软件工程第三次作业
作业信息:
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 首页 - 计科23级34班 - 广东工业大学 - 班级博客 - 博客园 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 结对项目 - 作业 - 计科23级34班 - 班级博客 - 博客园 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 与他人合作完成一个结对项目, 在过程中学习结对合作精神 |
3123004540--区泽明
3123004525--程思远
作业GitHub链接: https://github.com/Gerdiber/Calculator
PSP表格:
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 10 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | 240 | 225 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 20 | 15 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 10 | 7 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 10 | 5 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 20 | 15 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 120 | 135 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 20 | 16 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 22 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 110 | 81 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 60 | 48 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 13 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 20 |
| · 合计 | 360 | 316 |
效能改进:
改进耗时:
改进生成表达式生成树的内存占用: 10 min
改进表达式合法性检查的细节以及性能: 25 min
改进使用正则表达式将表达式改为计算算法可识别形式: 10 min
改进思路;
- 在验证表达式合法后生成表达式字符串并随之删除树, 及时回收空间
- 表达式检查中考虑细节, 提高程序可靠性
- 使用正则表达式匹配带分数并向算法可识别形式转换, 提高效率
性能分析图:
在生成模式中:
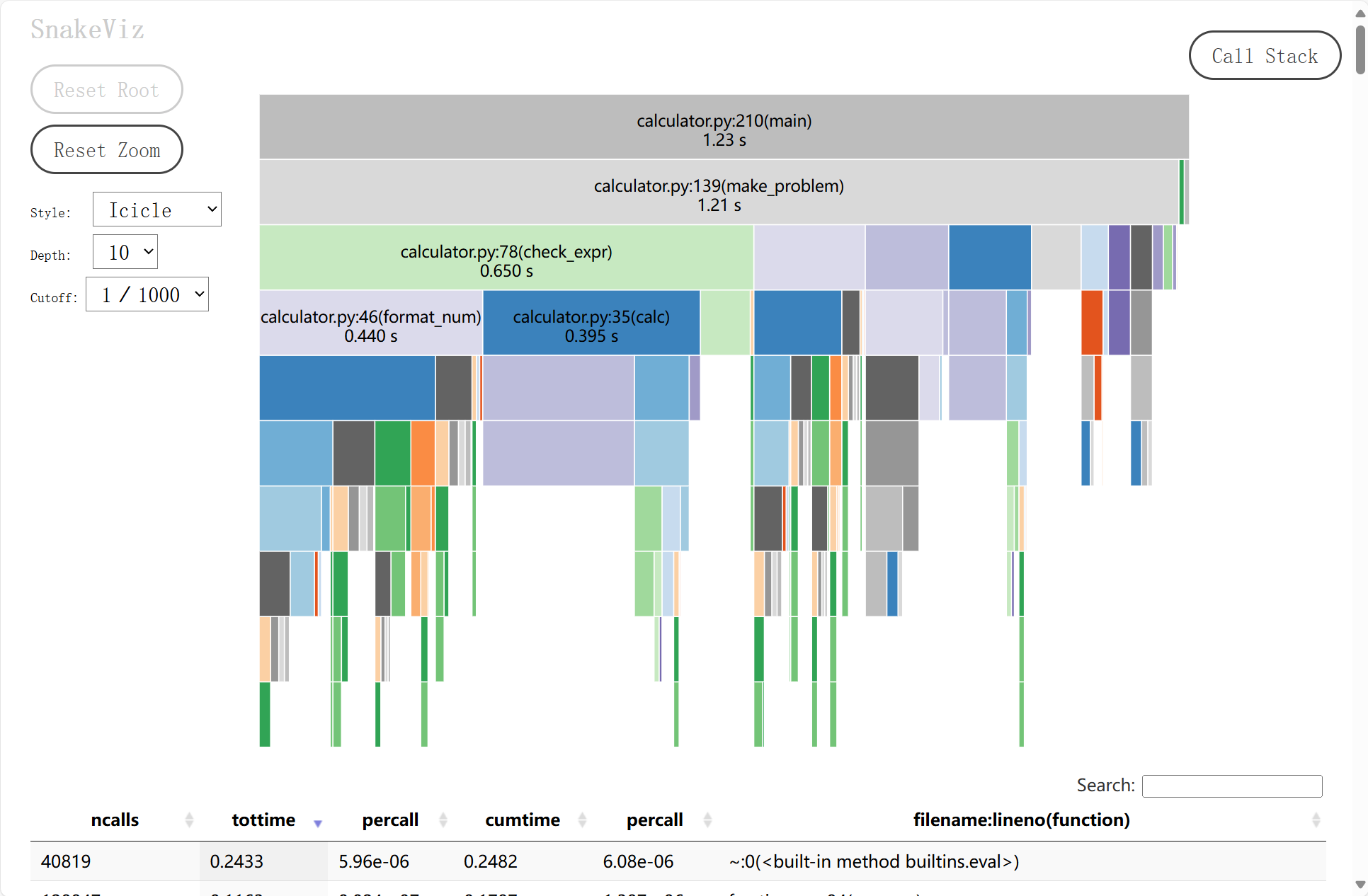
图中可见, 在10000次题目生成中, 消耗最大的函数为: make_problem 函数
而在批改模式中:
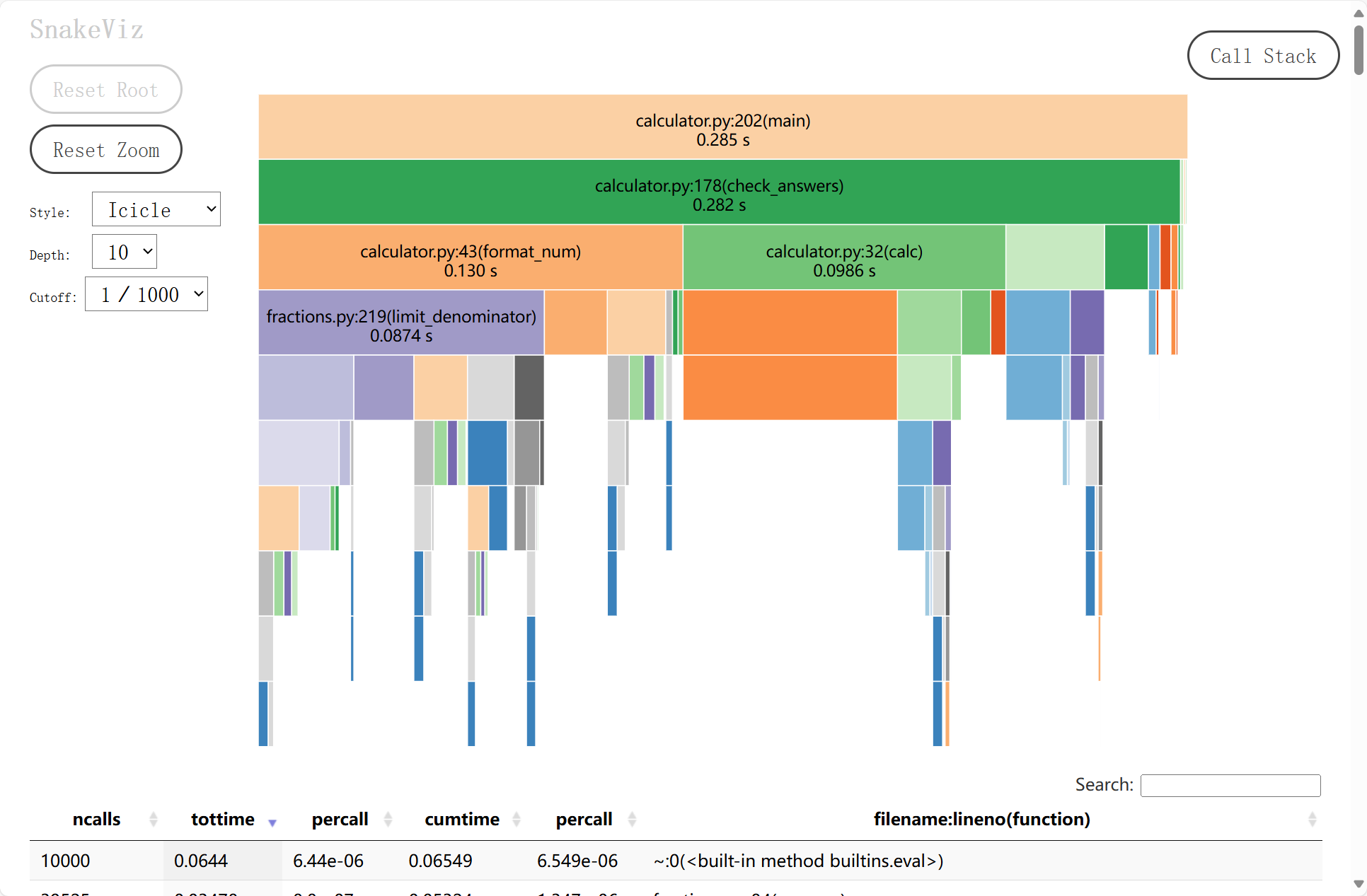
图中可见, 在10000个题目答案批改中, 消耗最大的函数为: check_answers 函数
设计实现:
程序整体根据输入参数分为两种模式: 生成模式 与 批改模式
程序有以下公有函数: 表达式计算函数
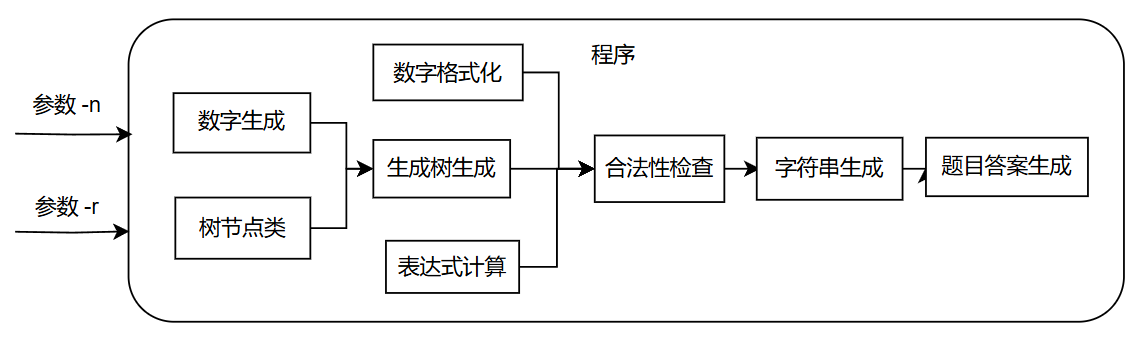
在生成模式中, 程序还有以下类和函数:
树节点类, 数字生成函数 , 数字生成格式化字符串函数 , 表达式生成树生成函数, 表达式合法性检查函数 , 表达式字符串生成函数 , 题目答案生成函数
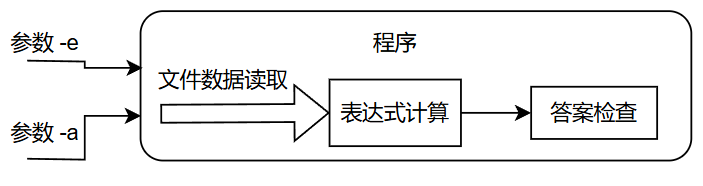
而在批改模式中, 程序有函数: 答案检查函数
两种模式流程图如下:
生成模式:
批改模式:
代码说明:
项目关键代码:
1. 表达式生成树合法性检查函数
def check_expr(root):
"""检查表达式合法性"""
if root == None: # 空树/空节点 则直接返回true
