Blog作业2
一.前言
题目集08和题目集09主要是考察类的设计和继承与多态以及接口,题量不多一个题目集三个题目加起来也就六个题目。难度的话,这两个题目集前两题都还好,就最后一题会要多花时间。题目集09的最后一题是在题目集08的最后一题的基础上划分了多种客户类型和货物类型以及支付方式,增加了功能需求。根据不同的客户类型,选着不同的折扣方式,根据不同的货物类型选择不同的费率。还有在输出货物重量时,输出的是货物的体积重量而不是货物的实际重量。想要完成题目集9的最后一题首先得要把题目集08的最后一题给做出来,不然题目集09的最后一题不好做。题目集08主要是类的设计要合理,要把类之间的关系弄清楚。题目集08要求满足:单一职责原则(40%)、里氏代换原则(20%)、开闭原则(20%),合成复用原则(20%)。题目集09要求满足::单一职责原则(20%)、里氏代换原则(20%)、开闭原则(20%)、合成复用原则(20%)、依赖倒转原则(20%)。这就更加要求我们设计的类的合理化来满足SOLID设计原则。总结来说就是,题目集09是在题目集08的基础上进行扩展,提高代码的可扩展性。
二.设计与分析
1.题目集08中“航空货运管理系统”
- 题目查看
点击查看题目
一、计费重量的确定
空运以实际重量(Gross Weight)和体积重量(Volume Weight)中的较
高者作为计费重量。
计算公式:
体积重量(kg) = 货物体积(长×宽×高,单位:厘米)÷ 6000
示例:
若货物实际重量为 80kg,体积为 120cm×80cm×60cm,则:
体积重量 = (120×80×60) ÷ 6000 = 96kg
计费重量取 96kg(因 96kg > 80kg)。
二、基础运费计算
费率(Rate):航空公司或货代根据航线、货物类型、市场行情等制定(如
CNY 30/kg)。本次作业费率采用分段计算方式:
𝐑𝐚te =
𝟑5 重量 < 𝟐0
30 𝟐0 ≤ 重量 < 50
25 50 ≤ 重量 < 100
15 重量 ≥ 100
公式:基础运费 = 计费重量 × 费率
三、题目说明
本次题目模拟某客户到该航空公司办理一次货运业务的过程:
航空公司提供如下信息:
航班信息(航班号,航班起飞机场所在城市,航班降落机场所在城市,航班
日期,航班最大载重量)
客户填写货运订单并进行支付,需要提供如下信息:
客户信息(姓名,电话号码等)
货物信息(货物名称,货物包装长、宽、高尺寸,货物重量等)
运送信息(发件人姓名、电话、地址,收件人姓名、电话、地址,所选
航班号,订单日期)
支付方式(支付宝支付、微信支付)
注:一个货运订单可以运送多件货物,每件货物均需要根据重量及费率单独
计费。
程序需要从键盘依次输入填写订单需要提供的信息,然后分别生成订单信
息报表及货物明细报表。
- 题目分析
首先我们需要根据题目来设计类图,先是粗略的分为客户类,货物类,还有航班类然后我们还需要一个订单类。当时编写代码时,思路主要是先完成各个实体类的基本属性和方法定义,保证数据的正确储存和简单操作。然后再把判断是否超重以及选择计费重量和进行计费操作写进相应类里面。因为题目要求要满足单一职责原则,所以一个类干一件事自己的事情自己做。各个类要分工明确,订单类要调用货物类,客户类,航班类,所以不能只有一个订单类包揽全部,这样违背了单一职责原则。类的设计要根据功能细分并要满足设计原则。 - 我的代码展示
点击查看代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
// 客户类,只负责存储客户信息
class Customer {
private final int custId;
private final String custName;
private final String custPhone;
private final String custAddress;
public Customer(int custId, String custName, String custPhone, String custAddress) {
this.custId = custId;
this.custName = custName;
this.custPhone = custPhone;
this.custAddress = custAddress;
}
public int getCustId() {
return custId;
}
public String getCustName() {
return custName;
}
public String getCustPhone() {
return custPhone;
}
public String getCustAddress() {
return custAddress;
}
}
// 货物类,只负责存储货物信息
class Goods {
private final int goodId;
private final String goodName;
private final int goodWidth;
private final int goodLength;
private final int goodHeight;
private final int goodWeight;
public Goods(int goodId, String goodName, int goodWidth, int goodLength, int goodHeight, int goodWeight) {
this.goodId = goodId;
this.goodName = goodName;
this.goodWidth = goodWidth;
this.goodLength = goodLength;
this.goodHeight = goodHeight;
this.goodWeight = goodWeight;
}
public int getGoodId() {
return goodId;
}
public String getGoodName() {
return goodName;
}
public int getGoodWidth() {
return goodWidth;
}
public int getGoodLength() {
return goodLength;
}
public int getGoodHeight() {
return goodHeight;
}
public int getGoodWeight() {
return goodWeight;
}
}
// 货物重量计算类,负责计算货物的体积重量和计费重量
class GoodsWeightCalculator {
public int calculateVolumeWeight(Goods goods) {
return (goods.getGoodWidth() * goods.getGoodLength() * goods.getGoodHeight()) / 6000;
}
public int getChargeableWeight(Goods goods) {
int volumeWeight = calculateVolumeWeight(goods);
return Math.max(goods.getGoodWeight(), volumeWeight);
}
}
// 航班类,只负责存储航班信息
class Airplane {
private final String flightNumber;
private final String departureAirport;
private final String arrivalAirport;
private final String flightDate;
private final int maxLoad;
public Airplane(String flightNumber, String departureAirport, String arrivalAirport, String flightDate, int maxLoad) {
this.flightNumber = flightNumber;
this.departureAirport = departureAirport;
this.arrivalAirport = arrivalAirport;
this.flightDate = flightDate;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flightNumber;
}
public String getDepartureAirport() {
return departureAirport;
}
public String getArrivalAirport() {
return arrivalAirport;
}
public String getFlightDate() {
return flightDate;
}
public int getMaxLoad() {
return maxLoad;
}
}
// 计费策略接口
interface FeeStrategy {
double calculateFee(int weight);
}
// 计费策略实现类
class CorrectFeeStrategy implements FeeStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateFee(int weight) {
if (weight < 20) {
return weight * 35;
} else if (weight < 50) {
return weight * 30;
} else if (weight < 100) {
return weight * 25;
} else {
return weight * 15;
}
}
}
// 订单信息类,只负责存储订单信息
class OrderInfo {
private final String orderId;
private final String orderDate;
private final String postAddress;
private final String postName;
private final String postPhone;
private final String receiveAddress;
private final String receiveName;
private final String receivePhone;
private final List<Goods> goodsList;
private final Customer customer;
private final Airplane airplane;
private final String paymentMethod = "微信";
public OrderInfo(String orderId, String orderDate, String postAddress, String postName, String postPhone,
