数据读写分离实现方式
随着业务的数据量的增长,很多大型网站,所处理的业务中,有大约70%是查询(select)相关的业务操作,而剩下的30%是写操作(insert、delete、update),故可使用读写分离的方式提升数据库的负载能力。
处理数据的方案:将所有的查询处理都放到从服务器上,写处理放在主服务器。
一、使用Spring基于应用层实现
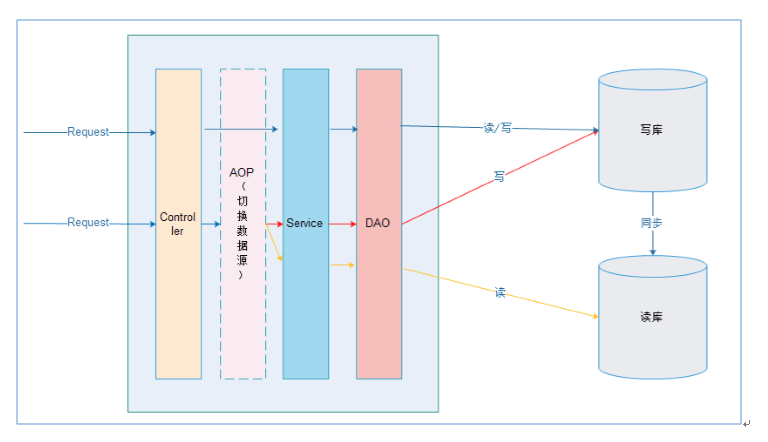
在进入Service之前,使用AOP来做出判断,是使用写库还是读库,判断依据可以根据方法名判断,比如说以query、find、get等开头的就走读库,其他的走写库。
继承AbstractRoutingDataSource实现动态数据源切换
mybatis配置文件
<bean id="masterDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<!-- 基本属性 url、user、password -->
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<!-- 配置初始化大小、最小、最大 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1" />
<property name="minIdle" value="1" />
<property name="maxActive" value="20" />
<!-- 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="60000" />
<!-- 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="60000" />
<!-- 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="300000" />
<property name="validationQuery" value="SELECT 'x'" />
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="false" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="false" />
<!-- 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 -->
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true" />
<property name="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize" value="20" />
</bean>
<bean id="slaveDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<!-- 基本属性 url、user、password -->
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.r.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.r.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.r.password}" />
<!-- 配置初始化大小、最小、最大 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1" />
<property name="minIdle" value="1" />
<property name="maxActive" value="20" />
<!-- 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="60000" />
<!-- 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="60000" />
<!-- 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="300000" />
<property name="validationQuery" value="SELECT 'x'" />
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="false" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="false" />
<!-- 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 -->
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true" />
<property name="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize" value="20" />
</bean>
<bean id="dynamicDataSource" class="com.boothsun.util.datasource.DynamicDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String">
<!-- write -->
<entry key="master" value-ref="masterDataSource"/>
<!-- read -->
<entry key="slave" value-ref="slaveDataSource"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="masterDataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- MyBatis配置 -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dynamicDataSource"/>
<!-- 显式指定Mapper文件位置 -->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:xmlmapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.boothsun.mybatismapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dynamicDataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="false"/>
spring获取数据源的源码:

DynamicDataSource方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { return DbContextHolder.getDbType(); }} |
DbContextHolder方法
public class DbContextHolder {
// 注意:数据源标识保存在线程变量中,避免多线程操作数据源时互相干扰
|
1
|
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder=new ThreadLocal<String>();<br><br> public static void setDbType(String dbType){ <br> contextHolder.set(dbType);<br> } <br><br>public static String getDbType(){<br> String dbType=(String) contextHolder.get(); <br> return dbType; <br>} <br><br>public static void clearDbType(){<br> contextHolder.remove();<br> }<br>} |
使用ThreadLocal实现简单的读写分离
@Component
@Aspect
public class DataSourceMethodInterceptor {
@Before("execution(* com.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void dynamicSetDataSoruce(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
// 查询读从库
if (methodName.startsWith("select") || methodName.startsWith("load") || methodName.startsWith("get") || methodName.startsWith("count") || methodName.startsWith("is")) {
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setDataSource("slave");
} else { // 其他读主库
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setDataSource("master");
}
}
}
优点:
1、多数据源切换方便,由程序自动完成;
2、不需要引入中间件;
3、理论上支持任何数据库;
缺点:
1、由程序员完成,运维参与不到;
2、不能做到动态增加数据源;
二、使用中间件实现读写分离
要求:
- 一主两从,做读写分离。
- 多个从库之间实现负载均衡。
- 可手动强制部分读请求到主库上。(因为主从同步有延迟,对实时性要求高的系统,可以将部分读请求也走主库)
mybatis配置文件
<bean id="master" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url.master}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username.master}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password.master}"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="100"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="10"/>
<property name="maxWait" value="60000"/>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean id="slave1" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url.slave1}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username.slave1}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password.slave1}"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="100"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="10"/>
<property name="maxWait" value="60000"/>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean id="slave2" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url.slave2}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username.slave2}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password.slave2}"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="100"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="10"/>
<property name="maxWait" value="60000"/>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean id="randomStrategy" class="io.shardingjdbc.core.api.algorithm.masterslave.RandomMasterSlaveLoadBalanceAlgorithm" />
<master-slave:data-source id="shardingDataSource" master-data-source-name="master" slave-data-source-names="slave1,slave2" strategy-ref="randomStrategy" />
强制路由
使用读写分离,可能会有主从同步延迟的问题,对于一些实时性要求比较高的业务,需强制部分读请求访问主库。
HintManager 分片键值管理器
我们可使用hintManager.setMasterRouteOnly() .@Test
public void HintManagerTest() {
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance() ;
hintManager.setMasterRouteOnly();
OrderExample example = new OrderExample();
example.createCriteria().andBusinessIdEqualTo(112);
List<Order> orderList = orderMapper.selectByExample(example);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(orderList));
hintManager.close();
}
阿里的mycat或360的Atlas也可以实现分库分表,读写分离和负载均衡等处理。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号