代码实现: 最小生成树问题--Prim算法&Kruskal算法
Prim 算法:
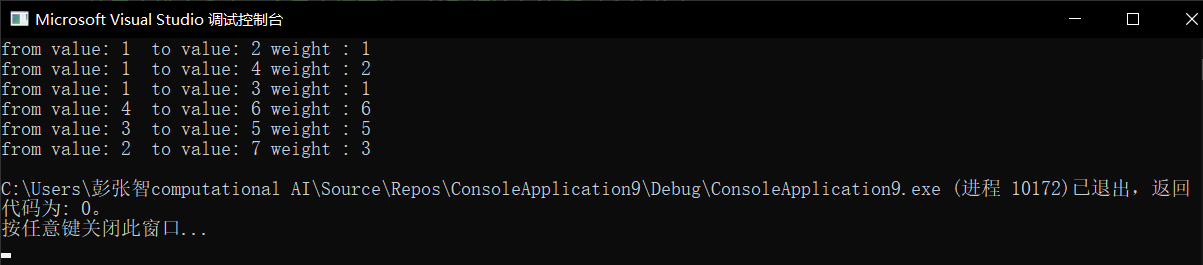
#include<iostream> #include<list> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<unordered_map> #include<unordered_set> using namespace std; //解依赖 class Edge; //并查集和 图公用一个Node class Node { public: int value; int in; int out; list<Node*> next; list<Edge*> edges; //Node 和 Edge 中都重新定义了 ==操作,是因为进入哈希表的,不仅要计算其哈希值,还要计算两节点是否相等 //在并查集的 union_函数中用到了Node类型的比较操作,所以得自己重新定义 bool operator == (const Node& n) const { return value == n.value; } //并查集中 father 要和 node节点比较 该node节点是否为代表节点 bool operator != (const Node& n) const { return value != n.value; } Node() {} Node(int value) { this->value = value; in = 0; out = 0; } }; class Edge { public: int weight; int for_hash; Node* from; Node* to; Edge(int weight, Node* from, Node* to) { this->weight = weight; this->from = from; this->to = to; this->for_hash = to->value; } // bool operator < (const Edge& edge) const{ // return weight < edge.weight; // } bool operator > (const Edge& edge) const { return weight > edge.weight; } bool operator == (const Edge& e) const { return weight == e.weight; } }; class Graph { public: unordered_map<int, Node*> nodes; unordered_set<Edge*> edges; }; class GraphGenerator { public: Graph createGraph(int matrix[][3], int rows, int col) { Graph graph; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { int weight = matrix[i][0]; int from = matrix[i][1]; int to = matrix[i][2]; if (graph.nodes.find(from) == graph.nodes.end()) { graph.nodes[from] = new Node(from); } if (graph.nodes.find(to) == graph.nodes.end()) { graph.nodes[to] = new Node(to); } //以上两个if操作后,必能找到 from 好人to节点 Node* fromNode = graph.nodes.find(from)->second; Node* toNode = graph.nodes.find(to)->second; //为 graph 和 from所在的node 准备 一条边 Edge* newEdge = new Edge(weight, fromNode, toNode); //对于新增的一条边, 被指向节点的入度+1 toNode->in++; //对于新增的一条边, 指向节点的出度+1,所指向的节点确定,指向该节点的边确定 fromNode->out++; fromNode->next.push_back(toNode); fromNode->edges.push_back(newEdge); //两个if会保证建立节点,这里保证 边的存在。 graph.edges.insert(newEdge); } return graph; } }; //由于使用了unoredred_map,以前我们使用基础的数据类型,系统能自己计算基础类型的hash值是什么, //但现在我们要在哈希表中使用自定义的类型,所以得告诉哈希表该如何计算这一类型的哈希值 struct NodeHash { size_t operator () (const Node& n) const { return hash<int>()(n.value); } }; struct EdgeHash { size_t operator () (const Edge& e) const { return (hash<int>()(e.weight) << 1) ^ (hash<int>()(e.for_hash) << 1); } }; //unordered_map/set是采用hash散列进行存储的,因此存储的对象必须提供两个方法, //1,hash告知此容器如何生成hash的值, //2,Equal_Edge 告知容器当出现hash冲突的时候,如何区分hash值相同的不同对象 struct Equal_Edge { bool operator()(const Edge& e1, const Edge& e2) const { return e1.weight == e2.weight && e1.for_hash == e2.for_hash; } }; struct Equal_Node { bool operator()(const Node& n1, const Node& n2) const { return n1.value == n2.value; } }; //primMST unordered_set<Edge, EdgeHash, Equal_Edge> primMST(Graph graph) { //装边的最小堆 priority_queue<Edge, vector<Edge>, greater<Edge> > small_queue; //判断节点是否访问过了 unordered_set<Node, NodeHash, Equal_Node> visited; unordered_set<Edge, EdgeHash, Equal_Edge> result; //解决森林的 情况 ,否则只要内层的if就够了 unordered_map<int, Node*>::iterator ite = graph.nodes.begin(); unordered_set<Edge, EdgeHash, Equal_Edge> ret; while (ite != graph.nodes.end()) { if (visited.find(*(ite->second)) == visited.end()) { visited.insert(*(ite->second)); for (auto edge : ite->second->edges) { small_queue.push(*(edge)); } while (!small_queue.empty()) { auto temp = small_queue.top(); small_queue.pop(); if (visited.find(*(temp.to)) == visited.end()) { visited.insert(*(temp.to)); ret.insert(temp); } for (auto edge : temp.to->edges) { small_queue.push(*(edge)); } } } return ret; } //对每一个节点,都问一下是否访问过了,如果没放过过,做以下操作 //把该节点表示为访问过了,再把该节点所解锁的边都加入最小堆中 //在当前这个图中,取找最小生成树 //从最小堆中拿出一个最小权重边,并取得这条边所对应的节点 //判断这个节点是否已经被访问过了,如果没有,则这条边就加入解集,并且我们 认可该点现在被访问了,把该点所有连接的边都加入最小堆 return result; } int main() { GraphGenerator g; int matrix[][3] = { {1,1,2},{1,1,3},{2,1,4},{2,2,3},{3,2,7},{4,7,3}, {5,3,5},{6,4,6} }; int length = sizeof(matrix) / sizeof(matrix[0]); Graph graph = g.createGraph(matrix, length, 3); unordered_set<Edge, EdgeHash, Equal_Edge> edge_set = primMST(graph); unordered_set<Edge, EdgeHash, Equal_Edge>::iterator ite2 = edge_set.begin(); while (ite2 != edge_set.end()) { cout << "from value: " << (*ite2).from->value << " "; cout << "to value: " << (*ite2).to->value << " "; cout << "weight : " << (*ite2).weight << endl; ite2++; } return 0; }
Kruskal算法:
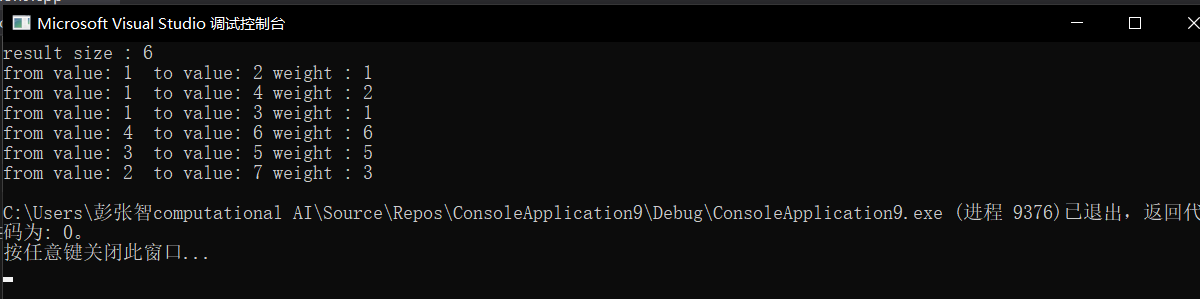
#include<iostream> #include<list> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<unordered_map> #include<unordered_set> using namespace std; //解依赖 class Edge; //并查集和 图公用一个Node class Node{ public: int value; int in; int out; list<Node*> next; list<Edge*> edges; //Node 和 Edge 中都重新定义了 ==操作,是因为进入哈希表的,不仅要计算其哈希值,还要计算两节点是否相等 //在并查集的 union_函数中用到了Node类型的比较操作,所以得自己重新定义 bool operator == (const Node& n) const{ return value == n.value; } //并查集中 father 要和 node节点比较 该node节点是否为代表节点 bool operator != (const Node& n) const{ return value != n.value; } Node(){} Node(int value){ this->value = value; in = 0; out =0; } }; class Edge{ public: int weight; int for_hash; Node* from; Node* to; Edge(int weight,Node* from, Node* to){ this->weight = weight; this->from = from; this->to = to; this->for_hash = to->value; } bool operator < (const Edge& edge) const{ return weight < edge.weight; } bool operator > (const Edge& edge) const{ return weight > edge.weight; } bool operator == (const Edge& e) const{ return weight == e.weight; } }; class Graph{ public: unordered_map<int, Node*> nodes; unordered_set<Edge*> edges; }; class GraphGenerator{ public: Graph createGraph(int matrix[][3],int rows, int col){ Graph graph; for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){ int weight = matrix[i][0]; int from = matrix[i][1]; int to = matrix[i][2]; if(graph.nodes.find(from) == graph.nodes.end()){ graph.nodes[from] = new Node(from); } if(graph.nodes.find(to) == graph.nodes.end()){ graph.nodes[to] = new Node(to); } //以上两个if操作后,必能找到 from 好人to节点 Node* fromNode = graph.nodes.find(from)->second; Node* toNode = graph.nodes.find(to)->second; //为 graph 和 from所在的node 准备 一条边 Edge* newEdge = new Edge(weight, fromNode, toNode); //对于新增的一条边, 被指向节点的入度+1 toNode->in++; //对于新增的一条边, 指向节点的出度+1,所指向的节点确定,指向该节点的边确定 fromNode->out++; fromNode->next.push_back(toNode); fromNode->edges.push_back(newEdge); //两个if会保证建立节点,这里保证 边的存在。 