一次Spring Transactional嵌套事务使用不同的rollbackFor的分析
起因:
项目期间由于一次异常回滚问题,发现自己在事务知识方面知识的遗漏,趁着这次机会,做了几次rollbackFor的测试。
测试:
现在有两个事务,事务oute包含事务Inner。事务A回滚规则是当事务抛出TestException,其中TestException继承RunTimeException。事务B的回滚规则是事务抛RuntimeException。事务的传播方式都是使用的默认,即 Propagation.REQUIRED。如以下代码:
1 @Override 2 @Transactional(rollbackFor = TestException.class) 3 public void transOuter() { 4 productMapper.updateOrderQuantityPessimistic(product_code1); 5 ((ProductService) AopContext.currentProxy()).transInner(); 6 } 7 8 @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) 9 public void transInner() { 10 productMapper.updateOrderQuantityPessimistic(product_code); 11 if (true) { 12 throw new RuntimeException(); 13 } 14 }
以下为TestException的代码。
1 public class TestException extends RuntimeException { 2 3 public TestException(String message) { 4 super(message); 5 } 6 }
一开始按照自己对事务的理解, 默认的传播属性之下。事务B启动的时候,会默认使用事务A的rollbackFor来进行回滚,所以该代码运行时候。程序不会回滚。
然而测试,测试完之后发现事务A、B都进行了回滚。
看着测试结果产生了疑问。难道是以innner的rollBack为准?接着进行测试。
1 @Override 2 @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) 3 public void transOuter() { 4 productMapper.updateOrderQuantityPessimistic(product_code1); 5 ((ProductService) AopContext.currentProxy()).transInner(); 6 } 7 8 @Transactional(rollbackFor = TestException.class) 9 public void transInner() { 10 productMapper.updateOrderQuantityPessimistic(product_code); 11 if (true) { 12 throw new RuntimeException(); 13 } 14 }
再次测试,测试完之后发现事务A、B依然进行了回滚。
感觉自己对事务的理解还是太浅薄了,是时候debug一波源码。
分析源码:
查看 org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport 类的 invokeWithinTransaction方法。该方法是事务执行的主要方法,这里我们主要看第20行的事务捕捉那一块。completeTransactionAfterThrowing的方法。
1 protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation) 2 throws Throwable { 3 4 // If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional. 5 final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass); 6 final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr); 7 final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass); 8 9 if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) { 10 // Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls. 11 TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); 12 Object retVal = null; 13 try { 14 // This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain. 15 // This will normally result in a target object being invoked. 16 retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); 17 } 18 catch (Throwable ex) { 19 // 事务异常捕捉主要在这边获取 20 completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); 21 throw ex; 22 } 23 finally { 24 cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); 25 } 26 commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); 27 return retVal; 28 } 29 30 else { 31 // It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in. 32 try { 33 Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, 34 new TransactionCallback<Object>() { 35 @Override 36 public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) { 37 TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); 38 try { 39 return invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); 40 } 41 catch (Throwable ex) { 42 if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) { 43 // A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback. 44 if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) { 45 throw (RuntimeException) ex; 46 } 47 else { 48 throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex); 49 } 50 } 51 else { 52 // A normal return value: will lead to a commit. 53 return new ThrowableHolder(ex); 54 } 55 } 56 finally { 57 cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); 58 } 59 } 60 }); 61 62 // Check result: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow. 63 if (result instanceof ThrowableHolder) { 64 throw ((ThrowableHolder) result).getThrowable(); 65 } 66 else { 67 return result; 68 } 69 } 70 catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) { 71 throw ex.getCause(); 72 } 73 } 74 }