String receiveAddress, String receiveName, String receivePhone, List<Goods> goodsList,
Customer customer, Airplane airplane) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.postAddress = postAddress;
this.postName = postName;
this.postPhone = postPhone;
this.receiveAddress = receiveAddress;
this.receiveName = receiveName;
this.receivePhone = receivePhone;
this.goodsList = goodsList;
this.customer = customer;
this.airplane = airplane;
}
public String getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public String getPostAddress() {
return postAddress;
}
public String getPostName() {
return postName;
}
public String getPostPhone() {
return postPhone;
}
public String getReceiveAddress() {
return receiveAddress;
}
public String getReceiveName() {
return receiveName;
}
public String getReceivePhone() {
return receivePhone;
}
public List<Goods> getGoodsList() {
return goodsList;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public Airplane getAirplane() {
return airplane;
}
public String getPaymentMethod() {
return paymentMethod;
}
}
// 订单计算类,负责计算订单的总重量和总费用
class OrderCalculator {
private final GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator;
private final FeeStrategy feeStrategy;
public OrderCalculator(GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator, FeeStrategy feeStrategy) {
this.goodsWeightCalculator = goodsWeightCalculator;
this.feeStrategy = feeStrategy;
}
public int calculateTotalWeight(List<Goods> goodsList) {
int totalWeight = 0;
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
totalWeight += goodsWeightCalculator.getChargeableWeight(goods);
}
return totalWeight;
}
public double calculateTotalFee(List<Goods> goodsList) {
double totalFee = 0;
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
int chargeableWeight = goodsWeightCalculator.getChargeableWeight(goods);
totalFee += feeStrategy.calculateFee(chargeableWeight);
}
return totalFee;
}
}
// 订单报告生成类,负责生成订单报告
class OrderReportGenerator {
private final GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator;
private final FeeStrategy feeStrategy;
private final OrderCalculator orderCalculator;
public OrderReportGenerator(GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator, FeeStrategy feeStrategy, OrderCalculator orderCalculator) {
this.goodsWeightCalculator = goodsWeightCalculator;
this.feeStrategy = feeStrategy;
this.orderCalculator = orderCalculator;
}
public void generateOrderReport(OrderInfo orderInfo) {
List<Goods> goodsList = orderInfo.getGoodsList();
Airplane airplane = orderInfo.getAirplane();
int totalWeight = orderCalculator.calculateTotalWeight(goodsList);
if (totalWeight > airplane.getMaxLoad()) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.\n", airplane.getFlightNumber());
return;
}
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:\n", orderInfo.getCustomer().getCustName(), orderInfo.getCustomer().getCustPhone());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("航班号:%s\n", airplane.getFlightNumber());
System.out.printf("订单号:%s\n", orderInfo.getOrderId());
System.out.printf("订单日期:%s\n", orderInfo.getOrderDate());
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s\n", orderInfo.getPostName());
System.out.printf("发件人电话:%s\n", orderInfo.getPostPhone());
System.out.printf("发件人地址:%s\n", orderInfo.getPostAddress());
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s\n", orderInfo.getReceiveName());
System.out.printf("收件人电话:%s\n", orderInfo.getReceivePhone());
System.out.printf("收件人地址:%s\n", orderInfo.getReceiveAddress());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n", (double) totalWeight);
System.out.printf("%s支付金额:%.1f\n", orderInfo.getPaymentMethod(), orderCalculator.calculateTotalFee(goodsList));
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int index = 1;
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
int chargeableWeight = goodsWeightCalculator.getChargeableWeight(goods);
double fee = feeStrategy.calculateFee(chargeableWeight);
double feeRate;
if (chargeableWeight < 20) {
feeRate = 35;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 50) {
feeRate = 30;
} else if (chargeableWeight < 100) {
feeRate = 25;
} else {
feeRate = 15;
}
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n", index++, goods.getGoodName(), (double) chargeableWeight, feeRate, fee);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 输入客户信息
int custId = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
String custName = scanner.nextLine();
String custPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String custAddress = scanner.nextLine();
Customer customer = new Customer(custId, custName, custPhone, custAddress);
// 输入货物信息
int goodsCount = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
List<Goods> goodsList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < goodsCount; i++) {
int goodId = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
