oracle使用(1)
纯粹是记录工作中使用的分析函数或是语法点,不做其他用处。
(1) with as
先举个例子吧:
有两张表,分别为A、B,求得一个字段的值先在表A中寻找,如果A表中存在数据,则输出A表的值;如果A表中不存在,则在B表中寻找,若B表中有相应记录,则输出B表的值;如果B表中也不存在,则输出"no records”字符串。
with
sql1 as (select to_char(a) s_name from test_tempa),
sql2 as (select to_char(b) s_name from test_tempb where not exists (select s_name from sql1 where rownum=1))
select * from sql1
union all
select * from sql2
union all
select 'no records' from dual
where not exists (select s_name from sql1 where rownum=1)
and not exists (select s_name from sql2 where rownum=1);
语法:
select ...
例:现在要从1-19中得到11-14。一般的sql如下:
(
--模拟生一个20行的数据
SELECT LEVEL AS lv
FROM DUAL
CONNECT BY LEVEL < 20
) tt
WHERE tt.lv > 10 AND tt.lv < 15
使用With as 的SQL为:
with TT as(
--模拟生一个20行的数据
SELECT LEVEL AS lv
FROM DUAL
CONNECT BY LEVEL < 20
)
select lv from TT
WHERE lv > 10 AND lv < 15
With查询语句不是以select开始的,而是以“WITH”关键字开头
可认为在真正进行查询之前预先构造了一个临时表TT,之后便可多次使用它做进一步的分析和处理
WITH Clause方法的优点
增加了SQL的易读性,如果构造了多个子查询,结构会更清晰;更重要的是:“一次分析,多次使用”,这也是为什么会提供性能的地方,达到了“少读”的目标。
第一种使用子查询的方法表被扫描了两次,而使用WITH Clause方法,表仅被扫描一次。这样可以大大的提高数据分析和查询的效率。
另外,观察WITH Clause方法执行计划,其中“SYS_TEMP_XXXX”便是在运行过程中构造的中间统计结果临时表。
(2) lead over 与lag over
一、简介
lag与lead函数是跟偏移量相关的两个分析函数,通过这两个函数可以在一次查询中取出同一字段的前N行的数据(lag)和后N行的数据(lead)作为独立的列,从而更方便地进行进行数据过滤。这种操作可以代替表的自联接,并且LAG和LEAD有更高的效率。
over()表示 lag()与lead()操作的数据都在over()的范围内,他里面可以使用partition by 语句(用于分组) order by 语句(用于排序)。partition by a order by b表示以a字段进行分组,再 以b字段进行排序,对数据进行查询。
例如:lead(field, num, defaultvalue) field需要查找的字段,num往后查找的num行的数据,defaultvalue没有符合条件的默认值。
二、示例
1、表机构与初始化数据如下
1 -- 表结构
2 create table tb_test(
3 id varchar2(64) not null,
4 cphm varchar2(10) not null,
5 create_date date not null,
6 primary key (id)
7 )
8 -- 初始化数据
9 insert into tb_test values ('1000001', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:18:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
10 insert into tb_test values ('1000002', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:22:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
11 insert into tb_test values ('1000003', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:28:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
12 insert into tb_test values ('1000004', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:29:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
13 insert into tb_test values ('1000005', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:39:13','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
14 insert into tb_test values ('1000006', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:45:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
15 insert into tb_test values ('1000007', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:56:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
16 insert into tb_test values ('1000008', 'AB7477', to_date('2015-11-30 10:57:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
17 -- ---------------------
18 insert into tb_test values ('1000009', 'AB3808', to_date('2015-11-30 11:00:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
19 insert into tb_test values ('1000010', 'AB3808', to_date('2015-11-30 11:10:13','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
20 insert into tb_test values ('1000011', 'AB3808', to_date('2015-11-30 11:15:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
21 insert into tb_test values ('1000012', 'AB3808', to_date('2015-11-30 11:26:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
22 insert into tb_test values ('1000013', 'AB3808', to_date('2015-11-30 11:30:12','YYYY-MM-DD HH24:mi:ss'));
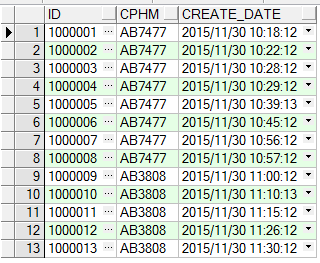
表初始化数据为:
2、示例
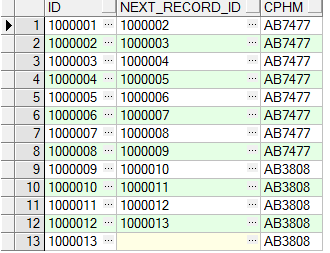
a、获取当前记录的id,以及下一条记录的id
select t.id id ,
lead(t.id, 1, null) over (order by t.id) next_record_id, t.cphm
from tb_test t
order by t.id asc
运行结果如下:
