Mysql基础知识
Mysql 基础总结
1. 什么是 SQL 结构查询语句
SQL 语句是一种what型语言【想要什么,给你】,语法相对简单易懂
-
SQL (Structured Query Language)语言的划分
-
DDL(Data Definition Language)- 数据库定义语言;用来定义数据库对象、数据表和列;使用DDL创建、删除、修改数据库的表和结构
-
DML(Data Manipulation Language)- 数据库操作语言;操作数据库的相关数据,比如增加、删除、修改表中的数据
-
DCL(Data Control Language)- 数据控制语言;用它来定义访问权限和安全等级
-
DQL(Data Query Language)- 数据查询语言;数据查询语言,用来查询数据
-
-
SQL 语句的执行顺序
select distinct player_id , player_name , count(*) as num # 顺序5 from player join team on player.team_id = team.team_id # 顺序1 where height > 1.80 # 顺序2 group by player.team_id # 顺序3 having num >2 # 顺序4 order by num desc # 顺序6 limit 2; # 顺序7 -
完整的顺序是
- from 子句组装数据(包括 join )
- where 子句进行条件筛选
- group by 分组
- 使用聚集函数进行计算、数据映射
- having 筛选分组
- 计算所有的表达式
- select 的字段
- order by 排序
- limit 筛选
-
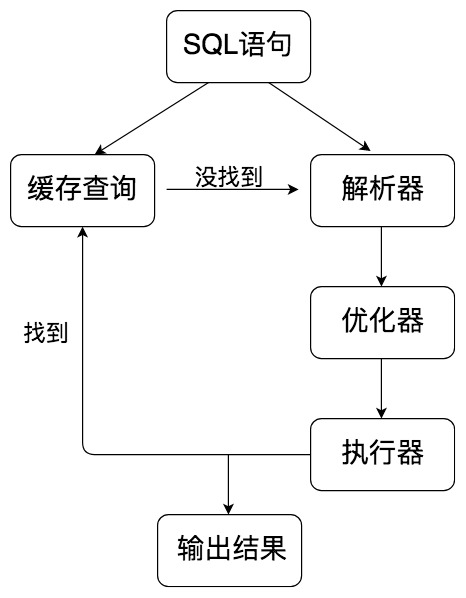
SQL 语句的执行流程
Mysql 中的流程:SQL 语句 → 缓存查询 → 解析器 → 优化器 → 执行器
-
查询缓存:Server 如何在查询缓存总发现了这条 SQL 语句,就会直接将结果返回给客户端;如果没有,就进入到解析器阶段。需要说明的是,因为查询缓存往往效率不高,所以在 Mysql 8.0 之后就抛弃了这个功能。
-
解析器:在解析器中队 SQL 语句进行语法分析、语义分析
-
优化器:在优化器中会确定 SQL 语句的执行路径,比如是根据全表检索,还是根据索引来检验等
-
执行器:在执行之前需要判断改用户是否具备权限,如果具备权限就执行 SQL 查询并返回结果。在 Mysql 8.0 以下的版本,如果设置了查询缓存,这时会将查询结果进行缓存。
-
2. Mysql 架构
- Mysql 是 Client/Server 架构,体系架构图如下

- 由以下几个部分组成
- 连接池组件(Connection Pool)
- 管理服务和工具组件(Enterprise Management Services & Utilities)
- SQL 接口组件(SQL Interface)
- 查询分析器(Parser)
- 优化器组件(Optimizer)
- 缓冲组件(Cache & Buffer)
- 插件式储存引擎(Pluggable Storage Engines)
- 物理文件(File System , Files & Logs)
-
关于储存引擎
-
InnoDB 储存引擎
Mysql 5.5 版本后默认的储存引擎,优点是支持事务、行级锁、外键约束、支持崩溃后的安全恢复
-
Myisam 储存引擎
不支持事务和外键,支持全文索引(只对英文有效),特点是查询速度快
-
Memory 储存引擎
数据放在内存当中(类似memcache)以便得到更快的响应速度,但是崩掉的话数据会丢失
-
NDB 储存引擎
主要用于 Mysql Cluster 分布式集群
-
Archive 储存引擎
有很好的压缩机制,用于文件文档,写入时会进行压缩
-
3. 常用库/表操作语句
1. mysql -h localhost -u root -p # 以root用户连接本地数据库
2. show databases; # 查看Mysql服务中的所有数据库
3. create database database_name; # 创建数据库
4. use databases; # 更改操作的数据库对象
5. \c # 取消执行当前未输入mysql语句
6. show tables; # 查看该操作数据库对象中所有的数据表名和视图名
7. desc table_name/view_name; # 查看表/视图结构
8. truncate table_name/delete from table_name ; # 清空表数据【表结构不变】
9. drop table_name; # 删除表 【表结构一起删除】
10. show create table table_name; # 查看建表/视图过程
11. show table status \G; # 查看数据库中的所有表信息;\G 竖行显示
12. show table status where name = table_name \G; # 指定表
13. alter table table_name rename to new_table_name; # 修改表名
14. drop table/view table_name/view_name; # 删除表/视图
15. create table table_name (id int primary key auto_increment,
saddres varchar(20) not null default '',colunm3,colunm4……)
default charset utf8/gbk; # 建表语句
16. set names gbk/utf8; # 将客户端、连接器、数据库字符集设为一致
4. 增删改查
1. insert
insert into table_name (column1,column2 ……) values (value1,value2 ……);
2. delete
delete from table_name where …… ; # where表示指定条件,不用where将针对表整表操作
3. update
update table_name set column1 = new_value , column2 = new_value …… where ……;
4. select
select cloumn1,cloumn2…… from table_name where …… group by …… having …… order by …… limit …… ;
# where|group by|having|order by|limit 可以没有其中某些项,若有必须按照先后顺序
5.深入理解 select
select 是增删改查的重点,也是难点,能否写出高性能的 sql 语句,select 是否熟练占很大一部分
-
列是变量,变量就可以进行各种运算,包括算术运算、逻辑运算 等
-
where 后面的语句是表达式,表达式的值为真或假 eg:where 1则恒为真 查询整张表,反之 where 0 恒位假 查询结果位 Empty
-
select 语句还可以配合算术运算符、逻辑运算符、位运算符以及相关函数写出更高性能的查询语句
-
常用的 select 用法(以goods表为例)
-
数字筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where shop_price > 300; -
字符筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where goods_name = 'kd876'; -
区间筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where shop_price between 300 and 3000; -
多条件筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where shop_price between 300 and 3000 and goods_id > 10 ; -
模糊条件筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where goods_name like '诺基亚%'; # 通配符% 表示任意多个字符 _ 表示任意单个字符 -
在字符串组里筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where goods_id in (3,10); # goods_id in(3,10)等价于goods_id = 3 or goods_id = 10 -
借助函数优化筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where left(goods_name,2)='kd'; # 函数left(a,n)表示在a字符串中从左到右取n个字符 -
全字符段筛选
select * from goods; -
不重复筛选
select distinct goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods; # distinct 不重复的意思 -
排序筛选
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods where shop_price >300 order by shop_price desc; # sc升序(默认)/ desc 降序
-
-
-
补上后续练习所需要的表格代码
