多线程的几种实现方式
先直接上代码,展示多线程的实现方式。
第一种:实现Runnabel接口。

1 package com.ceshi.sm; 2 3 public class RunnableDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable(); 7 Thread t = new Thread(myRunnable); 8 t.start(); 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); //打印线程的名称 10 } 11 12 13 } 14 15 16 class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ 17 18 //实现Runnale接口,重写run方法 19 @Override 20 public void run() { 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 22 } 23 24 }
第二种:继承Thread类

1 package com.ceshi.sm; 2 3 public class ThreadDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Thread t = new MyThread(); 7 t.start(); 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); //打印线程的名称 9 } 10 11 12 } 13 14 15 class MyThread extends Thread{ 16 17 //实现Runnale接口,重写run方法 18 @Override 19 public void run() { 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 21 } 22 23 }
第三种:实现Callable接口,通过FutureTask 实现类的支持来实现。

1 package com.ceshi.sm; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 5 import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; 6 7 8 public class CallableDemo{ 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable(); 12 //将myCallable对象作为myCallable的构造函数的参数传入 13 FutureTask<Integer> result = new FutureTask<Integer>(myCallable); 14 15 Thread t = new Thread(result); 16 t.start(); 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 18 try { 19 Integer sum = result.get(); 20 System.out.println(sum); 21 22 } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 //实现Callable<>接口,重写call方法 32 class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> { 33 34 @Override 35 public Integer call() throws Exception { 36 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 37 int sum = 0; 38 for(int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){ 39 sum += i; 40 } 41 return Integer.valueOf(sum); 42 } 43 }
前面两种形式大家都比较熟悉,我们来看一下第三种实现形式。

Callable接口的代码比较简单,与Runnable相似,只是方法名和返回值类型不同而已。所以,我们来看一下FutureTask类。
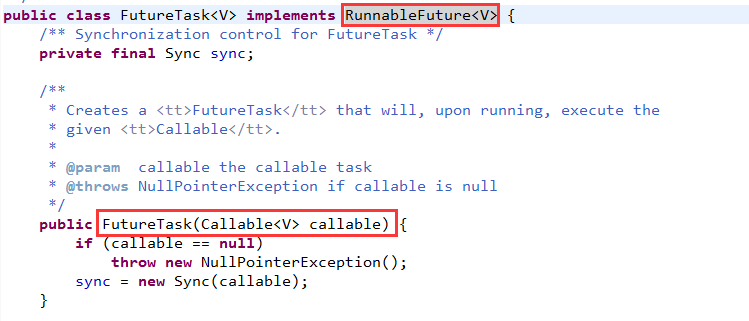
我们可以看出,获得Callable对象后,作为参数创建了匿名内部类sync对象。
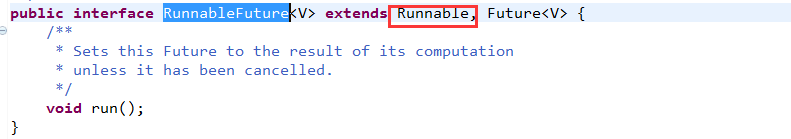
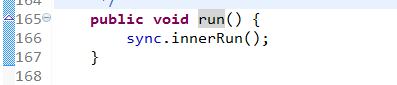
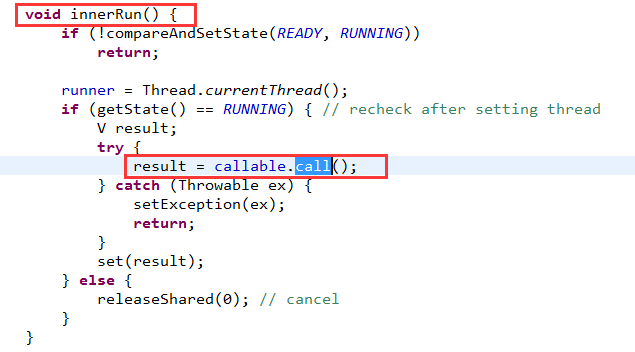
由于RunnableFuture接口继承自Runnable接口。所以,FutureTask类要重写run方法,在run方法中最终调用了call方法。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号