CNN笔记与Pytorch实现
卷积
卷积核
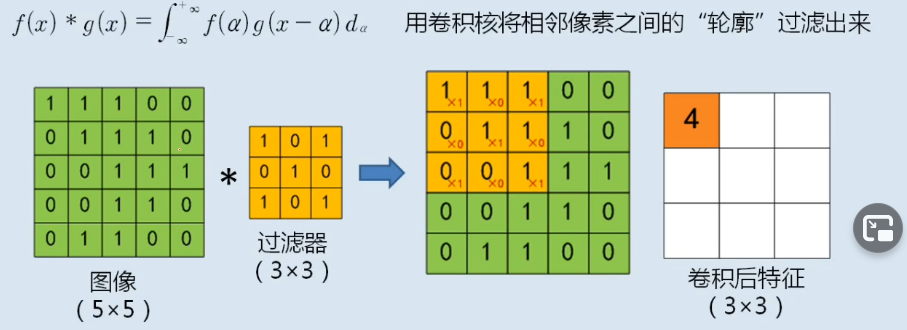
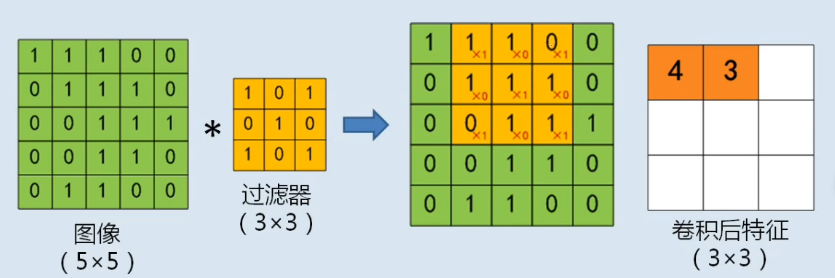
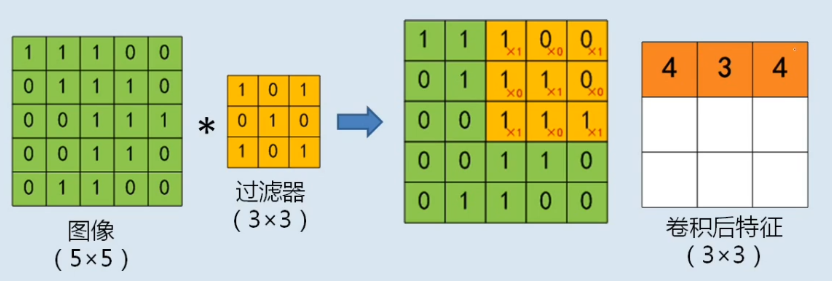
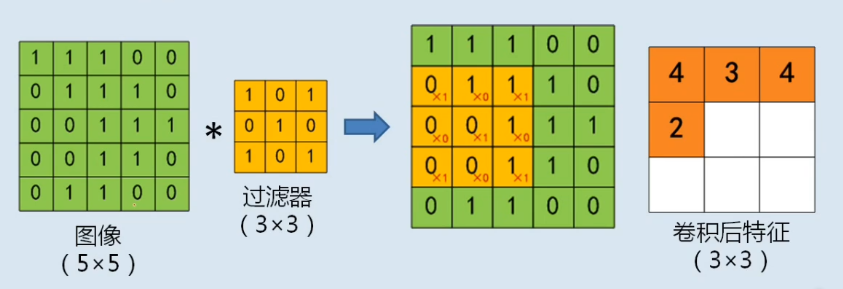
|
|
|
\ /
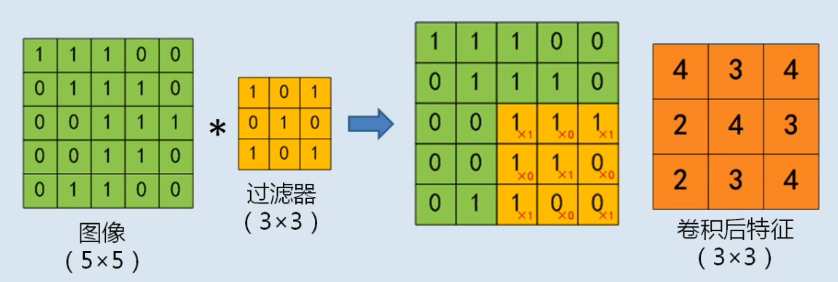
填充
\[p=(f-1)/2
\]
\[p:填充大小
\]
\[f:kernel/fillter 大小
\]
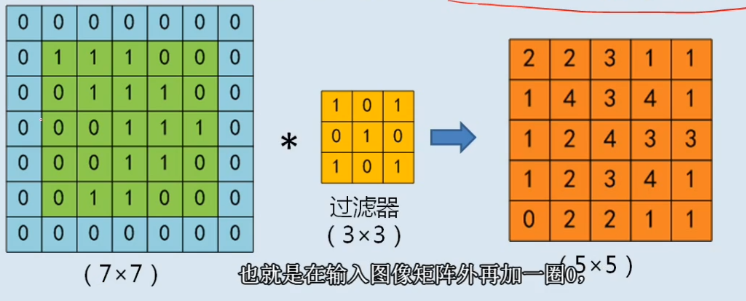
步长 stride
卷积核每次移动距离
公式:
\[O=(n-f+2p)/s + 1
\]
\[n: size { } of { }input
\]
\[f: size of filter
\]
\[p: size of padding
\]
\[s: size of stride
\]
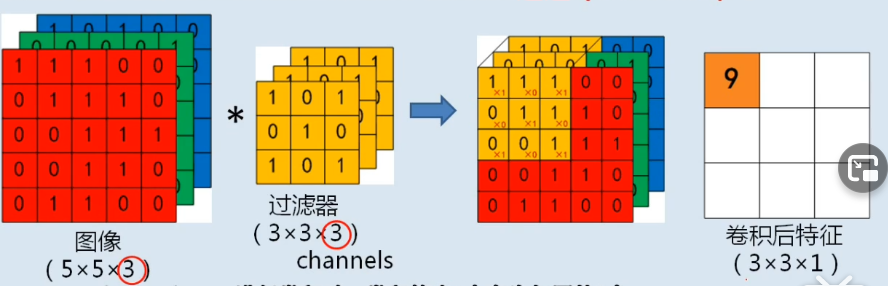
通道 channel
累加:
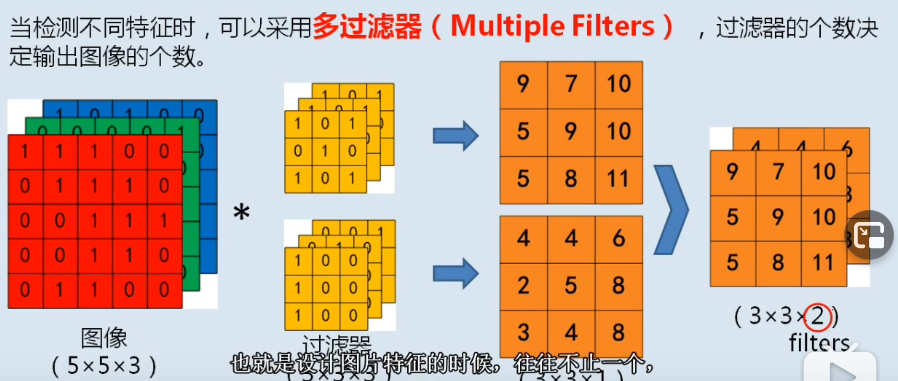
多过滤器
过滤器数量与output channel数量相同
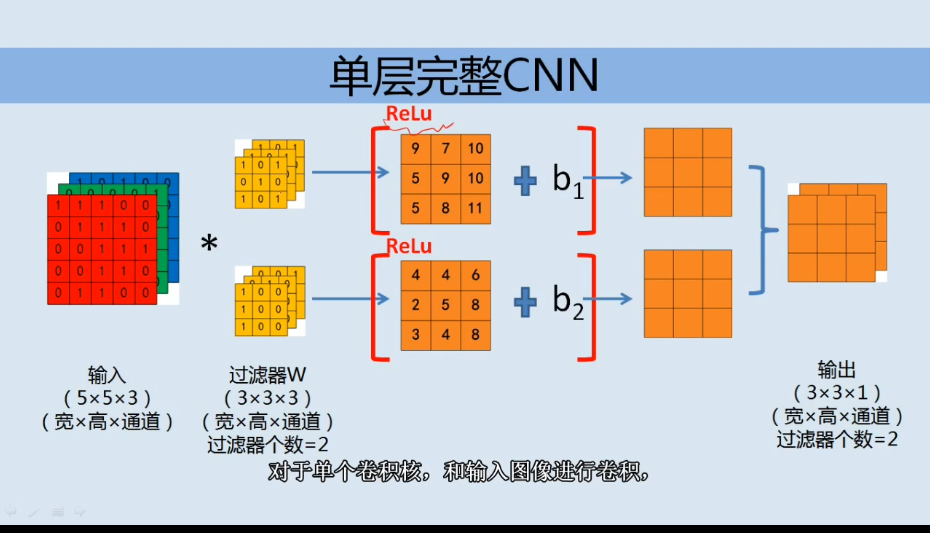
池化 pooling
常见池化层
- max-pooling
- average-pooling
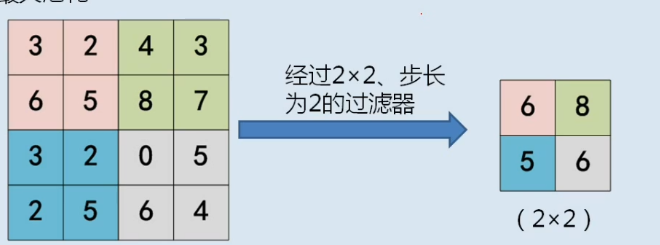
池化后与FC layer的连接