return True
LC = check_expr(root.left) # 左子树检查结果
RC = check_expr(root.right) # 右子树检查结果
if root.value in ops: # 节点为运算符
temp_str = f"{root.left.result}{root.value}{root.right.result}"
temp_result = calc(temp_str) #计算当前子表达式
if temp_result == None: # 有错误则重新生成
return False
if root.value == '−': # 减法情况
if temp_result < 0: # 结果小于0
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left # 左右子树互换
temp_result = temp_result * -1 # 结果取相反数
elif root.value == '÷': # 除法情况
if calc(root.right.result) == 0: # 除数为0
return False
if isinstance(temp_result, int) or (isinstance(temp_result, fractions.Fraction)
and temp_result.denominator == 1): # 结果为整数
return False
root.result = format_num(temp_result)
else: # 节点为数字
root.result = root.value # 运算结果即为节点值
return True and LC and RC # 左右子树与当前树均合法
思路: 先检验左右子树再检验当前树的根节点 . 检验节点时 , 若节点是运算符节点 , 则检查其减法和除法的合法性 : 减法结果不能小于 0 , 非法则交换该减法节点的左右子树 , 使结果为正 , 使表达式合法化 ; 除法则需要 除数不为 0 且 结果应为分数而非自然数 , 除法非法无法矫正 , 直接返回判为非法. 最后往上递归所有子树和节点的合法性 , 得出整个表达式生成树的合法性 .
