lab3
MIT6.5840(原MIT6.824)Lab3 总结(Raft)
资源分享:
官网地址:http://nil.csail.mit.edu/6.5840/2023/
Raft论文地址:http://nil.csail.mit.edu/6.5840/2023/papers/raft-extended.pdf
官方学生指导(又称官方避坑指导):https://thesquareplanet.com/blog/students-guide-to-raft/
注: raft论文和官方闭坑指南必看
如果觉得看论文无聊,推荐一个视频: 【解析分布式共识算法之Raft算法】https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Kz4y1H7gw?vd_source=c5fdcb7e8bfbd07851554854d73aa1fa
但是该实验基本上是和raft论文保持一致的, 而该视频与论文并不高度一致, 所以要想完成lab3, 论文还是必看的
最后再附一个对我有帮助的博客: MIT6.5840(6.824) Lec05笔记: raft论文解读1:选举和日志 - 知乎
内容简述
- lab3A实现election
- lab3B实现log
- lab3C实现persistence
- lab3D实现log compaction
给出官方代码关系图示:
每个lab我基本上都测试了成百上千次
lab3A-election
内容简述:
实现选举:
- 心跳接收方逻辑
- 心跳发送方逻辑
- 心跳超时检测逻辑
- 集群初始化
踩坑实录
raft算法是通过维持log链表的一致性从而维持replication的一致性, 关于raft算法的内容不在多言, 去看raft论文即可, 这里主要是记录一下完成lab所遇到的问题
前言
- 对于实验,请严格按照论文中所述实施, 尤其是图2, 注意是must不是maybe(raft说白了就是制定一些规则,而这些规则的制定,我相信作者一定是经过无数次实验验证过的,如此才能使集群中的节点在不可靠的网络环境中使状态保持一致,因此还是很有参考价值的)
- 只看raft论文也是完成不了实验的, 因为论文中对于一些细节并未说清楚, 因此官方闭坑指南也是必看的
- 或许你看了论文但并未严格实施也通过了测试,但是由于网络的不稳定, 如果你重复测试成千上万次,那就不一定百分百通过了…
代码分析
首先对lab3A的代码进行分析:
对于集群中的节点来说, 节点之间通过RPC通信, 每个节点既可以发送RPC,也可以接收RPC, 接收RPC的函数(该节点中供其他节点调用的接口)代码中已经给出:
- RequestVote : 这是当其他节点调用本节点的RequestVoteRPC时,本节点执行的函数。它负责处理投票请求,根据本节点的当前状态决定是否投票给请求的候选者
- AppendEntries 接收log / Heartbeat
- 在Make中实现集群节点的初始化
- 在ticker中实现心跳监测
状态设置
const (
Leader States = "leader"
Candidate = "candidate"
Follower = "follower"
)
// 单个日志节点结构
type logEntity struct {
TermId int
Command interface{}
}
// 时间设置
const (
heartbeatIntervalTime = 100 * time.Millisecond
)
// 实现单个 Raft peer节点的 Go 对象。
type Raft struct {
// mu sync.RWMutex // Lock to protect shared access to this peer's state
mu sync.Mutex
peers []*labrpc.ClientEnd // RPC end points of all peers
persister *tester.Persister // Object to hold this peer's persisted state
me int // this peer's index into peers[]
dead int32 // set by Kill()
// Your data here (3A, 3B, 3C).
// 查看论文的图 2 以了解
// 状态 Raft 服务器必须维护。
currentTerm int
votedFor int
log []*logEntity // 从下标1开始记录log, 并且下标就是logIndex
state States
commitIndex int
lastapplied int
lastHeartbeatTime time.Time
leaderCond *sync.Cond
nextIndex []int // 索引是peer的id, 值是下一次要发给该peer的logIndex
matchIndex []int // 索引是peer的id, 值是leader已知的、已经成功复制到该peer上的最高日志条目的索引
}
一些细节(踩过的坑):
-
仅当以下三种情况之一发生时,才应重置选举计时器:
-
收到当前领导者的
AppendEntriesRPC(且 RPC 中的任期未过时):领导者的心跳表明其仍存活,无需发起选举; -
自己发起选举(转为候选人):主动触发选举流程;
-
向其他节点授予投票(
RequestVote回复voteGranted=true):说明对方日志可能更优,需重新评估选举状态。
-
当candidate向你发送RequestVote RPC时, 不要重置选举计时器,否则会导致活锁
-
心跳是只是Entities为空的AppendEntities, 也要执行领导者身份检查(节点的term比较) 和 preLog的Index与term比较, 判断其成功与否
-
原因:心跳不仅是保活机制,更是领导者对日志一致性的声明。不检查会导致已失效领导者维持权威
-
重置计时器≠RPC成功:计时器重置基于RPC合法性(任期),而RPC成功基于日志匹配
-
-
发送心跳/日志不要用sync.waitGroup, 因为发送心跳要定时执行, 使用其会影响心跳的定期发送
-
关于图2中RequestVote RPC 投票条件的说明:
投票条件:若 votedFor为空或已是 candidateId,且候选者日志至少与接收者日志一样新,则授予投票
其中votedFor == candidateId 表示当前节点在当前term已经投票过(可能是回复RPC丢失)
-
如果 RPC 请求或响应包含任期 T > currentTerm:设置 currentTerm = T,转换为追随者
-
只要节点的term改变请重置voteFor
-
对于图2中AppendEntries RPC 接收者处理规则2和3的说明:
-
若日志在
prevLogIndex处无条目或任期不匹配,返回false: 比较的是follower在prevLogIndex处是否为空, 以及在prevLogIndex处的LogTerm与prevLogTerm是否相同 -
冲突处理:若新条目与现存条目冲突(同索引不同任期),删除冲突条目及其后所有条目:
- 如果现有条目与新条目冲突(相同索引但不同term),则删除现有条目及其后面的所有条目
- 如果Follower已经包含了领导者发送的所有条目(也就是没冲突),那么它绝不能截断其日志。
- 寻找第一个冲突的索引位置
-
代码如下:
-
conflictIndex := -1 for i, entry := range args.Entries { index := args.PrevLogIndex + 1 + i if index >= len(rf.log) { // Follower的日志比Leader的短,没有更多条目需要检查,后续全是新条目,直接追加 break } if rf.log[index].TermId != entry.TermId { // 发现了冲突:索引相同,但任期不同 conflictIndex = index break } } // 如果现有条目与新条目冲突(索引相同但术语不同),请删除现有条目及其后面的所有条目 if conflictIndex != -1 { // 发现冲突:删除Follower日志中从第一个冲突位置开始的所有后续条目 rf.log = rf.log[:conflictIndex] // 截断冲突点之后的日志 }
-
-
candidate收到了同Term的AppendEntities: 转为follower即可,不用重置votedFor
-
在闭坑指南中有这样一段话: 遵循图 2 关于何时应开始选举的指示。特别要注意,如果你是一个候选人(即,你当前正在运行一次选举),但选举计时器触发,你应该开始另一次选举。这对于避免由于 RPC 延迟或丢失而导致系统停滞很重要。
-
这段话说明了心跳监测和发起投票是并行的
-
见代码:
func (rf *Raft) ticker() { for rf.killed() == false { // 当前节点还没挂 // Your code here (3A) // 检查是否应该开始领导人选举。 electionTimeout := time.Duration(600+rand.Intn(600)) * time.Millisecond rf.mu.Lock() if rf.state != Leader && time.Since(rf.lastHeartbeatTime) >= electionTimeout { rf.mu.Unlock() // 开始选举 go rf.vote() // 此处用go routinue, 太细节了, 卡了我很久... rf.mu.Lock() } rf.mu.Unlock() time.Sleep(heartbeatIntervalTime / 2) } }
-
上代码
其他内容不再多说, 详情见代码:
// 节点状态
type States string
const (
Leader States = "leader"
Candidate = "candidate"
Follower = "follower"
)
// 单个日志节点结构
type logEntity struct {
TermId int
Command interface{}
}
// 时间设置
const (
heartbeatIntervalTime = 100 * time.Millisecond
)
// 实现单个 Raft peer节点的 Go 对象。
type Raft struct {
// mu sync.RWMutex // Lock to protect shared access to this peer's state
mu sync.Mutex
peers []*labrpc.ClientEnd // RPC end points of all peers
persister *tester.Persister // Object to hold this peer's persisted state
me int // this peer's index into peers[]
dead int32 // set by Kill()
// Your data here (3A, 3B, 3C).
// 查看论文的图 2 以了解
// 状态 Raft 服务器必须维护。
currentTerm int
votedFor int
log []*logEntity // 从下标1开始记录log, 并且下标就是logIndex
state States
commitIndex int
lastapplied int
lastHeartbeatTime time.Time
leaderCond *sync.Cond
nextIndex []int // 索引是peer的id, 值是下一次要发给该peer的logIndex
matchIndex []int // 索引是peer的id, 值是leader已知的、已经成功复制到该peer上的最高日志条目的索引
}
// return currentTerm 以及该服务器是否认为自己是领导者。
func (rf *Raft) GetState() (int, bool) {
var term int
var isleader bool
// Your code here (3A).
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
term = rf.currentTerm
if rf.state == Leader {
isleader = true
} else {
isleader = false
}
return term, isleader
}
// 示例 RequestVote RPC 参数结构。
// 字段名称必须以大写字母开头!
type RequestVoteArgs struct {
// Your data here (3A, 3B).
TermId int
CandidateId int
LastLogIndex int
LastLogTerm int
}
// 示例 RequestVote RPC 回复结构。
// 字段名称必须以大写字母开头!
type RequestVoteReply struct {
// Your data here (3A).
TermId int // 投票者的Term
VoteGranted bool // 是否投票
}
// example RequestVote RPC handler.
// 这是当其他节点调用本节点的RequestVoteRPC时,本节点执行的函数。它负责处理投票请求,根据本节点的当前状态决定是否投票给请求的候选者
// 1.如果term < currentTerm, 则回复false
// 2.如果votedFor为null或candidateId(投票回复丢失了),并且候选人的日志至少与接收者的日志一样新,则授予vote
func (rf *Raft) RequestVote(args *RequestVoteArgs, reply *RequestVoteReply) {
// Your code here (3A, 3B).
flag := true
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
// log.Printf("RequestVote--当前节点: %v 收到 %v 的投票请求, 当前节点状态为: %v, 当前节点termId: %v", rf.me, args.CandidateId, rf.state, rf.currentTerm)
if args.TermId < rf.currentTerm {
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm
reply.VoteGranted = false
return
}
for flag {
// // log.Printf("RequestVote--当前节点: %v 收到 %v 的投票请求, 当前节点状态为: %v, 当前节点termId: %v ", rf.me, args.CandidateId, rf.state, rf.currentTerm)
switch rf.state {
case Leader:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else {
reply.VoteGranted = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Candidate:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else {
reply.VoteGranted = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Follower:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
}
if rf.votedFor == -1 || rf.votedFor == args.CandidateId {
// 候选人的日志至少与接收者的日志一样新
if args.LastLogIndex >= len(rf.log)-1 && args.LastLogTerm >= rf.log[len(rf.log)-1].TermId {
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm
reply.VoteGranted = true
rf.votedFor = args.CandidateId
// 重置心跳检测-情况3: 您向另一个对等节点授予投票(该对等节点拥有较新的log)
rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now()
flag = false
break
}
}
reply.VoteGranted = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
// log.Printf("RequestVote--当前节点: %v 收到 %v 的投票请求, 当前节点状态为: %v, 当前节点termId: %v, 最终投票结果为: %v", rf.me, args.CandidateId, rf.state, rf.currentTerm, reply.VoteGranted)
}
}
// 投票逻辑
func (rf *Raft) vote() bool {
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state == Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
return false
}
rf.state = Candidate
rf.currentTerm++
rf.votedFor = rf.me // 投票给自己
// 重置心跳检测-情况2: 当前节点开始选举
rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now()
args := &RequestVoteArgs{ // 投票过程中这些内容应该保持不变
TermId: rf.currentTerm,
CandidateId: rf.me,
LastLogIndex: len(rf.log) - 1,
LastLogTerm: rf.log[len(rf.log)-1].TermId,
}
// currentTermId := rf.currentTerm
me := rf.me
length := len(rf.peers)
currentState := rf.state
done := false
rf.mu.Unlock()
// 使用原子变量保护 count
var count atomic.Int32
count.Add(1)
var syn sync.WaitGroup
// 向peer中其他节点发送sendRequestVote, 并统计投票数
for i := 0; i < length && currentState == Candidate; i++ {
if i == me {
continue
}
reply := RequestVoteReply{}
syn.Add(1)
go func(server int, args *RequestVoteArgs, reply RequestVoteReply) {
defer syn.Done()
newArgs := *args // 这里必须要拷贝一份, 否则多个go routine会共用一个args, 导致数据错误
// log.Printf("vote--节点: %v 向: %v 发送投票请求, 当前节点的termId : %v, LastLogIndex: %v, LastLogTerm: %v ", me, i, currentTermId, args.LastLogIndex, args.LastLogTerm)
ok := rf.sendRequestVote(server, &newArgs, &reply)
// log.Printf("vote--节点: %v 消息发送以及接受回复是否成功: %v", me, ok)
if !ok { // call失败: 服务器宕机、存活但不可达的服务器、请求丢失或回复丢失; 暂时不重发
return
}
// log.Printf("vote--节点: %v 最终发送投票的结果为: %v", me, reply.VoteGranted)
// // log.Printf("vote--节点: %v 向: %v 发送投票请求, 投票结果为: %v, 当前节点的termId : %v, 回复节点的termId: %v ", rf.me, i, reply.VoteGranted, currentTermId, reply.TermId)
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
if rf.currentTerm != args.TermId || rf.state != Candidate {
return
}
if !reply.VoteGranted { // 投了反对票
// 遇到了TermId更大的candidate
if rf.currentTerm < reply.TermId && rf.state == Candidate {
rf.currentTerm = reply.TermId
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票
}
return
}
// 投了赞成票
count.Add(1)
// // log.Printf("vote--节点: %v 获得了: %v 的票, 集群数为: %v, 目前获得票数为: %v", rf.me, i, length, count)
// 得到大多数支持
if !done && count.Load() > int32(length/2) {
if rf.state == Candidate && rf.currentTerm == args.TermId { // 使用调用投票时的参数args.TermId而非RPC回复的reply.TermId
rf.state = Leader
done = true
// log.Printf("vote--节点: %v 成为: %v ", rf.me, rf.state)
rf.leaderCond.Broadcast()
}
return
}
}(i, args, reply)
rf.mu.Lock() // 这里会有延迟, 也就是说这里执行完了, 上面的go routinue, 可能还没执行完, 没设置阻塞, 也是用go的初衷
if rf.state != Candidate {
rf.mu.Unlock()
break
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
syn.Wait()
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
if done && rf.state == Leader {
return true
}
return false
}
func (rf *Raft) sendRequestVote(server int, args *RequestVoteArgs, reply *RequestVoteReply) bool {
ok := rf.peers[server].Call("Raft.RequestVote", args, reply)
return ok
}
// 追加日志/心跳参数
type AppendEntriesArgs struct {
TermId int
LeaderId int
PrevLogIndex int
PrevLogTermId int
Entries []*logEntity
CommitIndex int
}
type AppendEntriesReply struct {
TermId int // 回复者的TermId
Success bool // 追加日志是否成功
}
// 接收日志/心跳
func (rf *Raft) AppendEntries(args *AppendEntriesArgs, reply *AppendEntriesReply) {
// Your code here (3A, 3B).