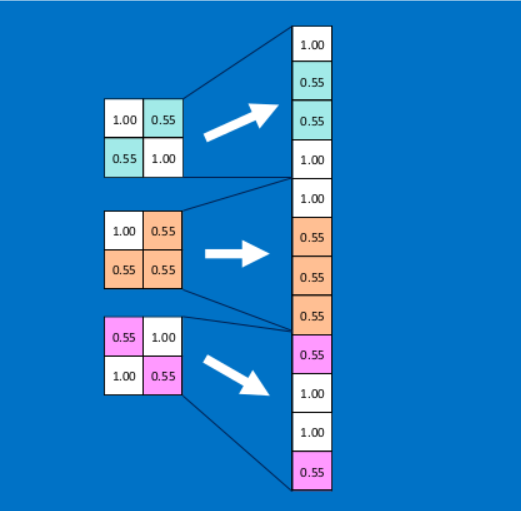
全连接层在整个卷积神经网络中起到“分类器”的作用,即通过卷积、激活函数、池化等深度网络后,再经过全连接层对结果进行识别分类。首先将经过卷积、激活函数、池化的深度网络后的结果串起来,如下图所示
代码
Pytorch conv2d 全部代码
:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as f
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
#两个卷积层
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
#三个全连接层
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
#1:先使用conv1 2:relu函数激活 3:max_pool激活(大小为 2x2)
x = f.max_pool2d(f.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
#上一步输出值进行同样操作
x = f.max_pool2d(f.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
#对两个卷积和池化后的数据处理为一维,以输入接下来的fc层
x = x.view(-1,self.num_flat_features(x))
x = f.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = f.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
def num_flat_features(self,x):
size = x.size()[1:]
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features
net = Net()
print(net)
conv2d源码:
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
#out_channels which equals to the numbers of kernels
out_channels: int,
kernel_size: _size_2_t,
stride: _size_2_t = 1,
padding: _size_2_t = 0,
dilation: _size_2_t = 1,
groups: int = 1,
bias: bool = True,
padding_mode: str = 'zeros' # TODO: refine this type
):
创建一个卷积层:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5)
也可写成
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)输入为一channel,即灰度图,输出为6通道,核为5,不分别指定长宽即为正方形
参考
图片参考自
006卷积神经网络CNN的基本概念
以及
卷积神经网络CNN【5】FC全连接层


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号