【SpringBoot1.x】SpringBoot1.x 缓存
SpringBoot1.x 缓存
JSR107
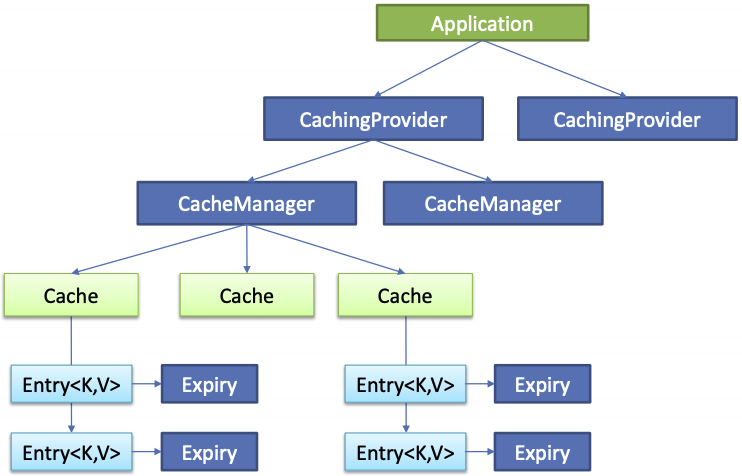
Java Caching 定义了 5 个核心接口,分别为:
- CachingProvider 定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个 CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个 CachingProvider。
- CacheManager 定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的 Cache,这些 Cache 存在于 CacheManager 的上下文中。一个 CacheManager 仅被一个 CachingProvider 拥有。
- Cache 是一个类似 Map 的数据结构并临时存储以 Key 为索引的值。一个 Chache 仅被一个 CacheManager 拥有。
- Entry 是一个存储在 Cache 中的 key-value 对。
- Expiry 指每一个存储在 Chche 中的条目有一个定义的有效期,一旦超过这个时间,条目就为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。有效期可以通过 ExpiryPolicy 设置。
Spring 缓存抽象
Spring3.1 后定义了 org.springframework.cache.Cache 和 org.springframework.cache.CacheManager 接口来统一不同的缓存技术,并支持使用 JCache(JSR107) 注解简化我们开发。
- Cache 接口 为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
- Cache 接口下 Spring 提供了各种 xxxCache 的实现,如 RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等;
- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring 会检查指定参数的指定目标方法是否被调用过。如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法就缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
- 使用 Spring 缓存抽象需注意:
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及它们的缓存策略;
- 从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据。
重要概念及缓存注解
- Chche 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有 RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等。
- ChacheManager 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存组件。
@EnableCaching开启基于注解的缓存,用在主配置类上。@Cacheable能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存@CachePut即调用方法,又更新缓存数据@CacheEvict清除缓存@Caching定义复杂的缓存规则
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@Caching 等注解主要的参数:
cacheNames/value缓存的名字,即将方法的返回结果放在那个缓存中,可以指定多个key缓存的数据,为空时默认是使用方法参数的值,可以为 SpEL 表达式,例如#idkeyGeneratorkey 的生成器,可以自己指定 key 的生成器的组件 id,它与 key 二选一cacheManager缓存管理器cacheResolver缓存解析器,它与 cacheManager 二选一condition执行符合条件才缓存unless执行不符合条件才缓存sync是否使用异步模式allEntries是否清空所有缓存,默认为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存beforeInvocation默认为 false,即缓存清除操作是在方法之后执行,出现异常不会清除缓存。如果指定为 true,即缓存清除操作是在方法之前执行。无论是否出现异常,缓存都会清除
SpEL 表达式
| 名字 | 位置 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| methodName | root object | 当前被调用的方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | root object | 当前被调用的方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象类 | #root.targetClass |
| args | root object | 当前被调用的方法的参数列表 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | root object | 当前方法调用使用的缓存列表,例如@Cacheable(value={"cache1", "cache2"}),则有两个 cache |
#root.caches[0].name |
| argument name | evaluation context | 方法参数的名字,可以直接 #参数名,也可以使用 #p0 或 #a0 的形式,0 代表参数的索引 |
#id、#a0、#p0 |
| result | evaluation context | 方法执行后的返回值,仅当方法执行之后的判断有效 | #result |
缓存使用
使用步骤:
- 第一步:建立相应表结构
- 第二步:编写相应的实体类
- 第三步:整合 MyBatis
- 配置数据源信息
- 使用注解版的 Mybatis,即在主配置类上加上
@MapperScan
- 第四步:使用缓存
- 在主配置类上加上
@EnableCaching - 在业务层方法加上
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict、@Caching等注解
- 在主配置类上加上
缓存配置原理:
- 使用
CacheAutoConfiguration自动配置类 - 扫描到各种缓存的配置类:
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration,这是默认生效的
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
- 给容器中注册了一个 CacheManager,默认是
ConcurrentMapCacheManager - 创建和获取 ConcurrentMapCache 类型的缓存组件,它的作用是将数据保存在 ConcurrentMap 中
EmployeeService:
/**
* @Author : parzulpan
* @Time : 2020-12
* @Desc : 员工业务层
*/
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
*
* 根据 Id 查询员工信息
*
* @Cacheable 运行流程:
* 1. 方法运行之前,先去查询 Cache 缓存组件,按照 cacheNames 指定的名字获取,第一次获取缓存时如果没有 Cache 组件会自动创建
* 2. 去 Cache 中查询缓存的内容,使用一个 key,默认是方法的参数。也可以按照某种策略生成,默认使用 SimpleKeyGenerator 生成 key
* SimpleKeyGenerator 生成 key 的默认策略为:
* 如果没有参数,key = new SimpleKey()
* 如果有一个参数,key = 参数的值
* 如果有多个参数,key = new SimpleKey(params)
* 3. 有查询到缓存,则直接使用缓存;没有查询到缓存,则调用目标方法并将目标方法返回的结果放进缓存中
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"})
public Employee getEmp(Integer id) {
return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
}
/**
*
* 更新员工信息
*
* @CachePut 运行流程
* 1. 先调用目标方法
* 2. 将目标方法的结果缓存起来
* 3. 比较适用与修改了数据库某个数据后,更新缓存
*/
@CachePut(value = {"emp"}, key = "#result.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
}
/**
*
* 删除员工信息
*
*/
@CacheEvict(value = {"emp"}, key = "#id")
public void deleteEmp(Integer id) {
employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);
}
/**
*
* 根据 lastName 查询员工信息
*
