再次聊一聊promise settimeout asycn awiat执行顺序---js执行机制 EVENT LOOP
2019-04-15 15:54 WEB前端小菜鸟 阅读(645) 评论(0) 收藏 举报
首先js是单线程
分为同步和异步,异步又分为(macrotask 宏任务 和 microtask微任务 ),
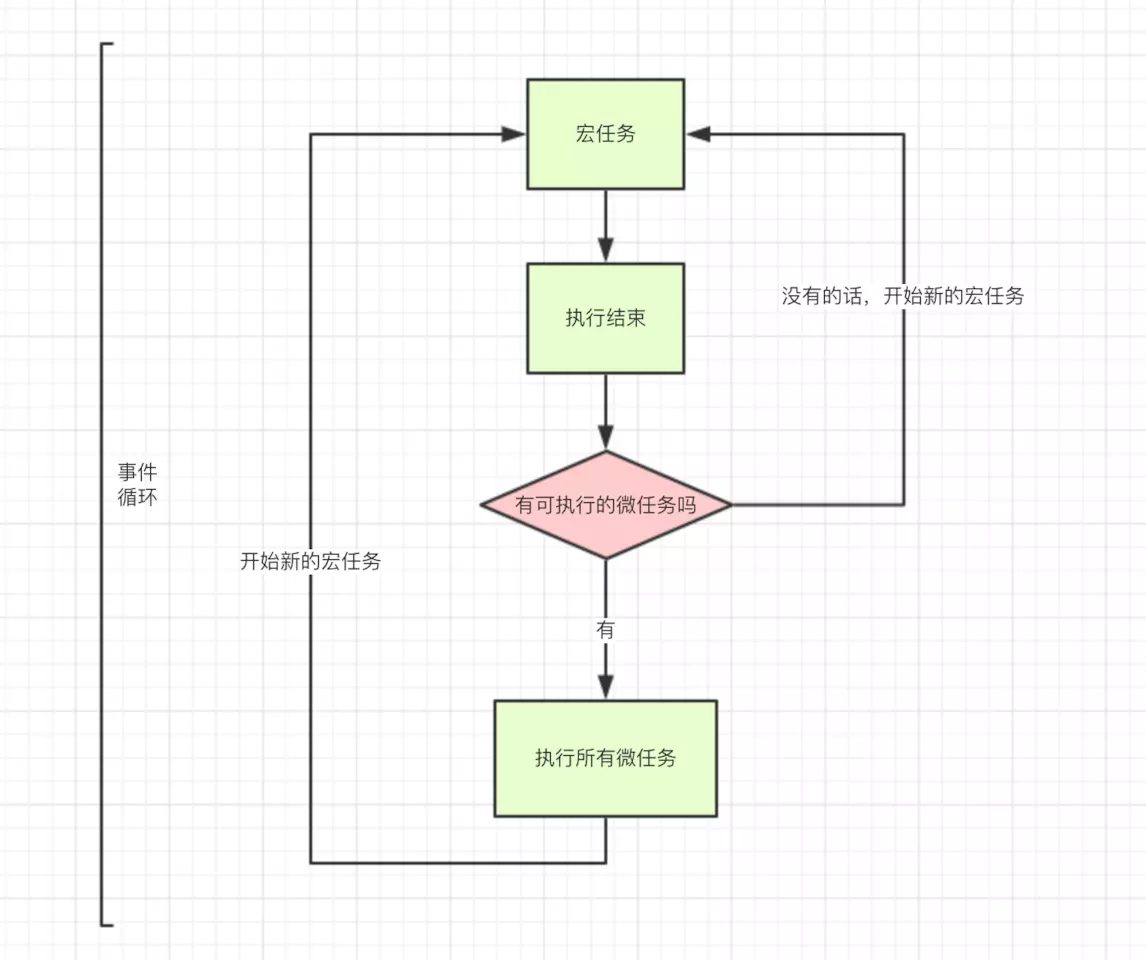
这图还是很清晰嘛,再来一张
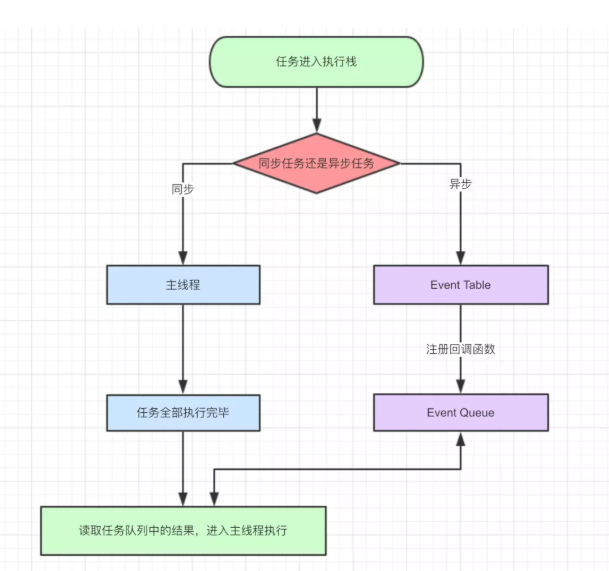
总结一下,就是遇到同步先执行同步,异步的丢到一边依次排队,先排队的异步先执行,等同步执行完了,在来处理异步,异步又分宏任务和微任务,一个宏任务执行完了才会轮到下一个
宏任务。
重点说一下微任务,微任务就像宏任务的小弟,这个微任务执行完了,才代表这论宏任务执行完,才会执行下一个宏任务,明白了瑟!(网上有篇文章来比喻这个很好,就像银行排队办业务一样,宏任务
根据拿号去排队,到你了你去办理,办理完了,又想办信用卡,办理财(这两个就相当于微任务),直到办完,才会轮到下一个号码来柜台办理业务)
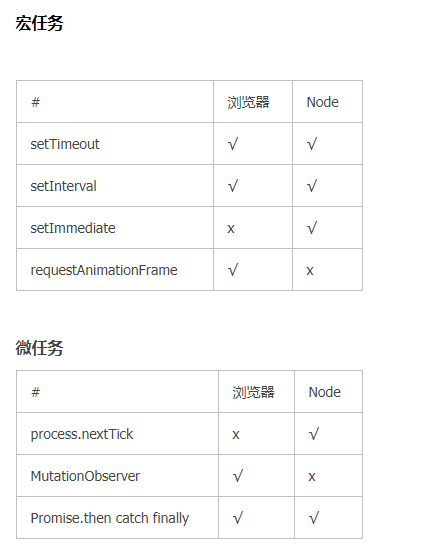
settimeout 这些定时器属于宏任务, promise.then.catch属于微任务
setTimeout(() => {
//执行后 回调一个宏事件
console.log("内层宏事件3");
}, 0);
console.log("外层宏事件1");
new Promise(resolve => {
console.log("外层宏事件2");
resolve();
})
.then(() => {
console.log("微事件1");
})
.then(() => {
console.log("微事件2");
});