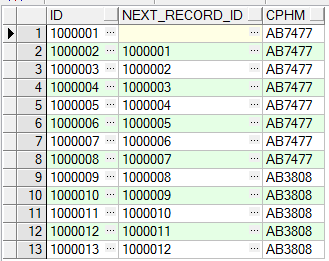
b、获取当前记录的id,以及上一条记录的id
select t.id id ,
lag(t.id, 1, null) over (order by t.id) next_record_id, t.cphm
from tb_test t
order by t.id asc
运行结果如下:
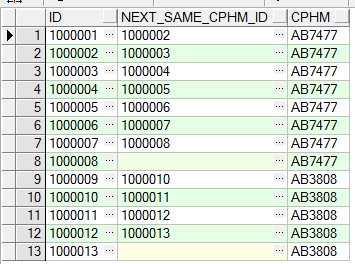
c、获取号牌号码相同的,当前记录的id与,下一条记录的id(使用partition by)
select t.id id,
lead(t.id, 1, null) over(partition by cphm order by t.id) next_same_cphm_id, t.cphm
from tb_test t
order by t.id asc
运行结果如下:
d、查询 cphm的总数,当create_date与下一条记录的create_date时间间隔不超过10分钟则忽略。
1 select cphm, count(1) total from 2 ( 3 select t.id, 4 t.create_date t1, 5 lead(t.create_date,1, null) over( partition by cphm order by create_date asc ) t2, 6 ( lead(t.create_date,1, null) over( partition by cphm order by create_date asc ) - t.create_date ) * 86400 as itvtime, 7 t.cphm 8 from tb_test t 9 order by t.cphm, t.create_date asc 10 ) tt 11 where tt.itvtime >= 600 or tt.itvtime is null 12 group by tt.cphm
结果如下:

(3) sum over(order by *****rows between ... preceding and ... following) 上下范围内求和
Oracle为这种情况提供了一个子句:rows between ... preceding and ... following。从字面上猜测它的意思是:在XXX之前和XXX之后的所有记录,实际情况如何让我们通过示例来验证:
SQL> select month,
2 sum(tot_sales) month_sales,
3 sum(sum(tot_sales)) over (order by month
4 rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) total_sales
5 from orders
6 group by month;
MONTH MONTH_SALES TOTAL_SALES
---------- ----------- -----------
1 610697 6307766
2 428676 6307766
3 637031 6307766
4 541146 6307766
5 592935 6307766
6 501485 6307766
7 606914 6307766
8 460520 6307766
9 392898 6307766
10 510117 6307766
11 532889 6307766
12 492458 6307766
已选择12行。
绿色高亮处的代码在这里发挥了关键作用,它告诉oracle统计从第一条记录开始至最后一条记录的每月销售额。这个统计在记录集形成的过程中执行了12次,这时相当费时的!但至少我们解决了问题。
unbounded preceding and unbouned following的意思针对当前所有记录的前一条、后一条记录,也就是表中的所有记录。那么假如我们直接指定从第一条记录开始直至末尾呢?看看下面的结果:
SQL> select month,
2 sum(tot_sales) month_sales,
3 sum(sum(tot_sales)) over (order by month
4 rows between 1 preceding and unbounded following) all_sales
5 from orders
6 group by month;
MONTH MONTH_SALES ALL_SALES
---------- ----------- ----------
1 610697 6307766
2 428676 6307766
3 637031 5697069
4 541146 5268393
5 592935 4631362
6 501485 4090216
7 606914 3497281
8 460520 2995796
9 392898 2388882
10 510117 1928362
11 532889 1535464
12 492458 1025347
已选择12行。
很明显这个语句错了。实际1在这里不是从第1条记录开始的意思,而是指当前记录的前一条记录。preceding前面的修饰符是告诉窗口函数执行时参考的记录数,如同unbounded就是告诉oracle不管当前记录是第几条,只要前面有多少条记录,都列入统计的范围。
窗口函数进阶-滚动统计(累积/均值):
考虑前面提到的第2个需求:列出每月的订单总额以及截至到当前月的订单总额。也就是说2月份的记录要显示当月的订单总额和1,2月份订单总额的和。3月份要显示当月的订单总额和1,2,3月份订单总额的和,依此类推。
很明显这个需求需要在统计第N月的订单总额时,还要再统计这N个月来的订单总额之和。想想上面的语句,假如我们能够把and unbounded following换成代表当前月份的逻辑多好啊!很幸运的是Oracle考虑到了我们这个需求,为此我们只需要将语句稍微改成: curreent row就可以了。
SQL> select month,
2 sum(tot_sales) month_sales,
3 sum(sum(tot_sales)) over(order by month
4 rows between unbounded preceding and current row) current_total_sales
5 from orders
6 group by month;
MONTH MONTH_SALES CURRENT_TOTAL_SALES
---------- ----------- -------------------
1 610697 610697
2 428676 1039373
3 637031 1676404
4 541146 2217550
5 592935 2810485
6 501485 3311970
7 606914 3918884
8 460520 4379404
9 392898 4772302
10 510117 5282419
11 532889 5815308
12 492458 6307766
已选择12行。
在一些销售报表中我们会时常看到求平均值的需求,有时可能是针对全年的数据求平均值,有时会是针对截至到当前的所有数据求平均值。很简单,只需要将:
sum(sum(tot_sales))换成avg(sum(tot_sales))即可。
窗口函数进阶-根据时间范围统计:
前面我们说过,窗口函数不单适用于指定记录集进行统计,而且也能适用于指定范围进行统计的情况,例如下面这个SQL语句就统计了当天销售额和五天内的评价销售额:
select trunc(order_dt) day,
sum(sale_price) daily_sales,
avg(sum(sale_price)) over (order by trunc(order_dt)
range between interval '2' day preceding
and interval '2' day following) five_day_avg
from cust_order
where sale_price is not null
and order_dt between to_date('01-jul-2001','dd-mon-yyyy')
and to_date('31-jul-2001','dd-mon-yyyy')
为了对指定范围进行统计,Oracle使用关键字range、interval来指定一个范围。上面的例子告诉Oracle查找当前日期的前2天,后2天范围内的记录,并统计其销售平均值。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号