String goodName = scanner.nextLine();
int goodWidth = scanner.nextInt();
int goodLength = scanner.nextInt();
int goodHeight = scanner.nextInt();
int goodWeight = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
Goods goods = new Goods(goodId, goodName, goodWidth, goodLength, goodHeight, goodWeight);
goodsList.add(goods);
}
// 输入航班信息
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departureAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String arrivalAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String flightDate = scanner.nextLine();
int maxLoad = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
Airplane airplane = new Airplane(flightNumber, departureAirport, arrivalAirport, flightDate, maxLoad);
// 输入订单信息
String orderId = scanner.nextLine();
String orderDate = scanner.nextLine();
String postAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String postName = scanner.nextLine();
String postPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String receiveAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String receiveName = scanner.nextLine();
String receivePhone = scanner.nextLine();
OrderInfo orderInfo = new OrderInfo(orderId, orderDate, postAddress, postName, postPhone,
receiveAddress, receiveName, receivePhone, goodsList, customer, airplane);
GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator = new GoodsWeightCalculator();
FeeStrategy feeStrategy = new CorrectFeeStrategy();
OrderCalculator orderCalculator = new OrderCalculator(goodsWeightCalculator, feeStrategy);
OrderReportGenerator orderReportGenerator = new OrderReportGenerator(goodsWeightCalculator, feeStrategy, orderCalculator);
orderReportGenerator.generateOrderReport(orderInfo);
scanner.close();
}
}

点击查看代码分析
Metrics Details For File '08.txt'
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Value
========= =====
Project Directory \
Project Name
Checkpoint Name Baseline
File Name 08.txt
Lines 374
Statements 176
Percent Branch Statements 4.0
Method Call Statements 19
Percent Lines with Comments 2.4
Classes and Interfaces 3
Methods per Class 27.33
Average Statements per Method 2.05
Line Number of Most Complex Method 79
Name of Most Complex Method OrderReportGenerator.getMaxLoad()
Maximum Complexity 1
Line Number of Deepest Block 268
Maximum Block Depth 3
Average Block Depth 0.79
Average Complexity 1.00
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Most Complex Methods in 2 Class(es): Complexity, Statements, Max Depth, Calls
GoodsWeightCalculator.calculateVolumeWeight() 1, 1, 2, 2
GoodsWeightCalculator.getChargeableWeight() 1, 2, 2, 2
OrderReportGenerator.getMaxLoad() 1, 3, 2, 0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Block Depth Statements
0 71
1 73
2 30
3 2
4 0
5 0
6 0
7 0
8 0
9+ 0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
基于度量指标的分析:
代码规模与结构
总行数(374)与语句数(176):
代码规模适中,但存在较多空行或注释行(约 53%)。
类与接口数量(3 个):
实体类(如Customer、Goods)未计入度量,仅统计了业务逻辑类。实际代码包含 8 个类,这里SourceMonitor仅分析了部分核心类。复杂度与可维护性
分支语句比例(4.0%):
代码中条件判断较少,逻辑简单。但CorrectFeeStrategy和OrderReportGenerator中存在重复的if-else分支,可通过策略模式优化。
方法复杂度(Max=1,Avg=1.00):
所有方法复杂度极低,表明逻辑简单。但OrderReportGenerator.generateOrderReport()方法较长(约 60 行)。
块深度(Max=3,Avg=0.79):
嵌套层级浅,代码扁平易读。但Main.main()方法中存在多层输入处理逻辑,可提取为独立方法。设计原则遵循情况
单一职责原则:
问题:OrderReportGenerator承担了订单校验、数据计算和报表生成,违反单一职责。
改进:将校验逻辑移至OrderValidator类,报表格式化为ReportFormatter类。
开闭原则:
问题:CorrectFeeStrategy硬编码费率逻辑,新增费率需修改类。
改进:使用配置文件或枚举存储费率,通过工厂模式创建策略实例。
合成复用原则:
优点:OrderCalculator和OrderReportGenerator通过组合依赖GoodsWeightCalculator和FeeStrategy,符合 CRP。性能与效率
方法调用语句(19 条):
方法间调用频繁,但逻辑简单,无明显性能瓶颈。
平均语句数(2.05 条 / 方法):
方法短小精悍,导致方法数量过多。可维护性与可读性
注释比例(2.4%):
注释严重不足。
代码重复:
OrderReportGenerator中计算费率的逻辑与CorrectFeeStrategy重复,需统一抽象。
![]()
在我的代码里有,客户类只负责存储客户信息,货物类只负责存储货物信息,货物重量计算类负责计算货物的体积重量和计费重量,航班类只负责存储航班信息,计费策略接口,计费接口实现类,订单信息类只负责存储订单信息,订单计算类负责计算订单的总重量和总费用,订单报告生成类负责生成订单报告以及主类来输入客户订单货物航班信息
对代码的设计原则分析及改进
- [1] 单一职责原则SRP分析
Customer、Goods、Airplane、OrderInfo 等类职责明确,仅负责数据存储。
GoodsWeightCalculator 专注于重量计算,OrderCalculator 专注于费用计算,OrderReportGenerator 专注于报告生成,符合单一职责。
可改进点
OrderReportGenerator 中重复实现了费率判断逻辑(如计算 feeRate 时的 if-else),应委托给策略类处理,避免职责交叉。 - [2] 里氏代换原则LSP分析
代码中未定义继承体系,因此不涉及里氏代换原则的直接违背。 - [3] 开闭原则OCP分析
CorrectFeeStrategy 中的费率分段逻辑硬编码在 calculateFee 方法中。若需修改费率(如调整分段阈值或价格),必须修改该类的代码,违反 “对扩展开放,对修改关闭” 原则
改进方案
将费率配置抽象为可配置的数据(如枚举、配置文件或 Map),或通过工厂模式动态创建策略对象。
改进代码实现
点击查看代码
// 定义费率配置(枚举或静态常量)
enum FeeTier {
TIER1(20, 35), // 重量 < 20,费率35
TIER2(50, 30), // 20 ≤ 重量 < 50,费率30
TIER3(100, 25), // 50 ≤ 重量 < 100,费率25
TIER4(0, 15); // 重量 ≥ 100,费率15(阈值0表示无上限)
private final int threshold;
private final double rate;
FeeTier(int threshold, double rate) {
this.threshold = threshold;
this.rate = rate;
}
public boolean appliesTo(int weight) {
return threshold == 0 ? weight >= 100 : weight < threshold;
}
public double getRate() {
return rate;
}
}
// 修改后的策略类(基于枚举匹配费率)