create table goods ( goods_id mediumint(8) unsigned primary key auto_increment, goods_name varchar(120) not null default '', cat_id smallint(5) unsigned not null default '0', brand_id smallint(5) unsigned not null default '0', goods_sn char(15) not null default '', goods_number smallint(5) unsigned not null default '0', shop_price decimal(10,2) unsigned not null default '0.00', market_price decimal(10,2) unsigned not null default '0.00', click_count int(10) unsigned not null default '0' ) engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8; insert into `goods` values (1,'kd876',4,8,'ecs000000',1,1388.00,1665.60,9), (4,'诺基亚n85原装充电器',8,1,'ecs000004',17,58.00,69.60,0), (3,'诺基亚原装5800耳机',8,1,'ecs000002',24,68.00,81.60,3), (5,'索爱原装m2卡读卡器',11,7,'ecs000005',8,20.00,24.00,3), (6,'胜创kingmax内存卡',11,0,'ecs000006',15,42.00,50.40,0), (7,'诺基亚n85原装立体声耳机hs-82',8,1,'ecs000007',20,100.00,120.00,0), (8,'飞利浦9@9v',3,4,'ecs000008',1,399.00,478.79,10), (9,'诺基亚e66',3,1,'ecs000009',4,2298.00,2757.60,20), (10,'索爱c702c',3,7,'ecs000010',7,1328.00,1593.60,11), (11,'索爱c702c',3,7,'ecs000011',1,1300.00,0.00,0), (12,'摩托罗拉a810',3,2,'ecs000012',8,983.00,1179.60,13), (13,'诺基亚5320 xpressmusic',3,1,'ecs000013',8,1311.00,1573.20,13), (14,'诺基亚5800xm',4,1,'ecs000014',1,2625.00,3150.00,6), (15,'摩托罗拉a810',3,2,'ecs000015',3,788.00,945.60,8), (16,'恒基伟业g101',2,11,'ecs000016',0,823.33,988.00,3), (17,'夏新n7',3,5,'ecs000017',1,2300.00,2760.00,2), (18,'夏新t5',4,5,'ecs000018',1,2878.00,3453.60,0), (19,'三星sgh-f258',3,6,'ecs000019',12,858.00,1029.60,7), (20,'三星bc01',3,6,'ecs000020',12,280.00,336.00,14), (21,'金立 a30',3,10,'ecs000021',40,2000.00,2400.00,4), (22,'多普达touch hd',3,3,'ecs000022',1,5999.00,7198.80,16), (23,'诺基亚n96',5,1,'ecs000023',8,3700.00,4440.00,17), (24,'p806',3,9,'ecs000024',100,2000.00,2400.00,35), (25,'小灵通/固话50元充值卡',13,0,'ecs000025',2,48.00,57.59,0), (26,'小灵通/固话20元充值卡',13,0,'ecs000026',2,19.00,22.80,0), (27,'联通100元充值卡',15,0,'ecs000027',2,95.00,100.00,0), (28,'联通50元充值卡',15,0,'ecs000028',0,45.00,50.00,0), (29,'移动100元充值卡',14,0,'ecs000029',0,90.00,0.00,0), (30,'移动20元充值卡',14,0,'ecs000030',9,18.00,21.00,1), (31,'摩托罗拉e8 ',3,2,'ecs000031',1,1337.00,1604.39,5), (32,'诺基亚n85',3,1,'ecs000032',4,3010.00,3612.00,9); create table category ( cat_id smallint unsigned auto_increment primary key, cat_name varchar(90) not null default '', parent_id smallint unsigned )engine=InnoDB charset utf8; INSERT INTO `category` VALUES (1,'手机类型',0), (2,'CDMA手机',1), (3,'GSM手机',1), (4,'3G手机',1), (5,'双模手机',1), (6,'手机配件',0), (7,'充电器',6), (8,'耳机',6), (9,'电池',6), (11,'读卡器和内存卡',6), (12,'充值卡',0), (13,'小灵通/固话充值卡',12), (14,'移动手机充值卡',12), (15,'联通手机充值卡',12); CREATE TABLE `result` ( `name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `subject` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `score` tinyint(4) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; insert into result values ('张三','数学',90), ('张三','语文',50), ('张三','地理',40), ('李四','语文',55), ('李四','政治',45), ('王五','政治',30); create table a ( id char(1), num int )engine=InnoDB charset utf8; insert into a values ('a',5),('b',10),('c',15),('d',10); create table b ( id char(1), num int )engine=InnoDB charset utf8; insert into b values ('b',5),('c',15),('d',20),('e',99); create table m( mid int, hid int, gid int, mres varchar(10), matime date )engine=InnoDB charset utf8; insert into m values (1,1,2,'2:0','2006-05-21'), (2,2,3,'1:2','2006-06-21'), (3,3,1,'2:5','2006-06-25'), (4,2,1,'3:2','2006-07-21'); create table t ( tid int, tname varchar(20) )engine=InnoDB charset utf8; insert into t values (1,'国安'), (2,'申花'), (3,'布尔联队'); create table mian ( num int) engine=InnoDB; insert into mian values (3), (12), (15), (25), (23), (29), (34), (37), (32); create table user ( uid int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null default '', age smallint unsigned not null default 0 ) engine=InnoDB charset utf8; create table boy ( hid char(1), bname varchar(20) )engine=InnoDB charset utf8; insert into boy (bname,hid) values ('屌丝','A'), ('杨过','B'), ('陈冠希','C'); create table girl ( hid char(1), gname varchar(20) )engine=InnoDB charset utf8; insert into girl(gname,hid) values ('小龙女','B'), ('张柏芝','C'), ('死宅女','D'); 注:上述包含的表格有
goods、category、result、a、b、m、t、mian、user、boy、girl
6.查询练习(以goods表为例)
-
查询出名字为 ’诺基亚NXX’ 的手机
select * from goods where goods_id in(4,11); -
查询出名字不以 ’诺基亚’ 开头的商品
select * from goods where goods_name not like '诺基亚%'; -
把 goods 表中商品名为 ’诺基亚xxxx’ 改为 ’HTCxxxx’
select goods_id, concat('HTC',substring(goods_name,4)) from goods where goods_name like '诺基亚%'; # 1. 函数concat(a,b) 将ab两个字符串连接成一个字符串 # 2. 函数substring(string,position)从特定位置开始的字符串返回一个给定长度的子字符串
- 小结:当涉及到多重条件查询需要用到运算符、and、or、not……之类来修饰条件时
* 一定要先弄清楚条件之间的分类
* 使用( )将其分类,避免优先级之类的问题
-
面试题 (mian表)
-
将 mian 表中处于 [20,29] 之间的 num 值改成 20 , [30,39] 之间的 num 值改成 30 ,一句 sql 完成。
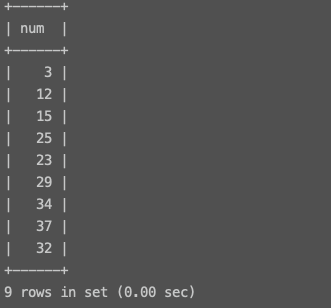
update mian set num = floor(num/10)*10 where num between 20 and 39; # 函数floor(n) 返回一个不大于n的最大整数
-
7. group by 分组与统计函数
-
常用统计函数
1. max() # 获取最大值 2. min() # 获取最小值 3. avg() # 求取平均值 4. sum() # 求和 5. count() # 计算行数/条数 *特别注意count()返回的是一个总行数 6. distinct() # 求有多少种不同解 -
另外注意:当出现 group by 分组种不能配对的情况,该字段取查询时候第一次出现的值
8. having 筛选结果集
注:having 并不一定 与 where共存(这种情况可以看做类似where 1这种语句可以忽略),但一定在 where 之后;可以存在只有 having 而没有 where 的情况
-
查询 goods 表中商品比市场价低出多少?