2. 题目答案生成函数
def make_problem(max_num, count):
"""生成题目"""
problems = [] # 题目数组
answers = [] # 答案数组
seen = set() # 合法题目集合
while len(problems) < count:
# 决定运算符数量
op_count = random.randint(1, 3) # 运算符数量
nums = [make_num(max_num) for _ in range(op_count + 1)] # 运算数字生成
op_list = [random.choice(ops) for _ in range(op_count)] # 运算符生成
#生成树根节点
root = exprNode(op_list[0])
#根据运算符数量生成
if op_count == 1: # 单运算符
root.left = exprNode(nums[0])
root.right = exprNode(nums[1])
elif op_count == 2: # 2运算符
LR = random.randint(0, 1) # 决定运算符在左/右子树
if LR == 0:
root.left = exprNode(op_list[1], exprNode(nums[0]), exprNode(nums[1]))
root.right = exprNode(nums[2])
else:
root.right = exprNode(op_list[1], exprNode(nums[0]), exprNode(nums[1]))
root.left = exprNode(nums[2])
else: # 3运算符
root.left = exprNode(op_list[1], exprNode(nums[0]), exprNode(nums[1]))
root.right = exprNode(op_list[2], exprNode(nums[2]), exprNode(nums[3]))
# 检查表达式合法性
if check_expr(root) is False:
continue
# 生成字符串并比对是否有重复
expr = make_expr_str(root)
deleteTree(root)
simple_expr=expr.replace(' ','')
if simple_expr in seen:
continue
seen.add(simple_expr)
# 生成答案
answer = calc(expr)
problems.append(f"{expr} = ")
answers.append(format_num(answer))
return problems, answers
思路: 先通过随机数生成决定: 运算符数量 n (1~3) , 数字数量 n+1 , n 个随机生成的数 . 接下来对运算符数量进行分情况构建生成树:
1 个运算符: 生成树只有 1 个根节点与 2 个叶子节点 . 将运算符填入根节点 , 数字填入叶子节点即可.
2个运算符: 生成树有 1 个根节点 , 左右子树随机存在一个 , 另一侧则为叶子节点 , 子树侧也携带 2 个叶子节点 . 将 3 个数字填入叶子节点 , 2个运算符填入上层节点即可.
3个运算符: 1 个根节点左右有 2 个子树 , 2个子树也各自有 2 个叶子节点 , 将 4 个数字 与 2 个运算符填入即可.
生成树生成完毕后先检查合法性 , 非法则直接略过重新生成 . 合法则生成题目并检查是否已经生成过 , 是否重复 , 重复则重新生成 . 合法且不重复则通过 , 生成对应答案 , 将题目与答案加入数组中 , 直至数组元素数量达到参数要求.
