【SpringMVC】(三)RestFul和控制器
RestFul和控制器
1.控制器Controller
-
Controller的配置方法:通过实现Controller接口,使用注解@Controller
2.RequestMapping
@RequestMapping
-
@RequestMapping注解用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理方法。
-
用在类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都以该地址作为父路径。
-
控制器
@Controller @RequestMapping("/hello") public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/h1") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","ControllerTest!"); return "hello"; } } -
访问url
http://localhost:8080/ssm/hello/h1
-
-
若jsp文件在文件夹下,注意控制器中返回的页面路径
-
控制器
@Controller public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/h1") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","ControllerTest!"); return "user/hello"; } } -
当控制器中有多个方法,需统一加上/user,可以直接在类上写
控制器
@Controller @RequestMapping("/user") public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/h1") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","ControllerTest!"); return "user/hello"; } }或
@Controller public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/user/h1") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","ControllerTest!"); return "user/hello"; } }
-
3.RestFul风格
-
RestFul是一个资源定位及资源操作的风格。
-
基于这种风格设计的软件可以更简洁、安全,更易于实现缓存(高效)的等机制。
-
功能-资源操作:使用Post、Delete、Put、Get,使用不同方法对资源进行操作。
-
可以通过不同的请求方式实现不同的效果。请求地址就算一样,功能可以不同。
3.1 原来的url请求
-
Controller
@Controller public class RestFulController { @RequestMapping("/add") public String test1(int a, int b, Model model) { int res = a + b; model.addAttribute("msg", "结果为" + res); return "test"; } } -
访问url
http://localhost:8080/add?a=1&b=2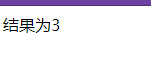
-
地址栏暴露变量名,不安全
3.2 RestFul风格
-
用斜杠分隔参数的值
-
注意方法中传参要加注解
@PathVariable -
@RequestMapping默认是GET方法,在url中传参
-
Controller
@Controller public class RestFulController { @RequestMapping("/add/{a}/{b}") public String test1(@PathVariable int a,@PathVariable int b, Model model) { int res = a + b; model.addAttribute("msg", "结果为" + res); return "test"; } } -
(错误)访问url:报错404
http://localhost:8080/add?a=1&b=2 -
访问url:
http://localhost:8080/add/1/2
3.3 使用@RequestMapping的method属性,指定请求类型
-
用于约束请求的类型,请求类型有GET、POST、DELETE、PUT、HEAD、PATCH、OPTIONS、TRACE。
-
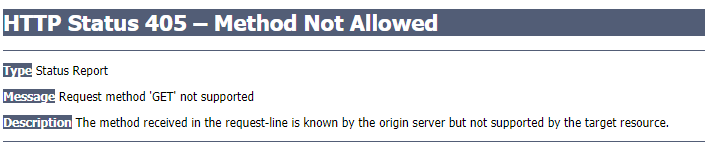
测试:指定为POST请求方式,用GET方式访问
1.Controller
@Controller public class RestFulController { @RequestMapping(value = "/add/{a}/{b}", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String test1(@PathVariable int a, @PathVariable int b, Model model) { int res = a + b; model.addAttribute("msg", "结果为" + res); return "test"; } }2.访问
http://localhost:8080/add/1/23.报错405:请求方式不支持
-
修改:
4.增加a.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form action="/add/1/2" method="post"> <input type="submit"/> </form> </body> </html>5.增加test.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> ${msg} </body> </html>注意jsp文件位置
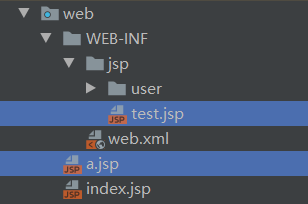
6.访问url。点击提交
http://localhost:8080/a.jsp
7.跳转url
- 也就是说,访问的url相同:
http://localhost:8080/add/1/2,但因为请求方式可以不同,所以实现功能可以不同。
3.4 方法级别的注解变体
-
组合注解
@GetMapping //默认请求方式 @PostMapping //相当于@RequestMapping(。。。,method = RequestMethod.POST) @PutMapping @DeleteMapping @PatchMapping



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号