一、DataFrame和series:
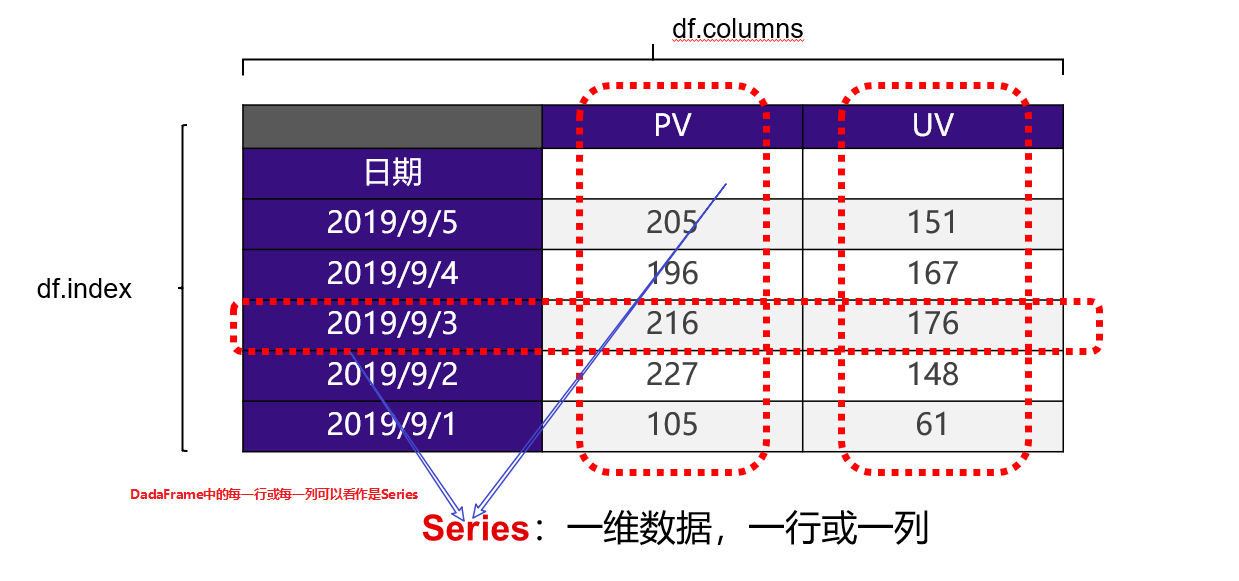
DataFrame:二维数据,是整个表格,为多行多列的
Series:是一维数据,DataFrame中的每一行或一列就是Series
区别:如果在表中查询出的是多行多列的,那么查询结果还是DataFrame结构的,如果查出的是一行或一列,那么查询结果是Series。
Series在python中是个字典,因此在操作中更为方便和快捷
二、三种创建Series实列方法:特别注意,DataFrame的index和columns必须是某种集合[],{},但不能是元组()
1、使用数据列表创建
import pandas as pd import numpy as np s1=pd.Series([1,2,7.2,9,'C']) #s1的打印结果 '''0 1 1 2 2 7.2 3 9 4 C dtype: object'''
s1.index
#输出:RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1)
s1.values
#输出:array([1, 2, 7.2, 9, 'C'], dtype=object)
2、创建带有index索引的Series
s2=pd.Series([1,2,3,4],index=['a','b','c','d']) #s2打印结果 ‘’‘a 1 b 2 c 3 d 4 dtype: int64’‘’
3、使用字典创建Series
s_={'a':100,'b':200,'c':300}
s3=pd.Series(s_)
#s3打印结果
‘’‘a 100
b 200
c 300
dtype: int64’‘’
4、根据标签索引查询数据:
方法类似查字典
s3['a'] #结果100 type(s3['a']) #结果numpy.int64 s3[['a','c']] ‘’‘结果:a 100 c 300’‘’ type(s3[['a','c']]) #结果:pandas.core.series.Series
1)查一个index是,结果是value值本身
2)查多个index时,结果是pandas的series
三、DataFrame
1、DataFrame:是表格型数据结构,
1)每列可以是不同的数值类型(数值、字符串、布尔)
2)既有索行引index,也有列索引columns
3)可以看做是有Series组成的字典
2、创建DataFrame:最常用的方法是读取.csv、.xlsx、txt文件创建
3、根据多个字典序列创建DataFrame
data={'class':[1,2,3,4],'year':[2019,2020,2021,2022],'course':[88,77,66,99]}
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
#打印df结果为:
‘’‘
clase year course
0 1 2019 88
1 2 2020 77
2 3 2021 66
3 4 2022 99
’‘’
4、从DataFrame中查询Series
如果查出的是一行或一列,返回的是Series。查询一行,index是列名(列索引);查询一列,index是行索引
如果是多行多列,则返回DataFrame
1)查询列
#查询一列
pd['year'] ''' 0 2019 1 2020 2 2021 3 2022 Name: year, dtype: int64''' type(df['year']) #结果是:pandas.core.series.Series
#查询多列,给dataframe传入列表,列表中为多个列名 df[['year','class']] ''' year class 0 2019 1 1 2020 2 2 2021 3 3 2022 4''' type(df[['year','class']]) #结果:pandas.core.frame.DataFrame
2)查询行
#查询一行,结果是Series df.loc[1] ''' class 2 year 2020 course 77 Name: 1, dtype: int64 ''' type(df.loc[1]) #pandas.core.series.Series #查询多行,使用列表切片方式 df.loc[1:3] ''' class year course 1 2 2020 77 2 3 2021 66 3 4 2022 99''' type(df.loc[1:3]) #结果:pandas.core.frame.DataFrame
注意,查询多行时,切片是包含最后值的。


