Java -day4
4.7稀疏数组
public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] array1 = new int[11][11]; array1[1][2] = 1; array1[2][3] = 2; System.out.println("原始数组"); for (int[] ints : array1) { for (int anInt : ints) { System.out.print(anInt + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) { if (array1[i][j] != 0){ sum++; } } } System.out.println("有效数组个数" + sum); //稀疏矩阵 array2【行数】【列数】【内容】 int array2[][] = new int[sum+1][3]; array2[0][0] = 11; array2[0][1] = 11; array2[0][2] = sum; int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < array1[i].length; j++) { if (array1[i][j] != 0){ count++; array2[count][0] = i; array2[count][1] = j; array2[count][2] = array1[i][j]; } } } System.out.println("稀疏数组"); for (int[] ints : array2) { for (int anInt : ints) { System.out.print(anInt + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } int[][] array3 = new int[array2[0][0]][array2[0][1]]; for (int i = 1; i < array2.length; i++) { array3[array2[i][0]][array2[i][1]] = array2[i][2]; } System.out.println("还原稀疏数组"); for (int[] ints : array3) { for (int anInt : ints) { System.out.print(anInt + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } }
五 面向对象OOP
5.1 方法回顾


方法的调用
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { new Demo02().add(1,3); } public int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; }
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { int add = Demo02.add(1, 3);//Demo02.add() alt+enter System.out.println(add); } public static int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; }//静态方法 直接通过类.方法 调用 }
类

public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(); //new Student() alt+enter student.say(); } }
值传递 引用传递
//值传递 public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a= 1; System.out.println(a); //1 change(a); System.out.println(a); //1 } public static void change(int a){ a = 10; } }
//引用传递 对象 本质还是值传递 public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); //NEW 创建一个对象 System.out.println(person.name); //null Demo04.change(person); System.out.println(person.name); //fxh } public static void change(Person person){ //person是一个对象 指向的Person person = new Person(); 是一个具体的人 可以改变属性 person.name = "fxh"; } } //定义一个person类 class Person{ String name; }
5.2 类与对象的创建