首先浏览器执行js进入第一个宏任务进入主线程, 遇到 setTimeout 分发到宏任务Event Queue中
• 遇到 console.log() 直接执行 输出 外层宏事件1(同步)
• 遇到 Promise, new Promise 直接执行 输出 外层宏事件2(实例化立即执行)
• 执行then 被分发到微任务Event Queue中(promise then catch属于微任务)
•第一轮宏任务执行结束,开始执行微任务 打印 '微事件1' '微事件2'(办理信用卡和理财)
•第一轮微任务执行完毕,执行第二轮宏事件,打印setTimeout里面内容'内层宏事件3'
async function async1() { console.log("async1 start"); await async2(); console.log("async1 end"); } async function async2() { console.log("async2"); } console.log("script start"); setTimeout(function() { console.log("settimeout"); }, 0); async1(); new Promise(function(resolve) { console.log("promise1"); resolve(); }).then(function() { console.log("promise2"); }); console.log("script end");

我自己这么理解的哈,先同步,在异步,虽然异步才分为宏任务和微任务,但是你也可以打个比方,把同步看成宏任务,异步看成微任务,这样好理解些。
第一步:script start (同步),遇到settimeout 放到异步队列中去排队,遇到函数async1()去执行函数,打印里面的async1 start,在执行await async2(); await会阻塞后面的代码(console.log("async1 end");但是
并不会阻塞右边的执行
多提一嘴async/await函数
async/await本质上还是基于Promise的一些封装,而Promise是属于微任务的一种。所以在使用await关键字与Promise.then效果类似:
setTimeout(_ => console.log(4))
async function main() {
console.log(1)
await Promise.resolve()
//相当于promise.then(包起来了)
console.log(3)
}
main()
console.log(2)
1,2,3,4打印
async函数在await之前的代码都是同步执行的,可以理解为await之前的代码属于new Promise时传入的代码,await之后的所有代码都是在Promise.then中的回调
自己在写写promise
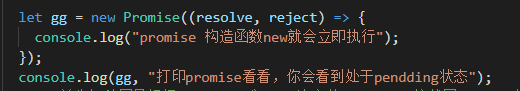

如果你不写的then cath的话一直处于pending状态,打印看它的原型上的方法then catch

打印与上面一致why?
因为你没有指明它的状态是处于成功还是失败啊



打印陈工
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangziye/p/9566454.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/jiasm/p/9482443.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号