flag := true
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
if args.TermId < rf.currentTerm {
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm
reply.Success = false
return
}
for flag {
// // log.Printf("RequestVote--当前节点: %v 收到 %v 的投票请求, 当前节点状态为: %v, 当前节点termId: %v ", rf.me, args.CandidateId, rf.state, rf.currentTerm)
switch rf.state {
case Leader:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else {
reply.Success = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Candidate:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else if args.TermId == rf.currentTerm {
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
rf.state = Follower
// rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else {
reply.Success = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Follower:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
}
// 从当前Leader那里收到AppendEntries RPC(本端Term和arg中的Term一定要一致!)
// 重置心跳检测
// if args.TermId == rf.currentTerm
rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now()
// 如果日志在prevLogIndex中不包含与prevLogTerm匹配的条目,则回复false
if len(rf.log)-1 < args.PrevLogIndex || rf.log[args.PrevLogIndex].TermId != args.PrevLogTermId {
reply.Success = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
break
}
// rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now()
if args.Entries == nil {
flag = false
reply.Success = true
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
// log.Printf("AppendEntries---当前节点: %v, 收到了leader: %v 的心跳", rf.me, args.LeaderId)
break
}
// 如果现有条目与新条目冲突(相同索引但不同term),则删除现有条目及其后面的所有条目
// 如果Follower已经包含了领导者发送的所有条目(也就是没冲突),那么它绝不能截断其日志。
// 寻找第一个冲突的索引位置
conflictIndex := -1
for i, entry := range args.Entries {
index := args.PrevLogIndex + 1 + i
if index >= len(rf.log) {
// Follower的日志比Leader的短,没有更多条目需要检查,后续全是新条目,直接追加
break
}
if rf.log[index].TermId != entry.TermId {
// 发现了冲突:索引相同,但任期不同
conflictIndex = index
break
}
}
// 如果现有条目与新条目冲突(索引相同但术语不同),请删除现有条目及其后面的所有条目
if conflictIndex != -1 {
// 发现冲突:删除Follower日志中从第一个冲突位置开始的所有后续条目
rf.log = rf.log[:conflictIndex] // 截断冲突点之后的日志
}
// 追加新log
rf.log = append(rf.log, args.Entries...)
// 如果leaderCommit > commitIndex,则设置commitIndex = min(leaderCommit,最后一个新条目的索引)
reply.Success = true
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
if args.CommitIndex > rf.commitIndex {
rf.commitIndex = min(args.CommitIndex, len(rf.log)-1)
}
flag = false
}
}
}
// 发送心跳
func (rf *Raft) sendHeartbeat() {
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
me := rf.me
length := len(rf.peers)
args := &AppendEntriesArgs{
TermId: rf.currentTerm,
LeaderId: rf.me,
PrevLogIndex: len(rf.log) - 1,
PrevLogTermId: rf.log[len(rf.log)-1].TermId,
Entries: nil, // 判断心跳依据
CommitIndex: rf.commitIndex,
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
if i == me {
continue
}
reply := AppendEntriesReply{}
go func(server int, args *AppendEntriesArgs, reply AppendEntriesReply) {
newArgs := *args // 这里必须要拷贝一份, 否则多个go routine会共用一个args, 导致数据错误
ok := rf.sendAppendEntries(server, &newArgs, &reply)
if !ok { // call失败: 服务器宕机、存活但不可达的服务器、请求丢失或回复丢失; 暂时不重发
return
}
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
// log.Printf("sendHeartbeat--节点: %v , 当前term: %v , 向 %v 发送了心跳", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, i)
if rf.currentTerm != args.TermId || rf.state != Leader {
return
}
if !reply.Success {
if rf.currentTerm < reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader { // 自身leader不合法
rf.state = Follower
rf.currentTerm = reply.TermId
rf.votedFor = -1
}
return
}
// // log.Printf("sendHeartbeat--节点: %v , 当前term: %v , 向 %v 发送了心跳, 并且发送成功", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, i)
// 心跳发送成功, 也意味着CommitedIndex发送成功
}(i, args, reply)
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
break
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
}
// leader发送日志/心跳
func (rf *Raft) sendLog(clientCommand interface{}) {
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
isHeartbeat := (clientCommand == nil)
// leader 先把log写到自己的log[]
var newLogEntry logEntity
if !isHeartbeat {
newLogEntry = logEntity{
TermId: rf.currentTerm,
Command: clientCommand,
}
rf.log = append(rf.log, &newLogEntry)
}
me := rf.me
length := len(rf.peers)
commitDone := false // 是否已获得大多数赞同追加日志, 表示日志可以Commit, 但是还要继续发,直到发给所有follower
rf.mu.Unlock()
var count atomic.Int32
count.Add(1)
// 提议阶段
// 向peer中其他节点发送sendRequestVote, 并统计投票数
// var syn sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
if i == me {
continue
}
// syn.Add(1)
// 设置传入参数
rf.mu.Lock()
var entry []*logEntity
if isHeartbeat {
entry = nil
} else {
entry = []*logEntity{
&newLogEntry,
}
}
args := AppendEntriesArgs{
TermId: rf.currentTerm,
LeaderId: rf.me,
PrevLogIndex: rf.nextIndex[i] - 1,
PrevLogTermId: rf.log[rf.nextIndex[i]-1].TermId,
Entries: entry,
CommitIndex: rf.commitIndex,
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
reply := AppendEntriesReply{}
go func(server int, args AppendEntriesArgs, reply AppendEntriesReply) {
// defer syn.Done()
ok := rf.sendAppendEntries(server, &args, &reply)
if !ok { // call失败: 服务器宕机、存活但不可达的服务器、请求丢失或回复丢失; 暂时不重发
return
}
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
if rf.currentTerm != args.TermId || rf.state != Leader {
return
}
if !reply.Success { // 没有追加成功
if rf.currentTerm < reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader { // 自身leader不合法
rf.state = Follower
rf.currentTerm = reply.TermId
rf.votedFor = -1
}
// 处理追加失败情况: 日志落后, 自身leader不合法
if !isHeartbeat && rf.currentTerm == reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader { // 自身leader合法, 那就是follower日志落后了
rf.nextIndex[i]--
idx := rf.nextIndex[i]
preIdx := idx - 1
newEntries := make([]*logEntity, 0, len(args.Entries)+1)
newEntries = append(newEntries, rf.log[idx])
newEntries = append(newEntries, args.Entries...)
args.Entries = newEntries
args.PrevLogIndex = preIdx
args.PrevLogTermId = rf.log[preIdx].TermId
}
return
}
count.Add(1)
// 追加成功
if !isHeartbeat {
rf.matchIndex[i]++
rf.nextIndex[i]++
}
// 得到大多数支持
if int(count.Load()) > len(rf.peers)/2 { // 可以提交了
commitDone = true
rf.commitIndex++
// return
}
}(i, args, reply)
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader || commitDone {
rf.mu.Unlock()
break
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
}
// 追加日志RPC
func (rf *Raft) sendAppendEntries(server int, args *AppendEntriesArgs, reply *AppendEntriesReply) bool {
ok := rf.peers[server].Call("Raft.AppendEntries", args, reply)
return ok
}
func (rf *Raft) Kill() {
atomic.StoreInt32(&rf.dead, 1) // 原子操作设置终止标志
// Your code here, if desired.
}
func (rf *Raft) killed() bool {
z := atomic.LoadInt32(&rf.dead) // 原子读取终止标志
return z == 1
}
func (rf *Raft) ticker() {
for rf.killed() == false { // 当前节点还没挂
// Your code here (3A)
// 检查是否应该开始领导人选举。
electionTimeout := time.Duration(600+rand.Intn(600)) * time.Millisecond
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader && time.Since(rf.lastHeartbeatTime) >= electionTimeout {
rf.mu.Unlock()
// 开始选举
go rf.vote()
rf.mu.Lock()
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
time.Sleep(heartbeatIntervalTime / 2)
}
}
func Make(peers []*labrpc.ClientEnd, me int,
persister *tester.Persister, applyCh chan raftapi.ApplyMsg) raftapi.Raft {
rf := &Raft{}
rf.peers = peers
rf.persister = persister
rf.me = me
rf.currentTerm = 0
rf.votedFor = -1
rf.log = make([]*logEntity, 1)
rf.log[0] = &logEntity{
TermId: 0,
Command: nil,
}
rf.state = Follower
rf.commitIndex = 0
rf.lastapplied = -1
rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now()
rf.nextIndex = make([]int, len(peers))
rf.matchIndex = make([]int, len(peers))
for i := range rf.matchIndex {
rf.matchIndex[i] = 0
}
for i := range rf.nextIndex {
rf.nextIndex[i] = 1
}
rf.leaderCond = sync.NewCond(&rf.mu)
// 初始化从崩溃前持久的状态
rf.readPersist(persister.ReadRaftState())
// start ticker goroutine to start elections
go rf.ticker()
go func() {
// LostContactCount := 0
for !rf.killed() {
rf.mu.Lock()
// 非 Leader 时休眠(释放锁并等待通知)
for rf.state != Leader {
rf.leaderCond.Wait() // 等待成为 Leader 的信号
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
// rf.Start(command) // 发送log
// 处理返回值
rf.sendLog(nil) //发送心跳
time.Sleep(heartbeatIntervalTime)
}
}()
return rf
}
测试结果:
前面说过网络具有不可靠性, 为了验证代码的正确性, 我将测试重复了3000次,
测试脚本
我懒得改测试代码,只是写了个脚本重复执行测试:
#!/bin/bash
# 清除之前的结果文件
> 3A-result.txt
# 记录脚本开始时间
start_time=$(date +%s)
# 初始化计数器
total_runs=3000
success_count=0
failure_count=0
for i in {1..3000}; do
echo "===== 开始第 $i 次测试 =====" >> 3A-result.txt
start_run=$(date +%s)
# 运行测试并捕获退出状态
go test -run 3A -v >> 3A-result.txt 2>&1
exit_status=$?