* @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
*/
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}, key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(value = {"emp"}, key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(value = {"emp"}, key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmp(String lastName) {
List<Employee> employees = employeeMapper.getEmpByName(lastName);
if (employees.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return employees.get(0);
}
}
EmployeeController:
/**
* @Author : parzulpan
* @Time : 2020-12
* @Desc : 员工控制器
*/
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeService employeeService;
// http://localhost:8080/emp/1
@GetMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee getEmp(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return employeeService.getEmp(id);
}
// http://localhost:8080/emp?id=1&lastName=ha&email=ha@gmail.com&gender=0&dId=1001
@GetMapping("/emp")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee) {
return employeeService.updateEmp(employee);
}
// http://localhost:8080/empDel?id=1
@GetMapping("/empDel")
public String deleteEmp(Integer id) {
employeeService.deleteEmp(id);
return "success";
}
// http://localhost:8080/emp/lastName/parzulpan
@GetMapping("/emp/lastName/{lastName}")
public Employee getEmp(@PathVariable("lastName") String lastName) {
return employeeService.getEmp(lastName);
}
}
开启 debug 配置后,可以观察缓存的作用:
logging:
level:
cn.parzulpan.mapper: debug
可以使用 @CacheConfig,它指定这个类的缓存配置,通常用于抽取公共配置。
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = {"emp"})
@Service
public class EmployeeService {}
整合 Redis
使用步骤:
-
引入 Redis 启动器依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> -
配置 Redis
spring: # 配置 Redis redis: host: localhost -
测试 Redis
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class IntegrationCacheApplicationTests { @Autowired RedisTemplate redisTemplate; // k-v 都是对象 @Autowired StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; // k-v 都是字符串 @Test public void testRedisString() { // 字符串操作 // String 类型 是 Redis 中最基本的数据类型,一个 key 对应一个 value 。 stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stringMsg", "hello"); stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().append("stringMsg", "world"); String msg = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stringMsg"); System.out.println(msg); } @Test public void testRedisList() { // 列表操作 // List 类型 是简单的字符串列表,按照插入顺序排序。可以添加一个元素到列表的头部(左边)或者尾部(右边)。 ListOperations<String, String> ops = redisTemplate.opsForList(); ops.leftPush("listMsg", "hello"); ops.leftPushAll("listMsg", "world", "parzulpan"); List<String> listMsg = ops.range("listMsg", 0, 2);// 索引 0 到2的 listMsg System.out.println(listMsg.toString()); } @Test public void testRedisSet() { // 集合操作 // Set 类型 是 String 类型 的无序集合。它的特点是无序且唯一,它是通过哈希表实现的,所以添加、删除、查找的复杂度都是 O(1)。 SetOperations<String, String> ops = redisTemplate.opsForSet(); ops.add("setMsg", "hello"); ops.add("setMsg", "world", "parzulpan"); Set<String> setMsg = ops.members("setMsg"); // 取 set System.out.println(setMsg.toString()); } @Test public void testRedisZSet() { // 有序集合操作 // ZSet 类型 和 Set 类型 一样,也是 String 类型元素的集合,且不允许有重复的成员。 // 不同的是每个元素都会关联一个 double 类型 的分数,它正是通过分数来为集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。 // ZSet 类型的成员是唯一的,但分数(score) 却可以重复。 ZSetOperations<String, String> ops = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); ops.add("zsetMsg", "hello", 1); ops.add("zsetMsg", "parzulpan", 3); ops.add("zsetMsg", "world", 2); Set<String> zsetMsg = ops.range("zsetMsg", 0, 2); System.out.println(zsetMsg.toString()); } @Test public void testRedisHash() { // 哈希操作 // Hash 类型 是一个键值对的集合。它是一个 String 类型 的 field 和 value 组合的映射表,它特别适合用于存储对象。 HashOperations<String, String, String> ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash(); ops.put("hashMsg", "key1", "hello"); ops.put("hashMsg", "key2", "world"); ops.put("hashMsg", "key3", "parzulpan"); String key2 = ops.get("hashMsg", "key2"); System.out.println(key2); } } -
对于上面的测试,Redis 默认保存对象,使用 JDK 序列化机制,序列化后的数据保存到 redis 中。可以使用自定义的序列化器。值得注意的是,无论是 json 序列化还是 jdk 序列化,redis 接受的都是字符串的文本,而 jdk 的序列化方式字符串会把 json 序列化方式字符串大几倍,性能较差,所以一般都使用自定义的序列化器。