select goods_id ,goods_name,market_price - shop_price from goods ; -
查询 goods 表中商品比市场价低出至少 200 元的商品
select goods_id ,goods_name,(market_price - shop_price) as discount from goods where market_price - shop_price ; # 注意为什么where后面不能用 discountselect goods_id,goods_name,(market_price-shop_price) as discount from goods having discount>200;
9. 综合练习(result表)

- 有以上 result 表,要求查询出 2 门及 2 门以上不及格的平均成绩 ※※※经典题目※※※
- 难点分析:如何找出 2 门及 2 门以上不及格的同学
-
一种典型错误 ❌ 【错误点:对 count 和比较运算两者结合的理解错误】
select name , count(score<60) as gks , avg(score) as pjf from result group by name having gks >= 2; +--------+-----+---------+ | name | gks | pjf | +--------+-----+---------+ | 张三 | 3 | 60.0000 | | 李四 | 2 | 50.0000 | +--------+-----+---------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 貌似是正确的,但只针对此种情况验证:假如增加 1 行数据
values('赵六','语文',88),('赵六','数学',99),('赵六','物理',100)再次执行上面的 sql 语句,将会得到如下结果
+--------+-----+---------+ | name | gks | pjf | +--------+-----+---------+ | 张三 | 3 | 60.0000 | | 李四 | 2 | 50.0000 | | 赵六 | 3 | 95.6667 | +--------+-----+---------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 很明显有语义上的错误! # 实际上count(score)和count(score<60)查询出的结果是一样的,函数count()返回的是总行数! -
正确解题思路✅(逆向思维)
1. select name ,avg(score),as pjf from result group by name; +--------+---------+ | name | pjf | +--------+---------+ | 张三 | 60.0000 | | 李四 | 50.0000 | | 王五 | 30.0000 | | 赵六 | 95.6667 | +--------+---------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 1. 查询出所有同学的平均分,并分组2. select name, score<60 from result; +--------+----------+ | name | score<60 | +--------+----------+ | 张三 | 0 | | 张三 | 1 | | 张三 | 1 | | 李四 | 1 | | 李四 | 1 | | 王五 | 1 | | 赵六 | 0 | | 赵六 | 0 | | 赵六 | 0 | +--------+----------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 2. 查看每个同学的挂科情况;这里运用了逻辑运算,这个点也很重要! # score<60 若真则返回0 若假则返回13. select name , sum(score<60) as gks from result group by name; +--------+------+ | name | gks | +--------+------+ | 张三 | 2 | | 李四 | 2 | | 王五 | 1 | | 赵六 | 0 | +--------+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 3. 计算每位同学的总挂科数4. select name ,sum(score<60) as gks ,avg(score) as pjf from result group by name having gks >=2; +--------+------+------------+ | name | gks | pjf | +--------+------+------------+ | 张三 | 2 | 60.0000 | | 李四 | 2 | 50.0000 | +--------+------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 4. 整合1.3步,得到结果集,并筛选出gks大于等于2的同学
10. order by 排序(在内存中排序)与 limit (限制范围)综合查询
-
按栏目由低到高排序,栏目内部按价格由高到低排序
select goods_id ,goods_name ,shop_price ,cat_id from goods order by cat_id desc,shop_price asc; -
取出价格最高的前 3 名商品
select goods_id ,goods_name,shop_price from goods order by shop_price desc limit 0,3; # limit x,y 其中x代表起始位置也就是偏移量,y代表返回最大行数;x初始值为0 -
取出商品市场价前 10 到 25 的商品信息
select goods_id ,goods_name,market_price from goods order by market_price limit 11,15;
11. 子查询
mysql 子查询是嵌套在另一个查询(如select、insert、update或者delete)中的查询。这里重点总结了嵌套在 select 中的子查询
- where 子查询【以内层查询结果(通常为变量)作为外层查询的比较条件】
- 如何查询每个栏目下面最新的那件产品?
- 语义解析:栏目列 :
cat_id;最新的那件产品⇔goods_id为最大值时所对应的那一件产品
- 语义解析:栏目列 :
# 1. 陷阱演示 ❌
# 思路:最新的商品 max(goods_id);每个栏目 group by cat_id
select max(goods_id) ,goods_name ,cat_id ,shop_price from goods group by cat_id ;
# 报错:ERROR 1055 (42000): Expression #2 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY clause and contains nonaggregated
# column 'zion.goods.goods_name' which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause;
# this is incompatible with sql_mode=only_full_group_by 大概意思是 语义缺陷,不兼容
#分析:”先查询再排序“ group by cat_id 但是goods_name,shop_price应该取谁的呢?
# 2. 正确方法 ✅
# 思路:”先排序再查询“ 需要用到子查询/连接查询
# ”先排序“
select max(goods_id),cat_id from goods group by cat_id;
+---------------+--------+
| max(goods_id) | cat_id |
+---------------+--------+
| 16 | 2 |
| 32 | 3 |
| 18 | 4 |
| 23 | 5 |
| 7 | 8 |
| 6 | 11 |
| 26 | 13 |
| 30 | 14 |
| 28 | 15 |
+---------------+--------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# ”再查询“
select cat_id ,goods_id, goods_name, shop_price from goods where goods_id in (select max(goods_id) from goods group by cat_id);
+--------+----------+----------------------------------------+------------+
| cat_id | goods_id | goods_name | shop_price |
+--------+----------+----------------------------------------+------------+
| 11 | 6 | 胜创kingmax内存卡 | 42.00 |
| 8 | 7 | 诺基亚n85原装立体声耳机hs-82 | 100.00 |
| 2 | 16 | 恒基伟业g101 | 823.33 |
| 4 | 18 | 夏新t5 | 2878.00 |
| 5 | 23 | 诺基亚n96 | 3700.00 |
| 13 | 26 | 小灵通/固话20元充值卡 | 19.00 |
| 15 | 28 | 联通50元充值卡 | 45.00 |
| 14 | 30 | 移动20元充值卡 | 18.00 |
| 3 | 32 | 诺基亚n85 | 3010.00 |
+--------+----------+----------------------------------------+------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 分析:1.由此可见 select max(goods_id) ,goods_name ,shop_price from goods 除了goods_id符合题意,其它的在语义上就是存在缺陷的;
# 这是一个有缺陷的语句。
# 2.列就是变量;把查询这个变量(列)的sql语句作为外层sql语句的比较条件,这么做的目的是为了我们每次更新商品后,都能取得最新的那个商品。
# 这样也不会出现 列与列不匹配错乱的情况
-
查询出编号位19的商品的栏目名称[栏目名称放在category表中]
select cat_id,cat_name from category where cat_id = ( select cat_id from goods where goods_id = 19 ); +--------+-----------+ | cat_id | cat_name | +--------+-----------+ | 3 | GSM手机 | +--------+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- from 子查询 【将查询出来的结果当成一个新”表“来操作】
-
如何用 from 子查询查出上面 where 子查询的面对的问题
# 解决思路 同样还是 ‘先排序’;‘再查询’ # 1. 先排序 按cat_id 升序 goods_id 降序 select goods_id , goods_name , cat_id ,shop_price from goods order by cat_id asc,goods_id desc ; # 2. 再查询 不同的cat_id对应的第一行都是最大的goods_id select goods_id , goods_name , cat_id ,shop_price from (select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price from goods order by cat_id asc,goods_id desc) group by cat_id ; # 上述只是一个理解from子查询的列子 # 可能在mysql 5.7 某些版本 和 8.0 会报错
- exists 子查询 【内层 sql 语句作为外层 sql 语句的表达判定式】
- 查出所有商品的栏目下有商品的栏目;用 exists 查询 涉及 goods 和 category 表
select cat_id , cat_name from category where exists (select * from goods where goods.cat_id = category.cat_id); +--------+---------------------------+ | cat_id | cat_name | +--------+---------------------------+ | 2 | CDMA手机 | | 3 | GSM手机 | | 4 | 3G手机 | | 5 | 双模手机 | | 8 | 耳机 | | 11 | 读卡器和内存卡 | | 13 | 小灵通/固话充值卡 | | 14 | 移动手机充值卡 | | 15 | 联通手机充值卡 | +--------+---------------------------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