end_run=$(date +%s)
run_time=$((end_run - start_run))
echo "===== 结束第 $i 次测试 ===== (耗时: ${run_time}秒)" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "" >> 3A-result.txt
# 更新成功/失败计数器
if [ $exit_status -eq 0 ]; then
success_count=$((success_count + 1))
# echo "第 $i 次测试: 成功 (耗时: ${run_time}秒)"
else
failure_count=$((failure_count + 1))
# echo "第 $i 次测试: 失败 (耗时: ${run_time}秒)"
fi
done
# 计算总耗时
end_time=$(date +%s)
total_time=$((end_time - start_time))
average_time=$((total_time / total_runs))
success_percent=$((success_count * 100 / total_runs))
# 添加统计摘要
echo "===== 测试统计摘要 =====" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "总测试次数: $total_runs" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "成功次数: $success_count" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "失败次数: $failure_count" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "成功率: ${success_percent}%" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "总耗时: ${total_time}秒" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "平均每次测试耗时: ${average_time}秒" >> 3A-result.txt
echo "===== 测试结束 =====" >> 3A-result.txt
测试3000次
结果如下:
===== 开始第 1 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestInitialElection3A
Test (3A): initial election (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 58 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestInitialElection3A (3.54s)
=== RUN TestReElection3A
Test (3A): election after network failure (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 124 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReElection3A (5.41s)
=== RUN TestManyElections3A
Test (3A): multiple elections (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.6s #peers 7 #RPCs 648 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestManyElections3A (6.59s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 15.545s
===== 结束第 1 次测试 ===== (耗时: 16秒)
... 太长了,省略中间部分
===== 开始第 3000 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestInitialElection3A
Test (3A): initial election (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 56 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestInitialElection3A (3.44s)
=== RUN TestReElection3A
Test (3A): election after network failure (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 130 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReElection3A (5.57s)
=== RUN TestManyElections3A
Test (3A): multiple elections (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 8.6s #peers 7 #RPCs 954 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestManyElections3A (8.60s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 17.615s
===== 结束第 3000 次测试 ===== (耗时: 18秒)
===== 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 3000
成功次数: 3000
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 48772秒
平均每次测试耗时: 16秒
===== 测试结束 =====
lab3B log
只要lab3A严格按照论文做好, 3B只不过是添加点东西
背景知识
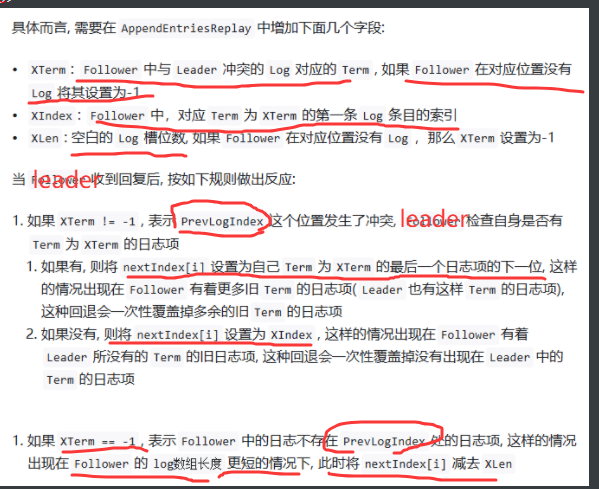
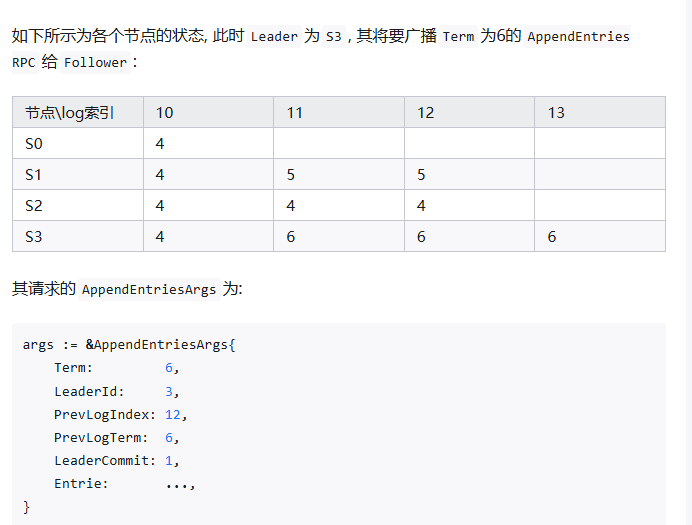
快速恢复不一致follower的Log


踩坑实录
-
这个lab的两阶段提交:
-
提议阶段同步Log,若得到大多数的回复true, 就更新当前leader的commitIndex, 然后通知(我是通过条件变量唤醒)apply(更新leader的applyIndex,并把结果通过applyCh发给应用层, 让它去应用)
-
更新后的commitIndex会作为下一次日志/心跳的参数,同步给follower, 让follower也更新自己的commitIndex, 然后也会更新自己的applyIndex,并把结果通过applyCh发给应用层, 让它去应用
-
-
在发送日志时最好不要用sync.waitGroup等待开启的go routinue都结束了, 再去判断是否达到大多数要去更新commitIndex, 举个例子,看下面代码:
-
// leader发送日志/心跳 func (rf *Raft) sendLog() { rf.mu.Lock() if rf.state != Leader { rf.mu.Unlock() return } // leader 先把log写到自己的log[] me := rf.me length := len(rf.peers) commitDone := false // 是否已获得大多数赞同追加日志, 表示日志可以Commit, 但是还要继续发,直到发给所有follower rf.mu.Unlock() var count atomic.Int32 count.Add(1) // 提议阶段 // 向peer中其他节点发送sendRequestVote, 并统计投票数 var syn sync.WaitGroup for i := 0; i < length; i++ { if i == me { continue } syn.Add(1) // 阻塞等待该follower上一个rpc调用完成 rf.mu.Lock() var isHeartbeat bool var entry []*logEntity if rf.nextIndex[i] >= len(rf.log) { entry = nil isHeartbeat = true } else { entry = rf.log[rf.nextIndex[i]:] isHeartbeat = false } args := AppendEntriesArgs{ TermId: rf.currentTerm, LeaderId: rf.me, PrevLogIndex: rf.nextIndex[i] - 1, PrevLogTermId: rf.log[rf.nextIndex[i]-1].TermId, Entries: entry, CommitIndex: rf.commitIndex, } rf.mu.Unlock() reply := AppendEntriesReply{} go func(server int, args AppendEntriesArgs, reply AppendEntriesReply) { defer syn.Done() ok := rf.sendAppendEntries(server, &args, &reply) // 有结果了, 修改rf.isSending if !ok { // call失败: 服务器宕机、存活但不可达的服务器、请求丢失或回复丢失; 暂时不重发 return } rf.mu.Lock() defer rf.mu.Unlock() if rf.currentTerm != args.TermId || rf.state != Leader { return } if !reply.Success { // 没有追加成功 // 处理追加失败情况 if rf.currentTerm < reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader { rf.state = Follower rf.currentTerm = reply.TermId rf.votedFor = -1 return } // 自身leader合法, 那就是follower日志落后了 if rf.currentTerm == reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader { // 快速回退nextIndex if reply.Xterm == -1 { rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.Xlen } else { // 存在冲突term // 1.如果leader的日志中不包含冲突term, 则将nextIndex[i]设置为XIndex if rf.log[reply.Xindex].TermId != reply.Xterm { rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.Xindex } else { // 2.如果leader的日志中包含冲突term, 则将nextIndex[i]设置为自己term==Xterm的最后一个索引+1 for j := reply.Xindex; j < len(rf.log); j++ { if rf.log[j].TermId != reply.Xterm { rf.nextIndex[server] = j break } } } } if isHeartbeat { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送心跳: %+v, 追加失败, 返回信息为: %+v, 已将nextIndex回退到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args, reply, rf.nextIndex[server]) } else { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志: %+v, 追加失败, 返回信息为: %+v, 已将nextIndex回退到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args, reply, rf.nextIndex[server]) } } return } count.Add(1) // 追加成功 rf.matchIndex[server] = args.PrevLogIndex + len(args.Entries) rf.nextIndex[server] = rf.matchIndex[server] + 1 if int(count.Load()) > length/2 && rf.state == Leader { commitDone = true } }(i, args, reply) rf.mu.Lock() if rf.state != Leader { rf.mu.Unlock() break } rf.mu.Unlock() } syn.wait() if commitDone && rf.state == Leader{ matchIndexes := make([]int, len(rf.peers)) copy(matchIndexes, rf.matchIndex) matchIndexes[rf.me] = len(rf.log) - 1 // leader自己的matchIndex就是当前log的最后一个index // 对matchIndex排序, 中位数就是大多数节点都复制了的最高日志条目索引 sort.Ints(matchIndexes) n := matchIndexes[len(matchIndexes)/2] // 中位数 // 领导者只能提交当前任期的日志条目,提交之前任期的日志条目可能导致数据不一致 if n > rf.commitIndex && n < len(rf.log) && rf.log[n].TermId == rf.currentTerm { rf.commitIndex = n // 唤醒applier rf.applyCond.Broadcast() if isHeartbeat { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向所有 follower 发送心跳, 已经获得大多数follower的认可, 已将commitIndex更新到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.commitIndex) } else { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向所有 follower 发送日志, 已经获得大多数follower的认可, 已将commitIndex更新到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.commitIndex) } } } } -
syn.wait() 错误就在这里, 因为其会阻塞等待开启的go routinue都结束了, 而不是大多数的Log同步成功了, 当然如果网络没问题影响不大, 但是..., 因此不必要的等待会延误更新commitIndex
-
还有一处细节:
-
// 领导者只能提交当前任期的日志条目,提交之前任期的日志条目可能导致数据不一致 if n > rf.commitIndex && n < len(rf.log) && rf.log[n].TermId == rf.currentTerm 这个点论文里也提到过, 因为你不确定之前term的log是否已经提交... -
上述代码中已经添加了快速恢复log(通过reply参数去修改nextIndex) 和 判断达到大多数可以提交的代码
-
修改后的代码如下:
-
// leader发送日志/心跳 func (rf *Raft) sendLog() { rf.mu.Lock() if rf.state != Leader { rf.mu.Unlock() return } // leader 先把log写到自己的log[] me := rf.me length := len(rf.peers) // commitDone := false // 是否已获得大多数赞同追加日志, 表示日志可以Commit, 但是还要继续发,直到发给所有follower rf.mu.Unlock() var count atomic.Int32 count.Add(1) // 提议阶段 // 向peer中其他节点发送sendRequestVote, 并统计投票数 // var syn sync.WaitGroup for i := 0; i < length; i++ { if i == me { continue } // syn.Add(1) // 阻塞等待该follower上一个rpc调用完成 rf.mu.Lock() var isHeartbeat bool var entry []*logEntity if rf.nextIndex[i] >= len(rf.log) { entry = nil isHeartbeat = true } else { entry = rf.log[rf.nextIndex[i]:] isHeartbeat = false } args := AppendEntriesArgs{ TermId: rf.currentTerm, LeaderId: rf.me, PrevLogIndex: rf.nextIndex[i] - 1, PrevLogTermId: rf.log[rf.nextIndex[i]-1].TermId, Entries: entry, CommitIndex: rf.commitIndex, } rf.mu.Unlock() reply := AppendEntriesReply{} go func(server int, args AppendEntriesArgs, reply AppendEntriesReply) { ok := rf.sendAppendEntries(server, &args, &reply) // 有结果了, 修改rf.isSending if !ok { // call失败: 服务器宕机、存活但不可达的服务器、请求丢失或回复丢失; 暂时不重发 return } rf.mu.Lock() defer rf.mu.Unlock() if rf.currentTerm != args.TermId || rf.state != Leader { return } if !reply.Success { // 没有追加成功 // 处理追加失败情况 if rf.currentTerm < reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader { rf.state = Follower rf.currentTerm = reply.TermId rf.votedFor = -1 return } // 自身leader合法, 那就是follower日志落后了 if rf.currentTerm == reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader { // 快速回退nextIndex if reply.Xterm == -1 { rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.Xlen } else { // 存在冲突term // 1.如果leader的日志中不包含冲突term, 则将nextIndex[i]设置为XIndex if rf.log[reply.Xindex].TermId != reply.Xterm { rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.Xindex } else { // 2.如果leader的日志中包含冲突term, 则将nextIndex[i]设置为自己term==Xterm的最后一个索引+1 for j := reply.Xindex; j < len(rf.log); j++ { if rf.log[j].TermId != reply.Xterm { rf.nextIndex[server] = j break } } } } if isHeartbeat { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送心跳: %+v, 追加失败, 返回信息为: %+v, 已将nextIndex回退到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args, reply, rf.nextIndex[server]) } else { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志: %+v, 追加失败, 返回信息为: %+v, 已将nextIndex回退到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args, reply, rf.nextIndex[server]) } } return } count.Add(1) // 追加成功 rf.matchIndex[server] = args.PrevLogIndex + len(args.Entries) rf.nextIndex[server] = rf.matchIndex[server] + 1 if int(count.Load()) > length/2 && rf.state == Leader { matchIndexes := make([]int, len(rf.peers)) copy(matchIndexes, rf.matchIndex) matchIndexes[rf.me] = len(rf.log) - 1 // leader自己的matchIndex就是当前log的最后一个index // 对matchIndex排序, 中位数就是大多数节点都复制了的最高日志条目索引 sort.Ints(matchIndexes) n := matchIndexes[len(matchIndexes)/2] // 中位数 // 领导者只能提交当前任期的日志条目,提交之前任期的日志条目可能导致数据不一致 if n > rf.commitIndex && n < len(rf.log) && rf.log[n].TermId == rf.currentTerm { rf.commitIndex = n // 唤醒applier rf.applyCond.Broadcast() if isHeartbeat { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向所有 follower 发送心跳, 已经获得大多数follower的认可, 已将commitIndex更新到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.commitIndex) } else { // DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向所有 follower 发送日志, 已经获得大多数follower的认可, 已将commitIndex更新到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.commitIndex) } } } }(i, args, reply) rf.mu.Lock() if rf.state != Leader { rf.mu.Unlock() break } rf.mu.Unlock() } }
-
-
start的实现
func (rf *Raft) Start(command interface{}) (int, int, bool) { // 调用start的时候已经加锁了 rf.mu.Lock() defer rf.mu.Unlock() // Your code here (3B). if rf.state != Leader { return -1, -1, false } // 是leader newLogEntry := logEntity{ TermId: rf.currentTerm, Command: command, } rf.log = append(rf.log, &newLogEntry) // if command != nil { // go rf.sendLog(command) // } // DPrintf("Start---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到客户端的命令: %v, 已追加到本地日志, 日志索引为: %v, 并开始日志同步\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, command, len(rf.log)-1) return len(rf.log) - 1, rf.currentTerm, true }这里我有过纠结, 按理来说应用层调用start的时候就应该go rf.sendLog(command), 但是并发测试的时候会有一个问题, 那就是同时有多个sendLog在执行, 那么由于RPC的存在加锁是间断性的,那么很有可能多个go routinue(执行不同的log同步), 但是却得到了相同的:
PrevLogIndex: rf.nextIndex[i] - 1, PrevLogTermId: rf.log[rf.nextIndex[i]-1].TermId,因为很有可能你前一个log还没同步完. rf.nextIndex[i]还没被更新, 暂时想不到很好的解决方法, 也比较麻烦
因此我把同步日志也和心跳一样作为定时任务了, 有log就发log, 没log就发心跳, 这样错开时间避免这种错误
-
接收日志/心跳
因为我在发送log并不像client发送command给raft(通过start)一样,是一个个发送的, 而是先把command插入log, 再截取,这样可以有序批量发送, 因此基本不用考虑网络不稳定带来的log乱序问题, 但仍然会有重发的问题, 代码如下:
// 接收日志/心跳
func (rf *Raft) AppendEntries(args *AppendEntriesArgs, reply *AppendEntriesReply) {
// Your code here (3A, 3B).