class CorrectFeeStrategy implements FeeStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateFee(int weight) {
for (FeeTier tier : FeeTier.values()) {
if (tier.appliesTo(weight)) {
return weight * tier.getRate();
}
}
return 0; // 默认情况
}
}
- [4] 合成复用原则CRP分析
OrderInfo 通过组合 Customer、Airplane、Goods 等类实现功能,而非继承,符合合成复用原则。
OrderCalculator 和 OrderReportGenerator 通过依赖注入组合 GoodsWeightCalculator 和 FeeStrategy,避免紧耦合。
可改进点
OrderReportGenerator 中直接调用 GoodsWeightCalculator 和 FeeStrategy,可进一步通过接口抽象依赖,提升灵活性。
2.题目集09中的"航空货运管理系统(继承与多态)"
点击查看题目
一、计费重量的确定
空运以实际重量(Gross Weight)和体积重量(Volume Weight)中的较
高者作为计费重量。
计算公式:
体积重量(kg) = 货物体积(长×宽×高,单位:厘米)÷ 6000
示例:
若货物实际重量为 80kg,体积为 120cm×80cm×60cm,则:
体积重量 = (120×80×60) ÷ 6000 = 96kg
计费重量取 96kg(因 96kg > 80kg)。
二、基础运费计算2
费率(Rate):航空公司或货代根据航线、货物类型、市场行情等制定(如
CNY 30/kg)。本次作业费率与货物类型有关,货物类型分为普通货物、危险货
物和加急货物三种,其费率分别为:
计算公式:基础运费 = 计费重量 × 费率 × 折扣率
其中,折扣率是指不同的用户类型针对每个订单的运费可以享受相应的折扣,
在本题中,用户分为个人用户和集团用户,其中个人用户可享受订单运费的 9
折优惠,集团用户可享受订单运费的 8 折优惠。
三、题目说明
本次题目模拟某客户到该航空公司办理一次货运业务的过程:
航空公司提供如下信息:
航班信息(航班号,航班起飞机场,航班降落机场,航班日期,航班最大载
重量)3
客户填写货运订单并进行支付,需要提供如下信息:
客户信息(姓名,电话号码等)
货物信息(货物名称,货物包装长、宽、高尺寸,货物重量等)
运送信息(发件人姓名、电话、地址,收件人姓名、电话、地址,所选
航班号,订单日期)
支付方式(支付宝支付、微信支付、现金支付)
注:一个货运订单可以运送多件货物,每件货物均需要根据重量及费率单独
计费。
程序需要从键盘依次输入填写订单需要提供的信息,然后分别生成订单信
息报表及货物明细报表。
四、题目要求
本次题目重点考核面向对象设计原则中的单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开
闭原则以及合成复用原则、依赖倒转原则,除需要在 PTA 平台提交源码外,还
需要在超星平台提交本次作业最终得分源码(首次提交最高分源码)的类图,
评判标准为:
基础得分:PTA 实际得分
设计因素:单一职责原则(20%)、里氏代换原则(20%)、开闭原则(20%)、
合成复用原则(20%)、依赖倒转原则(20%)。
最终得分:基础得分扣减所有违背设计原则分值(违背所有五个原则的设计
最终得分为 0 分)
注:提交源码时务必慎重,一定核查是否符合本次题目考核的四个设计原
则,否则一旦提交得到满分则无法修改。(文中红色字体部分为在上次作业基
础上新增的要求)
提醒:本题需求可扩展的类:用户、支付方式、货物

- 我的代码展示
点击查看代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
// 货物重量计算类,负责计算货物的体积重量和计费重量
class GoodsWeightCalculator {
public int calculateVolumeWeight(Goods goods) {
return (goods.getGoodWidth() * goods.getGoodLength() * goods.getGoodHeight()) / 6000;
}
public int getChargeableWeight(Goods goods) {
int volumeWeight = calculateVolumeWeight(goods);
return Math.max(goods.getGoodWeight(), volumeWeight);
}
}
// 航班类,只负责存储航班信息
class Airplane {
private final String flightNumber;
private final String departureAirport;
private final String arrivalAirport;
private final String flightDate;
private final int maxLoad;
public Airplane(String flightNumber, String departureAirport, String arrivalAirport,
String flightDate, int maxLoad) {
this.flightNumber = flightNumber;
this.departureAirport = departureAirport;
this.arrivalAirport = arrivalAirport;
this.flightDate = flightDate;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
}
public String getFlightNumber() {
return flightNumber;
}
public String getDepartureAirport() {
return departureAirport;
}
public String getArrivalAirport() {
return arrivalAirport;
}
public String getFlightDate() {
return flightDate;
}
public int getMaxLoad() {
return maxLoad;
}
}
// 订单信息类,只负责存储订单信息
class OrderInfo {
private final String orderId;
private final String orderDate;
private final String postAddress;
private final String postName;
private final String postPhone;
private final String receiveAddress;
private final String receiveName;
private final String receivePhone;
private final List<Goods> goodsList;
private final Customer customer;
private final Airplane airplane;
private final PaymentMethod paymentMethod;
public OrderInfo(String orderId, String orderDate, String postAddress, String postName, String postPhone,
String receiveAddress, String receiveName, String receivePhone, List<Goods> goodsList,
Customer customer, Airplane airplane, PaymentMethod paymentMethod) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
this.postAddress = postAddress;
this.postName = postName;
this.postPhone = postPhone;
this.receiveAddress = receiveAddress;
this.receiveName = receiveName;
this.receivePhone = receivePhone;
this.goodsList = goodsList;
this.customer = customer;
this.airplane = airplane;
this.paymentMethod = paymentMethod;
}
public String getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public String getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public String getPostAddress() {
return postAddress;
}
public String getPostName() {
return postName;
}
public String getPostPhone() {
return postPhone;
}
public String getReceiveAddress() {
return receiveAddress;
}
public String getReceiveName() {
return receiveName;
}
public String getReceivePhone() {
return receivePhone;
}
public List<Goods> getGoodsList() {
return goodsList;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public Airplane getAirplane() {
return airplane;
}
public PaymentMethod getPaymentMethod() {
return paymentMethod;
}
}
// 客户类,只负责存储客户信息
abstract class Customer {
private final int custId;
private final String custName;
private final String custPhone;
private final String custAddress;
private final String custType;
public Customer(int custId, String custName, String custPhone, String custAddress, String custType) {
