java中的IO流
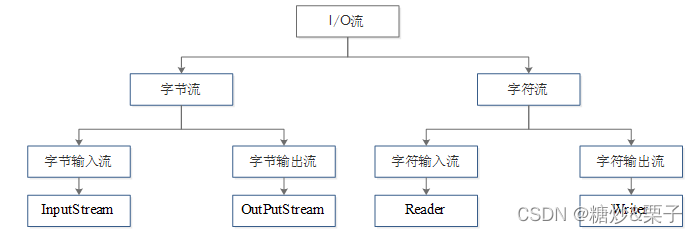
1、JDK所提供的所有流类位于java.io包中,都分别继承自以下四种抽象流类。
InputStream:继承自InputStream的流都是用于向程序中输入数据的,且数据单位都是字节(8位)。
OutputStream:继承自OutputStream的流都是程序用于向外输出数据的,且数据单位都是字节(8位)。
Reader:继承自Reader的流都是用于向程序中输入数据的,且数据单位都是字符(16位)。
Writer:继承自Writer的流都是程序用于向外输出数据的,且数据单位都是字符(16位)。
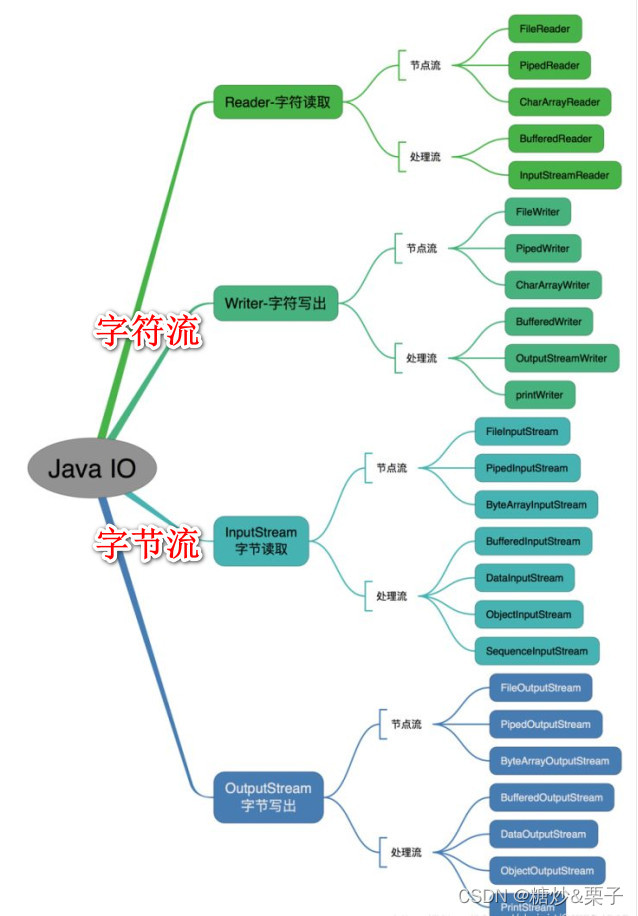
1.1 Writer字符输出流
它是所有字符输出流的跟类。---FileWriter类
1 public class TestWriter {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
3 //字符输出流 ---指定对哪个文件(路径)进行写操作
4 Writer writer=new FileWriter("D:/AAA/d.txt");
//true:表示允许追加内容到文件中
//Writer writer=new FileWriter("D:/AAA/d.txt",true);
6 String str="你好 你今天真漂亮"; 7 writer.write(str); 8 9 writer.flush(); //刷新流 10 writer.close(); //关闭流资源 11 } 12 }
1.2 Reader字符输入流
它是所有字符输入流的根类 它的实现类有很多,我们使用FileReader实现类。
1 public class TestReader { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 3 //创建字符输入流对象. 作用:就是读取aaaa.txt里的内容 4 Reader reader=new FileReader("D:/BBB/aaa.txt"); 5 6 int r=0;//表示读取字符的个数 7 while ((r=reader.read())!=-1){ 8 System.out.print((char)r); 9 } 10 } 11 }
1.3经典题 要求: D:/AAA/d.txt 复制到 C:/AAA/d.txt.
