DAY4
练习
一:
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int (*ptr)[2];
int a[2][2]={12,14,16};
ptr=a;
printf("%d\n",**ptr);
printf("%d",**(ptr+1));
}输出结果:
12
16二:
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int *ptr;
int a[2][2]={12,14,16};
ptr=a[0];
printf("%d\n",*ptr);
printf("%d",*(ptr+2));
}
输出结果:
12
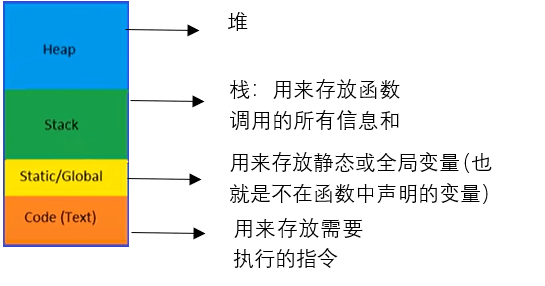
16三:指针和动态内存(栈 VS 堆)
1.栈
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int total;
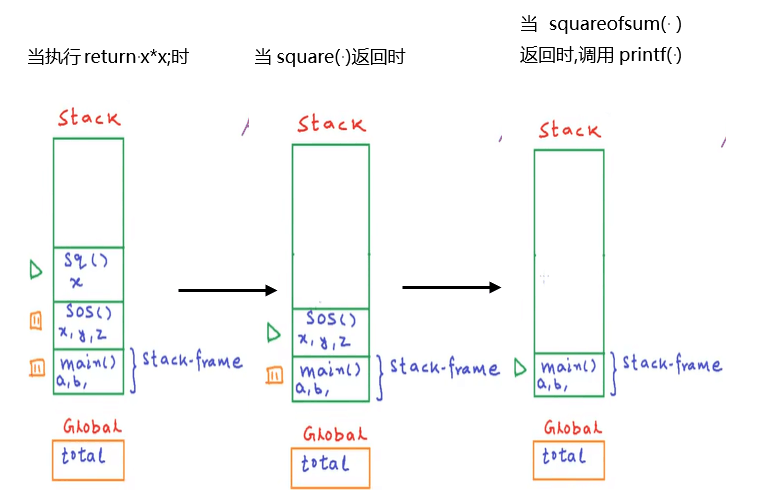
int square(int x){
return x*x;
}
int squareofsum(int x,int y){
int z = square(x+y);
return z;
}
int main(){
int a = 4 , b = 8;
total = squareofsum(a,b);
printf("output = %d",total);
}输出结果:
output = 144-
结构:
![]()
-
运行过程:
![]()
-
total是全局变量,因为他没有在函数内声明,我们可以任何地点访问它
所有的局部变量,参数,函数返回地址都存在栈帧上
pritnf结束,控制再次返回到main函数,然后main函数结束,程序也会结束,最后全局变量也会被清除
2.堆
堆(heap)被称作为动态内存,使用堆意味着动态内存分配。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int a;
int *p;
p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*p = 10;
free(p);//使用malloc分配的内存,最终通过调用free释放
p=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*p = 20;//前面通过free释放了内存,然后现在p指向另一内存
} 前面的(int*)是在做类型转换,因为在C中malloc返回void,所以需要转型成整型指针
p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
为了在C中使用动态内存,我们需要知道4个函数:
malloc:从堆上找到空闲的内存,然后预留空间通过指针返回给我们
calloc
realloc
free:释放内存
在C++中:
new
delete
在堆上储存一个整型的数组:指针会指向基地址
p = (int*)malloc(20*sizeof(int));//向malloc传入(20*整型的大小)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号