this.custId = custId;
this.custName = custName;
this.custPhone = custPhone;
this.custAddress = custAddress;
this.custType = custType;
}
public String getCustType() {
return custType;
}
public int getCustId() {
return custId;
}
public String getCustName() {
return custName;
}
public String getCustPhone() {
return custPhone;
}
public String getCustAddress() {
return custAddress;
}
public abstract double calculateDiscount(double price);
}
class Individual extends Customer {
public Individual(int custId, String custName, String custPhone, String custAddress) {
super(custId, custName, custPhone, custAddress, "Individual");
}
@Override
public double calculateDiscount(double price) {
return price * 0.9; // 个人客户9折
}
}
class Corporate extends Customer {
public Corporate(int custId, String custName, String custPhone, String custAddress) {
super(custId, custName, custPhone, custAddress, "Corporate");
}
@Override
public double calculateDiscount(double price) {
return price * 0.8; // 企业客户8折
}
}
// 支付方式接口
interface PaymentMethod {
void pay(double amount);
String getType();
}
// 微信支付
class Wechat implements PaymentMethod {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("微信支付金额:" + amount);
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return "微信";
}
}
// 支付宝
class ALiPay implements PaymentMethod {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("支付宝支付金额:" + amount);
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return "支付宝";
}
}
// 现金
class Cash implements PaymentMethod {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("现金支付金额:" + amount);
}
@Override
public String getType() {
return "现金";
}
}
// 支付方式工厂
class PaymentMethodFactory {
public static PaymentMethod createPaymentMethod(String type) {
return switch (type) {
case "Wechat" -> new Wechat();
case "ALiPay" -> new ALiPay();
case "Cash" -> new Cash();
default -> throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的支付方式: " + type);
};
}
}
// 货物接口 - 所有货物类型必须实现此接口
interface Goods {
String getGoodType();
int getGoodId();
String getGoodName();
int getGoodWidth();
int getGoodLength();
int getGoodHeight();
int getGoodWeight();
int getChargeableWeight(); // 获取计费重量
double calculateFee(); // 计算运费
}
// 抽象货物类 - 实现公共方法
abstract class AbstractGoods implements Goods {
private final int goodId;
private final String goodName;
private final int goodWidth;
private final int goodLength;
private final int goodHeight;
private final int goodWeight;
private final String goodType;
private final GoodsWeightCalculator weightCalculator;
public AbstractGoods(int goodId, String goodName, int goodWidth, int goodLength,
int goodHeight, int goodWeight, String goodType) {
this.goodId = goodId;
this.goodName = goodName;
this.goodWidth = goodWidth;
this.goodLength = goodLength;
this.goodHeight = goodHeight;
this.goodWeight = goodWeight;
this.goodType = goodType;
this.weightCalculator = new GoodsWeightCalculator();
}
@Override
public String getGoodType() {
return goodType;
}
@Override
public int getGoodId() {
return goodId;
}
@Override
public String getGoodName() {
return goodName;
}
@Override
public int getGoodWidth() {
return goodWidth;
}
@Override
public int getGoodLength() {
return goodLength;
}
@Override
public int getGoodHeight() {
return goodHeight;
}
@Override
public int getGoodWeight() {
return goodWeight;
}
@Override
public int getChargeableWeight() {
return weightCalculator.getChargeableWeight(this);
}
}
// 普通货物
class NormalGoods extends AbstractGoods {
public NormalGoods(int goodId, String goodName, int goodWidth, int goodLength,
int goodHeight, int goodWeight, String goodType) {
super(goodId, goodName, goodWidth, goodLength, goodHeight, goodWeight, goodType);
}
@Override
public double calculateFee() {
int weight = getChargeableWeight();
if (weight < 20) return weight * 35;
else if (weight < 50) return weight * 30;
else if (weight < 100) return weight * 25;
else return weight * 15;
}
}
// 危险货物
class DangerousGoods extends AbstractGoods {
public DangerousGoods(int goodId, String goodName, int goodWidth, int goodLength,
int goodHeight, int goodWeight, String goodType) {
super(goodId, goodName, goodWidth, goodLength, goodHeight, goodWeight, goodType);
}
@Override
public double calculateFee() {
int weight = getChargeableWeight();
if (weight < 20) return weight * 80;
else if (weight < 50) return weight * 50;
else if (weight < 100) return weight * 30;
else return weight * 20;
}
}
// 加急货物
class ExpediteGoods extends AbstractGoods {
public ExpediteGoods(int goodId, String goodName, int goodWidth, int goodLength,
int goodHeight, int goodWeight, String goodType) {
super(goodId, goodName, goodWidth, goodLength, goodHeight, goodWeight, goodType);
}
@Override
public double calculateFee() {
int weight = getChargeableWeight();
if (weight < 20) return weight * 60;
else if (weight < 50) return weight * 50;
else if (weight < 100) return weight * 40;
