编译原理实验(NFA转DFA,LL1文法)
编译原理实验
- 实验一:实现对 C/C++ 变量定义串的分析
- 实验二:实现 NFA 转 DFA 并可视化
- 实验三:实现对文法的 First,Follow集,预测分析表的求解,判别是否是LL1文法,以及对符号串的分析过程
实验一:实现对 C/C++ 变量定义串的分析
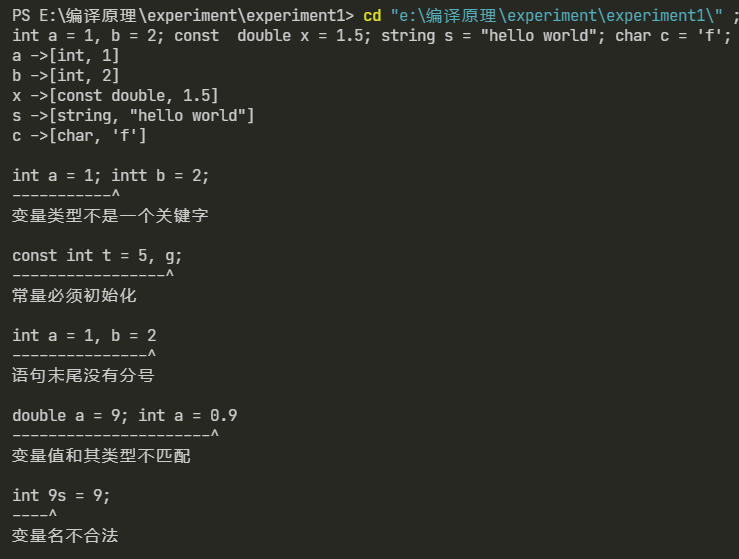
1. 分析的串如下:
string text1 = "int a = 1, b = 2; const double x = 1.5; string s = \"hello world\"; char c = 'f';";
string text2 = "int a = 1; intt b = 2;";
string text3 = "const int t = 5, g;";
string text4 = "int a = 1, b = 2";
string text5 = "double a = 9; int a = 0.9";
string text6 = "int 9s = 9;";
2. 分析结果如下:
实验二:实现 NFA 转 DFA 并可视化
1. NFA 的存储:
nfa_k = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4'] #状态集
nfa_t = ['a', 'b'] # 边
nfa_f = [('0', 'a', '0'), ('0', 'a', '3'), # 图的信息
('0', 'b', '0'), ('0', 'b', '1'),
('1', 'b', '2'), ('2', 'a', '2'),
('2', 'b', '2'), ('3', 'a', '4'),
('4', 'a', '4'), ('4', 'b', '4')]
nfa_s = ['0'] # 初态
nfa_z = ['2', '4'] # 终态集
2. ε_closure 和 move 操作:
def ε_closure(S, f):
res = []
vis = {}
q = Queue(maxsize = 0)
for i in S:
q.put(i)
vis[i] = 1
while q.empty() is False:
node = q.get()
if node not in res: res.append(node)
for i in f:
if i[0] == node and i[1] == 'ε' and i[2] not in vis:
q.put(i[2])
vis[i[2]] = 1
res.sort()
return res
def move(S, f, a):
res = []
for i in S:
for j in f:
if j[0] == i and j[1] == a:
res.append(j[2])
return res
3. 可视化:
-
工具:graphviz
-
画图:
def draw(K, f, S, Z, pic_name):
dot = Digraph(name = pic_name, format = "png")
for i in S:
dot.node(name = i, label = i, color = 'green')
for i in Z:
dot.node(name = i, label = i, color = 'red')
for i in K:
if i not in S and i not in Z:
dot.node(name = i, label = i)
for i in f:
dot.edge(i[0], i[2], label = i[1])
dot.view(filename = pic_name, directory = "./picture")
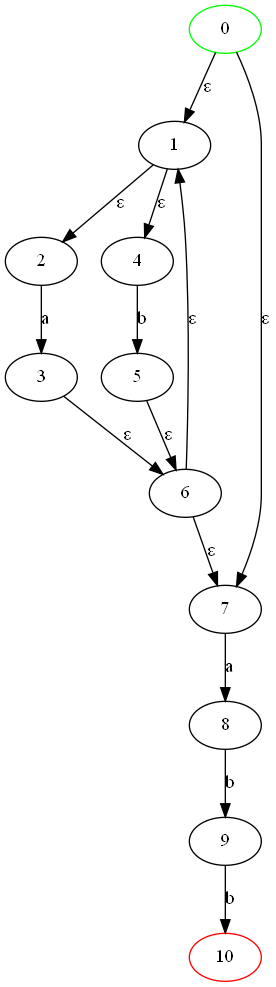
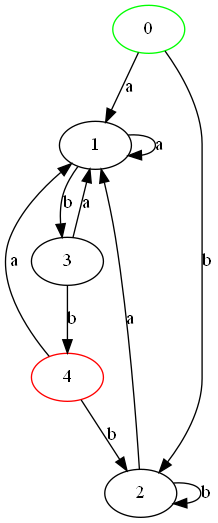
4. 效果:
-
NFA图:
-
DFA图:
实验三:LL1文法的分析
1. 数据的存储:
non_term = set() # 非终结符集合
term = set() # 终结符集合
First = {} # First 集
