Integer的比较==和String的比较==总结
public class IntegerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //Integer Integer a=10,b=10,c=150,d=150; System.out.println(a==b); System.out.println(c==d); System.out.println(a.equals(b)); System.out.println(c.equals(d)); //String String str=new String("AB"); String str1 ="A"; String str2 = str1+"B"; String str3="AB"; System.out.println(str==str3); System.out.println(str==str2); System.out.println(str2==str3); } }
1、上面代码的 a==b会输答案是true,但是c==d会输出是false
(1)Integer是基本数据类型的int的引用类型,官方语言叫做装箱类型,我们来看一下Integer的源码
//Integer的取值
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low));
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
从源码我们可以看出,Integer的值为-128-127之间的时候就会自动的从Integer的缓存(IntegerCache)中去取,如果超过这个范围就会新建一个Integer的对象。
所以a==b(a=10,b=10)为true,c==d(c=150,d=150)为false。
2、我们来看一下String的这个问题
(1)str==str3 为false,因为,str新建了一个对象,str3是常量池中的对象,所以这两个为false。
(2)str2==str3,这个解释引用我群友 成都-119-EbranHan-Java 的解释:

new 了一个 StringBuilder,然后调用了append方法,对应的就是:String str2 = str1+"B";
这里还提到了字面量和引用,String str3="AB",这就是字面量,而引用就是,String str=new String("AB");我们自己定义的。
字面量 jvm 优化过,直接就扔到常量池去了。
下面是StringBuilder的toString方法,这里也是新建了一个String方法
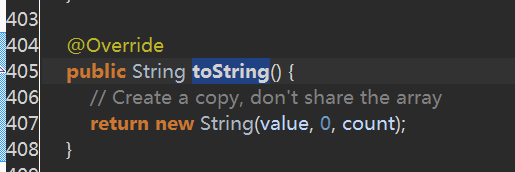
综上所述,str2==str3也为false。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号