12. 联表查询
- 左连接查询 [left join]
- 以左表为基础的查询
-
语法:select …… from table1 left join table2 on table1.column1 = table2.column2 ;
-
练习:查询价格大于2000元的商品及栏目名称[左连接]
select goods.goods_id, category.cat_name,goods.goods_name,goods.shop_price from goods left join category on goods.cat_id = category.cat_id where goods.shop_price > 2000; +----------+--------------+-------------------+------------+ | goods_id | cat_name | goods_name | shop_price | +----------+--------------+-------------------+------------+ | 9 | GSM手机 | 诺基亚e66 | 2298.00 | | 14 | 3G手机 | 诺基亚5800xm | 2625.00 | | 17 | GSM手机 | 夏新n7 | 2300.00 | | 18 | 3G手机 | 夏新t5 | 2878.00 | | 22 | GSM手机 | 多普达touch hd | 5999.00 | | 23 | 双模手机 | 诺基亚n96 | 3700.00 | | 32 | GSM手机 | 诺基亚n85 | 3010.00 | +----------+--------------+-------------------+------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 右连接查询 [right join]
- 以右表为基础的查询
-
语法:select …… from table1 right join table2 on table1.column1 = table2.column2 ;
-
练习:查询价格大于2000元的商品及栏目名称[右连接]
select goods.goods_id,category.cat_name ,goods.goods_name,goods.shop_price from goods right join category on goods.cat_id = category.cat_id where goods.shop_price > 2000; +----------+--------------+-------------------+------------+ | goods_id | cat_name | goods_name | shop_price | +----------+--------------+-------------------+------------+ | 9 | GSM手机 | 诺基亚e66 | 2298.00 | | 14 | 3G手机 | 诺基亚5800xm | 2625.00 | | 17 | GSM手机 | 夏新n7 | 2300.00 | | 18 | 3G手机 | 夏新t5 | 2878.00 | | 22 | GSM手机 | 多普达touch hd | 5999.00 | | 23 | 双模手机 | 诺基亚n96 | 3700.00 | | 32 | GSM手机 | 诺基亚n85 | 3010.00 | +----------+--------------+-------------------+------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 比较left join 和 right jion 发现查询出来的结果是一样的 # 其实两者是一种对称关系,只不过人们更习惯以左表为基础
- 内连接查询 [inner join]
- 把表当做一个集合概念,查询结果是两表的交集
-
语法:select …… from table1 inner join table2 on table1.column1 = table2.column2 ;
-
练习:查询出所有栏目下有商品的商品信息
select goods.goods_id ,category.cat_id ,goods.goods_name, category.cat_name,goods.shop_price from goods inner join category on goods.cat_id = category.cat_id;
13. 经典面试题(用友)
-
根据给出的表结构按要求写出sql语句
-
Match 赛程表
字段名称 字段类型 描述 matchID int 主键 hostTeamID int 主队的ID guestTeamID int 客队的ID matchResult varchar(20) 比赛结果,如(2:0) matchTime date 比赛开始时间 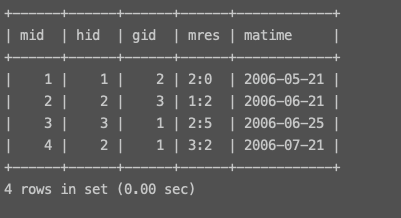
-
Team 参赛队伍表
字段名称 字段类型 描述 teamID int 主键 teamName varchar(20) 队伍名称 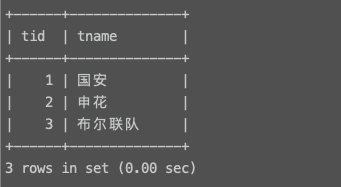
※ Match表中的hostTeamID与guestTeamID都与Team表中的teamID关联
※ 查出2006-6-1 到 2006-7-1 之间举行的所有比赛,并用以下形式列出:
※ 拜仁 2:0 不莱梅 2006-6-21
# 我最开始的做法: select gTeam.tname,Matc.mres,hTeam.tname,Matc.matime from (select Matc.gid,Team.tname from Matc left join Team on Matc.gid = Team.tid) as gTeam, (select Matc.hid,Team.tname from Matc left join Team on Matc.hid = Team.tid) as hTeam, Matc where Matc.matime between "2006-6-1" and "2006-7-1"; # 实现思路: # 第一步先查出Matc.gid与Team.tid相关联的表格命名为gTeam select Matc.gid,Team.tname from Matc left join Team on Matc.gid = Team.tid; +------+--------------+ | gid | tname | +------+--------------+ | 1 | 国安 | | 1 | 国安 | | 2 | 申花 | | 3 | 布尔联队 | +------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 第二步再查出Matc.hid与Team.tid相关联的表格命名为hTeam select Matc.hid,Team.tname from Matc left join Team on Matc.hid = Team.tid; +------+--------------+ | hid | tname | +------+--------------+ | 1 | 国安 | | 2 | 申花 | | 2 | 申花 | | 3 | 布尔联队 | +------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 第三步再针对gTeam,hTeam,Matc3表联合查询并筛选出符合日期的比赛 # 题意理解错误
# 正确思路 # 1. 使用team表中tname代替mat表中对应的hid select matchs.*,team.tname as hname from matchs left join team on matchs.hid = team.tid; +------+------+------+------+------------+--------------+ | mid | hid | gid | mres | matime | hname | +------+------+------+------+------------+--------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2:0 | 2006-05-21 | 国安 | | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1:2 | 2006-06-21 | 申花 | | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3:2 | 2006-07-21 | 申花 | | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2:5 | 2006-06-25 | 布尔联队 | +------+------+------+------+------------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 2. 再将查询出来的结果集当做是一张新的表对team表再来一次左连接查询 select matchs.*,team.tname as hname,t1.tname as gname from matchs left join team on matchs.hid = team.tid left join team as t1 on matchs.gid = t1.tid; +------+------+------+------+------------+--------------+--------------+ | mid | hid | gid | mres | matime | hname | gname | +------+------+------+------+------------+--------------+--------------+ | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3:2 | 2006-07-21 | 申花 | 国安 | | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2:5 | 2006-06-25 | 布尔联队 | 国安 | | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2:0 | 2006-05-21 | 国安 | 申花 | | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1:2 | 2006-06-21 | 申花 | 布尔联队 | +------+------+------+------+------------+--------------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 3. 替换对应的hid,gid select hid,t1.tname as hname,mres,t2.tname as gname,matime from matchs left join team as t1 on matchs.hid = t1.tid left join team as t2 on matchs.gid = t2.tid; +------+--------------+------+--------------+------------+ | hid | hname | mres | gname | matime | +------+--------------+------+--------------+------------+ | 2 | 申花 | 3:2 | 国安 | 2006-07-21 | | 3 | 布尔联队 | 2:5 | 国安 | 2006-06-25 | | 1 | 国安 | 2:0 | 申花 | 2006-05-21 | | 2 | 申花 | 1:2 | 布尔联队 | 2006-06-21 | +------+--------------+------+--------------+------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 4. 筛选最终结果 select t1.tname as hname,mres,t2.tname as gname,matime from matchs left join team as t1 on matchs.hid = t1.tid left join team as t2 on matchs.gid = t2.tid where matime between "2006-06-01" and "2006-07-01"; +--------------+------+--------------+------------+ | hname | mres | gname | matime | +--------------+------+--------------+------------+ | 布尔联队 | 2:5 | 国安 | 2006-06-25 | | 申花 | 1:2 | 布尔联队 | 2006-06-21 | +--------------+------+--------------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) -
14. union查询