else return weight * 30;
}
}
// 货物工厂 - 负责创建不同类型的货物对象
class GoodsFactory {
public static Goods createGoods(String type, int goodId, String goodName,
int width, int length, int height, int weight) {
return switch (type) {
case "Normal" -> new NormalGoods(goodId, goodName, width, length, height, weight, type);
case "Dangerous" -> new DangerousGoods(goodId, goodName, width, length, height, weight, type);
case "Expedite" -> new ExpediteGoods(goodId, goodName, width, length, height, weight, type);
default -> throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的货物类型: " + type);
};
}
}
// 客户工厂 - 负责创建不同类型的客户对象
class CustomerFactory {
public static Customer createCustomer(String type, int custId, String custName,
String custPhone, String custAddress) {
return switch (type) {
case "Individual" -> new Individual(custId, custName, custPhone, custAddress);
case "Corporate" -> new Corporate(custId, custName, custPhone, custAddress);
default -> throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的客户类型: " + type);
};
}
}
// 订单计算类,负责计算订单的总重量和总费用
class OrderCalculator {
private final GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator;
public OrderCalculator(GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator) {
this.goodsWeightCalculator = goodsWeightCalculator;
}
public int calculateTotalWeight(List<Goods> goodsList) {
int totalWeight = 0;
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
totalWeight += goods.getChargeableWeight();
}
return totalWeight;
}
public double calculateTotalFee(List<Goods> goodsList) {
double totalFee = 0;
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
totalFee += goods.calculateFee();
}
return totalFee;
}
// 计算应用客户折扣后的最终费用
public double calculateFinalFee(List<Goods> goodsList, Customer customer) {
double totalFee = calculateTotalFee(goodsList);
return customer.calculateDiscount(totalFee);
}
}
// 订单报告生成类,负责生成订单报告
class OrderReportGenerator {
private final GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator;
public OrderReportGenerator(GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator) {
this.goodsWeightCalculator = goodsWeightCalculator;
}
public void generateOrderReport(OrderInfo orderInfo) {
List<Goods> goodsList = orderInfo.getGoodsList();
Airplane airplane = orderInfo.getAirplane();
OrderCalculator orderCalculator = new OrderCalculator(goodsWeightCalculator);
int totalWeight = orderCalculator.calculateTotalWeight(goodsList);
if (totalWeight > airplane.getMaxLoad()) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.\n", airplane.getFlightNumber());
return;
}
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:\n", orderInfo.getCustomer().getCustName(), orderInfo.getCustomer().getCustPhone());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.printf("航班号:%s\n", airplane.getFlightNumber());
System.out.printf("订单号:%s\n", orderInfo.getOrderId());
System.out.printf("订单日期:%s\n", orderInfo.getOrderDate());
System.out.printf("发件人姓名:%s\n", orderInfo.getPostName());
System.out.printf("发件人电话:%s\n", orderInfo.getPostPhone());
System.out.printf("发件人地址:%s\n", orderInfo.getPostAddress());
System.out.printf("收件人姓名:%s\n", orderInfo.getReceiveName());
System.out.printf("收件人电话:%s\n", orderInfo.getReceivePhone());
System.out.printf("收件人地址:%s\n", orderInfo.getReceiveAddress());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n", (double) totalWeight);
double originalFee = orderCalculator.calculateTotalFee(goodsList);
double finalFee = orderCalculator.calculateFinalFee(goodsList, orderInfo.getCustomer());
double discountRate = finalFee / originalFee;
System.out.printf("%s支付金额:%.1f\n", orderInfo.getPaymentMethod().getType(), finalFee);
System.out.println("\n货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int index = 1;
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
int chargeableWeight = goods.getChargeableWeight();
double fee = goods.calculateFee();
double feeRate = fee / chargeableWeight;
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n",
index++,
goods.getGoodName(),
(double) chargeableWeight,
feeRate,
fee
);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 输入客户信息
String custType = scanner.nextLine();
int custId = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗换行符
String custName = scanner.nextLine();
String custPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String custAddress = scanner.nextLine();
// 使用工厂创建客户对象
Customer customer = CustomerFactory.createCustomer(custType, custId, custName, custPhone, custAddress);
// 输入货物信息
String goodType = scanner.nextLine();
int goodsCount = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗换行符
List<Goods> goodsList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < goodsCount; i++) {
int goodId = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗换行符
String goodName = scanner.nextLine();
int goodWidth = scanner.nextInt();