1 public class TestDemo1{ 2 @Test 3 public void test02() throws Exception{ 4 //创建一个字符输入流 5 FileReader fr=new FileReader("D:/AAA/d.txt"); 6 7 //创建一个字符输出流 8 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("C:/AAA/f.txt"); 9 10 int c=0;//读取到字符的个数 11 char[] cs=new char[10];//每次读取的内容放入该数组中 12 13 while( (c=fr.read(cs)) !=-1 ){ 14 fw.write(cs,0,c); 15 fw.flush(); //刷新 16 } 17 18 fw.close();//关闭资源 19 fr.close(); 20 } 21 }
2.1字节输出流--OutputStream
它可以对任意文件进行操作,对文件进行输出操作。以字节为单位。 它是所有字节输出流的父类,FileOutputStream
1 //测试字节输出流 2 @Test 3 public void testOutStream() throws Exception{ 4 OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("D:/AAA/f.txt"); 5 String str="abcd"; 6 //把字符串转换为字节数组. 7 byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); 8 9 os.write(bytes); 10 11 os.flush(); 12 os.close(); 13 14 }
2.2字节输入流---InputStream
它可以对任意文件进行读操作 ,以字节为单位,它是所有字节输入流的父类,子类有FileInputStream
1 //一次一次的读取 2 @Test 3 public void testInputStream() throws Exception{ 4 InputStream is=new FileInputStream("D:/AAA/f.txt"); 5 6 byte [] bytes=new byte[3]; 7 int c1=is.read(bytes);//一次读取三个字节 并把读取的内容放入字节数组中 返回读取到字节的个数 8 System.out.println(bytes+"=============>个数:"+c1); 9 10 c1=is.read(bytes); 11 System.out.println(bytes+"=============>个数:"+c1); 12 13 c1=is.read(bytes); 14 System.out.println(bytes+"=============>个数:"+c1); 15 16 } 17 18 19 //如果文件中内容非常大 使用循环来读取 20 @Test 21 public void testInputStream2() throws Exception{ 22 InputStream is=new FileInputStream("D:/AAA/f.txt"); 23 byte [] bytes=new byte[300]; 24 int c=0; //读取到的个数 25 while( (c=is.read(bytes))!=-1 ){ 26 //把byte数组转换为字符串 27 String str=new String(bytes,0,c); 28 System.out.println(str); 29 } 30 31 is.close(); 32 }
2.3使用字节输入和输出流完成文件的复制功能:
1 @Test 2 public void testCopy() throws Exception{ 3 //创建字节输入流 视频 4 InputStream is=new FileInputStream("D:/AAA/56.jpg"); 5 //字节输出流 6 OutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("C:/AAA/57.jpg"); 7 byte[] bytes=new byte[10]; 8 int c=0; 9 10 while( (c=is.read(bytes)) !=-1 ){ 11 fos.write(bytes,0,c); 12 } 13 14 is.close(); 15 fos.close(); 16 }
3.1缓存流是在基础流[InputStream OutputStream Reader Writer]之上 添加了一个缓存池功能.
BufferInutStream BufferOutputStream BufferReader BufferWriter 提高IO的效率,降低IO的次数
1 @Test 2 public void TestBuffer() throws Exception{ 3 OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("D:/AAA/g.txt"); 4 5 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(out);//缓存流要作用再基础流上 6 String str="abcdefhijglmn"; 7 8 byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); 9 bos.write(bytes); //因为你写的内容 暂时放入缓存池中 并没有直接放入文件中。 所以文件中没有你的内容 10 11 bos.flush();//刷新缓存池---把池子中的内容输入到文件上 12 13 bos.close(); //关闭----先刷新缓冲池 再关闭流资源 14 15 }
4.1对象流--对java对象进行IO操作
为什么需要对象流?
我们现在操作IO流的时候 都是将字符串读写操作 可不可以将java对象在文件中进行读写呢? 可以的 Student st=new Student();对象
将java对象进行读写操作 意义在于持久化信息 例如: 游戏存档
因为运行的时候 所有的数据都是在运行内存中的 持久化 将运行内存的数据 保存到硬盘上 存档(写) 读档(读)
源代码
1 public class Role implements Serializable { 2 private String roleName; 3 private String level;//级别 4 private int id; 5 private String other;//其他属性 6 7 public Role(){ 8 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public String toString() { 13 return "Role{" + 14 "roleName='" + roleName + '\'' + 15 ", level='" + level + '\'' + 16 ", id=" + id + 17 ", other='" + other + '\'' + 18 '}'; 19 } 20 21 public Role(String roleName, String level, int id, String other) { 22 this.roleName = roleName; 23 this.level = level; 24 this.id = id; 25 this.other = other; 26 } 27 } 28 29 public class TestDemo2 { 30 //存档:----序列化: 31 @Test 32 public void testObjectStream() throws Exception{ 33 OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("D:/AAA/a.txt"); 34 ObjectOutputStream os=new ObjectOutputStream(out); 35 36 //使用对象流调用输出方法 输出的类对象 该类必须实现Serializable 序列化接口 37 Role r=new Role("狄仁杰","6",001,"射手"); 38 os.writeObject(r); 39 os.close(); 40 } 41 //测试读档,反序列化 42 @Test 43 public void testObjectStream2() throws Exception{ 44 InputStream input=new FileInputStream("D:/AAA/a.txt"); 45 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(input); 46 Object o = ois.readObject(); 47 48 System.out.println(o); 49 ois.close(); 50 } 51 }
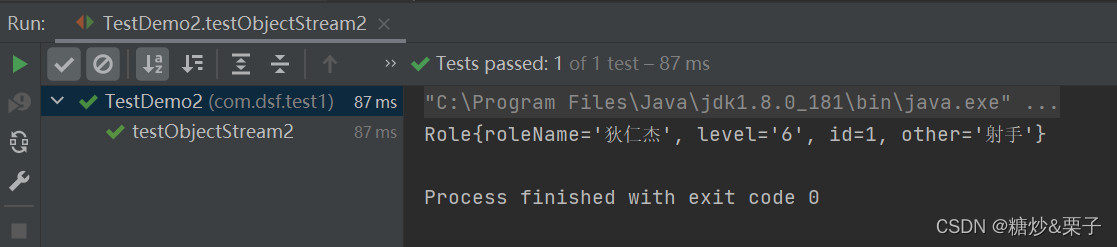
运行结果图:
1. 序列化: 把内存中的java对象存储到磁盘[网盘]的过程。
---java对象所属的类必须实现序列化接口.implements Serializable
2. 反序列化: 把磁盘中的内容读取到java对象内存中的过程。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号