3. 批改答案函数
def check_answers(ex_file, ans_file):
"""批改答案"""
pattern = r'^\d+\.\s*'
with open(ex_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
ex_list = [line.strip() for line in f] # 题目列表
with open(ans_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
ans_list = [line.strip() for line in f] # 答案列表
right = [] # 正确数组
wrong = [] # 错误数组
for i, (ex, ans) in enumerate(zip(ex_list, ans_list), 1):
expr = re.sub(pattern,'', ex.replace('=', ''))
ans = re.sub(pattern,'', ans)
correct_ans = format_num(calc(expr)) # 计算正确答案
if ans == correct_ans: # 正确
right.append(i) # 将题目编号加入正确数组中
else: # 错误
wrong.append(i) # 将题目编号加入错误数组中
return right, wrong
思路: 通过传入的路径参数读取要批改的题目列表与答案列表 , 先使用正则表达式去除题目与答案的题号排除干扰 , 再使用计算函数 calc 计算题目的正确答案并与文件答案对比 , 不一致则认为错误 , 一致则认为正确 , 将批改的题号加入批改结果对应的数组中.
测试运行:
单元测试脚本如下:
import unittest
from unittest.mock import patch
import os
import tempfile
import fractions
import calculator
from calculator import make_num, calc, format_num, check_expr, exprNode, make_problem, check_answers
class TestCalculator(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
"""测试前的准备工作"""
self.temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
def tearDown(self):
"""测试后的清理工作"""
import shutil
shutil.rmtree(self.temp_dir)
def test_make_num(self):
"""测试数字生成函数"""
# 测试多次生成,确保不会崩溃
for _ in range(100):
num = make_num(10)
self.assertIsNotNone(num)
self.assertIsInstance(num, str)
def test_calc(self):
"""测试表达式计算函数"""
# 测试基本运算
self.assertEqual(calc("3+4"), 7)
self.assertEqual(calc("3-1"), 2)
self.assertEqual(calc("5×7"), 35)
self.assertEqual(calc("6÷2"), 3)
# 测试分数运算
self.assertEqual(calc("1/2+1/2"), 1)
self.assertEqual(calc("1/2×2"), 1)
# 测试带分数
self.assertEqual(calc("1'1/2"), fractions.Fraction(3, 2))
# 测试无效表达式
self.assertIsNone(calc("1/0"))
self.assertIsNone(calc("1+"))
def test_format_num(self):
"""测试数字格式化函数"""
# 测试整数
self.assertEqual(format_num(5), "5")
self.assertEqual(format_num(0), "0")
# 测试真分数
self.assertEqual(format_num(fractions.Fraction(1, 2)), "1/2")
# 测试假分数转换为带分数
self.assertEqual(format_num(fractions.Fraction(5, 2)), "2'1/2")
# 测试等于1的分数
self.assertEqual(format_num(fractions.Fraction(2, 2)), "1")
def test_check_expr(self):
"""测试表达式检查函数"""
# 测试有效的表达式
root = exprNode('+', exprNode('1'), exprNode('2'))
self.assertTrue(check_expr(root))
self.assertEqual(root.result, "3")
# 测试无效的表达式(除零)
root = exprNode('÷', exprNode('1'), exprNode('0'))
self.assertFalse(check_expr(root))
def test_make_problem_small(self):
"""测试生成少量题目"""
problems, answers = make_problem(10, 5)
self.assertEqual(len(problems), 5)
self.assertEqual(len(answers), 5)
# 检查每个问题都有答案
for i in range(5):
self.assertTrue(problems[i].endswith("= "))
self.assertIsNotNone(answers[i])
def test_make_problem_large(self):
"""测试生成大量题目"""
problems, answers = make_problem(10, 100)
self.assertEqual(len(problems), 100)
self.assertEqual(len(answers), 100)
def test_check_answers_correct(self):
"""测试批改正确答案"""
# 创建测试文件
ex_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "test_ex.txt")
ans_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "test_ans.txt")
with open(ex_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("1. 1 + 1 = \n")
f.write("2. 2 × 2 = \n")
with open(ans_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("1. 2\n")