int goodLength = scanner.nextInt();
int goodHeight = scanner.nextInt();
int goodWeight = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗换行符
// 使用工厂创建货物对象
Goods goods = GoodsFactory.createGoods(goodType, goodId, goodName,
goodWidth, goodLength, goodHeight, goodWeight);
goodsList.add(goods);
}
// 输入航班信息
String flightNumber = scanner.nextLine();
String departureAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String arrivalAirport = scanner.nextLine();
String flightDate = scanner.nextLine();
int maxLoad = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine(); // 消耗换行符
Airplane airplane = new Airplane(flightNumber, departureAirport, arrivalAirport, flightDate, maxLoad);
// 输入订单信息
String orderId = scanner.nextLine();
String orderDate = scanner.nextLine();
String postAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String postName = scanner.nextLine();
String postPhone = scanner.nextLine();
String receiveAddress = scanner.nextLine();
String receiveName = scanner.nextLine();
String receivePhone = scanner.nextLine();
String paymentType = scanner.nextLine();
// 使用工厂创建支付方式
PaymentMethod paymentMethod = PaymentMethodFactory.createPaymentMethod(paymentType);
// 创建订单信息
OrderInfo orderInfo = new OrderInfo(
orderId, orderDate, postAddress, postName, postPhone,
receiveAddress, receiveName, receivePhone, goodsList,
customer, airplane, paymentMethod
);
// 生成订单报告
GoodsWeightCalculator goodsWeightCalculator = new GoodsWeightCalculator();
OrderReportGenerator orderReportGenerator = new OrderReportGenerator(goodsWeightCalculator);
orderReportGenerator.generateOrderReport(orderInfo);
scanner.close();
}
}
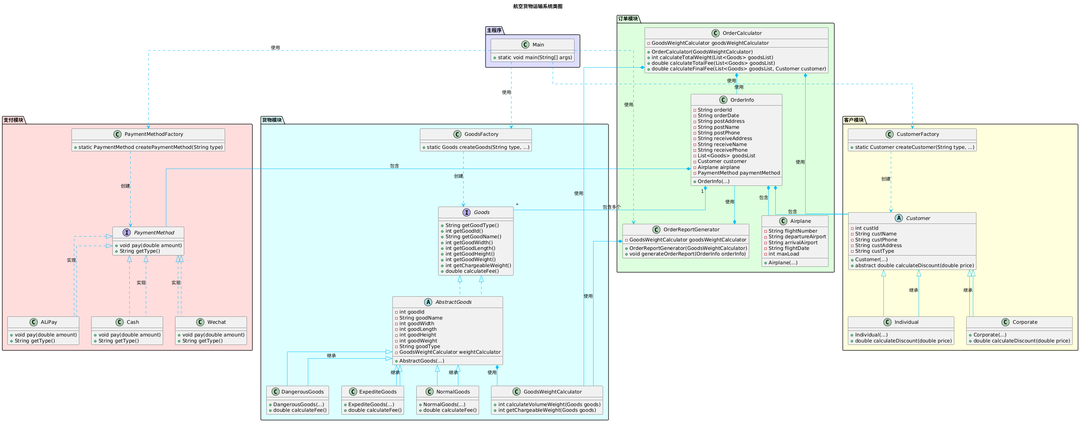
- 题目分析
题目集09在题目集08的基础上进行了扩展,增添了客户类型以及不同的客户类型对应不同的折扣方式,不同的货物类型以及不同的计费方式,需要对题目集中的类图进行改进。一些基本的航班类只存储航班信息,货物重量计算类负责计算货物的体积重量计费重量,订单信息类只负责存储订单信息不变。这里的客户类型有两种,个人客户和企业客户。所以,我把客户类抽象出来创建个人类和企业类继承客户类重写calculateDiscount方法。这里有三种支付方式微信支付,现金支付,支付宝支付。我创建一个支付方式接口,然后创建Wechat类和ALiPay类和Cash类来实现接口。这里需要一个支付方式工厂来根据支付类型创建相应的支付类型实例。这里还有一个货物接口,接口下面有一个抽象类,抽象类下面还有三个不同货物类继承这个抽象类,再加一个客户工厂创建相应的客户类实例

点击查看代码分析
> Metrics Details For File '09.txt'
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Value
========= =====
Project Directory \
Project Name
Checkpoint Name Baseline
File Name 09.txt
Lines 571
Statements 188
Percent Branch Statements 2.1
Method Call Statements 54
Percent Lines with Comments 4.2
Classes and Interfaces 8
Methods per Class 4.75
Average Statements per Method 4.63
Line Number of Most Complex Method 238
Name of Most Complex Method PaymentMethodFactory.createPaymentMethod()
Maximum Complexity 3
Line Number of Deepest Block 469
Maximum Block Depth 6
Average Block Depth 2.00
Average Complexity 1.27
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Most Complex Methods in 7 Class(es): Complexity, Statements, Max Depth, Calls
Cash.getType() 1, 1, 4, 0
Cash.pay() 1, 1, 4, 1
Corporate.calculateDiscount() 1, 1, 3, 0
Corporate.Corporate() 1, 1, 3, 1
GoodsWeightCalculator.calculateVolumeWeight() 1, 1, 2, 2
GoodsWeightCalculator.getChargeableWeight() 1, 2, 2, 2
Individual.calculateDiscount() 1, 1, 2, 0
Individual.Individual() 1, 1, 2, 1
Main.main() 2, 45, 5, 39
PaymentMethodFactory.createPaymentMethod() 3, 12, 6, 6
Wechat.pay() 1, 1, 4, 1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Block Depth Statements
0 53
1 50
2 13
3 12
4 40
5 16
6 4
7 0
8 0
9+ 0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
基于度量数据的代码分析
代码规模与结构
- 总行数(571)与语句数(188):
代码规模中等,包含较多的类和接口(8 个),实体类、接口、工厂类和工具类分工明确。 - 类和接口数量(8 个):
抽象类与接口:定义了Customer(客户)、PaymentMethod(支付方式)、Goods(货物)等抽象类 / 接口,通过多态实现不同类型的业务逻辑(如个人客户与企业客户的折扣差异)。
工厂类:CustomerFactory、GoodsFactory、PaymentMethodFactory负责对象创建,符合工厂模式,解耦对象创建逻辑。 - 方法数量(Methods per Class: 4.75):
平均每个类约 4-5 个方法,方法数量适中。实体类(如Airplane)以 getter 为主,业务类(如OrderCalculator)包含核心计算逻辑,符合单一职责原则。
复杂度分析
- 分支语句比例(2.1%):
代码中条件判断较少,主要集中在工厂类的switch语句(如PaymentMethodFactory.createPaymentMethod)和货物计费逻辑(如NormalGoods.calculateFee)。switch语句替代了多层if-else,提升了代码简洁性。 - 最大复杂度(3)与平均复杂度(1.27):
PaymentMethodFactory.createPaymentMethod复杂度 3:来自switch的多个分支,但逻辑集中在类型判断,符合工厂类的单一职责,复杂度可控。 - 其他方法复杂度≤2:业务逻辑(如计费、折扣计算)通过多态实现,避免了复杂条件嵌套,保持低复杂度。
- 块深度(Max=6,Avg=2.00):
Main.main块深度 5:输入处理存在多层嵌套(如循环和条件判断),但未超过合理范围。 - 其他方法块深度≤4:代码结构扁平,易于理解。
设计原则遵循情况
- 单一职责原则(SRP):
优点:
GoodsWeightCalculator专注重量计算,OrderCalculator专注费用计算,OrderReportGenerator仅生成报告。
工厂类仅负责对象创建,实体类仅存储数据,接口定义行为,职责划分清晰。
待改进:
Main.main方法同时处理输入、对象创建和流程控制,可拆分为独立的输入处理类。 - 开闭原则(OCP):
优点:
新增客户类型(如VIPCustomer)、货物类型(如FragileGoods)或支付方式(如UnionPay)时,只需新增子类并实现接口,无需修改现有代码。
潜在问题:
货物计费规则(如NormalGoods.calculateFee中的费率)仍硬编码在子类中,可进一步抽象为策略接口(如FeeStrategy),提升扩展性。 - 里氏代换原则(LSP):
实现良好:
Individual/Corporate可无缝替换Customer,Wechat/ALiPay可替换PaymentMethod,子类完全遵循父类接口契约。 - 合成复用原则(CRP):
优点:
OrderInfo通过组合Customer、Goods、PaymentMethod等对象实现功能,而非继承,降低类间耦合。
AbstractGoods通过组合GoodsWeightCalculator计算重量,符合合成复用原则。
可维护性与可读性
- 注释比例(4.2%):
注释仍然不足,关键逻辑(如工厂支持的类型、折扣比例、费率规则)缺乏说明。例如:
PaymentMethodFactory未注释支持的支付类型。