-
union查询的特点是将2条或者多条sql的查询结果合并成1个结果集
-
注意点
- 取的两个表投影查找的字段列数要相同,列名可不一致(默认使用第一个表的列名)
- 碰到完全相同的行,将会被合并【合并是非常耗时的,union all 就不需要比较字段合并】
- union查询的内部子句中不用写order by子句,意义不大! 但可以对查询结果集进行排序
-
练习题
-
同时查询goods表中cat_id为2和4的商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name from goods where cat_id =2 union select goods_id,cat_id,godos_name from goods where cat_id =4;
-
-
union查询面试题
+------+------+ | id | num | +------+------+ | a | 5 | | b | 10 | # a表 | c | 15 | | d | 10 | +------+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) +------+------+ | id | num | +------+------+ | b | 5 | | c | 15 | # b表 | d | 20 | | e | 99 | +------+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 将a、b表中id相同的两个num值相加 # 合并a、b两表 mysql> select * from a union all select * from b; +------+------+ | id | num | +------+------+ | a | 5 | | b | 10 | | c | 15 | | d | 10 | | b | 5 | | c | 15 | | d | 20 | | e | 99 | +------+------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 将id分组,并将相同id用sum()函数求和 select id,sum(num) from (select * from a union all select * from b) as tmp group by id ; +------+----------+ | id | sum(num) | +------+----------+ | a | 5 | | b | 15 | | c | 30 | | d | 30 | | e | 99 | +------+----------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) # union all 合并所有行
15. 相关列类型
-
数值型
- 整型(tinyint、smallint、mediumint、int、bigint)
- 浮点型(float、double)
- 定点型(decimal)
-
字符型
- 定长字符串(char)
- 变长字符串(varchar)
-
日期时间
- 日期(date)
- 时间(time)
- 日期时间(datetime)
- 时间戳(int型)
-
整型列
类型 长度 范围 tinyint 1个字节 signed: [-128,127] ; unsigned: [0,255] smallint 2个字节 signed :[-215,215-1] or [-32768,32767] ; unsigned: [0,65535] mediumint 3个字节 signed: [-223,223-1] or [-8388608,8838607] ; unsigned: [0,16777215] int 4个字节 signed:[-231,231-1] or[-2.1billion,2.1billion] ; unsigned: [0,4.2billion] bigint 8个字节 signed:[-263,263-1] ; unsigned: [0,264-1]
- 注
- unsigned 【无符号属性】
- zerofill 【用 0填充至固定宽度;填充宽度】
- ※ 若用zerofill修饰,就代表已经是unsigned属性了; 即负数不需要用0填充
- int(M)其中的M代表储存宽度;M属性只有和zerofill配合使用才有意义
-
浮点列与定点列
类型 长度 其它 float(M,D) 4个字节 范围:[-2128,2128] double(M,D) 8个字节 范围:[-21024,21024] decimal(M,D) (M+2)个字节 范围无限;M表示【总位数】;D表示【小数点后面的位数】 -
字符型列
类型 长度 其它 char(M) 定长:M字节 固定M字节,磁盘空间利用率可能达到100% varchar(M) 变长:(M+1或2)字节 在储存时,表头会增加1到2字节说明该字符串的长度
-
注
-
varchar的利用率一定低于100%
-
内存的定长寻址会快很多,建议M相对较小的,都用char
-
char型,如果字符串不够M个宽度,内存存储是会用空格在字符右边补齐,取出再删除
- eg: 对于字符’ hello ’
char取出之后是’ hello’ ,而varchar取出之后是’ hello ’ (注意空格)
- eg: 对于字符’ hello ’
-
text --大文本类型 ;blob(不必考虑字符集的问题) --二进制类型
- 对于如:论文、博客……等大段文本用text ;图像、音频等二进制信息用blob来储存
-
enum(‘value1’,’value2’……) --枚举类型 ;set(‘value1’,’value2’……) --集合类型
- eg: enum(‘男’,’女’) 该列所储存的值只能是’男’或’女’ 单选值储存
- 而set() 是复选值储存,但值也只能在列举的元素种选取且set()最多列举64个值
-
-
日期时间型列
类型 其它 year 【1个字节】 范围: [1901,2155] Date 格式:’YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ ;范围: {[1000-01-01 00:00:00],[9999-12-31 23:59”59]} time 格式: ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ ;范围: {[1000-01-01],[9999-12-31]} datetime 格式:’YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ ;范围: {[1000-01-01 00:00:00],[9999-12-31 23:59”59]} timestamp 范围: {从1970-01-01 00:00:00为初始状态,到2038-01-19 03:14:08} ;[0,231]
- 小技巧:一般存注册时间、商品发布时间等,并不是用datetime,而是用时间戳存储,因为便于计算
16. 日期(date) 字符串(str) 时间戳(timestamp) 互转
-
date转字符串、date转时间戳、字符串转date、字符串转时间戳、时间戳转date、时间戳转字符串
# 涉及相关函数 date_format(date, format) 函数,MySQL日期格式化函数date_format() unix_timestamp() 函数 str_to_date(str, format) 函数 from_unixtime(unix_timestamp, format) 函数,MySQL时间戳格式化函数from_unixtime
-
date转str
select date_farmat(now(),'%Y-%m-%d'); +-------------------------------+ | date_format(now(),'%Y-%m-%d') | +-------------------------------+ | 2021-01-05 | +-------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
date转timestamp
select unix_timestamp(now()); +-----------------------+ | unix_timestamp(now()) | +-----------------------+ | 1609779395 | +-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
str转date
select str_to_date('2021-01-05','%Y-%m-%d'); +--------------------------------------+ | str_to_date('2021-01-05','%Y-%m-%d') | +--------------------------------------+ | 2021-01-05 | +--------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
str转timestamp
select unix_timestamp('2021-01-05'); +------------------------------+ | unix_timestamp('2021-01-05') | +------------------------------+ | 1609776000 | +------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
timestamp转date
select from_unixtime(1609779395); +---------------------------+ | from_unixtime(1609779395) | +---------------------------+ | 2021-01-05 00:56:35 | +---------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
timestamp转str
select from_unixtime(1609779395,'%Y-%m-%d %h:%m:%s'); +-----------------------------------------------+ | from_unixtime(1609779395,'%Y-%m-%d %h:%m:%s') | +-----------------------------------------------+ | 2021-01-05 12:01:35 | +-----------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) # UTC时间
-
附表 (Mysql 日期格式化(format)取值范围)
值 含义 秒 %S、%s 两位数字形式的秒( 00,01, ..., 59) 分 %I、%i 两位数字形式的分( 00,01, ..., 59) 小时 %H 24小时制 两位数形式小时(00,01, ...,23) %h 12小时制 两位数形式小时(00,01, ...,12) %k 24小时制 数形式小时(0,1, ...,23) %l 12小时制 数形式小时(0,1, ...,12) %T 24小时制 时间形式(HH:mm:ss) %r 12小时制 时间形式(hh:mm:ss AM 或 PM) %p AM上午或PM下午 周 %W 一周中每一天的名称 (Sunday,Monday, ...,Saturday) %a 一周中每一天名称的缩写(Sun,Mon, ...,Sat) %w 以数字形式标识周 (0=Sunday,1=Monday, ...,6=Saturday) %U 数字表示周数 星期天为周中第一天 %u 数字表示周数 星期一为周中第一天 天 %d 两位数字表示月中天数(01,02, ...,31) %e 数字表示月中天数(1,2, ...,31) %D 英文后缀表示月中天数(1st,2nd,3rd ...) %j 以三位数字表示年中天数(001,002, ...,366) 月 %M 英文月名(January,February, ...,December) %b 英文缩写月名(Jan,Feb, ...,Dec) %m 两位数字表示月份(01,02, ...,12) %c 数字表示月份(1,2, ...,12) 年 %Y 四位数字表示的年份(2015,2016...) %y 两位数字表示的年份(15,16...) %文字 文字输出 直接输出文字内容
