链表相关
链表节点结构:
public static class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } }
1.判断链表是否存在环:通过快慢节点
public boolean isLoop(ListNode node) { ListNode slow=node; ListNode fast=node.next; while(slow.next!=null) { if(fast==slow)
{
//这一段是新需求,返回入口节点,相等的地方退出while循环就是入口节点,首先分为两个链表,一个就是原来的,起点就是原来的起点,一个是现在的,
//把当前相遇的这个节点slow当成新节点的初始节点,两个节点同时向后一定,相遇的位置就是初始节点,其实我们这里可以把这两个链表当成相同长度的链表,往后遍历。
fast=pHead; while(fast!=slow){ fast=fast.next; slow=slow.next; }return true;
}
if(fast.next==null) return false;//就两个节点不存在环 slow=slow.next; fast=fast.next.next; if(fast==null) return false; }
return false; }
2.头插法和尾插法建立单链表
public ListNode CreateListHead(int a[]) { ListNode L=new ListNode(0); L.next=null; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { ListNode temp=new ListNode(a[i]); temp.next=L.next; L.next=temp; } return L; } public ListNode CreateListTail(int a[]) { ListNode L=new ListNode(0); ListNode r=L; for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { ListNode temp=new ListNode(a[i]); r.next=temp; r=temp; } return L; }
3.逆向输出单链表(通过栈和链表的头插法来实现)
public void reverseNodeStack(ListNode node){ Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>() ; while (node != null){ stack.push(node) ; node = node.next ; } while (!stack.isEmpty()){ System.out.print(stack.pop().val); } } public ListNode reverseNode(ListNode head) { if (head == null) { return null; } ListNode node ; ListNode pre = head; ListNode cur = head.next; ListNode next ; while(cur != null){ next = cur.next;//首先保存后面一个节点 cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } head.next = null;//最后一个节点尾节点置空 return pre; }
//递归的方式
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { if(head==null||head.next==null) { return head; } ListNode newHead=reverseList(head.next); head.next.next=head; head.next=null; return new Head; }
对逆置更复杂的解决,逆置一个链表中间的一段,需要保存前一段的最后一个节点,对中间这一段逆置
//对第start个节点到end节点逆置 public ListNode reverseNode(ListNode head,int start,int end) { if (head == null) { return null; } ListNode cur=head; ListNode precur = null;//用来保存原先的最后一个节点 for(int i=0;i<start-1;i++) { precur=cur; cur=cur.next; } ListNode pre = cur;//要逆置的这段的前一个节点 ListNode revercur = cur.next;//要逆置的后一个节点 ListNode next = null ; int j=0; while(cur != null&&j<end-start){ next = revercur.next;//首先保存后面一个节点 revercur.next = pre; pre = revercur; revercur = next; j++; } precur.next=pre; cur.next = next;//逆置的最后一个节点指向后面 return head; }
4.对一个链表进行排序:使用归并排序
问题描述,给定一个Int的链表,要求在时间最优的情况下完成链表元素由大到小的排序, e.g: 1->5->4->3->2 排序后结果 5->4->3->2->1
