Java面经之排序算法
排序算法
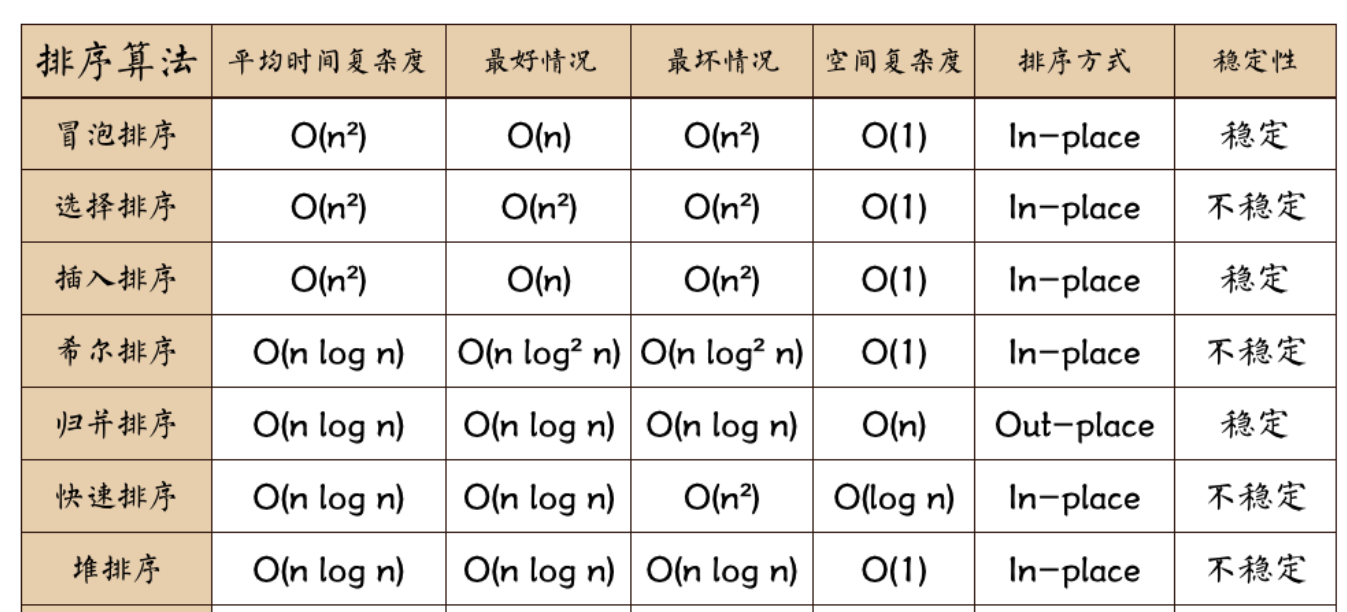
一、冒泡排序
public static int bubbleSort(int[] array) {
if (array.length == 0)
return array;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j + 1] < array[j]) {
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
return array;
}
二、选择排序
public static int selectionSort(int[] array) {
if (array.length == 0)
return array;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i; j < array.length; j++) {
if(array[j] < array[minIndex])
minIndex = j;
}
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[minIndex];
array[minIndex] = tmp;
}
}
三、插入排序
public static int[] insertionSort(int[] array) {
if (array.length == 0)
return array;
int current;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
current = array[i + 1];
int preIndex = i;
while (preIndex >= 0 && current < array[preIndex]) {
array[preIndex + 1] = array[preIndex];
preIndex--;
}
array[preIndex + 1] = current;
}
return array;
}
四、快速排序
int Partion(ElemType A[], int low, int high){
ElemType pivot=A[low];
while(low<high){
while(low<high&&A[high]>=pivot)
high--;
A[low]=A[high];
while(low<high&&A[low]<=pivot)
low++;
A[high]=A[low];
}
A[low]=pivot;
return low;
}
void QuickSort(ElemType A[], int low, int high){
if(low<high){
int pivotpos=Partion(A,low,high);
QuickSort(A,low,pivotpos-1);
QuickSort(A,pivotpos+1,high);
}
}
五、堆排序
每个结点的值都大于其左孩子和右孩子结点的值,称之为大根堆;每个结点的值都小于其左孩子和右孩子结点的值,称之为小根堆。

大根堆:arr(i)>arr(2i+1) && arr(i)>arr(2i+2)
小根堆:arr(i)<arr(2i+1) && arr(i)<arr(2i+2)
void BuildMaxHeap(ElemType A[], int len){
for(int i=len/2;i>0;i--)
AdjustDown(A,i,len);
}
void AdjustDown(ElemType A[], int k, int len){
A[0]=A[k];
for(int i=2*k;i<=len;i*=2){
if(i<len&&A[i]<A[i+1])
i++;
if(A[0]>=A[i])
break;
else{
A[k]=A[i];
k=i;
}
}
A[k]=A[0];
}
void HeapSort(ElemType A[], int len){
BuildMaxHeap(A,len);
for(int i=len;i>1;i--){
swap(A[i],A[1]);
AdjustDown(A,1,i-1);
}
}
六、归并排序
public static int[] MergeSort(int[] array) {
if (array.length < 2) return array;
int mid = array.length / 2;
int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, 0, mid);
int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, mid, array.length);
return merge(MergeSort(left), MergeSort(right));
}
public static int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) {
int[] result = new int[left.length + right.length];
for (int index = 0, i = 0, j = 0; index < result.length; index++) {
if (i >= left.length)
result[index] = right[j++];
else if (j >= right.length)
result[index] = left[i++];
else if (left[i] > right[j])
result[index] = right[j++];
else
result[index] = left[i++];
}
return result;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号