flag := true
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()if args.TermId < rf.currentTerm {
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm
reply.Success = false
return
}
for flag {
switch rf.state {
case Leader:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else {
reply.Success = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Candidate:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else if args.TermId == rf.currentTerm {
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
rf.state = Follower
// rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else {
reply.Success = false
reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Follower:
if args.TermId > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.TermId
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
}
// 从当前Leader那里收到AppendEntries RPC(本端Term和arg中的Term一定要一致!)
// 重置心跳检测
// if args.TermId == rf.currentTerm
rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now()// 如果日志在prevLogIndex中不包含与prevLogTerm匹配的条目,则回复false if len(rf.log) <= args.PrevLogIndex || rf.log[args.PrevLogIndex].TermId != args.PrevLogTermId { reply.Success = false reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID flag = false // 快速回退 // 日志不一致,返回冲突信息 reply.Xlen = len(rf.log) if len(rf.log) <= args.PrevLogIndex { // follower日志比leader短, 没有冲突term reply.Xterm = -1 reply.Xindex = -1 } else if rf.log[args.PrevLogIndex].TermId != args.PrevLogTermId { // 日志在prevLogIndex中不包含与prevLogTerm匹配的条目 reply.Xterm = rf.log[args.PrevLogIndex].TermId // 找到冲突term的第一个日志索引 reply.Xindex = args.PrevLogIndex for reply.Xindex > 0 && rf.log[reply.Xindex-1].TermId == reply.Xterm { reply.Xindex-- } } break } // rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now() if args.Entries != nil { // 如果现有条目与新条目冲突(相同索引但不同term),则删除现有条目及其后面的所有条目 // 如果Follower已经包含了领导者发送的所有条目(也就是没冲突),那么它绝不能截断其日志。 // 寻找第一个冲突的索引位置 conflictIndex := -1 for i, entry := range args.Entries { index := args.PrevLogIndex + 1 + i // 新条目应该在的Index if index >= len(rf.log) { // Follower的日志比Leader的短,没有更多条目需要检查,后续全是新条目,直接追加 break } if rf.log[index].TermId != entry.TermId { // 发现了冲突:索引相同,但任期不同 conflictIndex = index break } } // 如果现有条目与新条目冲突(索引相同但术语不同),请删除现有条目及其后面的所有条目 if conflictIndex != -1 { // 发现冲突:删除Follower日志中从第一个冲突位置开始的所有后续条目 rf.log = rf.log[:conflictIndex] // 截断冲突点之后的日志 } // 追加新log rf.log = append(rf.log, args.Entries...) } // 如果leaderCommit > commitIndex,则设置commitIndex = min(leaderCommit,最后一个新条目的索引) reply.Success = true reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID if args.CommitIndex > rf.commitIndex { // 更新的commitIndex是之前的,不涉及当前logIndex rf.commitIndex = min(args.CommitIndex, len(rf.log)-1) // 唤醒apply rf.applyCond.Broadcast() } flag = false }}
if args.Entries == nil {
// 心跳函数
// DPrintf("AppendEntries---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 接收到 leader %v 的心跳: %+v, 结果为: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, args.LeaderId, args, reply.Success)
} else {
// // DPrintf("AppendEntries---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到 leader %v 的AppendEntries: %+v, 结果为: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, args.LeaderId, args.Entries, reply.Success)
// 打印接收到的日志条目命令
receivedCommands := make([]interface{}, len(args.Entries))
for i, entry := range args.Entries {
receivedCommands[i] = entry.Command
}// 打印当前节点的日志命令 currentLogCommands := make([]interface{}, len(rf.log)) for i, entry := range rf.log { currentLogCommands[i] = entry.Command } // DPrintf("AppendEntries---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到 leader %v 的AppendEntries:\n"+" 接收到的日志命令: %v\n"+" 当前节点日志命令: %v\n"+" 完整参数: %+v\n"+" 结果: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, args.LeaderId, receivedCommands, currentLogCommands, args, reply.Success)}
}
-
apply(及时更新applyIndex, 并把可以应用的command发送给applyCh)
// rf.commitIndex++时唤醒 func (rf *Raft) applier(applyCh chan raftapi.ApplyMsg) { for !rf.killed() { rf.mu.Lock() // 等待直到有新的日志可以应用 for rf.commitIndex <= rf.lastapplied { rf.applyCond.Wait() // 使用条件变量等待 } applyMsgs := make([]raftapi.ApplyMsg, 0) // 应用所有新的已提交日志 for rf.commitIndex > rf.lastapplied { rf.lastapplied++ applyMsg := raftapi.ApplyMsg{ CommandValid: true, Command: rf.log[rf.lastapplied].Command, CommandIndex: rf.lastapplied, } applyMsgs = append(applyMsgs, applyMsg) } rf.mu.Unlock() // 发送 ApplyMsg 到 applyCh 通道 for _, applyMsg := range applyMsgs { applyCh <- applyMsg } rf.mu.Lock() // DPrintf("applier---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 已将日志应用到状态机, 最新应用的日志索引为: %v, 日志内容为: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.lastapplied, rf.log[rf.lastapplied].Command) rf.mu.Unlock() } }然后在make()中 go applier() 即可
测试结果
因为3B测试时间长一点, 所以我只搞了300次
测试脚本:
#!/bin/bash
# 清除之前的结果文件
> 3B-result.txt
# 记录脚本开始时间
start_time=$(date +%s)
# 初始化计数器
total_runs=300
success_count=0
failure_count=0
for i in {1..300}; do
echo "===== 开始第 $i 次测试 =====" >> 3B-result.txt
start_run=$(date +%s)
# 运行测试并捕获退出状态
time go test -run 3B -v >> 3B-result.txt 2>&1
exit_status=$?
end_run=$(date +%s)
run_time=$((end_run - start_run))
echo "===== 结束第 $i 次测试 ===== (耗时: ${run_time}秒)" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "" >> 3B-result.txt
# 更新成功/失败计数器
if [ $exit_status -eq 0 ]; then
success_count=$((success_count + 1))
# echo "第 $i 次测试: 成功 (耗时: ${run_time}秒)"
else
failure_count=$((failure_count + 1))
# echo "第 $i 次测试: 失败 (耗时: ${run_time}秒)"
fi
done
# 计算总耗时
end_time=$(date +%s)
total_time=$((end_time - start_time))
average_time=$((total_time / total_runs))
success_percent=$((success_count * 100 / total_runs))
# 添加统计摘要
echo "===== 测试统计摘要 =====" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "总测试次数: $total_runs" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "成功次数: $success_count" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "失败次数: $failure_count" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "成功率: ${success_percent}%" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "总耗时: ${total_time}秒" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "平均每次测试耗时: ${average_time}秒" >> 3B-result.txt
echo "===== 测试结束 =====" >> 3B-result.txt
测试300次:
===== 开始第 1 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestBasicAgree3B
Test (3B): basic agreement (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 16 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBasicAgree3B (1.38s)
=== RUN TestRPCBytes3B
Test (3B): RPC byte count (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 50 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRPCBytes3B (2.93s)
=== RUN TestFollowerFailure3B
Test (3B): test progressive failure of followers (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 102 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFollowerFailure3B (5.10s)
=== RUN TestLeaderFailure3B
Test (3B): test failure of leaders (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 196 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestLeaderFailure3B (5.97s)
=== RUN TestFailAgree3B
Test (3B): agreement after follower reconnects (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 92 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailAgree3B (4.70s)
=== RUN TestFailNoAgree3B
Test (3B): no agreement if too many followers disconnect (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.1s #peers 5 #RPCs 172 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailNoAgree3B (4.09s)
=== RUN TestConcurrentStarts3B
Test (3B): concurrent Start()s (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.3s #peers 3 #RPCs 14 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestConcurrentStarts3B (1.26s)
=== RUN TestRejoin3B
Test (3B): rejoin of partitioned leader (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.3s #peers 3 #RPCs 176 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRejoin3B (7.32s)
=== RUN TestBackup3B
Test (3B): leader backs up quickly over incorrect follower logs (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 26.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 2052 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBackup3B (25.96s)
=== RUN TestCount3B
Test (3B): RPC counts aren't too high (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 42 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestCount3B (2.77s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 61.493s
===== 结束第 1 次测试 ===== (耗时: 62秒)
..........................
===== 开始第 300 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestBasicAgree3B
Test (3B): basic agreement (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.3s #peers 3 #RPCs 18 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBasicAgree3B (1.28s)
=== RUN TestRPCBytes3B
Test (3B): RPC byte count (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 48 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRPCBytes3B (2.98s)
=== RUN TestFollowerFailure3B
Test (3B): test progressive failure of followers (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 106 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFollowerFailure3B (5.21s)
=== RUN TestLeaderFailure3B
Test (3B): test failure of leaders (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 196 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestLeaderFailure3B (6.16s)
=== RUN TestFailAgree3B
Test (3B): agreement after follower reconnects (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 126 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailAgree3B (6.57s)
=== RUN TestFailNoAgree3B
Test (3B): no agreement if too many followers disconnect (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.1s #peers 5 #RPCs 172 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailNoAgree3B (4.10s)
=== RUN TestConcurrentStarts3B
Test (3B): concurrent Start()s (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 12 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestConcurrentStarts3B (1.12s)
=== RUN TestRejoin3B
Test (3B): rejoin of partitioned leader (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 194 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRejoin3B (7.24s)
=== RUN TestBackup3B
Test (3B): leader backs up quickly over incorrect follower logs (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 25.4s #peers 5 #RPCs 2040 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBackup3B (25.36s)
=== RUN TestCount3B
Test (3B): RPC counts aren't too high (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 42 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestCount3B (2.66s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 62.681s
===== 结束第 300 次测试 ===== (耗时: 63秒)
===== 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 300
成功次数: 300
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 19016秒
平均每次测试耗时: 63秒
===== 测试结束 =====
lab3C
持久化的内容
持久化存储的目的是为了在服务器重启时利用持久化存储的数据恢复节点上一个工作时刻的状态。并且,持久化的内容仅仅是Raft层, 其应用层不做要求。
论文中提到需要持久花的数据包括:
-
votedFor:
votedFor记录了一个节点在某个Term内的投票记录, 因此如果不将这个数据持久化, 可能会导致如下情况: -
- 在一个
Term内某个节点向某个Candidate投票, 随后故障 - 故障重启后, 又收到了另一个
RequestVote RPC, 由于其没有将votedFor持久化, 因此其不知道自己已经投过票, 结果是再次投票, 这将导致同一个Term可能出现2个Leader
- 在一个
-
currentTerm:
currentTerm的作用也是实现一个任期内最多只有一个Leader, 因为如果一个几点重启后不知道现在的Term时多少, 其无法再进行投票时将currentTerm递增到正确的值, 也可能导致有多个Leader在同一个Term中出现 -
Log
: 这个很好理解, 需要用Log`来恢复自身的状态
这里值得思考的是:为什么只需要持久化votedFor, currentTerm, Log?