public ListNode MergeSort(ListNode first,int length) { if(length==1) { return first; } else { ListNode middle = new ListNode(0); ListNode tmp=first; for(int i=0;i<length;i++) { if(i==length/2) break; middle=tmp; tmp=tmp.next; } ListNode right=middle.next; middle.next=null; ListNode leftStart=MergeSort(first,length/2); ListNode rightStart; if(length%2==0) rightStart=MergeSort(right,length/2); else rightStart=MergeSort(right,length/2+1); return MergeList(leftStart,rightStart); } } public ListNode MergeList(ListNode left,ListNode right) { ListNode head=new ListNode(0); ListNode result=head; ListNode tmp; while(left!=null&&right!=null) { if(left.val>right.val) { tmp=left; result.next=left; result = tmp; left=left.next; } else { tmp = right; result.next = right; result = tmp; right = right.next; } if(left==null) { result.next=right; break; } if(right==null) { result.next=left; break; } } return head.next; }
5.删除一个链表里面重复的节点: 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) { if(pHead==null||pHead.next==null) return pHead; if(pHead.val==pHead.next.val) { ListNode tmp=pHead.next; while(tmp!=null&&tmp.val==pHead.val) { tmp=tmp.next; } return deleteDuplication(tmp); } else { pHead.next=deleteDuplication(pHead.next); return pHead; } }
还有一种删除 1-2-3-3-4-4-5 -> 1-2-3-4-5
public static ListNode dels(ListNode head){ ListNode p=head.next,q; while(p.next!=null) { if(p.val==p.next.val) { q=p.next; p.next=q.next; } else p=p.next; } return head; }
6.两个单链表求差集A-B
思想:从头遍历链表A,如果当前元素不在链表B中,将其加到链表C中,最后返回链表C。
public static ListNode diff(ListNode A,ListNode B) { ListNode pa=A.next,pb; ListNode cHead=new ListNode(0); ListNode r=cHead; while(pa!=null) { pb=B.next; while(pb!=null&&pb.val!=pa.val) pb=pb.next; if(pb==null) { ListNode s=new ListNode(pa.val); r.next=s; r=s; } pa=pa.next; } return cHead; }
关于链表读取的处理:
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); int n=scan.nextInt(); ListNode A=new ListNode(0); ListNode Ta=A; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { ListNode s=new ListNode(scan.nextInt()); Ta.next=s; Ta=s; } int m=scan.nextInt(); ListNode B=new ListNode(0); ListNode Tb=B; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { ListNode s=new ListNode(scan.nextInt()); Tb.next=s; Tb=s; } ListNode c=List.diff(A, B); ListNode tc=c; while(tc!=null) { System.out.println(tc.val); tc=tc.next; } }
两个链表求并集A U B
思想:首先将A链表复制到C链表中,从头遍历单链表B,判断当前元素是否在A链表中,若不在,将其加到单链表C中
两个链表求交集A交B
思想:从头遍历A链表,判断当前元素是否在B链表中,在的话将其插入到C链表中
7.查单链表的倒数第k个节点
思想:使用两个指针,让前面的指针先走到k个节点,然后两个指针同时往后移动,当前一个指针到达最后一位的时候,后面的指针的位置就是倒数第k个节点。
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) { if(head==null||k<=0) return null; ListNode fir=head,sec=head; for(int i=1;i<k;i++) { if(sec.next!=null) sec=sec.next; else return null; } while(sec.next!=null){ sec=sec.next; fir=fir.next; } return fir; }
8.查找单链表的中间节点
思想,也可以设置两个指针,快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次只走一步,当快指针到达最后一位的时候,慢指针的位置就是中间的额位置,这样的方法时间复杂度只有O(n/2)
9.只给定一个节点,能否把他删除?
复制这个节点的后面一个节点到当前这个节点,然后删除后面一个节点,时间复杂度O(1)
10.判断两个链表是否相交?
如果两个链表相交,那么他们的尾节点一定是相同的,我们就直接遍历到尾节点判断是否相同即可
11.如果两个链表已经相交,我们去求出两个链表相交的首节点。
求出两个链表的差值,长的链表先走差值步,然后两个链表同时向后遍历,遇到的第一个相同的节点就是第一个相交的首节点。
上面这种应该是O(2*n)。
两个指针同时从头结点往后移动,短的先到尾部,然后再从短的头部开始移动,当长的到达尾部时,这个短的指向的就是相交节点
这种是O(n)只用遍历一遍。
12.用冒泡排序的方法对一个链表排序?