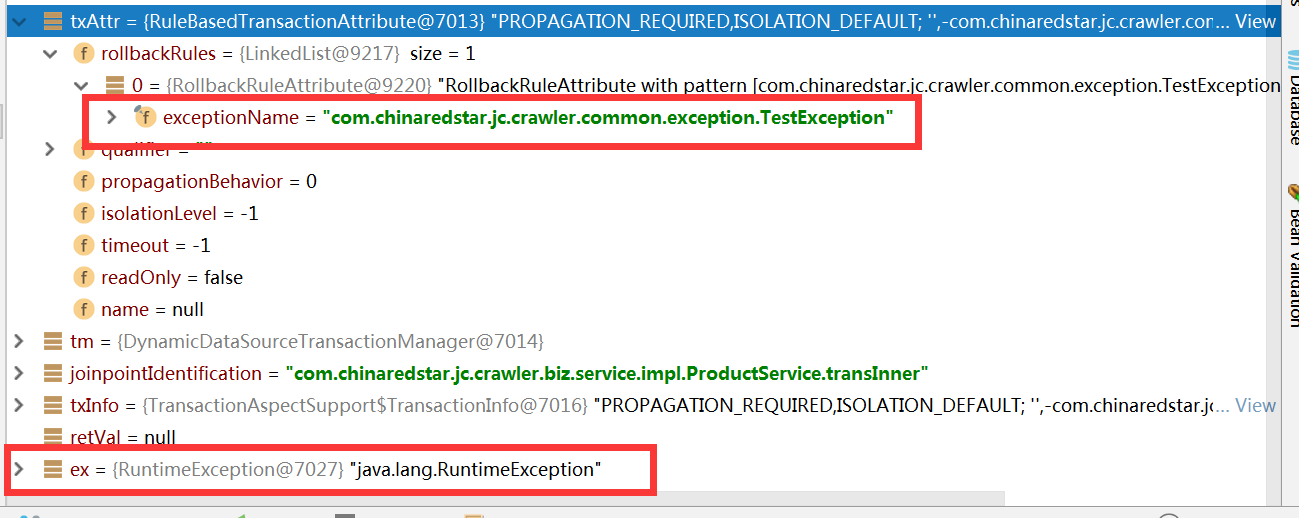
这边显示当事务的rollbackFor为TestException,而抛出的异常为RunTimeException时候。跟我们的transInner一致。接着往下看 completeTransactionAfterThrowing 方法。主要看第8行,第8行对事务进行判断,是否对该抛出的异常进行回滚。
1 protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(TransactionAspectSupport.TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) { 2 if (txInfo != null && txInfo.hasTransaction()) { 3 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 4 logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + 5 "] after exception: " + ex); 6 } 7 //这里主要判断事务捕获了异常以后,是否进行回滚 8 if (txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) { 9 try { 10 txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus()); 11 } 12 catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) { 13 logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex); 14 ex2.initApplicationException(ex); 15 throw ex2; 16 } 17 catch (RuntimeException ex2) { 18 logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex); 19 throw ex2; 20 } 21 catch (Error err) { 22 logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback error", ex); 23 throw err; 24 } 25 } 26 else { 27 // We don't roll back on this exception. 28 // Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true. 29 try { 30 txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus()); 31 } 32 catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) { 33 logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex); 34 ex2.initApplicationException(ex); 35 throw ex2; 36 } 37 catch (RuntimeException ex2) { 38 logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex); 39 throw ex2; 40 } 41 catch (Error err) { 42 logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit error", ex); 43 throw err; 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }
再深入点进去看,看到第11行,这边获取该异常的深度。跳转到片段二进行代码查看。
1 public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) { 2 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 3 logger.trace("Applying rules to determine whether transaction should rollback on " + ex); 4 } 5 6 RollbackRuleAttribute winner = null; 7 int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 8 9 if (this.rollbackRules != null) { 10 for (RollbackRuleAttribute rule : this.rollbackRules) { 11 //获取异常的深度? 12 int depth = rule.getDepth(ex); 13 if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) { 14 deepest = depth; 15 winner = rule; 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 21 logger.trace("Winning rollback rule is: " + winner); 22 } 23 24 // User superclass behavior (rollback on unchecked) if no rule matches. 25 if (winner == null) { 26 logger.trace("No relevant rollback rule found: applying default rules"); 27 //如果depth为-1之后,父类的回滚方式 28 return super.rollbackOn(ex); 29 } 30 31 return !(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute); 32 }
根据深度代码查看,rollbackFor和抛出异常ex不一致,返回-1。再回去看上面的代码片段,当返回-1之后,代码走到第28行。进行父类的回滚方法。
1 private int getDepth(Class<?> exceptionClass, int depth) { 2 if (exceptionClass.getName().contains(this.exceptionName)) { 3 // Found it! 4 return depth; 5 } 6 // If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it... 7 //此处RuntimeException 跟TestException不一致,返回-1 8 if (exceptionClass == Throwable.class) { 9 return -1; 10 } 11 return getDepth(exceptionClass.getSuperclass(), depth + 1); 12 }
以下是父类的代码是否回滚判断方法,有没有很眼熟,只要抛出的异常的是RunTimeExcpetion或者Error则进行回滚。
1 public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) { 2 return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error); 3 }
总结
根据上面的代码,我们可以推断出以下几个结论:
1、当我们抛出的异常为RunTime及其子类或者Error和其子类的时候。不论rollbackFor的异常是啥,都会进行事务的回滚。
2、当我们抛出的异常不是RunTime及其子类或者Error和其子类的时候,必须根据rollbackfor进行回滚。比如rollbackfor=RuntimeException,而抛出IOException时候,事务是不进行回滚的。
3、当我们抛出的异常不是RunTime及其子类或者Error和其子类的时候,如果嵌套事务中,只要有一个rollbackfor允许回滚,则整个事务回滚。
经过测试,上述的结论也没发现什么问题。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号