原因是其他的数据, 包括 commitIndex、lastApplied、nextIndex、matchIndex都可以通过心跳的发送和回复逐步被重建, Leader会根据回复信息判断出哪些Log被commit了。
什么时候持久化
由于将任何数据持久化到硬盘上都是巨大的开销, 其开销远大于RPC, 因此需要仔细考虑什么时候将数据持久化。
如果每次修改三个需要持久化的数据: votedFor, currentTerm, Log时, 都进行持久化, 其持久化的开销将会很大, 很容易想到的解决方案是进行批量化操作, 例如只在回复一个RPC或者发送一个RPC时,才进行持久化操作。
踩坑实录
实现persist函数和readPersist函数, 按照例子写就行, 这里主要说一下在并发测试的时候, 从输出的log.Printf里遇到的log重复发送的问题(主要是在并发测试时, 前一个发给某个follower的log的RPC还没结束, rf.nextIndex[]等信息还没更新, 第二次log发送就开始了, 导致log重复发送):
-
场景一:
2025/09/09 23:07:42 AppendEntries---节点server 0, 在term: 1, 收到 leader 1 的AppendEntries: 接收到的日志命令: [6 602 600 601 603] 当前节点日志命令: [<nil> 100 102 1 101 103 2 200 201 203 202 3 301 300 302 303 4 401 400 402 403 5 500 501 502 503 6 602 600 601 603] 完整参数: &{TermId:1 LeaderId:1 PrevLogIndex:25 PrevLogTermId:1 Entries:[0xc00029da58 0xc00029da70 0xc00029da88 0xc00029daa0 0xc00029dab8] CommitIndex:25} 结果: true 2025/09/09 23:07:42 AppendEntries---节点server 0, 在term: 1, 收到 leader 1 的AppendEntries: 接收到的日志命令: [6 602 600 601 603 7 700 701 702 703] 当前节点日志命令: [<nil> 100 102 1 101 103 2 200 201 203 202 3 301 300 302 303 4 401 400 402 403 5 500 501 502 503 6 602 600 601 603 6 602 600 601 603 7 700 701 702 703] 完整参数: &{TermId:1 LeaderId:1 PrevLogIndex:25 PrevLogTermId:1 Entries:[0xc00033d1a0 0xc00033d1b8 0xc00033d1d0 0xc00033d1e8 0xc00033d200 0xc00033d218 0xc00033d230 0xc00033d248 0xc00033d260 0xc00033d278] CommitIndex:30} 结果: true可以看到PrevLogIndex都是25, 通过了PrevLogIndex的检测, 导致重复添加了[6 602 600 601 603], 解决如下:
argsEntriesStartIndex := 0 // 新条目在Follower的log中应该开始的位置 for i, entry := range args.Entries { index := args.PrevLogIndex + 1 + i // 新条目应该在的Index if index >= len(rf.log) { // Follower的日志比Leader的短,没有更多条目需要检查,后续全是新条目,直接追加 argsEntriesStartIndex = i break } if rf.log[index].TermId != entry.TermId { // 发现了冲突:索引相同,但任期不同 conflictIndex = index break } } // 如果现有条目与新条目冲突(索引相同但术语不同),请删除现有条目及其后面的所有条目 if conflictIndex != -1 { // 发现冲突:删除Follower日志中从第一个冲突位置开始的所有后续条目 rf.log = rf.log[:conflictIndex] // 截断冲突点之后的日志 } -
场景二:
rf.nextIndex还没更新, 下一次log就开始发送了, 会导致如下场景: 2025/09/09 22:13:59 AppendEntries---节点server 0, 在term: 1, 收到 leader 3 的AppendEntries: 接收到的日志命令: [3 301 302 303 300] 当前节点日志命令: [<nil> 1 103 102 100 101 2 201 202 203 200 3 301 302 303 300] 完整参数: &{TermId:1 LeaderId:3 PrevLogIndex:10 PrevLogTermId:1 Entries:[0xc0003b0210 0xc0003b0228 0xc0003b0240 0xc0003b0258 0xc0003b0270] CommitIndex:10} 结果: true 2025/09/09 22:13:59 applier---节点server 0, 在term: 1, 已将日志应用到状态机, 最新应用的日志索引为: 10, 日志内容为: 200 2025/09/09 22:13:59 AppendEntries---节点server 0, 在term: 1, 收到 leader 3 的AppendEntries: 接收到的日志命令: [3 301 302 303 300 4 401 403 402 400] 当前节点日志命令: [<nil> 1 103 102 100 101 2 201 202 203 200 3 301 302 303 300 3 301 302 303 300 4 401 403 402 400] 完整参数: &{TermId:1 LeaderId:3 PrevLogIndex:10 PrevLogTermId:1 Entries:[0xc0002d8930 0xc0002d8948 0xc0002d8960 0xc0002d8978 0xc0002d8990 0xc0002d89a8 0xc0002d89c0 0xc0002d89d8 0xc0002d89f0 0xc0002d8a08] CommitIndex:15} 结果: true 2025/09/09 22:13:59 applier---节点server 0, 在term: 1, 已将日志应用到状态机, 最新应用的日志索引为: 15, 日志内容为: 300重复发送了3 301 302 303 300, PrevLogIndex都是10
解决如下:
// 幂等性检查:如果日志已经包含所有条目,则直接返回成功 if len(args.Entries) > 0 { lastNewIndex := args.PrevLogIndex + len(args.Entries) if lastNewIndex < len(rf.log) { // 检查所有条目是否已经存在且匹配 allExist := true for i, entry := range args.Entries { idx := args.PrevLogIndex + 1 + i if idx >= len(rf.log) || rf.log[idx].TermId != entry.TermId { allExist = false break } } if allExist { // 所有条目已经存在且匹配,直接返回成功 reply.Success = true reply.TermId = rf.currentTerm if args.CommitIndex > rf.commitIndex { rf.commitIndex = min(args.CommitIndex, len(rf.log)-1) rf.applyCond.Broadcast() } flag = false break } } }
测试结果
测试脚本:
#!/bin/bash
# 清除之前的结果文件
> 3C-result.txt
# 记录脚本开始时间
start_time=$(date +%s)
# 初始化计数器
total_runs=300
success_count=0
failure_count=0
for i in {1..300}; do
echo "===== 开始第 $i 次测试 =====" >> 3C-result.txt
start_run=$(date +%s)
# 运行测试并捕获退出状态
time go test -run 3C -v >> 3C-result.txt 2>&1
exit_status=$?
end_run=$(date +%s)
run_time=$((end_run - start_run))
echo "===== 结束第 $i 次测试 ===== (耗时: ${run_time}秒)" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "" >> 3C-result.txt
# 更新成功/失败计数器
if [ $exit_status -eq 0 ]; then
success_count=$((success_count + 1))
# echo "第 $i 次测试: 成功 (耗时: ${run_time}秒)"
else
failure_count=$((failure_count + 1))
# echo "第 $i 次测试: 失败 (耗时: ${run_time}秒)"
fi
done
# 计算总耗时
end_time=$(date +%s)
total_time=$((end_time - start_time))
average_time=$((total_time / total_runs))
success_percent=$((success_count * 100 / total_runs))
# 添加统计摘要
echo "===== 测试统计摘要 =====" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "总测试次数: $total_runs" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "成功次数: $success_count" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "失败次数: $failure_count" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "成功率: ${success_percent}%" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "总耗时: ${total_time}秒" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "平均每次测试耗时: ${average_time}秒" >> 3C-result.txt
echo "===== 测试结束 =====" >> 3C-result.txt
测试300次:
===== 开始第 1 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestPersist13C
Test (3C): basic persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 72 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist13C (5.88s)
=== RUN TestPersist23C
Test (3C): more persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 15.7s #peers 5 #RPCs 312 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist23C (15.72s)
=== RUN TestPersist33C
Test (3C): partitioned leader and one follower crash, leader restarts (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 36 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist33C (2.97s)
=== RUN TestFigure83C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 32.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 536 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure83C (32.19s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableAgree3C
Test (3C): unreliable agreement (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.9s #peers 5 #RPCs 216 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableAgree3C (5.90s)
=== RUN TestFigure8Unreliable3C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (unreliable) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 33.6s #peers 5 #RPCs 2812 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure8Unreliable3C (33.58s)
=== RUN TestReliableChurn3C
Test (3C): churn (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.3s #peers 5 #RPCs 628 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReliableChurn3C (16.28s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableChurn3C
Test (3C): unreliable churn (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 1092 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableChurn3C (16.25s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 128.767s
===== 结束第 1 次测试 ===== (耗时: 128秒)
.............................
===== 开始第 300 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestPersist13C
Test (3C): basic persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 70 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist13C (5.77s)
=== RUN TestPersist23C
Test (3C): more persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 15.4s #peers 5 #RPCs 316 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist23C (15.44s)
=== RUN TestPersist33C
Test (3C): partitioned leader and one follower crash, leader restarts (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 36 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist33C (2.85s)
=== RUN TestFigure83C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 41.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 664 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure83C (41.03s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableAgree3C
Test (3C): unreliable agreement (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 220 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableAgree3C (5.97s)
=== RUN TestFigure8Unreliable3C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (unreliable) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 35.3s #peers 5 #RPCs 2880 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure8Unreliable3C (35.28s)
=== RUN TestReliableChurn3C
Test (3C): churn (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 788 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReliableChurn3C (16.25s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableChurn3C
Test (3C): unreliable churn (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.3s #peers 5 #RPCs 664 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableChurn3C (16.27s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 138.870s
===== 结束第 300 次测试 ===== (耗时: 139秒)
===== 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 300
成功次数: 300
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 38872秒
平均每次测试耗时: 129秒
===== 测试结束 =====
lab3D
SnapShot设计
日志截断和结构体设计
由于发送SnapShot后需要截断日志, 而raft结构体中的字段如commitIndex, lastApplied等, 存储的仍然是全局递增的索引, 由官方的
因此, 在raft结构体中额外增加字段:
type Raft struct {
...
globalLastIncludedIndex int // 全局的最后包含的日志索引
globalLastIncludedTerm int // 全局的最后包含的日志任期
snapShot []byte // 快照内容
}
我将全局递增的索引称为global Index, 将log切片使用的索引称为local Index, 转换的函数应该为:
// 索引变换辅助函数
func (rf *Raft) toLocalIndex(globalIndex int) int {
// globalIndex 是全局的日志索引, 需要转换为本地的日志索引
return globalIndex - rf.globalLastIncludedIndex
}
func (rf *Raft) toGlobalIndex(localIndex int) int {
// localIndex 是本地的日志索引, 需要转换为全局的日志索引
return localIndex + rf.globalLastIncludedIndex
}
有了toLocalIndex和toGlobalIndex, 我的代码将遵循以下的规则:
- 访问
rf.log一律使用真实的切片索引, 即Real Index - 其余情况, 一律使用全局递增的索引
Virtual Index
设计完成这两个函数后, 修改所有代码中对索引的操作, 调用RealLogIdx将Virtual Index转化为Real Index, 或调用VirtualLogIdx将Real Index转化为Virtual Index, 由于涉及代码太多且并不复杂, 此处不贴代码
Snapshot函数设计
Snapshot很简单, 接收service层的快照请求, 并截断自己的log数组, 但还是有几个点需要说明:
-
判断是否接受
Snapshot -
- 创建
Snapshot时, 必须保证其index小于等于commitIndex, 如果index大于commitIndex, 则会有包括未提交日志项的风险。快照中不应包含未被提交的日志项 - 创建
Snapshot时, 必须保证其index小于等于lastIncludedIndex, 因为这可能是一个重复的或者更旧的快照请求RPC, 应当被忽略
- 创建
-
还需要检查
lastApplied是否位于Snapshot之前, 如果是, 需要调整到与index一致 -
将
snapshot保存
因为后续Follower可能需要snapshot, 以及持久化时需要找到snapshot进行保存, 因此此时要保存以便后续发送给Follower -
调用
persist持久化
func (rf *Raft) Snapshot(index int, snapshot []byte) {
// Your code here (3D).
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
defer rf.persist()
// 快照的索引必须已经提交
if index <= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex || index > rf.commitIndex {
return
}
// 督促apllier尽快应用快照
for index > rf.lastapplied {
rf.applyCond.Broadcast()
time.Sleep(10 * time.Millisecond)
}
// 更新快照
rf.snapShot = snapshot
// 截断log
rf.log = rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(index):]
rf.globalLastIncludedIndex = index
rf.globalLastIncludedTerm = rf.log[0].TermId
DPrintf("server %v 创建快照成功, 全局LastIncludedIndex: %v, 全局LastIncludedTerm: %v, 快照大小: %v\n", rf.me, rf.globalLastIncludedIndex, rf.globalLastIncludedTerm, len(rf.snapShot))
}
相关持久化函数
persist函数
添加快照后, 调用persist时还需要编码额外的字段lastIncludedIndex和lastIncludedTerm, 在调用Save函数时需要传入快照rf.snapShot
func (rf *Raft) persist() {
// Your code here (3C).
