Interpreter Patterns
GoF定义:如果有一种语言,那么需要定义语法结构并且需要一个翻译器来解释语言中的语句
概念
这里我们为一种语言定义一个语法规范,并且提供了解释器来处理语法。简单来说,这个模式表达的是如何计算语言中语句的值(真实含义)
例子
现实世界:语言翻译就是这个模式最恰当的例子。乐谱也是一个例子
代码世界:Java编译器将源代码解释(广义含义)成字节码。这个字节码可以被JVM读取。C#中源码被转换成MSIL码,它可以被CLR解释。在执行过程中,MSIL会被JIT(just in time)编译器转换为二进制执行码
展示
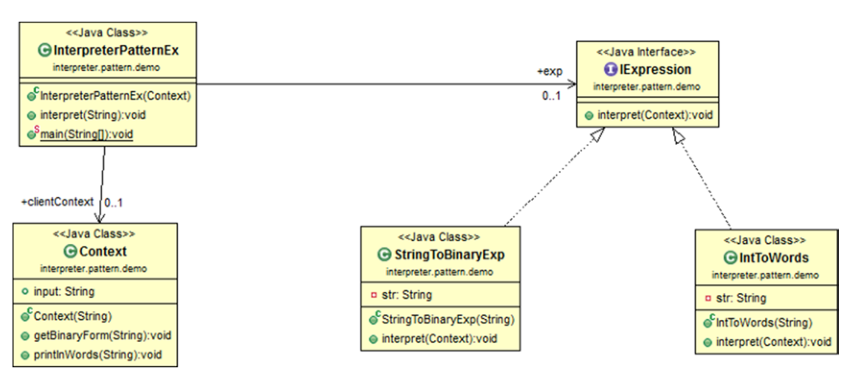
首先要创建一个解释器上下文(context),然后创建一个表达式的实现,最后要创建一个客户端来接收用户请求并生成翻译结果。客户端也会决定超过一条语句的情况下哪个表达式被使用
代码
public class InterpreterPatternEx {
private Context context;
private IExpression expression;
public InterpreterPatternEx(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public void interpret(String str) {
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.println("\nEnter ur choice(1 or 2)");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String c = in.nextLine();
if ("1".equals(c))
{
expression = new IntToWords(str);
}
else
{
expression = new StringToBinaryEx(str);
}
expression.interpret(this.context);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\n***Interpreter Pattern Demo***\n");
System.out.println("Enter a number :");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = in.nextLine();
Context context=new Context(input);
InterpreterPatternEx client = new InterpreterPatternEx(context);
client.interpret(input);
}
}
class Context {
public String input;
public Context(String input) {
this.input = input;
}
public void getBinaryForm(String input) {
int i = Integer.parseInt(input);
String binaryString = Integer.toBinaryString(i);
System.out.println("Binary equivalent of "+input+ " is "+ binaryString);
}
public void printInWords(String input) {
this.input = input;
System.out.println("Printing the input in words:");
char[] c = input.toCharArray();
for (char cs: c) {
switch (cs)
{
case '1':
System.out.print("One ");
break;
case '2':
System.out.print("Two ");
break;
case '3':
System.out.print("Three ");
break;
case '4':
System.out.print("Four ");
break;
case '5':
System.out.print("Five ");
break;
case '6':
System.out.print("Six ");
break;
case '7':
System.out.print("Seven ");
break;
case '8':
System.out.print("Eight ");
break;
case '9':
System.out.print("Nine ");
break;
case '0':
System.out.print("Zero ");
break;
default:
System.out.print("* ");
break;
}
}
}
}
interface IExpression {
void interpret(Context context);
}
class StringToBinaryEx implements IExpression {
private String s;
public StringToBinaryEx(String s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void interpret(Context context) {
context.printInWords(this.s);
}
}
class IntToWords implements IExpression {
private String s;
public IntToWords(String s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void interpret(Context context) {
context.getBinaryForm(this.s);
}
}
Note
- 这个模式广泛用于解释一种语言中的语句(以抽象语法树的方式),当语法简单易读时这种模式表现很好
- 可以容易地表示、修改和实现一种语法
- 我们可以以自己更喜欢的方式来计算表达式的值。取决于我们要怎么解释这些语句
- 如果语法很复杂,实现这个模式会变得非常难。对每个规则,我们都需要实现一个新类,这也是一个很繁复的过程
思考
这个模式将解释器(context)和表达式(语句)分离开,所有的转换规则都在解释器中。开发应用这个模式应该不是很常用,开发一些(简单)语言解释库可以应用



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号