graph.edges.insert(newEdge); } return graph; } }; //由于使用了unoredred_map,以前我们使用基础的数据类型,系统能自己计算基础类型的hash值是什么, //但现在我们要在哈希表中使用自定义的类型,所以得告诉哈希表该如何计算这一类型的哈希值 struct NodeHash{ size_t operator () (const Node& n) const{ return hash<int>()(n.value); } }; struct EdgeHash{ size_t operator () (const Edge& e) const{ return ( hash<int>()(e.weight) <<1) ^ (hash<int>()(e.for_hash) << 1); } }; //unordered_map/set是采用hash散列进行存储的,因此存储的对象必须提供两个方法, //1,hash告知此容器如何生成hash的值, //2,equal_to 告知容器当出现hash冲突的时候,如何区分hash值相同的不同对象 struct Equal_to { bool operator()(const Edge& e1, const Edge& e2) const{ return e1.weight == e2.weight && e1.for_hash == e2.for_hash; } }; class UnionFindSet{ private: unordered_map<Node, Node, NodeHash> fatherMap; unordered_map<Node, int,NodeHash> sizeMap; public: //一开始,就要给我们所有的集合中的元素,然后让它们各自是一个集合,然后设每个集合的size为1 void setUnionFindSet(Node nodes[], int length){ for(int i=0; i<length; i++){ fatherMap[nodes[i]] = nodes[i]; sizeMap[nodes[i]] = 1; } } //往上 用递归帮忙找代表节点 Node findDaiBiao(Node node){ Node father = fatherMap.find(node)->second; if(father != node){ father = findDaiBiao(father); } fatherMap[node] = father; return father; } //借助 找到的代表节点,判断两个节点是否在一个集合中 bool isSameSet(Node n1, Node n2){ Node daibiao_n1 = findDaiBiao(n1); Node daibiao_n2 = findDaiBiao(n2); if(daibiao_n1 != daibiao_n2) return false; return true; } //如果两个节点不在同一个集合里,那么我们就要把他们合并起来,size小的集合的代表节点, //其parentmap中value改成size大的代表节点,更新size大的集合的size void union_(Node n1, Node n2){ Node daibiao_n1 = findDaiBiao(n1); Node daibiao_n2 = findDaiBiao(n2); if(daibiao_n1 != daibiao_n2){ int size1 = sizeMap.find(daibiao_n1)->second; int size2 = sizeMap.find(daibiao_n2)->second; if(size1 < size2){ fatherMap[daibiao_n1]=daibiao_n2; sizeMap[daibiao_n2]=(size1 + size2); } else{ fatherMap[daibiao_n2]=daibiao_n1; sizeMap[daibiao_n1]=(size1+size2); } } } }; unordered_set<Edge,EdgeHash,Equal_to> kruskalMST(Graph graph){ UnionFindSet ufset; int length = graph.nodes.size(); Node node[length]; int i =0; //构造好用于给并查集输入的点集 unordered_map<int, Node*>::iterator ite = graph.nodes.begin(); while(ite != graph.nodes.end()){ node[i] = *(ite->second); ite++; i++; } //初始化并查集 ufset.setUnionFindSet(node, length); priority_queue<Edge,vector<Edge>,greater<Edge> > small_queue; for(auto edge : graph.edges){ small_queue.push(*edge); } //构造选中的输出边集 unordered_set<Edge,EdgeHash,Equal_to> result; while(!small_queue.empty()){ Edge edge = small_queue.top(); small_queue.pop(); if(!ufset.isSameSet(*(edge.from), *(edge.to))){ result.insert(edge); ufset.union_(*(edge.from), *(edge.to)); } } cout << "result size : " << result.size()<<endl; return result; } int main(){ GraphGenerator g; int matrix[][3]={{1,1,2},{1,1,3},{2,1,4},{2,2,3},{3,2,7},{4,7,3}, {5,3,5},{6,4,6}}; int length = sizeof(matrix)/sizeof(matrix[0]); Graph graph = g.createGraph(matrix, length,3); unordered_set<Edge,EdgeHash,Equal_to> edge_set = kruskalMST(graph); unordered_set<Edge,EdgeHash,Equal_to>::iterator ite2 = edge_set.begin(); while(ite2 != edge_set.end()){ cout<< "from value: "<<(*ite2).from->value<<" "; cout<< "to value: "<<(*ite2).to->value<<" "; cout << "weight : " << (*ite2).weight << endl; ite2++; } return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号