//学生类 public class Student1 { String name; int age; //方法 public void study(){ System.out.println(this.name+"学习呢"); } }
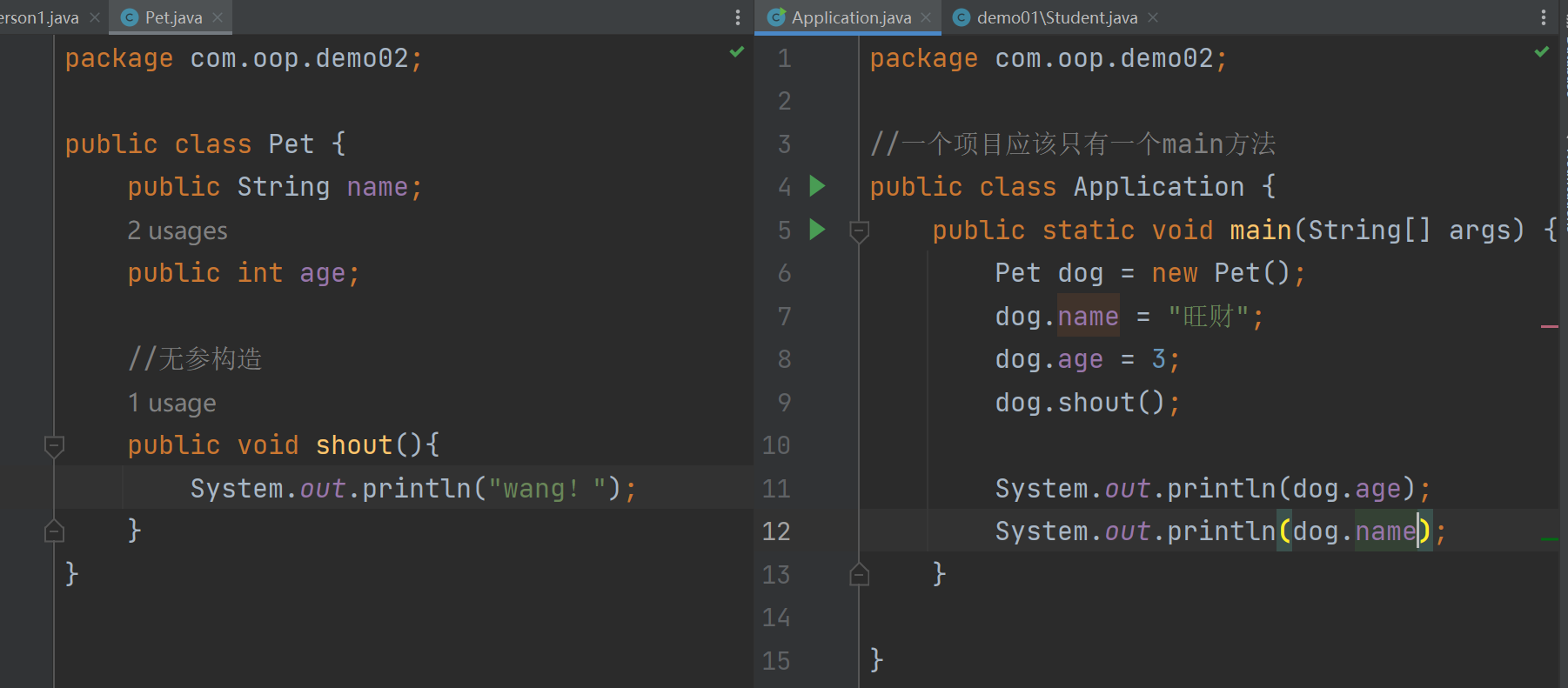
//一个项目应该只有一个main方法 public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //类 是抽象的 要实例化 //实例化后会返回一个自己的对象 //student对象就是一个Student类的具体实例 Student1 student1 = new Student1(); student1.name = "hula"; student1.age = 2; System.out.println(student1.name); System.out.println(student1.age); student1.study(); } }
5.3 构造器
构造器:
* 1.和类名相同
* 2.没有返回值
* 作用:
* 1.new本质在调用构造方法
* 2.初始化对象的值
* 注意点:
* 1,定义有参的前提是定义了无参
*
* alt + insert 构造器快捷键
public class Person1 { //一个类即使什么都不写 也会存在一个方法 //显示的定义构造器 String name; int age; //alt+insert 添加构造器 //1.使用new关键字 本质是在调用构造器 //2.用来初始化 public Person1() { } //有参构造 一旦定义了有参构造,无参构造就必须显示定义(定义有参的前提是定义了无参) public Person1(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } } /** * public static void main(String[] args) { * Person1 person1 = new Person1(); * * System.out.println(person1.name); * } * * 构造器: * 1.和类名相同 * 2.没有返回值 * 作用: * 1.new本质在调用构造方法 * 2.初始化对象的值 * 注意点: * 1,定义有参的前提是定义了无参 * * alt + insert 构造器快捷键 * */
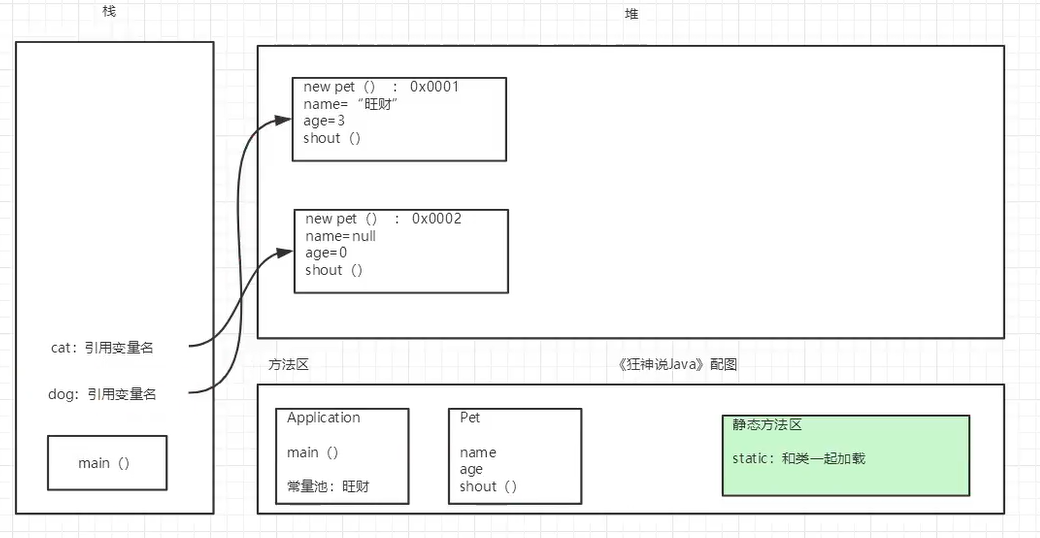
5.4 床创建对象内存分析


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号