/** * @Author : parzulpan * @Time : 2021-01 * @Desc : 自定义 Redis 配置类 */ @Configuration public class CustomRedisConfig { // 使用 Jackson 序列化器,不使用默认的 JDK 的 @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> employeeRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory rcf){ RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setConnectionFactory(rcf); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> jrs = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Employee.class); template.setDefaultSerializer(jrs); return template; } }@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class IntegrationCacheApplicationTests { @Autowired RedisTemplate employeeRedisTemplate; // 使用自定义的 RedisTemplate @Test public void testEmployeeRedisTemplate() { ValueOperations ops = employeeRedisTemplate.opsForValue(); Employee employee = employeeMapper.getEmpById(1); ops.set("emp-01", employee); } } -
使用 Redis 缓存,它的原理是:
-
CacheManager,生成一个 Cache 缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
-
引入 redis 的 starter,容器中保存的是 RedisCacheManager;
-
RedisCacheManager 帮我们创建 RedisCache 来作为缓存组件,RedisCache 通过操作 redis 缓存数据
-
默认保存数据 k-v 都是 Object。利用序列化保存,所以实体类需要继承 Serializable。它默认使用的是
RedisTemplate<Object, Object>,它是 jdk 默认的序列化机制 -
可以通过自定义
CacheManager,更改序列化机制:/** * @Author : parzulpan * @Time : 2021-01 * @Desc : 自定义 Redis 配置类 */ @Configuration public class CustomRedisConfig { // 使用 Jackson 序列化器,不使用默认的 JDK 的 @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> employeeRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory rcf){ RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setConnectionFactory(rcf); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> jrs = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Employee.class); template.setDefaultSerializer(jrs); return template; } // 自定义缓存管理器 @Bean public RedisCacheManager employeeCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> employeeRedisTemplate) { RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(employeeRedisTemplate); // 使用前缀,默认将 CacheName 作为 key 的前缀 redisCacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return redisCacheManager; } }
-
-
使用示例:
/** * @Author : parzulpan * @Time : 2021-01 * @Desc : 部门业务层 */ @Service public class DepartmentService { @Autowired DepartmentMapper departmentMapper; @Autowired RedisCacheManager departmentCacheManager; // 注解的方式 @Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept", cacheManager = "departmentCacheManager") public Department getDeptById(Integer id) { return departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); } // api 调用的方式 public Department getDeptById2(Integer id) { Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); // 获取某个缓存 Cache dept = departmentCacheManager.getCache("dept"); dept.put("dept2:" + id, department); return department; } }
总之,相对于默认的 Cache,使用 Redis,需要多写如下的一个 Redis 配置类:
/**
* @Author : parzulpan
* @Time : 2021-01
* @Desc : 自定义 Redis 配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class CustomRedisConfig {
// 使用 Jackson 序列化器,不使用默认的 JDK 的
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> employeeRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory rcf){
RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(rcf);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> jrs = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Employee.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(jrs);
return template;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Department> departmentRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory rcf){
RedisTemplate<Object, Department> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(rcf);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department> jrs = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Department.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(jrs);
return template;
}
// 自定义缓存管理器
@Primary // 将其作为默认的
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager employeeCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> employeeRedisTemplate) {
RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(employeeRedisTemplate);
// 使用前缀,默认将 CacheName 作为 key 的前缀
redisCacheManager.setUsePrefix(true);
return redisCacheManager;
}
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager departmentCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Department> departmentRedisTemplate) {
RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(departmentRedisTemplate);
// 使用前缀,默认将 CacheName 作为 key 的前缀
redisCacheManager.setUsePrefix(true);
return redisCacheManager;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号