C#(Java)将List集合构建成Tree树
C#(Java)将List集合构建成Tree树
子安树构建算法,可以通过空间换时间进一步优化速度
树结构的类
public class MyTreeNode
{
public MyTreeNode(long? iD, long? parentId)
{
ID = iD;
ParentId = parentId;
}
public long? ID { set; get; }
public long? ParentId { set; get; }
public MyTreeNode Parent { set; get; }
public List<MyTreeNode> Children { set; get; }
}
构建数的方法
/// <summary>
/// 构建数
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static List<MyTreeNode> BuildMenuTree(List<MyTreeNode> menus)
{
List<MyTreeNode> roots = new List<MyTreeNode>(); // 根节点集合
if (menus == null)
{
return roots;
}
List<MyTreeNode> children = new List<MyTreeNode>(); // 保存所有子节点
// 查找所有的根节点
foreach (var menu in menus)
{
bool isTop = true;
foreach (var m in menus)
{
// 跳过自身节点
if (m == menu || m.ID == menu.ID)
{
continue;
}
// 如果父ID是其他节点的ID,那么一定不是根节点
if (menu.ParentId == m.ID)
{
isTop = false;
break;
}
}
if (isTop)
{
roots.Add(menu);
}
else
{
children.Add(menu);
}
}
// 递归查找根节点
if (children.Any())
{
// 对子节点求根节点
var nextRoots = BuildMenuTree(children);
// 设置根节点与子根节点引用关系
foreach (var root in roots)
{
foreach (var nextRoot in nextRoots)
{
if (root.ID == nextRoot.ParentId)
{
if (root.Children == null)
{
root.Children = new List<MyTreeNode>() { nextRoot };
}
else
{
root.Children.Add(nextRoot);
}
nextRoot.Parent = root;
}
}
}
}
return roots;
}
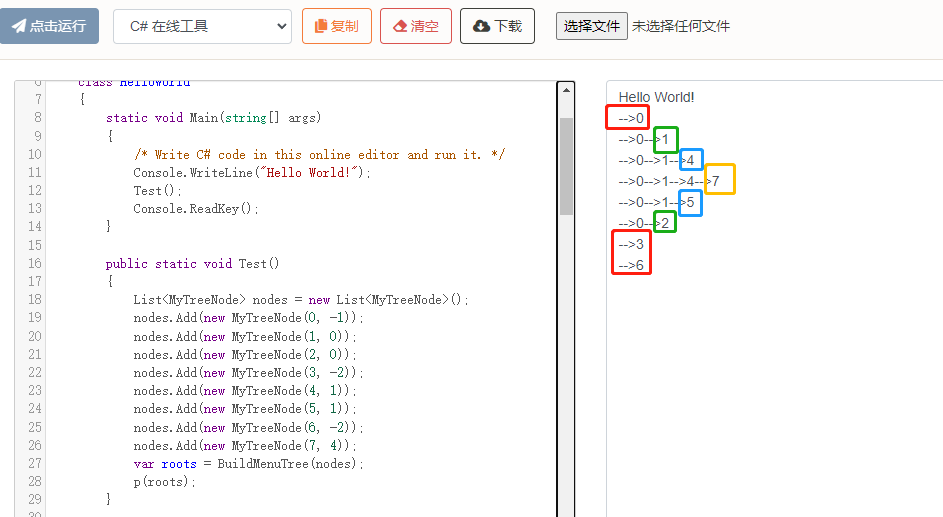
测试一下
public static void Main()
{
List<MyTreeNode> nodes = new List<MyTreeNode>();
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(0, -1));
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(1, 0));
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(2, 0));
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(3, -2));
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(4, 1));
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(5, 1));
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(6, -2));
nodes.Add(new MyTreeNode(7, 4));
var roots = BuildMenuTree(nodes);
p(roots);
}
// 打印
public static void p(List<MyTreeNode> roots, string pid = "")
{
if (roots == null)
{
return;
}
foreach (var root in roots)
{
Console.WriteLine(pid + "-->" + root.ID);
p(root.Children, pid + "-->" + root.ID);
}
}
测试结果
JavaScript版本
点击查看代码
function buildTree(data) {
function f(list) {
list = list || [];
let roots = []; // 根节点集合
if (list.length === 0) {
return roots;
}
let children = []; // 保存所有子节点
// 查找所有的根节点
for (let l of list) {
let isTop = true;
for (let m of list) {
// 跳过自身节点
if (m === l || m.id === l.id) {
continue;
}
// 如果父ID是其他节点的ID,那么一定不是根节点
if (l.parentId === m.id) {
isTop = false;
break;
}
}
if (isTop) {
roots.push(l);
} else {
children.push(l);
}
}
// 递归查找根节点
if (children.length > 0) {
// 对子节点求根节点
let nextRoots = f(children);
// 设置根节点与子根节点引用关系
for (let root of roots) {
for (let nextRoot of nextRoots) {
if (root.id === nextRoot.parentId) {
if (root.children) {
root.children.push(nextRoot);
} else {
root.children = [nextRoot];
}
//nextRoot.Parent = root;
}
}
}
}
return roots;
}
return f(data);
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号