Follow = {} # Follow 集
Gram = [] # 读入的文法
production = {} #预处理过后的产生式 格式为:'S':{'a', 'EF'}
AnalysisList = {} # 预测分析表
start_sym = '' # 文法开始符号
end_sym = '#' # 结束符号
epsilon = 'ε' # 空符
isLL1 = True
2. 求解 First集:
def getFirst() -> None:
global non_term, term, First
# 初始化非终结符的First集为空
for it in non_term: First[it] = set()
# 初始化终结符的First集合为自己
for it in term: First[it] = set(it)
flag = True
while flag: # 当First集没有更新就结束
flag = False
for X in non_term:
for Y in production[X]:
i = 0
mark = True
while mark and i < len(Y):
if not First[Y[i]] - set(epsilon) <= First[X]: # 还存在没有添加的
# print('First[' , X, '] = ', " ", First[X], 'First[', Y[i] , '] = ' , First[Y[i]])
# First[Yi] 中没有 ε
if epsilon not in First[Y[i]] and Y[i] in non_term and i > 0:
First[X] |= First[Y[i]]
mark = False
else:
First[X] |= First[Y[i]] - set(epsilon)
flag = True
# Yi 不能推出 ε 就标记为 False
if epsilon not in First[Y[i]]: mark = False
i += 1
if mark: First[X] |= set(epsilon)
return None
3. 求解 Follow集:
def getFollow() -> None:
global non_term, term, First, Follow, start_sym
for A in non_term: Follow[A] = set() # 初始化
Follow[start_sym].add(end_sym) # 1. 将 # 号加入到Follow[s] 中
flag = True
while flag: # 当Follow集不再更新,算法结束
flag = False
for A in non_term:
for B in production[A]:
for i in range(len(B)):
# bi 是终结符则跳过
if B[i] in term: continue
mark = True
for j in range(i + 1, len(B)):
if not First[B[j]] - set(epsilon) <= Follow[B[i]]: # 可以更新
Follow[B[i]] |= First[B[j]] - set(epsilon) # 对应书上的步骤 2
flag = True # 发生了改变
if epsilon not in First[B[j]]: mark = False
break
if mark: # A->αBβ and β->ε
if not Follow[A] <= Follow[B[i]]: # 可以更新
Follow[B[i]] |= Follow[A]
flag = True
return None
4. 构造预测分析表:
# 计算 预测分析表|Select集,并判断是否是LL1文法
def getAnalysisList() -> bool:
# 初始化
res = True
for i in non_term:
AnalysisList[i] = dict()
for j in term:
if j != epsilon: AnalysisList[i][j] = None
AnalysisList[i][end_sym] = None