17. 列属性
- 列属性:约束,真正约束字段的是数据类型,但是数据类型的约束很单一,需要一些额外的约束,来更加保证数据的合法性。
- 列属性有:null , not null , default , primary key , unique key , auto_increment , comment
-
空属性
- null(不存在) 【 一般列属性不设置为null,null不便于查询】
- not null 【常用 default not null】
-
主键(primary key)
- 一张表中只有一个字段可以使用对应的键,用来唯一约束该字段里面的数据,不能重复;主键也是索引
-
增加主键
-
1.在创建表时直接在字段后面跟primary key关键字(且不能为空)
create table my_pri( name varchar(20) not null, number char(10) primary key ) charset utf8; +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | | | number | char(10) | NO | PRI | NULL | | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 优点:非常直接,确定只能使用一个字段作为主键 -
2.在创建表的时候,在所有的字段之后,使用primary key(主键字段列表)来创建主键(若有多个字段作为主键,则称为复合主键)
# 复合主键 create table my_pri2( number char(10) comment '学号', course char(10) comment '课程', score tinyint unsigned default 0, # 增加主键限制:学号和课程应该是对应的,具有唯一性 primary key(number,course) ) charset utf8; +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | number | char(10) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | course | char(10) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | score | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | 0 | | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 复合主键还是一个主键,只不过是多个字段共同组合而成的 # 唯一性的标准是字段组合起来不同 -
3.当表已经创建好之后,可以额外追加主键:通过修改表字段属性,或者直接追加
alter table table_name add primary key(字段列表) # 前提是表中字段对应的数据是不重复的
-
- 自动增长属性 (auto_increment)
-
1.自增长特点
-
任何一个字段做自增长,前提是本身是一个索引(key那一栏有值)
-
自增长的数据类型必须是整数型
-
一张表最多有一个自增长
-
自增长属性若需要属性,则需要先删除这个自增长属性,再增加芯的自增长
-
如果修改自增长的基数,则该值必须比当前自增长的值要大
alter table table_name auto_increment = 值;
-
-
2.删除主键
alter table table_name drop primary key ; # 自增长通常跟主键搭配 -
3.为什么自增长从1开始,为什么自增都为1(由系统变量控制)
show variables like 'auto_increment%'; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | auto_increment_increment | 1 | | auto_increment_offset | 1 | +--------------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 可以修改,但无意义 -
4.删除自增长
alter table table_name modify 字段 类型 # 自增长是字段的一个属性:可以通过modify来修改(保证字段没有auto_increment即可)
- 唯一键 (unique key)
- 一张表往往有很多字段具有唯一性,但是主键只有一个;唯一键unique key 就可以解决此问题
- 唯一键默认允许字段为空,而且是多个字段为空;空值不做比较
-
1.创建唯一键
-
在创建表时直接放在字段后面跟unique key 或者 unique关键字
create table my_unique1 ( number char(10) unique )charset utf8; +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | number | char(10) | YES | UNI | NULL | | +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
在创建表时,在所有的字段之后,使用unique key(唯一键字段列表)来创建唯一键(如果有多个字段作为唯一键,则称为复合唯一键)
create table my_unique2( number char(10) comment '学号', course char(10) comment '课程', score tinyint unsigned default 0, # 增加唯一键列表 unique key(number,course) ) charset utf8; +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | number | char(10) | YES | MUL | NULL | | | course | char(10) | YES | | NULL | | | score | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | 0 | | +--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) -
当表已经创建好了之后,可以额外追加唯一键
alter table table_name add unique key (字段列表)
-
-
2.唯一键特点以及与主键的区别
-
唯一键与主键本质相同,区别就是唯一键允许字段的值为空,并且是多个值为空;如果唯一键添加not null 属性,约束和主键一样
-
更新/删除唯一键
-
更新:先删除后增加(唯一键有多个,可以不删除)
-
删除:
alter table table_name drop index 索引名 # 唯一键默认是用字段名作为索引名
-
-
-
列操作语法
# 增 alter table 表名 add 列名 列类型[列属性] # 默认该列是存放在表最后的【使用after 列名 可以放在指定列】 # 删 alter table 表名 drop column 列名 列类型 [列属性] # 改 alter table 表名 change 旧列名 新列名 [新列类型][新列属性] alter table 表名 modify 列名 [新列类型][新列属性] # modify不能修改列名
18. 视图(view)
-
视图简介
- view 又称虚拟表,view 其实就是一条查询 sql 语句的结果集(将常用的 sql 查询结果集虚拟成一张表存放在内存中)
-
语法
- create view 视图名 as (查询sql语句结果集)
- select ** from 视图名 # 当再次使用时*
-
视图特点
-
权限的控制
- 比如某几个列允许用户查询,而其他列不允许,可以通过视图开放一种一部分列,达到权限的控制
-
简化复杂的查询
# 查询每个栏目下商品的平均价格并按平均价格排序,然后查出平均价格前3高的栏目 # 正常做法 select cat_id ,avg(shop_price) as balance from goods group by cat_id order by balance desc limit 0,3; # 视图简化 duck视图 create view duck as select cat_id, avg(shop_price) as balance from goods group by cat_id; select * from duck order by balance desc limit 0,3; -
对视图的操作
- 视图是对物理表的一个“投影”,两者相互影响;即一方改动,另一方随之改动
- 若虚拟表中含有函数(经过计算),则不能修改;两表一一对应
# eg: create view duck as select cat_id, avg(shop_price) as balance from goods group by cat_id; update duck set balance =80 where cat_id = 11; # ERROR 1288 (HY000): The target table duck of the UPDATE is not updatable # duck目标不可更新 # 因为duck和goods为一一对应关系,duck修改了,不能正确映射回goods表对应的列
-
19. 索引(index)
-
索引简介
- 索引是对数据库中一列或多列的值进行排序的一种结构,使用索引可快速访问数据库中特定信息
- 想当天图书的“目录”,根据目录,迅速定位查找内容的位置
-
索引的优缺点
- 优点
- 加快了查询时对数据的检索速度
- 创建唯一性索引,保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性
- 加速表和表之间的连接
- 在使用分组和排序子句进行数据检索时,可以显著减少查询中分组和排序的时间
- 缺点
- 索引是另外独立于数据外存放的一个二进制文件【需要物理空间/.MYI】
- 对表数据进行增删改的维护操作中,索引也要动态的变化【降低维护速度】
- 其它特点
- 在创建索引之前,您必须确定要使用那些列以及要创建的索引类型
- 索引不是越多越好(一般在查询频率多、且重复度小的列上加)
- 优点
-
索引类型
- key 列名(索引名) ==> 普通索引 ==> 纯粹提高查询速度
- unique key 列名(索引名)==>唯一索引==>提高速度,且约束数据唯一性
- primary key 列名 ==> 主键索引==>唯一主键
- fulltext ==> 全文索引==>中文下,不起作用,要分词索引;用第三方解决方案 (sphinx)
-
操作索引
1. show index from 表名 # 查看索引 2. alter table 表名 add index column(索引名) # 添加索引 3. alter table 表名 drop index 索引名 # 删除索引 -
其它
- 在建立索引是,对列中一部分字符进行索引 eg:unique key /key 列名(索引名(索引长度))
- 在建立索引时,对2个或多个列进行索引
- 索引存在覆盖 ==> 冗余索引有时候在开发中是必要的
20. 常用九大函数
-
数学函数
1. abs(x) 返回x的绝对值 2. bin(x) 返回x的二进制(oct返回八进制,hex返回十六进制) 3. ceiling(x) 返回大于x的最小整数值==>向上取整 4. exp(x) 返回值e(自然对数的底)的x次方 5. floor(x) 返回小于x的最大整数值==>向下取整 6. greatest(x1,x2,...,xn) 返回集合中最大的值 7. least(x1,x2,...,xn) 返回集合中最小的值 8. ln(x) 返回x的自然对数 9. log(x,y) 返回x的以y为底的对数 10.mod(x,y) 返回x/y的模(余数) 11.pi() 返回pi的值(圆周率) 12.rand() 返回0或1的随机值,可以通过提供一个参数(种子)使rand()生成器生成1. 13.round(x,y) 返回参数x的四舍五入的有y位小数的值 14.sign(x) 返回代表数字x的符号的值 15.sqrt(x) 返回一个数的平方根 16.truncate(x,y) 返回数字x截短为y位小数的结果 -
聚合函数
1. avg(col)返回指定列的平均值 2. count(col)返回指定列中非null值的个数 3. min(col)返回指定列的最小值 4. max(col)返回指定列的最大值 5. sum(col)返回指定列的所有值之和 6. group_concat(col) 返回由属于一组的列值连接组合而成的结果 -
字符串函数
