Kubernetes Volume
非持久化Volume
容器中的文件和容器的声明周期一样,容器崩溃,文件就没了。Kubernetes Volume的声明周期和Pod相同,容器在Pod里面重启时,数据得以在容器重启期间保留。当然,如果Pod被删除,那么文件还是会消失的。够清楚吧
A Kubernetes volume, on the other hand, has an explicit lifetime - the
same as the Pod that encloses it. Consequently, a volume outlives any
Containers that run within the Pod, and data is preserved across
Container restarts.
ConfigMap
ConfigMap作为一个Volume挂在到Pod上面,用于外部配置应用。
Step 1 :创建一个ConfigMap对象
参考:Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
ConfigMap也是一个普通Kubernetes对象,使用语法创建.
kubectl create configmap <map-name> <data-source>
Step 2:为Pod指定Volume
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: configmap-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test
image: busybox
volumeMounts:
- name: config-vol
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-vol
configMap:
name: log-config
items:
- key: log_level
path: log_level
log-config ConfigMap作为一个Volume挂载到名为configmap-pod的Pod上, 挂载路径为/etc/config/log_level. 这个路径是由mountPath和key---log_level决定的.
hostPath
这个有持久化Volume的功能,用于映射主机文件系统的路径:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hostpath-test
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: hostpathtest
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
name: test-volume
volumes:
- name: test-volume
hostPath:
# directory location on host
path: /root/pv
type: Directory
比如删除Pod,主机上的这个路径/root/pv不会删除,数据也不会丢失。这算是一种特殊情况吧。
持久化Volume
PersistentVolumes and PersistentVolumeClaims are independent from Pod lifecycles and preserve data through restarting, rescheduling, and even deleting Pods.
上面所说的Volume的声明周期是和它所挂载到的Pod声明周期是相同的,在某些场景下,比如MySQL需要持久化的存储,那么也就引入了持久化数据卷(PersistentVolumes)。
持久卷分成两种类型,一种是静态的,一种是动态的。静态卷需要管理员申请一块固定大小的存储空间放到一个类似池的空间。应用需要从池中申请(claim)空间。动态卷则是管理员只注册Volume的类型,用户向池中申请时,池会向存储提供者(provisioner)申请。
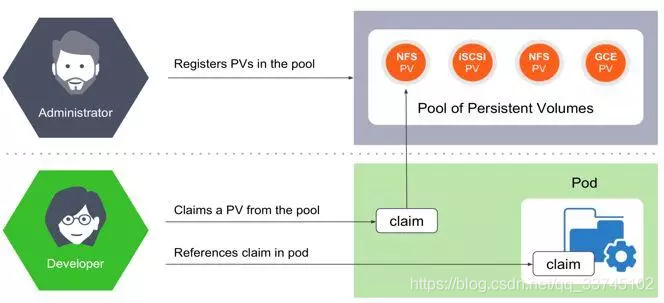
静态PV: 管理员手动创建并给PV一个名字,Pod引用名字来使用PV
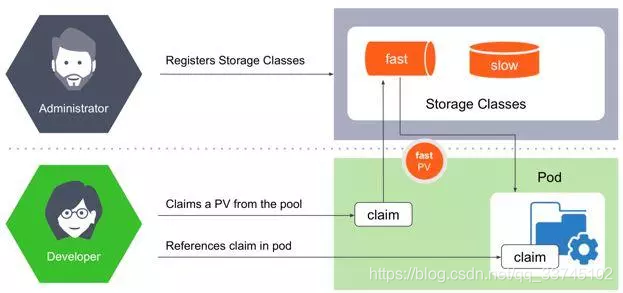
动态PV: 管理员注册一种类型的存储实现,Pod使用PV时不通过名字
来引用PV,而是仅声明需要什么类型的PV实现
动态PV相比静态PV的好处是:管理员不用再手动创建PV供Pod使用。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号