丢弃法(drop out)
一、介绍
1.动机
- 一个好的模型需要对输入数据的扰动鲁棒
- 使用有噪音的数据等价于Tikhonov正则
- 丢弃法:在层之间加入噪音
2.丢弃法的定义

这里除以\(1-p\)是为了\(x_i^{'}\)与原来的\(x_i\)的期望相同。
\[ 0\times p + (1-p)\times \dfrac{x_i}{1-p} = x_i
\]
3.使用丢弃法
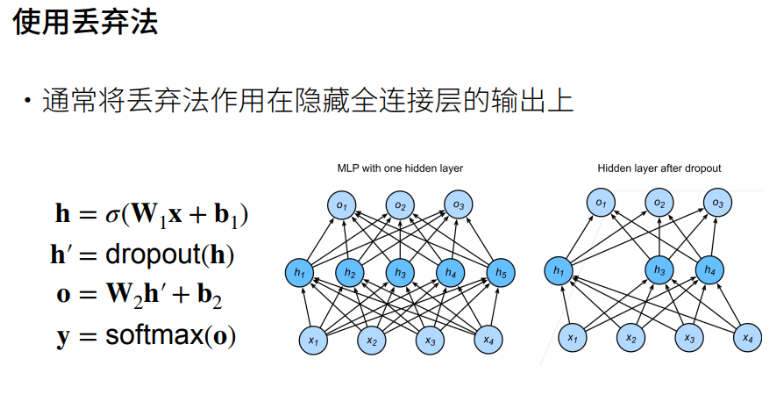
其中:
- \(h\) 为隐藏层
- \(\sigma\) 为激活函数
- \(o\) 为输出
- \(y\) 将 \(o\) 经过 \(softmax\) 层得到分类结果

4.总结

二、代码部分
1.丢弃法(使用自定义)
实现dropout_layer函数,该函数以dropout的概率丢弃张量输入x中的元素
# 实现dropout_layer函数,该函数以dropout的概率丢弃张量输入x中的元素
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
def dropout_layer(X, dropout):
assert 0 <= dropout <= 1 # dropout大于等于0,小于等于1,否则报错
if dropout == 1:
return torch.zeros_like(X) # 如果dropout为1,则X返回为全0
if dropout == 0:
return X # 如果dropout为1,则X返回为全原值
mask = (torch.rand(X.shape)>dropout).float() # 取X.shape里面0到1之间的均匀分布,如果值大于dropout,则把它选出来
#print((torch.randn(X.shape)>dropout)) # 返回的是布尔值,然后转布尔值为0、1
return mask * X / (1.0 - dropout)
X = torch.arange(16,dtype=torch.float32).reshape((2,8))
print(X)
print(dropout_layer(X, 0.))
print(dropout_layer(X, 0.5)) # 有百分之50的概率变为0
print(dropout_layer(X, 1.))
输出
tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15.]])
tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15.]])
tensor([[ 0., 0., 4., 6., 0., 0., 0., 14.],
[16., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 30.]])
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
定义具有两个隐藏层的多层感知机,每个隐藏层包含256个单元
# 定义具有两个隐藏层的多层感知机,每个隐藏层包含256个单元
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2 = 784, 10 ,256, 256
dropout1, dropout2 = 0.2, 0.5
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2,is_training=True):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.num_inputs = num_inputs
self.training = is_training
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_hiddens1)
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2)
self.lin3 = nn.Linear(num_hiddens2, num_outputs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, X):
H1 = self.relu(self.lin1(X.reshape((-1,self.num_inputs))))
if self.training == True: # 如果是在训练,则作用dropout,否则则不作用
H1 = dropout_layer(H1, dropout1)
H2 = self.relu(self.lin2(H1))
if self.training == True:
H2 = dropout_layer(H2,dropout2)
out = self.lin3(H2) # 输出层不作用dropout
return out
net = Net(num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2)
# 训练和测试
num_epochs, lr, batch_size = 10, 0.5, 256
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=lr)
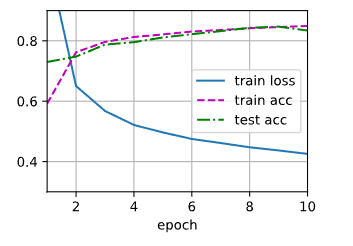
d2l.train_ch3(net,train_iter,test_iter,loss,num_epochs,trainer)
2.丢弃法(使用框架)
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 简洁实现
num_epochs, lr, batch_size = 10, 0.5, 256
dropout1, dropout2 = 0.2, 0.5
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(),nn.Linear(784,256),nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout1),nn.Linear(256,256),nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout2),nn.Linear(256,10))
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight,std=0.01)
net.apply(init_weights)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=lr)
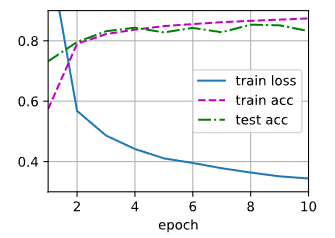
d2l.train_ch3(net,train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs,trainer)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号