1. ascii(char) 返回字符的ascii码值 2. bit_length(str) 返回字符串的比特长度 3. concat(s1,s2...,sn) 将s1,s2...,sn连接成字符串 4. concat_ws(sep,s1,s2...,sn) 将s1,s2...,sn连接成字符串,并用sep字符间隔 5. insert(str,x,y,instr) # 将字符串str从第x位置开始,y个字符长的子串替换为字符串instr,返回结果 6. find_in_set(str,list) 分析逗号分隔的list列表,如果发现str,返回str在list中的位置 7. lcase(str)或lower(str) 返回将字符串str中所有字符改变为小写后的结果 8. left(str,x) 返回字符串str中最左边的x个字符 9. length(s) 返回字符串str中的字符数 10.ltrim(str) 从字符串str中切掉开头的空格 11.position(substr,str) 返回子串substr在字符串str中第一次出现的位置 12.quote(str) 用反斜杠转义str中的单引号 13.repeat(str,srchstr,rplcstr) 返回字符串str重复x次的结果 14.reverse(str) 返回颠倒字符串str的结果 15.right(str,x) 返回字符串str中最右边的x个字符 16.rtrim(str) 返回字符串str尾部的空格 17.strcmp(s1,s2) 比较字符串s1和s2 18.trim(str) 去除字符串首部和尾部的所有空格 19.ucase(str)或upper(str) 返回将字符串str中所有字符转变为大写后的结果 -
日期和时间函数
1. curdate()或current_date() 返回当前的日期 2. curtime()或current_time() 返回当前的时间 3. date_add(date,interval int keyword) # 返回日期date加上间隔时间int的结果(int必须按照关键字进行格式化) # 如:select date_add(current_date,interval 6 month); +-----------------------------------------+ | date_add(current_date,interval 6 month) | +-----------------------------------------+ | 2021-07-05 | +-----------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 4. date_format(date,fmt) 依照指定的fmt格式格式化日期date值 5. date_sub(date,interval int keyword) # 返回日期date加上间隔时间int的结果(int必须按照关键字进行格式化) # 如:select date_sub(current_date,interval 6 month); +-----------------------------------------+ | date_sub(current_date,interval 6 month) | +-----------------------------------------+ | 2020-07-05 | +-----------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 6. dayofweek(date) 返回date所代表的一星期中的第几天(1~7) 7. dayofmonth(date) 返回date是一个月的第几天(1~31) 8. dayofyear(date) 返回date是一年的第几天(1~366) 9. dayname(date) 返回date的星期名 # 如:select dayname(current_date); +-----------------------+ | dayname(current_date) | +-----------------------+ | Tuesday | +-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 10.from_unixtime(ts,fmt) 根据指定的fmt格式,格式化unix时间戳ts 11.hour(time) 返回time的小时值(0~23) 12.minute(time) 返回time的分钟值(0~59) 13.month(date) 返回date的月份值(1~12) 15.monthname(date) 返回date的月份名, # 如:select monthname(current_date); +-------------------------+ | monthname(current_date) | +-------------------------+ | January | +-------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 16.now() 返回当前的日期和时间 +---------------------+ | now() | +---------------------+ | 2021-01-05 14:45:57 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 17.quarter(date) 返回date在一年中的季度(1~4) # 如select quarter(current_date); +-----------------------+ | quarter(current_date) | +-----------------------+ | 1 | +-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 18.week(date) 返回日期date为一年中第几周(0~53) 19.year(date) 返回日期date的年份(1000~9999) # 示例 # 获取当前系统时间 1. select from_unixtime(unix_timestamp()); +---------------------------------+ | from_unixtime(unix_timestamp()) | +---------------------------------+ | 2021-01-05 14:50:14 | +---------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 2. select extract(year_month from current_date); +---------------------------------------+ | extract(year_month from current_date) | +---------------------------------------+ | 202101 | +---------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) # extract 提取 3. select period_diff(202101,199605); +----------------------------+ | period_diff(202101,199605) | +----------------------------+ | 296 | +----------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) # 返回两个日期之间的差值(月数) Σ(⊙▽⊙"a 不知不觉已经296个月了…… -
加密函数
1. aes_encrypt(str,key) # 返回用密钥key对字符串str利用高级加密标准算法加密后的结果 # 调用aes_encrypt的结果是一个二进制字符串,以blob类型存储 2. aes_decrypt(str,key) # 返回用密钥key对字符串str利用高级加密标准算法解密后的结果 3. decode(str,key) 使用key作为密钥解密加密字符串str 4. encrypt(str,salt) # 使用unixcrypt()函数,用关键词salt(一个可以惟一确定口令的字符串,就像钥匙一样) # 加密字符串str 5. encode(str,key) # 使用key作为密钥加密字符串str,调用encode()的结果是一个二进制字符串,它以blob类型存储 6. md5() 计算字符串str的md5校验和 7. password(str) # 返回字符串str的加密版本,这个加密过程是不可逆转的,和unix密码加密过程使用不同的算法。 8. sha() 计算字符串str的安全散列算法(sha)校验和 # 示例 1. select encrypt('root','salt'); +------------------------+ | encrypt('root','salt') | +------------------------+ | saFKJij3eLACw | +------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) 2. select decode(encode('renjun','key'),'key'); +--------------------------------------+ | decode(encode('renjun','key'),'key') | +--------------------------------------+ | renjun | +--------------------------------------+ 1 row in set, 2 warnings (0.00 sec) # 加解密放一起 3. select md5('9527'); +----------------------------------+ | md5('9527') | +----------------------------------+ | 52569c045dc348f12dfc4c85000ad832 | +----------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 4. select sha('9527'); +------------------------------------------+ | sha('9527') | +------------------------------------------+ | ed2abfe64348a34c34926f1714939d93d4f62607 | +------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
控制流函数
1. case when[test1] then [result1]...else [default] end # 如果testn是真,则返回resultn,否则返回default 2. case [test] when[val1] then [result]...else [default]end # 如果test和valn相等,则返回resultn,否则返回default 3. if(test,t,f) 如果test是真,返回t;否则返回f 4. ifnull(arg1,arg2) 如果arg1不是空,返回arg1,否则返回arg2 5. nullif(arg1,arg2) 如果arg1=arg2返回null;否则返回arg1 # if()函数在只有两种可能结果时才适合使用 # 然而,在现实世界中,我们可能发现在条件测试中会需要多个分支 # 在这种情况下,mysql提供了case函数 6. case [expression to be evaluated] when [val 1] then [result 1] when [val 2] then [result 2] when [val 3] then [result 3] …… when [val n] then [result n] else [default result] end # 若每个一个when-then都不匹配,则返回else指定的默认结果 # 若此种情况下没有指定else块,mysql将会返回null # 此外,case函数还有另外一种句法 case when[conditional test 1] then [result 1] when[conditional test 2] then [result 2] else [default result] end # 这种条件下,返回的结果取决于相对应的条件测试是否为真 # 示例 1. select ifnull(1,2), ifnull(null,10),ifnull(4*null,'false'); +-------------+-----------------+------------------------+ | ifnull(1,2) | ifnull(null,10) | ifnull(4*null,'false') | +-------------+-----------------+------------------------+ | 1 | 10 | false | +-------------+-----------------+------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 