Individual.calculateDiscount未说明 “9 折” 的业务规则。
代码重复:
货物计费逻辑在NormalGoods、DangerousGoods、ExpediteGoods中重复实现,可通过策略模式统一抽象,避免冗余。
输入处理:
Main.main中输入顺序固定,未对非法输入(如无效的客户类型、负数重量)进行校验,可能导致程序异常终止。需添加输入校验逻辑(如使用正则表达式或条件判断)。
性能与效率
- 方法调用语句(54 条):
方法间调用频繁,但多为对象创建(工厂类)和业务计算(如orderCalculator.calculateTotalWeight),逻辑合理。工厂模式的switch语句效率较高,无需担心性能瓶颈。
循环与集合:
使用ArrayList存储货物列表,遍历效率高。
双重循环仅出现在报告生成的明细输出中,数据规模较小时无性能问题。
三.踩坑心得
在这两次的题目集里,计算总重量然后根据这个重量来判断是否超重,这里的总重量是用的计费重量相加并不是用实际重量或者体积重量,这里的getGoodWeight是货物的实际重量要改成getChargeableWeight取计费重量
心得就是最好一开始就把类设计好这样对于后面的扩展和复用会方便很多,如果在题目集08的时候就把类设计好具有很强的扩展性那题目集09就会方便很多,从题目集08到题目集09也就类的设计优化的过程。菜就多做多练吧,只有不断的运用才会越来越熟练。理论永远停留在表层,只有在不断的运用实践过程中才算的上掌握。
四.改进建议
题目集09的改进建议:
- 优化工厂模式与策略模式
问题:货物计费规则重复,工厂类缺乏参数化配置。
改进:
抽象计费策略,消除代码重复。
工厂类支持参数化配置,避免硬编码。
// 定义计费策略接口
interface FeeStrategy {
double calculateFee(int weight);
}
// 实现不同货物的计费策略
class NormalFeeStrategy implements FeeStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateFee(int weight) {
if (weight < 20) return weight * 35;
else if (weight < 50) return weight * 30;
else return weight * 25;
}
}
// 工厂类支持策略配置
class GoodsFactory {
private static final Map<String, FeeStrategy> STRATEGY_MAP = Map.of(
"Normal", new NormalFeeStrategy(),
"Dangerous", new DangerousFeeStrategy(),
"Expedite", new ExpediteFeeStrategy()
);
public static Goods createGoods(String type, int id, String name, int width, int length, int height, int weight) {
FeeStrategy strategy = STRATEGY_MAP.get(type);
if (strategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的货物类型: " + type);
}
return new StandardGoods(id, name, width, length, height, weight, type, strategy);
}
}
- 增强可维护性与注释
问题:业务规则和类职责缺乏明确注释。
改进:
添加类级注释说明设计意图。
为关键业务规则添加注释(如折扣策略、计费规则)。
3.优化数据结构与配置
问题:费率和折扣比例硬编码在类中,不利于配置修改。
改进:
使用配置文件或枚举存储费率和折扣。
通过依赖注入配置参数。
// 配置枚举
enum FeeConfig {
NORMAL_GOODS(20, 35, 50, 30, 100, 25, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 15),
DANGEROUS_GOODS(20, 80, 50, 50, 100, 30, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 20);
private final Map<Integer, Double> tierRates;
FeeConfig(int tier1Max, double tier1Rate, int tier2Max, double tier2Rate,
int tier3Max, double tier3Rate, int tier4Max, double tier4Rate) {
this.tierRates = Map.of(
tier1Max, tier1Rate,
tier2Max, tier2Rate,
tier3Max, tier3Rate,
tier4Max, tier4Rate
);
}
public double getRate(int weight) {
return tierRates.entrySet().stream()
.filter(e -> weight < e.getKey())
.findFirst()
.map(Map.Entry::getValue)
.orElse(0.0);
}
}
// 使用配置的计费策略
class ConfigurableFeeStrategy implements FeeStrategy {
private final FeeConfig config;
public ConfigurableFeeStrategy(FeeConfig config) {
this.config = config;
}
@Override
public double calculateFee(int weight) {
return weight * config.getRate(weight);
}
}
题目集08的改进建议:
类设计优化
1.单一职责原则
问题:OrderReportGenerator 同时处理计算和报告生成。
改进:分离计算和报告职责。
// 仅负责生成报告
class OrderReportGenerator {
public void generateOrderReport(OrderInfo orderInfo, OrderCalculator calculator) {
// 生成报告逻辑
}
}
// 仅负责计算
class OrderCalculator {
public double calculateTotalWeight(ListgoodsList) {
// 计算总重量
}
public double calculateTotalFee(ListgoodsList) {
// 计算总费用
}
}
2.改进计费策略(基于枚举法)
interface FeeStrategy {
double calculateFee(int weight);
double getRate(int weight); // 新增获取费率方法
}
class CorrectFeeStrategy implements FeeStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateFee(int weight) {
for (FeeTier tier : FeeTier.values()) {
if (tier.appliesTo(weight)) {
return weight * tier.getRate();
}
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public double getRate(int weight) {
for (FeeTier tier : FeeTier.values()) {
if (tier.appliesTo(weight)) {
return tier.getRate();
}
}
return 0;
}
}
3.简化订单报告生成
public void generateOrderReport(OrderInfo orderInfo) {
// ...(原有逻辑)
for (Goods goods : goodsList) {
int chargeableWeight = goodsWeightCalculator.getChargeableWeight(goods);
double fee = feeStrategy.calculateFee(chargeableWeight);
double feeRate = feeStrategy.getRate(chargeableWeight); // 直接获取费率
System.out.printf(... , feeRate, fee);
}
}
| 类名 | 职责 | 设计原则遵循 |
|---|---|---|
| Customer | 存储客户信息 | 单一职责 |
| Goods | 存储货物信息 | 单一职责 |
| Airplane | 存储航班信息 | 单一职责 |
| OrderInfo | 存储订单信息 | 单一职责,通过组合复用其他类 |
| GoodsWeightCalculator | 计算货物重量(体积重量、计费重量) | 单一职责 |
| FeeStrategy | 计费策略接口 | 里氏代换(可扩展不同策略实现) |
| CorrectFeeStrategy | 具体计费策略实现(基于枚举配置) | 开闭原则(通过枚举扩展配置) |
| OrderCalculator | 计算订单总重量和总费用 | 单一职责,依赖注入重量和费用计算类 |
| OrderReportGenerator | 生成订单报告 | 单一职责,依赖注入计算类和策略类 |
五.总结
经过这两次题目集的练习,我学会了接口与抽象类和子类这三者一层一层的关系,抽象类实现接口,子类继承抽象类重写抽象类里面的方法同时子类也可以实现接口,这三者的复合运用。题目集09主要是在题目集08上进行扩展,通过这次作业的迭代让我对抽象类和接口以及类的设计的使用更加熟练。对工厂的使用,我觉得我需要进一步的学习和研究,例如这次作业里的货物工厂和客户工厂和支付方式工厂。还有就是类的设计吧,对于这次类的数量有点多又要满足设计原则单一职责所以觉得自己对类的设计这一方面还是不够熟练。还有一点就是对于什么时候用接口什么时候用抽象类什么时候用抽象类和接口这一点有点模糊不清,这还需要我进一步的去学习。对课程以及老师的建议是上课的时候多进行代码演示吧多把理论运用起来用代码来演示,一些理论我觉得操作展示比理论讲解更加容易理解。对作业的建议就说少出现上次电梯梯度的题目吧,这次的作业难度以及各个方面都很不错。感谢老师们的辛勤努力




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号