// Example:
// w := new(bytes.Buffer)
// e := labgob.NewEncoder(w)
// e.Encode(rf.xxx)
// e.Encode(rf.yyy)
// raftstate := w.Bytes()
// rf.persister.Save(raftstate, nil)
w := new(bytes.Buffer)
e := labgob.NewEncoder(w)
e.Encode(rf.currentTerm)
e.Encode(rf.votedFor)
e.Encode(rf.log)
e.Encode(rf.globalLastIncludedIndex)
e.Encode(rf.globalLastIncludedTerm)
raftstate := w.Bytes()
rf.persister.Save(raftstate, rf.snapShot)
}
读取持久化状态和快照
readPersist和readSnapshot分别读取持久化状态和快照:
// 还原以前持久化的状态。
func (rf *Raft) readPersist(data []byte) {
if data == nil || len(data) < 1 { // bootstrap without any state?
return
}
// Your code here (3C).
// Example:
// r := bytes.NewBuffer(data)
// d := labgob.NewDecoder(r)
// var xxx
// var yyy
// if d.Decode(&xxx) != nil ||
// d.Decode(&yyy) != nil {
// error...
// } else {
// rf.xxx = xxx
// rf.yyy = yyy
// }
r := bytes.NewBuffer(data)
d := labgob.NewDecoder(r)
var currentTerm int
var votedFor int
var logs []*logEntity
var globalLastIncludedIndex int
var globalLastIncludedTerm int
if d.Decode(¤tTerm) != nil ||
d.Decode(&votedFor) != nil ||
d.Decode(&logs) != nil ||
d.Decode(&globalLastIncludedIndex) != nil ||
d.Decode(&globalLastIncludedTerm) != nil {
// 解码错误
log.Fatal("Failed to decode persisted state")
} else {
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
rf.currentTerm = currentTerm
rf.votedFor = votedFor
rf.log = logs
// 快照包含的索引一定是被提交和应用的, 此操作可以避免后续的索引越界问题
rf.globalLastIncludedIndex = globalLastIncludedIndex
rf.globalLastIncludedTerm = globalLastIncludedTerm
rf.commitIndex = globalLastIncludedIndex
rf.lastapplied = globalLastIncludedIndex
}
}
// 读取快照内容, 快照持久化的时候没有编码, 因此读取快照也不需要解码
func (rf *Raft) readSnapShot(data []byte) {
// 目前只在Make中调用, 因此不需要锁
if len(data) == 0 {
DPrintf("server %v 读取快照失败: 无快照\n", rf.me)
return
}
rf.snapShot = data
DPrintf("server %v 读取快照c成功\n", rf.me)
}
由于目前仅在Make函数中调用这两个函数, 此时没有协程在执行, 因此不需要加锁, 需要额外注意的是:
rf.commitIndex = lastIncludedIndex
rf.lastApplied = lastIncludedIndex
此操作保证了commitIndex和lastApplied的下限, 因为快照包含的索引一定是被提交和应用的, 此操作可以避免后续的索引越界问题
InstallSnapshot RPC设计
RPC结构体设计
先贴上原论文的描述图

根据图中的描述, 设计RPC结构体如下:
type InstallSnapshotArgs struct {
Term int // 领导者的任期
LeaderId int
LastIncludedIndex int // 第一个包含在快照中的日志条目的索引
LastIncludedTerm int // 第一个包含在快照中的日志条目的任期
Data []byte // 快照内容
}
type InstallSnapshotReply struct {
Term int // 回复者 当前任期,用于领导者更新自己
}
注意, 为了保证在日志同步回退到Index==0处一定成功,即对preLogvIndex的检查通过,我做了如下设计:
-
当不存在快照时
log数据组索引从1开始, 0索引处的command==nil// 在Make中初始化 rf.log[0] = &logEntity{ TermId: 0, Command: nil, } -
当创建快照时,会截断,此时Index==0处都是rf.globalLastIncludedIndex, 不用管
-
当follower的log落后leader的快照, 此时需要舍弃follower的整个log, 需要再次在0索引处设置command==nil的log
// 如果现有日志有与快照最后条目索引和任期相同的条目,保留该条目之后的日志并回复 if args.LastIncludedIndex < rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log)) && rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(args.LastIncludedIndex)].TermId == args.LastIncludedTerm { // 保留该条目之后的日志 rf.log = rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(args.LastIncludedIndex):] } else { // 否则,丢弃整个日志 rf.log = make([]*logEntity, 1) // 初始化日志,保留一个占位符 rf.log[0] = &logEntity{TermId: args.LastIncludedTerm, Command: nil} // 在0位置放一个nil占位 }
发送快照
比较简单, 不需要管失败了怎么样, 不需要管多数派原则
// 发送快照
func (rf *Raft) sendSnapShot(server int) {
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
args := InstallSnapshotArgs{
Term: rf.currentTerm,
LeaderId: rf.me,
LastIncludedIndex: rf.globalLastIncludedIndex,
LastIncludedTerm: rf.globalLastIncludedTerm,
Data: rf.snapShot,
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
reply := InstallSnapshotReply{}
ok := rf.sendInstallSnapshot(server, &args, &reply)
if !ok { // call失败: 服务器宕机、存活但不可达的服务器、请求丢失或回复丢失; 暂时不重发
return
}
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
if rf.currentTerm != args.Term || rf.state != Leader {
return
}
if rf.currentTerm < reply.Term && rf.state == Leader {
rf.state = Follower
rf.currentTerm = reply.Term
rf.votedFor = -1
rf.persist()
return
}
// 发送成功, 更新nextIndex和matchIndex
rf.nextIndex[server] = rf.globalLastIncludedIndex + 1
rf.matchIndex[server] = rf.globalLastIncludedIndex
// DPrintf("sendSnapshot---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送快照: %+v, 发送成功, 已将nextIndex更新到: %v, matchIndex更新到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args, rf.nextIndex[server], rf.matchIndex[server])
}
接收快照
按照论文的图13处理即可,
注意事项:
- 需要保存快照, 添加rf.snapShot
- 快照更新需要向applyCh发消息, 增加rf.applyCh
- 别忘了更新快照相关的状态
// 接收快照RPC
func (rf *Raft) InstallSnapShot(args *InstallSnapshotArgs, reply *InstallSnapshotReply) {
flag := true
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
defer rf.persist()
if args.Term < rf.currentTerm {
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm
return
}
for flag {
switch rf.state {
case Leader:
if args.Term > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.Term
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else {
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Candidate:
if args.Term > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.Term
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
} else if args.Term == rf.currentTerm {
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
rf.state = Follower
} else {
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID
flag = false
}
case Follower:
if args.Term > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.Term
rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人
}
rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now() // 重置心跳检测
// 如果快照比现有快照旧,则忽略它
if args.LastIncludedIndex <= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm
flag = false
break
}
// 保存快照文件,丢弃任何索引更小的现有或部分 快照
rf.snapShot = args.Data
// 如果现有日志有与快照最后条目索引和任期相同的条目,保留该条目之后的日志并回复
if args.LastIncludedIndex < rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log)) && rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(args.LastIncludedIndex)].TermId == args.LastIncludedTerm {
// 保留该条目之后的日志
rf.log = rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(args.LastIncludedIndex):]
} else {
// 否则,丢弃整个日志
rf.log = make([]*logEntity, 1) // 初始化日志,保留一个占位符
rf.log[0] = &logEntity{TermId: args.LastIncludedTerm, Command: nil} // 在0位置放一个占位符
}
// 更新快照相关状态
rf.globalLastIncludedIndex = args.LastIncludedIndex
rf.globalLastIncludedTerm = args.LastIncludedTerm
if rf.commitIndex < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
rf.commitIndex = rf.globalLastIncludedIndex
}
if rf.lastapplied < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex && !rf.applyLock {
rf.lastapplied = rf.globalLastIncludedIndex
}
// 通知服务应用快照
applyMsg := raftapi.ApplyMsg{
SnapshotValid: true,
Snapshot: args.Data,
SnapshotTerm: args.LastIncludedTerm,
SnapshotIndex: args.LastIncludedIndex,
}
rf.applyCh <- applyMsg
// DPrintf("InstallSnapshot---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到 leader %v 的快照: %+v, 已安装快照, 日志更新为: %+v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, args.LeaderId, args, rf.log)
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm
flag = false
}
}
}
发送快照的时机
- 在sendLog的时候察觉到某个follower的log落后(即发送后,同步失败时), 不管是否发生冲突,你都要去判断是否需要给它发送快照(rf.nextIndex[server] < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex)
- 在时机发送前follower的log可能就落后很多了(rf.nextIndex[server] < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex)
// leader发送日志/心跳
func (rf *Raft) sendLog() {
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
// leader 先把log写到自己的log[]
me := rf.me
length := len(rf.peers)
// commitDone := false // 是否已获得大多数赞同追加日志, 表示日志可以Commit, 但是还要继续发,直到发给所有follower
rf.mu.Unlock()
var count atomic.Int32
count.Add(1)
// 提议阶段
// 向peer中其他节点发送sendRequestVote, 并统计投票数
// var syn sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
if i == me {
continue
}
// syn.Add(1)
rf.mu.Lock()
var isHeartbeat bool
var entry []*logEntity
if rf.nextIndex[i] >= rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log)) {
entry = nil
isHeartbeat = true
} else {
if rf.nextIndex[i] <= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
// 说明follower的日志落后太多了, 需要先同步快照
rf.mu.Unlock()
go rf.sendSnapShot(i)
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志失败, 因为PrevLogIndex小于全局LastIncludedIndex, 需要先安装快照\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, i)
continue
}
entry = rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(rf.nextIndex[i]):]
isHeartbeat = false
}
args := AppendEntriesArgs{
TermId: rf.currentTerm,
LeaderId: rf.me,
PrevLogIndex: rf.nextIndex[i] - 1,
PrevLogTermId: rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(rf.nextIndex[i]-1)].TermId,
Entries: entry,
CommitIndex: rf.commitIndex,
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
reply := AppendEntriesReply{}
// 判断该follower的日志是否落后太多,是否需要先同步快照
if args.PrevLogIndex < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
// 说明follower的日志落后太多了, 需要先同步快照
go rf.sendSnapShot(i)
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志: %+v, 追加失败, 因为PrevLogIndex小于全局LastIncludedIndex, 需要先安装快照\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, i, args)
continue
}
go func(server int, args AppendEntriesArgs, reply AppendEntriesReply) {
ok := rf.sendAppendEntries(server, &args, &reply)
if !ok { // call失败: 服务器宕机、存活但不可达的服务器、请求丢失或回复丢失; 暂时不重发
return
}
rf.mu.Lock()
// defer rf.mu.Unlock()
if rf.currentTerm != args.TermId || rf.state != Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
if !reply.Success { // 没有追加成功
// 处理追加失败情况
if rf.currentTerm < reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader {
rf.state = Follower
rf.currentTerm = reply.TermId
rf.votedFor = -1
rf.persist()
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
// 自身leader合法, 那就是follower日志落后了
if rf.currentTerm == reply.TermId && rf.state == Leader {
// 快速回退nextIndex
if reply.Xterm == -1 {
rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.Xlen
// 判断是否需要同步快照
if rf.nextIndex[server] < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
// 说明follower的日志落后太多了, 需要先同步快照
rf.mu.Unlock()
go rf.sendSnapShot(server)
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志: %+v, 追加失败, 因为PrevLogIndex小于全局LastIncludedIndex, 需要先安装快照\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args)
return
}
} else {
// 存在冲突term
// 1.如果leader的日志中不包含冲突term, 则将nextIndex[i]设置为XIndex
if reply.Xindex >= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex && rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(reply.Xindex)].TermId != reply.Xterm {
rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.Xindex
// 判断是否需要同步快照
if rf.nextIndex[server] < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
// 说明follower的日志落后太多了, 需要先同步快照
rf.mu.Unlock()
go rf.sendSnapShot(server)
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志: %+v, 追加失败, 因为PrevLogIndex小于全局LastIncludedIndex, 需要先安装快照\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args)
return
}
} else {
// 2.如果leader的日志中包含冲突term, 则将nextIndex[i]设置为自己term==Xterm的最后一个索引+1
for j := reply.Xindex; j < rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log)); j++ {
if rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(j)].TermId != reply.Xterm {
rf.nextIndex[server] = j
break
}
}
// 判断是否需要同步快照
if rf.nextIndex[server] < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
// 说明follower的日志落后太多了, 需要先同步快照
rf.mu.Unlock()
go rf.sendSnapShot(server)
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志: %+v, 追加失败, 因为PrevLogIndex小于全局LastIncludedIndex, 需要先安装快照\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args)
return
}
}
}
if isHeartbeat {
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送心跳: %+v, 追加失败, 返回信息为: %+v, 已将nextIndex回退到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args, reply, rf.nextIndex[server])
} else {
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向 follower %v 发送日志: %+v, 追加失败, 返回信息为: %+v, 已将nextIndex回退到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, server, args, reply, rf.nextIndex[server])
}
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
count.Add(1)
// 追加成功
rf.matchIndex[server] = args.PrevLogIndex + len(args.Entries)
rf.nextIndex[server] = rf.matchIndex[server] + 1
if int(count.Load()) > length/2 && rf.state == Leader {
matchIndexes := make([]int, len(rf.peers))
copy(matchIndexes, rf.matchIndex)
matchIndexes[rf.me] = rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log) - 1) // leader自己的matchIndex就是当前log的最后一个index
// 对matchIndex排序, 中位数就是大多数节点都复制了的最高日志条目索引
sort.Ints(matchIndexes)
n := matchIndexes[len(matchIndexes)/2] // 中位数
// 领导者只能提交当前任期的日志条目,提交之前任期的日志条目可能导致数据不一致
if n > rf.commitIndex && n < rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log)) && rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(n)].TermId == rf.currentTerm {
rf.commitIndex = n
// 唤醒applier
rf.applyCond.Broadcast()
if isHeartbeat {
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向所有 follower 发送心跳, 已经获得大多数follower的认可, 已将commitIndex更新到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.commitIndex)
} else {
// DPrintf("sendLog---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 向所有 follower 发送日志, 已经获得大多数follower的认可, 已将commitIndex更新到: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.commitIndex)
}
}
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
}(i, args, reply)
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state != Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
break
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
}
应用log时的数据竞争问题
// rf.commitIndex++时唤醒
func (rf *Raft) applier(applyCh chan raftapi.ApplyMsg) {
for !rf.killed() {
rf.mu.Lock()
// 等待直到有新的日志可以应用
for rf.commitIndex <= rf.lastapplied {
rf.applyCond.Wait() // 使用条件变量等待
}
applyMsgs := make([]raftapi.ApplyMsg, 0)
// 应用所有新的已提交日志
for rf.commitIndex > rf.lastapplied {
rf.lastapplied++
if rf.lastapplied < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
// 该日志已经被快照覆盖,跳过
continue
}
// 应用日志到状态机
applyMsg := raftapi.ApplyMsg{
CommandValid: true,
Command: rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(rf.lastapplied)].Command,
CommandIndex: rf.lastapplied,
}
applyMsgs = append(applyMsgs, applyMsg)
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
// 发送 ApplyMsg 到 applyCh 通道
for _, applyMsg := range applyMsgs {
applyCh <- applyMsg
}
rf.mu.Lock()
// DPrintf("applier---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 已将日志应用到状态机, 最新应用的日志索引为: %v, 日志内容为: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.lastapplied, rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(rf.lastapplied)].Command)
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
}
流程为:
- rf.mu.Lock()
- 收集待应用的log数据
- rf.mu.Unlock()
- 向应用层发送
这个代码看起来没有问题, 但是实际运行测例时发现, 仍然会出现与预期不一样的要apply的日志项, 原因在于高并发场景下, 执行rf.mu.Unlock()释放锁后, 可能切换到了InstallSnapshot响应函数, 并更新了lastApplied, 这也意味着, 之后发送到applyCh要应用的日志项已经包含在了快照中, 会有重复应用相同log的问题(可能会重置回之前的某个状态)
解决方法:
这个问题如果通过mutex加锁, 没办法完全解决, 因为你只要解锁去发送 ApplyMsg 到 applyCh 通道就会有lastApplied被其他go routinue 更改的可能, 我的做法是通过在Raft struct中添加bool变量rf.applyLock, 把2 和 4逻辑上组成原子操作
