06异常
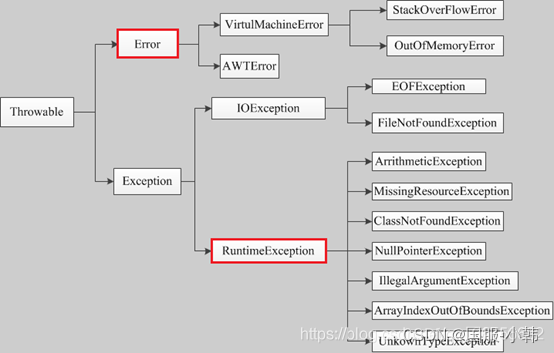
异常体系结构
Java把异常当作对象来处理,定义一个基类java.lang.Throwable作为所有异常的超类
Error类对象由Java虚拟机生成并抛出,大多数与代码编写所执行的操作无关
JVM运行错误:OutOfMemoryError内存溢出
RuntimeException(运行时异常)
1、数组越界(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)
2、空指针异常(NullPointerException)
3、算术异常(ArithmeticException)
4、丢失资源(MissingResourceException)
5、找不到类(ClassNotFoundException)
Java异常处理机制
- 抛出异常
try、catch、finally、throw、throws
选中代码,按快捷键ctrl + alt + t
int a =1;
int b = 0;
try{//try监控区域
System.out.println(a/b);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){//catch捕获异常
System.out.println("程序出现错误,分母不能为0");
}finally{
System.out.println("finally");
}
//可以不用finally,finally一般用于善后工作,关闭IO等操作
自定义异常
//自定义的异常类
public class myException extends Exception{
//
private int a;
public myException(int a){
this.a = a;
}
//toString异常打印信息
@Override
public String toString(){
return "myException{" +
"a="+a+'}';
}
}
public class Test{
static void test(int a) throws myException{
System.out.println("传递的参数为:"+a);
if(a>0){
throw new myException(a);//抛出
}
System.out.println("ok");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
test(1);
}catch(myException e){
System.out.println("myException=>"+e);
}
}
}






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号