for i in production:
r = production[i]
for s in r:
mark = False
for si in s:
if epsilon not in First[si]: # 不能推出空
for j in First[si]:
if AnalysisList[i][j] != None:
AnalysisList[i][j] += ', ->' + s
res = False
else: AnalysisList[i][j] = s
mark = False
break
else:
mark = True
for j in First[si] - set(epsilon):
if AnalysisList[i][j] != None:
res = False
AnalysisList[i][j] += ', ->' + s
else: AnalysisList[i][j] = s
if mark: #First[s] 可以推出空
for j in Follow[i]:
if AnalysisList[i][j] != None:
res = False
AnalysisList[i][j] += ', ->' + s
else: AnalysisList[i][j] = s
return res
5. 分析符号串:
def analysis(s: str) -> PrettyTable():
res = PrettyTable()
res.field_names = ['步骤', '分析栈', '剩余输入串', '推导所用产生式或匹配']
stk = ''
stk += end_sym
stk += start_sym
step = 0
while len(stk) and len(s):
step += 1
top = stk[len(stk) - 1]
row = []
row.append(step)
row.append(stk)
row.append(s)
if top in term or top == end_sym: # 栈顶是终结符或 # 号
if top == end_sym: # 结束:
row.append('接受')
res.add_row(row)
return res
if top == s[0]: # 匹配成功
row.append('"' + s[0] + '"匹配')
res.add_row(row)
stk = stk.replace(stk[len(stk) - 1], '', 1)
s = s.replace(s[0], '', 1)
continue
else: # 匹配失败
row.append('匹配失败')
res.add_row(row)
return res
tmp_production = AnalysisList[top][s[0]] # 推导所用的产生式
if tmp_production == None: #产生式为空
row.append('推导失败')
res.add_row(row)
return res
row.append(top + '->' + tmp_production)
res.add_row(row)
stk = stk.replace(stk[len(stk) - 1], '', 1)
if tmp_production== epsilon: #推出了空字符则不push进栈中
continue
tmp_production = tmp_production[::-1]
stk += tmp_production
# print(row)
step += 1
row = []
row.append(step)
row.append(stk)
row.append(s)
row.append('失败')
res.add_row(row)
return res
6. 分析LL1文法结果:
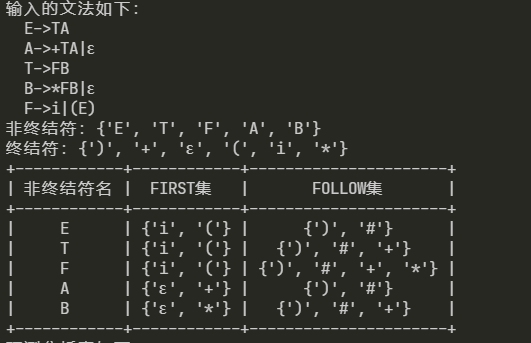
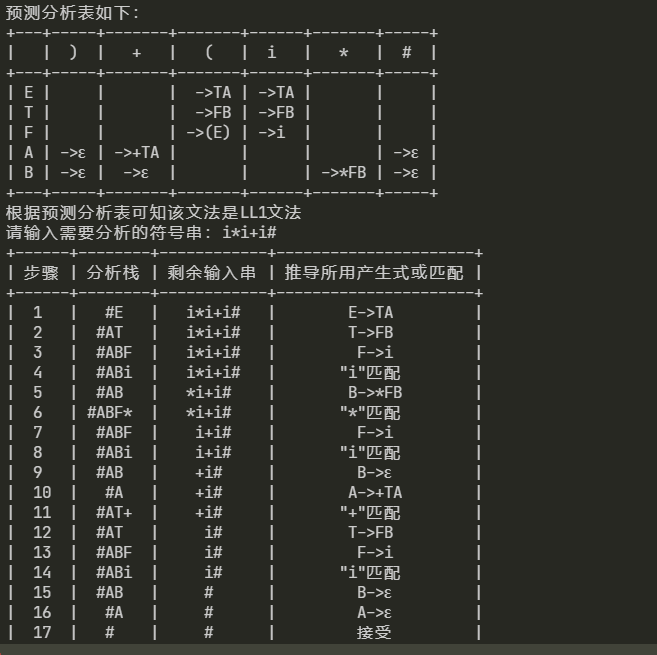
7. 分析非LL1文法结果:
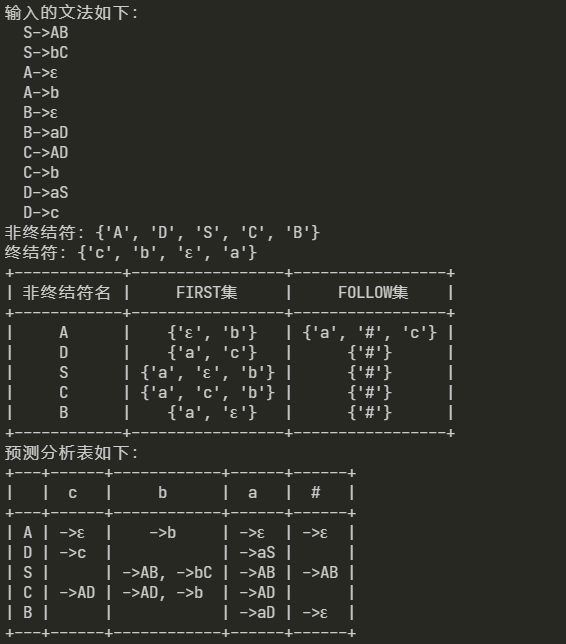


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号