// rf.commitIndex++时唤醒
func (rf *Raft) applier(applyCh chan raftapi.ApplyMsg) {
for !rf.killed() {
rf.mu.Lock()
// 等待直到有新的日志可以应用
for rf.commitIndex <= rf.lastapplied {
rf.applyCond.Wait() // 使用条件变量等待
}
applyMsgs := make([]raftapi.ApplyMsg, 0)
// 应用所有新的已提交日志
for rf.commitIndex > rf.lastapplied {
rf.applyLock = true
rf.lastapplied++
if rf.lastapplied < rf.globalLastIncludedIndex {
// 该日志已经被快照覆盖,跳过
continue
}
// 应用日志到状态机
applyMsg := raftapi.ApplyMsg{
CommandValid: true,
Command: rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(rf.lastapplied)].Command,
CommandIndex: rf.lastapplied,
}
applyMsgs = append(applyMsgs, applyMsg)
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
// 发送 ApplyMsg 到 applyCh 通道
for _, applyMsg := range applyMsgs {
applyCh <- applyMsg
}
rf.mu.Lock()
rf.applyLock = false
// DPrintf("applier---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 已将日志应用到状态机, 最新应用的日志索引为: %v, 日志内容为: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.lastapplied, rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(rf.lastapplied)].Command)
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
}
这样其他go routinue在修改rf.lastapplied时判断一下 rf.applyLock == false, 不满足条件就放弃更新(不用担心, 随后applier会把rf.lastapplied更新到rf.commitIndex > rf.globalLastIncludedIndex的)
测试
测试300次
===== 开始第 1 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestSnapshotBasic3D
Test (3D): snapshots basic (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 138 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotBasic3D (7.50s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstall3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 58.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 1268 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstall3D (58.36s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 65.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 1451 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D (65.07s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 40.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 687 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D (40.49s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 46.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 782 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D (46.04s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotAllCrash3D
Test (3D): crash and restart all servers (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 19.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 328 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotAllCrash3D (19.54s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInit3D
Test (3D): snapshot initialization after crash (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 72 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInit3D (5.23s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 242.225s
===== 结束第 1 次测试 ===== (耗时: 242秒)
......................
===== 开始第 300 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestSnapshotBasic3D
Test (3D): snapshots basic (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 138 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotBasic3D (7.41s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstall3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 58.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 1267 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstall3D (58.38s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 67.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 1524 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D (67.51s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 41.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 686 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D (41.13s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 47.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 803 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D (47.87s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotAllCrash3D
Test (3D): crash and restart all servers (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 17.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 280 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotAllCrash3D (17.43s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInit3D
Test (3D): snapshot initialization after crash (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 78 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInit3D (5.55s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 245.287s
===== 结束第 300 次测试 ===== (耗时: 245秒)
===== 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 300
成功次数: 300
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 72865秒
平均每次测试耗时: 242秒
===== 测试结束 =====
BUG修复
在lab3A中, kv数据库的命令要求命令能够尽快被commit, 且要求比一个心跳间隔更快, 因此之前我把发日志和发心跳一样按心跳间隔发送的偷懒行为是不行了, 哈哈哈
首先声明以下修改都是在多次(几次到几十次)测试下, 才暴露的问题, 只能说,如果你测试了一次侥幸通过了, 不代表你写的就是对的…, 当然我也只做了几百次测试, 说不定在成千上万次测试下我也会出错, 谁知道呢…
修改如下:
-
首先是start, 在start中触发发送log
func (rf *Raft) Start(command interface{}) (int, int, bool) { // 调用start的时候已经加锁了 rf.mu.Lock() // Your code here (3B). if rf.state != Leader { rf.mu.Unlock() return -1, -1, false } // 是leader newLogEntry := logEntity{ TermId: rf.currentTerm, Command: command, } rf.log = append(rf.log, &newLogEntry) rf.mu.Unlock() go rf.sendLog(command) rf.mu.Lock() defer rf.mu.Unlock() // DPrintf("Start---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到客户端的命令: %v, 已追加到本地日志, 日志索引为: %v, 并开始日志同步\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, command, len(rf.log)-1) return len(rf.log) - 1, rf.currentTerm, true }这样改会有一个问题, 有几率通不过TestConcurrentStarts3B, 因为在多个start被并发调用的情况下, 在14行我解锁后, 很有可能多个go routinue 都到达了此处, 那就导致最终返回的Index重复, 修改如下:
func (rf *Raft) Start(command interface{}) (int, int, bool) { // 调用start的时候已经加锁了 rf.mu.Lock() // Your code here (3B). if rf.state != Leader { rf.mu.Unlock() return -1, -1, false } // 是leader newLogEntry := logEntity{ TermId: rf.currentTerm, Command: command, } rf.log = append(rf.log, &newLogEntry) index := rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log) - 1) term := rf.currentTerm // DPrintf("Start---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到客户端的命令: %v, 已追加到本地日志, 日志索引为: %v, 并开始日志同步\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, command, len(rf.log)-1) rf.persist() // 持久化日志 rf.mu.Unlock() go rf.sendLog() return index, term, true } -
避免log在创建快照后被重复应用(还是因为需要解锁向applyCh发送消息导致的发送)
func (rf *Raft) applier(applyCh chan raftapi.ApplyMsg) { for !rf.killed() { rf.mu.Lock() // 等待直到有新的日志可以应用 for rf.commitIndex <= rf.lastapplied || rf.snapShotLock { rf.applyCond.Wait() // 使用条件变量等待 } applyMsgs := make([]*raftapi.ApplyMsg, 0) // 应用所有新的已提交日志 tmpApplied := rf.lastapplied for rf.commitIndex > tmpApplied { // rf.applyLock = true tmpApplied++ // // DPrintf("applier---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 欲将日志添加到applyMsgs, 最新应用的日志索引为: %v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, tmpApplied) if tmpApplied <= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex { // 该日志已经被快照覆盖,跳过 continue } // 应用日志到状态机 applyMsg := &raftapi.ApplyMsg{ CommandValid: true, Command: rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(tmpApplied)].Command, CommandIndex: tmpApplied, } applyMsgs = append(applyMsgs, applyMsg) } rf.mu.Unlock() // 发送 ApplyMsg 到 applyCh 通道 for _, applyMsg := range applyMsgs { rf.mu.Lock() if applyMsg.CommandIndex != rf.lastapplied+1 || rf.snapShotLock { rf.mu.Unlock() continue } // DPrintf("applier---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 欲将日志应用到状态机, 最新应用的日志索引为: %v, 日志内容为: %v,rf.lastapplied更新到:%v, rf.commitIndex更新到:%v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, applyMsg.CommandIndex, rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(applyMsg.CommandIndex)].Command, rf.lastapplied, rf.commitIndex) rf.mu.Unlock() applyCh <- *applyMsg rf.mu.Lock() if applyMsg.CommandIndex != rf.lastapplied+1 || rf.snapShotLock { rf.mu.Unlock() continue } rf.lastapplied = applyMsg.CommandIndex // DPrintf("applier---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 已将日志应用到状态机, 最新应用的日志索引为: %v, 日志内容为: %v,rf.lastapplied更新到:%v, rf.commitIndex更新到:%v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, applyMsg.CommandIndex, rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(applyMsg.CommandIndex)].Command, rf.lastapplied, rf.commitIndex) rf.mu.Unlock() } } } -
向applyCh发消息时不要加锁, 避免因为channel满了阻塞该节点导致一直占有锁, 同时要保证发送快照的原子性
// 接收快照RPC func (rf *Raft) InstallSnapShot(args *InstallSnapshotArgs, reply *InstallSnapshotReply) { flag := true rf.mu.Lock() defer rf.mu.Unlock() // DPrintf("InstallSnapshot---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到 leader %v 的快照: %+v, 准备安装快照, rf.lastapplied=%v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, args.LeaderId, args, rf.lastapplied) if args.Term < rf.currentTerm { reply.Term = rf.currentTerm rf.persist() return } for flag { switch rf.state { case Leader: if args.Term > rf.currentTerm { rf.currentTerm = args.Term rf.state = Follower rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人 rf.persist() } else { reply.Term = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID flag = false rf.persist() } case Candidate: if args.Term > rf.currentTerm { rf.currentTerm = args.Term rf.state = Follower rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人 rf.persist() } else if args.Term == rf.currentTerm { reply.Term = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID rf.state = Follower rf.persist() } else { reply.Term = rf.currentTerm // 回复者termID flag = false rf.persist() } case Follower: if args.Term > rf.currentTerm { rf.currentTerm = args.Term rf.votedFor = -1 // 重置投票人 } rf.lastHeartbeatTime = time.Now() // 重置心跳检测 // 如果快照比现有快照旧,则忽略它 if args.LastIncludedIndex <= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex || args.LastIncludedIndex <= rf.lastapplied { reply.Term = rf.currentTerm rf.persist() return } // 保存快照文件,丢弃任何索引更小的现有或部分 快照 rf.snapShot = args.Data // 如果现有日志有与快照最后条目索引和任期相同的条目,保留该条目之后的日志并回复 if args.LastIncludedIndex < rf.toGlobalIndex(len(rf.log)) && args.LastIncludedIndex >= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex && rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(args.LastIncludedIndex)].TermId == args.LastIncludedTerm { // 保留该条目之后的日志 rf.log = rf.log[rf.toLocalIndex(args.LastIncludedIndex):] } else { // 否则,丢弃整个日志 rf.log = make([]*logEntity, 1) // 初始化日志,保留一个占位符 rf.log[0] = &logEntity{TermId: args.LastIncludedTerm, Command: nil} // 在0位置放一个占位符 } // 通知服务应用快照 applyMsg := &raftapi.ApplyMsg{ SnapshotValid: true, Snapshot: args.Data, SnapshotTerm: args.LastIncludedTerm, SnapshotIndex: args.LastIncludedIndex, } reply.Term = rf.currentTerm flag = false // 更新快照相关状态 rf.snapShot = args.Data rf.globalLastIncludedIndex = args.LastIncludedIndex rf.globalLastIncludedTerm = args.LastIncludedTerm if rf.commitIndex < args.LastIncludedIndex { rf.commitIndex = args.LastIncludedIndex } // if rf.lastapplied < args.LastIncludedIndex { // rf.lastapplied = args.LastIncludedIndex // } if args.LastIncludedIndex > rf.globalLastIncludedIndex || rf.lastapplied < args.LastIncludedIndex { rf.lastapplied = args.LastIncludedIndex } // rf.applyCh <- *applyMsg // 复制需要的数据,避免在无锁状态下访问 Raft 结构体 snapshotData := make([]byte, len(applyMsg.Snapshot)) copy(snapshotData, applyMsg.Snapshot) snapshotIndex := applyMsg.SnapshotIndex snapshotTerm := applyMsg.SnapshotTerm // 释放锁后再发送消息 rf.persist() rf.snapShotLock = true rf.mu.Unlock() rf.applyCh <- raftapi.ApplyMsg{ SnapshotValid: true, Snapshot: snapshotData, SnapshotTerm: snapshotTerm, SnapshotIndex: snapshotIndex, } rf.mu.Lock() // 重新获取锁,因为 defer 中还需要解锁 rf.snapShotLock = false if rf.lastapplied < rf.commitIndex { // 唤醒apply rf.applyCond.Broadcast() } // DPrintf("InstallSnapshot---节点server %v, 在term: %v, 收到 leader %v 的快照: %+v, 已安装快照, rf.lastapplied=%v\n", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, args.LeaderId, args, rf.lastapplied) } } } -
发送快照和日志并行带来的log应用的顺序问题
根据在多次测试时log的输出, 发现了一个问题, 那就是有可能某个log已经应用了(applier在39行后解锁), 比如说40已经发送到应用层, 然后此时才收到InstallSnapShot, 快照截止到39, 然后applier继续运行应用了41, 导致应用层认为40没有被应用…
InstallSnapShot中修改如下:
if args.LastIncludedIndex <= rf.globalLastIncludedIndex || args.LastIncludedIndex <= rf.lastapplied {
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm
rf.persist()
return
}
其中args.LastIncludedIndex <= rf.lastapplied保证, 快照必须覆盖所有已应用的日志, 至于为什么是等于是应为在applier39行还没更新rf.lastapplied为40, 但实际上已经应用到40了
- 不用担心快照不被安装, 应用层会调用snapshot()的…
重新测试
修改对lab3A没什么影响, 重测了一下,还是16秒, 比lab官网给出的19.834要快一点点…
lab3B 300次
===== 开始第 1 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestBasicAgree3B
Test (3B): basic agreement (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 16 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBasicAgree3B (1.02s)
=== RUN TestRPCBytes3B
Test (3B): RPC byte count (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 48 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRPCBytes3B (1.81s)
=== RUN TestFollowerFailure3B
Test (3B): test progressive failure of followers (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 110 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFollowerFailure3B (4.93s)
=== RUN TestLeaderFailure3B
Test (3B): test failure of leaders (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 196 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestLeaderFailure3B (5.74s)
=== RUN TestFailAgree3B
Test (3B): agreement after follower reconnects (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 86 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailAgree3B (3.94s)
=== RUN TestFailNoAgree3B
Test (3B): no agreement if too many followers disconnect (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.8s #peers 5 #RPCs 180 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailNoAgree3B (3.83s)
=== RUN TestConcurrentStarts3B
Test (3B): concurrent Start()s (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 22 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestConcurrentStarts3B (1.06s)
=== RUN TestRejoin3B
Test (3B): rejoin of partitioned leader (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 214 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRejoin3B (7.63s)
=== RUN TestBackup3B
Test (3B): leader backs up quickly over incorrect follower logs (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 15.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 1980 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBackup3B (15.19s)
=== RUN TestCount3B
Test (3B): RPC counts aren't too high (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 64 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestCount3B (2.54s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 47.701s
===== 结束第 1 次测试 ===== (耗时: 48秒)
...............................