f.write("2. 4\n")
right, wrong = check_answers(ex_file, ans_file)
self.assertEqual(len(right), 2)
self.assertEqual(len(wrong), 0)
self.assertEqual(right, [1, 2])
def test_check_answers_wrong(self):
"""测试批改错误答案"""
# 创建测试文件
ex_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "test_ex.txt")
ans_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "test_ans.txt")
with open(ex_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("1. 1 + 1 = \n")
f.write("2. 2 × 2 = \n")
with open(ans_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("1. 3\n") # 错误答案
f.write("2. 5\n") # 错误答案
right, wrong = check_answers(ex_file, ans_file)
self.assertEqual(len(right), 0)
self.assertEqual(len(wrong), 2)
self.assertEqual(wrong, [1, 2])
def test_check_answers_mixed(self):
"""测试批改混合答案"""
# 创建测试文件
ex_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "test_ex.txt")
ans_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "test_ans.txt")
with open(ex_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("1. 1 + 1 = \n")
f.write("2. 2 × 2 = \n")
f.write("3. 3 - 1 = \n")
with open(ans_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("1. 2\n") # 正确答案
f.write("2. 5\n") # 错误答案
f.write("3. 2\n") # 正确答案
right, wrong = check_answers(ex_file, ans_file)
self.assertEqual(len(right), 2)
self.assertEqual(len(wrong), 1)
self.assertEqual(right, [1, 3])
self.assertEqual(wrong, [2])
def test_integration(self):
"""测试完整流程"""
# 生成题目
problems, answers = make_problem(10, 10)
# 保存题目和答案
ex_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "exercises.txt")
ans_file = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "answers.txt")
with open(ex_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i, p in enumerate(problems):
f.write(f"{i + 1}. {p}\n")
with open(ans_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i, a in enumerate(answers):
f.write(f"{i + 1}. {a}\n")
# 批改答案
right, wrong = check_answers(ex_file, ans_file)
# 所有答案应该都是正确的
self.assertEqual(len(wrong), 0)
self.assertEqual(len(right), 10)
class TestCommandLine(unittest.TestCase):
@patch('sys.argv', ['calculator.py', '-n', '10', '-r', '10'])
def test_generate_mode(self):
# 测试生成模式
# 由于main函数会使用sys.argv,我们通过patch模拟命令行参数
# 这里我们检查是否成功解析了参数,并且进入了生成模式
args = calculator.parser.parse_args()
self.assertEqual(args.n, 10)
self.assertEqual(args.r, 10)
self.assertIsNone(args.e)
self.assertIsNone(args.a)
@patch('sys.argv', ['calculator.py', '-e', 'exercises.txt', '-a', 'answers.txt'])
def test_grade_mode(self):
# 测试批改模式
args = calculator.parser.parse_args()
self.assertIsNone(args.n)
self.assertIsNone(args.r)
self.assertEqual(args.e, 'exercises.txt')
self.assertEqual(args.a, 'answers.txt')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main(verbosity=2)
通过12个简单测试例子测试了程序的: 数字生成函数稳定性 , 表达式计算函数准确性 , 数字格式化函数准确性 , 表达式检查函数准确性 , 题目生成函数稳定性 , 批改函数准确性 , 整体流程的稳定性 , 程序接收参数的稳定性
测试覆盖率:
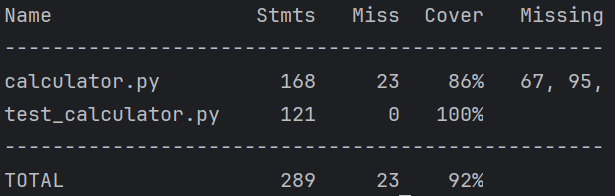
可以相信 , 程序是可以正确运行的
项目小结:
在这次结对项目中 , 程思远 负责程序的大体设计和简要编写 , 区泽明负责程序的完善与Debug测试 . 在这个过程中对程序实现的理解方面的交流是关键 , 将二人想法融会贯通 , 最终实现完整程序 . 这个过程中外卖体会到结对合作的工作效率比一人工作更高 , 也更容易发现各自想法的缺陷 ,更早发现问题 , 更高效地解决问题 .
闪光点:
区泽明: 对程序的各环节测试和完善都很细节 , 能快速发现程序的问题所在并加以解决 . 对程序实现的想法也很有启发性 .
程思远; 能快速地理解题目需求并设计出程序大体流程 , 为后面的程序开发提供较为明确的方向 .



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号