2. select nullif(1,1),nullif('a','b'),nullif(2+3,4+1); +-------------+-----------------+-----------------+ | nullif(1,1) | nullif('a','b') | nullif(2+3,4+1) | +-------------+-----------------+-----------------+ | NULL | a | NULL | +-------------+-----------------+-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 3. select if(1<10,2,3),if(56>100,'true','false'); +--------------+---------------------------+ | if(1<10,2,3) | if(56>100,'true','false') | +--------------+---------------------------+ | 2 | false | +--------------+---------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 4. select case 'green' when 'red' then 'stop' when 'green' then 'go' end status; +--------+ | status | +--------+ | go | +--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 5. select case when (2+2)=4 then 'ok' when (2+2)<>4 then 'not ok' end asstatus; +----------+ | asstatus | +----------+ | ok | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 6. select name,subject,if((score > 60),'及格','不及格') as results from result; +--------+---------+-----------+ | name | subject | results | +--------+---------+-----------+ | 张三 | 数学 | 及格 | | 张三 | 语文 | 不及格 | | 张三 | 地理 | 不及格 | | 李四 | 语文 | 不及格 | | 李四 | 政治 | 不及格 | | 王五 | 政治 | 不及格 | | 赵六 | 语文 | 及格 | | 赵六 | 数学 | 及格 | | 赵六 | 物理 | 及格 | +--------+---------+-----------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) 7. select name,total case when total<150 then'd' when total>150 or total<180 then'c' when total between 181 and 240 then'b' # when sum(score) > 241 then 'a' else 'a' end as grade from select name,sum(score) as total from result group by name order by name ; # 报错记录 # ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; # check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for # the right syntax to use near 'case # when sum(score) < 150 then 'd' # when sum(score) between 150 and 180 th' at line 2 8. select * from marks; +----+--------+------+-----+-----+ | id | fname | math | sci | lit | +----+--------+------+-----+-----+ | 1 | 张三 | 22 | 21 | 3 | | 2 | 李四 | 33 | 21 | 47 | | 3 | 王五 | 48 | 55 | 65 | | 4 | 赵六 | 95 | 90 | 92 | +----+--------+------+-----+-----+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) select fname,(math+sci+lit) as total, case when (math+sci+lit) < 50 then 'd' when (math+sci+lit) between 50 and 150 then 'c' when (math+sci+lit) between 151 and 250 then 'b' else 'a' end as grade from marks; +--------+-------+-------+ | fname | total | grade | +--------+-------+-------+ | 张三 | 46 | d | | 李四 | 101 | c | | 王五 | 168 | b | | 赵六 | 277 | a | +--------+-------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) -
格式化函数
1. date_format(date,fmt) 依照字符串fmt格式化日期date值 2. format(x,y) 把x格式化为以逗号隔开的数字序列,y是结果的小数位数 3. inet_aton(ip) 返回ip地址的数字表示 4. inet_ntoa(num) 返回数字所代表的ip地址 5. time_format(time,fmt) 依照字符串fmt格式化时间time值 # 其中最简单的是format()函数,它可以把大的数值格式化为以逗号间隔的易读的序列。 # 示例 1. select format(34234.34323432,3) as number1; +------------+ | number1 | +------------+ | 34,234.343 | +------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 2. select date_format(now(),'%w,%d %m %y %r') as now; +------------------------+ | now | +------------------------+ | 2,05 01 21 05:09:11 PM | +------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 3. select inet_aton('192.168.1.1') as ip_number; +------------+ | ip_number | +------------+ | 3232235777 | +------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) 4. select inet_ntoa(3232235777 ) as ip; +-------------+ | ip | +-------------+ | 192.168.1.1 | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
类型转化函数
-
为了进行数据类型转化,mysql 提供了cast() 函数,可以把一个值转化位指定数据类型
-
包含的类型有: binary、 char、date、time 、datetime、signed、unsigned
# 示例 select cast(now() as signed integer) as now_num; +----------------+ | now_num | +----------------+ | 20210105172444 | +----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) select 'f'=cast('f'as binary) +------------------------+ | 'f'=cast('f'as binary) | +------------------------+ | 1 | +------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
系统信息函数
1. database() 返回当前数据库名 2. benchmark(count,expr) 将表达式expr重复运行count次 3. connection_id() 返回当前客户的连接id 4. found_rows() 返回最后一个select查询进行检索的总行数 5. user()或system_user() 返回当前登陆用户名 6. version() 返回mysql服务器的版本
21. 事务机制
-
事务简介
- 将一个业务下的 sql 语句作为一个单元统一操作(同生共死)
- 事务处理是保证数据安全的重要机制,Myisam不支持事务
-
事务属性 (ACID)
- 原子性 (Atomic)
- 事务操作是不可分割的;事务只存在已执行和未执行两种状态,不存在只执行了部分指令的情况
- 一致性 (Consistency)
- 数据库总是从一个一致的状态转换到另一个一致状态
- 隔离型 (Isolation)
- 同时执行的事务之间相互隔离,不会互相影响
- 持久性 (Durability)
- 事务成功提交后,其写入的数据直到被覆盖永久有效
- 原子性 (Atomic)
-
并发事务的潜在问题
- 脏读: 事务A修改了一个数据,但未提交,事务B读到了事务A未提交的更新结果(即脏数据);如果事务A在执行转账的操作,从转出账户扣除了余额但未修改转入账户余额,此时事务B读取了转入账户余额,即发生了脏读
- 不可重复读: 在同一个事务种,对于同一条数据两次查询读到的结果不一致;比如在事务A两次查询中间,事务B修改了某条记录,那么事务A两次查询会读取到不同的结果
- 幻读: 在同一个事务种,对于同一个查询返回的记录数不一致;造成这种现象的原因是在事务A的两次查询中间,事务B添加或删除了记录,导致事务A两次查询读到不同的结果
-
事务隔离级别
- Read Uncommitted: 禁止多个事务同时修改同一条记录,其他事务可以读取未提交的修改;隔离级别最低,并发性能最高,会出现脏读、不可重复读和幻读
- Read Commited: 禁止多个事务同时修改同一条记录,修改在提交前其它事务只能读取修改前的版本;不会出现脏读,但会出现不可重复读和幻读
- Repeated Read: 禁止多个事务同时修改同一条记录,事务提交前会锁定所有读取到的行,禁止其它事务修改它正在读取的行;默认隔离级别,不会出现脏读和不可重复读。
- Serializable: 串行化执行,会锁定所有涉及的数据表; 可以解决脏读、不可重复读和幻读;隔离级别最高,并发性能最低
-
事务并发控制原理
- 悲观锁
- 在事务进行过程中数据总是处于被锁定状态;悲观锁对数据被其它事务修改的可能性持悲观态度(倾向于可能发生),常用与数据争用激烈的情景;我们通常使用的锁即是悲观锁
- 乐观锁
- 在事务执行过程中数据不被锁定,在事务提交时会对是否发生数据争用进行判断,若未发生冲突则完成提交,否则回滚事务
- 快照
- 所有对数据的修改都是在原有数据上产生了一个新的版本,对数据的读取是在快照(历史版本)上进行的;写操作产生新的版本不会影响在旧版本执行的读操作
- Mysql默认使用的 InnoDB 存储引擎使用悲观锁和快照(多版本控制,Multi Version Concurrent Control,MVCC )来实现事务的并发控制
- InnoDB 采用两阶段锁协议,即事务分为扩张阶段和收缩阶段,扩张阶段只允许加锁不能释放锁;收缩阶段只能释放锁不能加锁
- 悲观锁
-
事务相关操作
- 启用事务: start transaction ;
- 结束事务: commit ;
- 回滚事务: rollback ;
此次笔记引用自以下网站:
Mysql 基础总结:https://www.cnblogs.com/lms520/p/5427685.html
Mysql 基础总结:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020278837
Select 用法小结:https://www.taodudu.cc/news/show-239284.html
时间/字符串/时间戳互转:https://www.jianshu.com/p/394b75784738


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号