===== 开始第 300 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestBasicAgree3B
Test (3B): basic agreement (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 18 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBasicAgree3B (1.12s)
=== RUN TestRPCBytes3B
Test (3B): RPC byte count (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 48 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRPCBytes3B (1.93s)
=== RUN TestFollowerFailure3B
Test (3B): test progressive failure of followers (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 108 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFollowerFailure3B (4.99s)
=== RUN TestLeaderFailure3B
Test (3B): test failure of leaders (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 194 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestLeaderFailure3B (5.64s)
=== RUN TestFailAgree3B
Test (3B): agreement after follower reconnects (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 86 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailAgree3B (3.94s)
=== RUN TestFailNoAgree3B
Test (3B): no agreement if too many followers disconnect (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.8s #peers 5 #RPCs 176 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailNoAgree3B (3.78s)
=== RUN TestConcurrentStarts3B
Test (3B): concurrent Start()s (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 22 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestConcurrentStarts3B (1.08s)
=== RUN TestRejoin3B
Test (3B): rejoin of partitioned leader (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 192 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRejoin3B (6.76s)
=== RUN TestBackup3B
Test (3B): leader backs up quickly over incorrect follower logs (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 17.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 2040 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBackup3B (17.02s)
=== RUN TestCount3B
Test (3B): RPC counts aren't too high (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 62 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestCount3B (2.48s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 48.749s
===== 结束第 300 次测试 ===== (耗时: 49秒)
===== 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 300
成功次数: 300
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 14640秒
平均每次测试耗时: 48秒
===== 测试结束 =====
平均耗时从63秒 减到了48秒, 跟官方给出的基本上一样都是48秒
lab3C 300次
===== 开始运行 3C 测试 =====
===== 开始第 1 次 3C 测试 =====
=== RUN TestPersist13C
Test (3C): basic persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 70 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist13C (5.02s)
=== RUN TestPersist23C
Test (3C): more persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 13.7s #peers 5 #RPCs 324 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist23C (13.67s)
=== RUN TestPersist33C
Test (3C): partitioned leader and one follower crash, leader restarts (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 36 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist33C (2.45s)
=== RUN TestFigure83C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 31.3s #peers 5 #RPCs 660 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure83C (31.29s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableAgree3C
Test (3C): unreliable agreement (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.5s #peers 5 #RPCs 1196 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableAgree3C (5.50s)
=== RUN TestFigure8Unreliable3C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (unreliable) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 37.7s #peers 5 #RPCs 9516 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure8Unreliable3C (37.70s)
=== RUN TestReliableChurn3C
Test (3C): churn (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.1s #peers 5 #RPCs 15744 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReliableChurn3C (16.07s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableChurn3C
Test (3C): unreliable churn (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.1s #peers 5 #RPCs 1960 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableChurn3C (16.15s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 127.861s
===== 结束第 1 次 3C 测试 ===== (耗时: 128秒)
......................
===== 开始第 300 次 3C 测试 =====
=== RUN TestPersist13C
Test (3C): basic persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 78 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist13C (6.24s)
=== RUN TestPersist23C
Test (3C): more persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 14.6s #peers 5 #RPCs 324 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist23C (14.59s)
=== RUN TestPersist33C
Test (3C): partitioned leader and one follower crash, leader restarts (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 36 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist33C (2.65s)
=== RUN TestFigure83C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 31.4s #peers 5 #RPCs 616 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure83C (31.42s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableAgree3C
Test (3C): unreliable agreement (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.5s #peers 5 #RPCs 1116 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableAgree3C (3.54s)
=== RUN TestFigure8Unreliable3C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (unreliable) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 33.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 8780 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure8Unreliable3C (32.98s)
=== RUN TestReliableChurn3C
Test (3C): churn (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.1s #peers 5 #RPCs 4552 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReliableChurn3C (16.13s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableChurn3C
Test (3C): unreliable churn (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.3s #peers 5 #RPCs 3000 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableChurn3C (16.33s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 123.897s
===== 结束第 300 次 3C 测试 ===== (耗时: 124秒)
===== 3C 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 300
成功次数: 300
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 37147秒
平均每次测试耗时: 123秒
===== 3C 测试结束 =====
平均耗时从129减到了123, 比官方给出的126快一点点…
lab3D 300次
===== 开始运行 3D 测试 =====
===== 开始第 1 次 3D 测试 =====
=== RUN TestSnapshotBasic3D
Test (3D): snapshots basic (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 498 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotBasic3D (2.41s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstall3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 39.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 1422 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstall3D (39.06s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 47.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 1629 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D (47.81s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 29.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 1158 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D (29.44s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 40.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 1246 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D (40.92s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotAllCrash3D
Test (3D): crash and restart all servers (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 13.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 324 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotAllCrash3D (13.75s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInit3D
Test (3D): snapshot initialization after crash (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 72 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInit3D (3.93s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 177.319s
===== 结束第 1 次 3D 测试 ===== (耗时: 177秒)
.....................................
===== 开始第 300 次 3D 测试 =====
=== RUN TestSnapshotBasic3D
Test (3D): snapshots basic (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 490 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotBasic3D (2.71s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstall3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 42.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 1553 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstall3D (42.47s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 46.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 1683 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D (46.91s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 29.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 1096 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D (29.47s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 37.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 1239 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D (37.10s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotAllCrash3D
Test (3D): crash and restart all servers (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 13.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 314 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotAllCrash3D (13.74s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInit3D
Test (3D): snapshot initialization after crash (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 80 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInit3D (4.38s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 176.785s
===== 结束第 300 次 3D 测试 ===== (耗时: 177秒)
===== 3D 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 300
成功次数: 300
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 53210秒
平均每次测试耗时: 177秒
===== 3D 测试结束 =====
平均耗时提升了70秒左右, 比官方的快20秒左右
lab3 300次
===== 开始第 300 次测试 =====
=== RUN TestInitialElection3A
Test (3A): initial election (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 62 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestInitialElection3A (3.64s)
=== RUN TestReElection3A
Test (3A): election after network failure (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 122 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReElection3A (5.47s)
=== RUN TestManyElections3A
Test (3A): multiple elections (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.9s #peers 7 #RPCs 504 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestManyElections3A (5.94s)
=== RUN TestBasicAgree3B
Test (3B): basic agreement (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 18 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBasicAgree3B (0.96s)
=== RUN TestRPCBytes3B
Test (3B): RPC byte count (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 48 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRPCBytes3B (1.77s)
=== RUN TestFollowerFailure3B
Test (3B): test progressive failure of followers (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 110 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFollowerFailure3B (5.00s)
=== RUN TestLeaderFailure3B
Test (3B): test failure of leaders (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 216 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestLeaderFailure3B (6.56s)
=== RUN TestFailAgree3B
Test (3B): agreement after follower reconnects (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 128 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailAgree3B (6.00s)
=== RUN TestFailNoAgree3B
Test (3B): no agreement if too many followers disconnect (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.6s #peers 5 #RPCs 188 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFailNoAgree3B (4.59s)
=== RUN TestConcurrentStarts3B
Test (3B): concurrent Start()s (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 24 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestConcurrentStarts3B (1.06s)
=== RUN TestRejoin3B
Test (3B): rejoin of partitioned leader (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 192 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRejoin3B (6.71s)
=== RUN TestBackup3B
Test (3B): leader backs up quickly over incorrect follower logs (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.9s #peers 5 #RPCs 2068 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBackup3B (16.94s)
=== RUN TestCount3B
Test (3B): RPC counts aren't too high (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 62 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestCount3B (2.42s)
=== RUN TestPersist13C
Test (3C): basic persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 70 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist13C (4.95s)
=== RUN TestPersist23C
Test (3C): more persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 14.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 312 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist23C (14.01s)
=== RUN TestPersist33C
Test (3C): partitioned leader and one follower crash, leader restarts (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.3s #peers 3 #RPCs 36 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestPersist33C (2.33s)
=== RUN TestFigure83C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 28.6s #peers 5 #RPCs 580 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure83C (28.58s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableAgree3C
Test (3C): unreliable agreement (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.8s #peers 5 #RPCs 1036 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableAgree3C (1.80s)
=== RUN TestFigure8Unreliable3C
Test (3C): Figure 8 (unreliable) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 32.8s #peers 5 #RPCs 10068 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestFigure8Unreliable3C (32.82s)
=== RUN TestReliableChurn3C
Test (3C): churn (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.1s #peers 5 #RPCs 10640 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReliableChurn3C (16.10s)
=== RUN TestUnreliableChurn3C
Test (3C): unreliable churn (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.4s #peers 5 #RPCs 3628 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestUnreliableChurn3C (16.39s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotBasic3D
Test (3D): snapshots basic (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 510 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotBasic3D (2.65s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstall3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 42.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 1549 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstall3D (42.24s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 46.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 1694 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnreliable3D (46.71s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 29.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 1085 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallCrash3D (29.45s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 37.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 1209 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInstallUnCrash3D (37.88s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotAllCrash3D
Test (3D): crash and restart all servers (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 13.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 316 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotAllCrash3D (13.57s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotInit3D
Test (3D): snapshot initialization after crash (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 78 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSnapshotInit3D (4.14s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 360.676s
===== 结束第 300 次测试 ===== (耗时: 361秒)
===== 测试统计摘要 =====
总测试次数: 300
成功次数: 300
失败次数: 0
成功率: 100%
总耗时: 108466秒
平均每次测试耗时: 361秒
===== 测试结束 =====


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号