和之前数组用冒泡有点不一样,这里是从链表的头部往后冒泡。用了两个指针cur用来继续冒泡的,tail用来保存还没排好序的最后一个位置
public static ListNode BubbleSort(ListNode head) { ListNode cur=head.next;//指向第一个节点 ListNode tail=null; while(cur!=tail) { //只要首尾节点不重合,就需要继续冒泡 while(cur.next!=tail) {//只要cur指针没有到达tail的前一位,就需要向后移动 if(cur.val>cur.next.val) { int temp=cur.next.val; cur.next.val=cur.val; cur.val=temp; } cur=cur.next; } tail=cur; cur=head.next; } return head; }
13,最后一个难点,重排链表问题
https://juejin.im/post/5aa299c1518825557b4c5806
14,复杂链表的复制
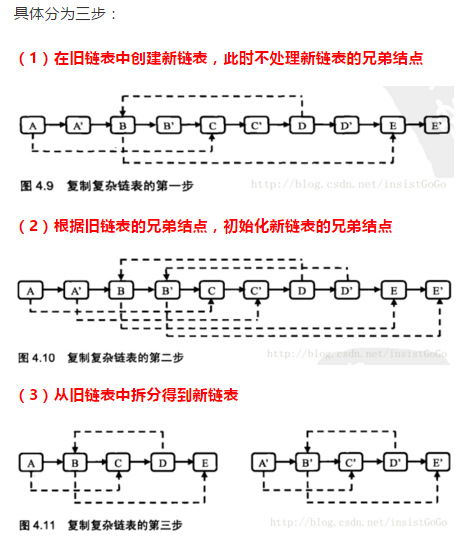
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) { if(pHead==null) return null; RandomListNode cur=pHead; while(cur!=null) { RandomListNode clone=new RandomListNode(cur.label); clone.next=cur.next; cur.next=clone; cur=clone.next; } cur=pHead; while(cur!=null) { cur.next.random=cur.random==null?null:cur.random.next; cur=cur.next.next; } cur=pHead; RandomListNode cHead=cur.next; while(cur!=null) { RandomListNode cloneNode=cur.next; cur.next=cloneNode.next; cloneNode.next=cloneNode.next==null?null:cloneNode.next.next; cur=cur.next; } return cHead; }
15.排好序的链表的归并排序
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) { if(list1==null) return list2; if(list2==null) return list1; ListNode head=new ListNode(0); ListNode cur=head; ListNode temp; while(list1!=null&&list2!=null) { if(list1.val<list2.val) { temp=list1; cur.next=list1; cur=list1; list1=list1.next; } else { temp=list2; cur.next=list2; cur=list2; list2=list2.next; } } if(list1==null) { cur.next=list2; } if(list2==null) { cur.next=list1; } return head.next; }
16.判断是否是回文链表
前count/2逆置,然后判断
public boolean huiwen(ListNode head) { if(head==null||head.next==null) return true; int count=0; ListNode cur=head; while(cur!=null) { cur=cur.next; count++; } if(count==2) { if(head.val==head.next.val) return true; else return false; } int offset=count/2; ListNode pre=head; cur=head.next; ListNode tempnext; while(--offset>0) { tempnext=cur.next; cur.next=pre; pre=cur; cur=tempnext; } head.next=null; if(count%2==1) { cur=cur.next; } while(pre!=null) { if(pre.val!=cur.val) return false; pre=pre.next; cur=cur.next; } return true; }
17.用链表去实现队列,需要维持一个首尾指针
class LinkedQueue<T> { private class Node { T data; Node next; Node pre; public Node(T data) { this.data = data; } } private int maxSize; private Node front = null; private Node rear = null; private int nItems; public LinkedQueue(int maxSize) { this.maxSize = maxSize; front = null; rear = null; this.nItems = 0; } public void enqueue(T data) { Node node = new Node(data); if (isEmpty()) {//插入第一个节点 front = node; front.next = null; rear = node; rear.pre = null; nItems++; return; } if (size() == 1) { rear = node; front.next = rear; rear.pre = front; nItems++; return; } if (isFull()) { System.out.print("超过队列已满,无法入队"); return; } node.pre = rear; rear.next = node; rear = node; nItems++; } public T dequeue() { Node temp = null; if (isEmpty()) { System.out.println("队列已空,无法出队"); return null; } if (size() == 1) { temp = front; front = null; rear = null; nItems--; return temp.data; } if (size() == 2) { temp = front; front = rear; front.next = null; rear.pre = null; nItems--; return temp.data; } temp = front; front = front.next; nItems--; return temp.data; } public boolean isEmpty() { return nItems == 0; } public boolean isFull() { return nItems == maxSize; } public int size() { return nItems; } }
本文来自博客园,作者:LeeJuly,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/peterleee/p/10612418.html





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号