入流
- 字符缓冲输出流
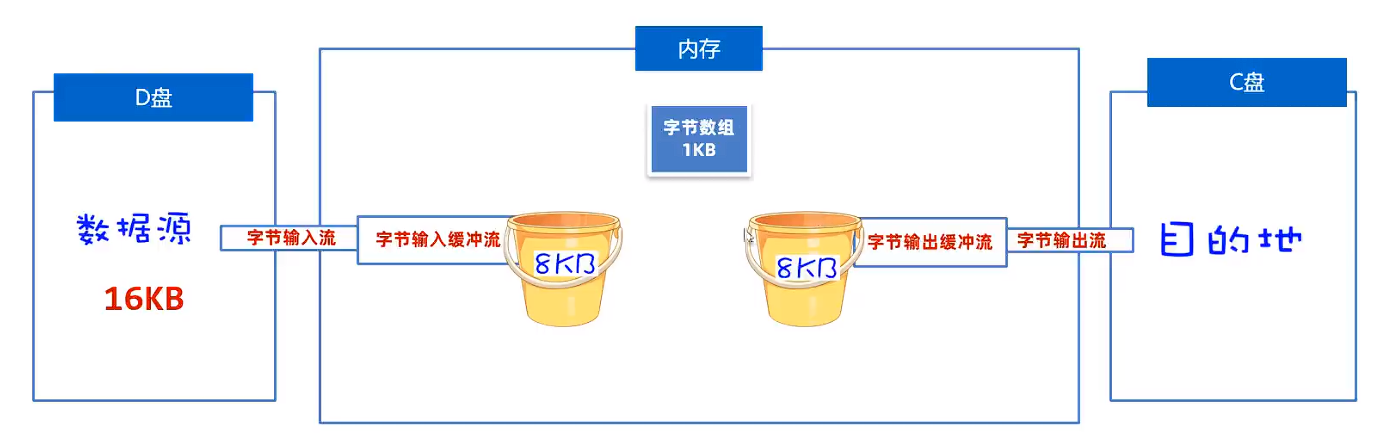
作用:对原始流进行包装,以提高原始流读写数据的性能

字节缓冲流
原理
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author Pickle
* @version V1.0
* @date 2024/3/11 13:08
*/
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
try (
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("src/File1.txt");
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
OutputStream ops = new FileOutputStream("src/File2.txt");
OutputStream bops = new BufferedOutputStream(ops);
){
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
bops.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符缓冲流
作用:对原始流进行包装,以提高原始流读写数据的性能
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.Reader;
/**
* @author Pickle
* @version V1.0
* @date 2024/3/11 13:47
*/
public class BufferReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
Reader fr = new FileReader("src/File1.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
){
// char[] buffer = new char[3];
// int len;
// while((len = br.read(buffer)) != -1){
// System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len));
String line;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
案例:恢复原来的顺序
转换流
字符输入转换流
控制读取特定格式的字符流

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* @author Pickle
* @version V1.0
* @date 2024/3/11 14:59
*/
public class InputStreamReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream("src/File1.txt");
final InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fs,"GBK");
final BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
) {
final String s = br.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符输出转换流
控制字符输出的格式

打印流
- PrintStream
- PrintWriter
数据流
DataOutputStream(数据输出流)
允许把数据和其他类型一并写出去
字节输出流
DataInputStream(数据输入流)
序列化流
实现Serializable
ObjectInputStream
ObjectOutputStream


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号