用程序理解nms
转载 https://github.com/SnailTyan/deep-learning-tools/blob/master/nms.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
import cv2
import numpy as np
"""
Non-max Suppression Algorithm
@param list Object candidate bounding boxes
@param list Confidence score of bounding boxes
@param float IoU threshold
@return Rest boxes after nms operation
"""
def nms(bounding_boxes, confidence_score, threshold):
# If no bounding boxes, return empty list
if len(bounding_boxes) == 0:
return [], []
# Bounding boxes
boxes = np.array(bounding_boxes)
# coordinates of bounding boxes
start_x = boxes[:, 0]
start_y = boxes[:, 1]
end_x = boxes[:, 2]
end_y = boxes[:, 3]
# Confidence scores of bounding boxes
score = np.array(confidence_score)
# Picked bounding boxes
picked_boxes = []
picked_score = []
# Compute areas of bounding boxes
areas = (end_x - start_x + 1) * (end_y - start_y + 1)
# Sort by confidence score of bounding boxes
order = np.argsort(score)
# Iterate bounding boxes
while order.size > 0:
# The index of largest confidence score
index = order[-1]
# Pick the bounding box with largest confidence score
picked_boxes.append(bounding_boxes[index])
picked_score.append(confidence_score[index])
# Compute ordinates of intersection-over-union(IOU)
x1 = np.maximum(start_x[index], start_x[order[:-1]])
x2 = np.minimum(end_x[index], end_x[order[:-1]])
y1 = np.maximum(start_y[index], start_y[order[:-1]])
y2 = np.minimum(end_y[index], end_y[order[:-1]])
# Compute areas of intersection-over-union
w = np.maximum(0.0, x2 - x1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, y2 - y1 + 1)
intersection = w * h
# Compute the ratio between intersection and union
ratio = intersection / (areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]] - intersection)
left = np.where(ratio < threshold)
order = order[left]
return picked_boxes, picked_score
# Image name
image_name = 'nms.jpg'
# Bounding boxes
bounding_boxes = [(187, 82, 337, 317), (150, 67, 305, 282), (246, 121, 368, 304)]
confidence_score = [0.9, 0.75, 0.8]
# Read image
image = cv2.imread(image_name)
# Copy image as original
org = image.copy()
# Draw parameters
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
font_scale = 1
thickness = 2
# IoU threshold
threshold = 0.4
# Draw bounding boxes and confidence score
for (start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y), confidence in zip(bounding_boxes, confidence_score):
(w, h), baseline = cv2.getTextSize(str(confidence), font, font_scale, thickness)
cv2.rectangle(org, (start_x, start_y - (2 * baseline + 5)), (start_x + w, start_y), (0, 255, 255), -1)
cv2.rectangle(org, (start_x, start_y), (end_x, end_y), (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(org, str(confidence), (start_x, start_y), font, font_scale, (0, 0, 0), thickness)
# Run non-max suppression algorithm
picked_boxes, picked_score = nms(bounding_boxes, confidence_score, threshold)
# Draw bounding boxes and confidence score after non-maximum supression
for (start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y), confidence in zip(picked_boxes, picked_score):
(w, h), baseline = cv2.getTextSize(str(confidence), font, font_scale, thickness)
cv2.rectangle(image, (start_x, start_y - (2 * baseline + 5)), (start_x + w, start_y), (0, 255, 255), -1)
cv2.rectangle(image, (start_x, start_y), (end_x, end_y), (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(image, str(confidence), (start_x, start_y), font, font_scale, (0, 0, 0), thickness)
# Show image
cv2.imshow('Original', org)
cv2.imshow('NMS', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
Python 3.6.10 (default, Dec 19 2019, 23:04:32)
[GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> [(187, 82, 337, 317), (150, 67, 305, 282), (246, 121, 368, 304)]
KeyboardInterrupt
>>> bounding_boxes = [(187, 82, 337, 317), (150, 67, 305, 282), (246, 121, 368, 304)]
>>> bounding_boxes[:, 0]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: list indices must be integers or slices, not tuple
>>> bounding_boxes[ 0]
(187, 82, 337, 317)
>>> bounding_boxes[0]
(187, 82, 337, 317)
>>> bounding_boxes[1]
(150, 67, 305, 282)
>>> bounding_boxes[:1]
[(187, 82, 337, 317)]
>>> bounding_boxes[:0]
[]
>>> bounding_boxes[:,0]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: list indices must be integers or slices, not tuple
>>> bounding_boxes[:0]
[]
>>> bounding_boxes[:1]
[(187, 82, 337, 317)]
>>> bounding_boxes[:2]
[(187, 82, 337, 317), (150, 67, 305, 282)]
>>> boxes = np.array(bounding_boxes)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'np' is not defined
>>> import numpy as np
>>> boxes = np.array(bounding_boxes)
>>> boxes
array([[187, 82, 337, 317],
[150, 67, 305, 282],
[246, 121, 368, 304]])
>>> boxes[0]
array([187, 82, 337, 317])
>>> boxes[:0]
array([], shape=(0, 4), dtype=int64)
>>> boxes[:,0]
array([187, 150, 246])
>>>
>>> boxes[:,1]
array([ 82, 67, 121])
>>> boxes[:,2]
array([337, 305, 368])
>>> boxes[:,3]
array([317, 282, 304])
>>> start_x = boxes[:, 0]
>>> start_x
array([187, 150, 246])
>>> start_y = boxes[:, 1]
>>> end_x = boxes[:, 2]
>>> end_y = boxes[:, 3]
>>> confidence_score = [0.9, 0.75, 0.8]
>>> score = np.array(confidence_score)
>>> score
array([0.9 , 0.75, 0.8 ])
>>> picked_boxes = []
>>> picked_score = []
>>> areas = (end_x - start_x + 1) * (end_y - start_y + 1)
>>> areas
array([35636, 33696, 22632])
>>> order = np.argsort(score)
>>> order
array([1, 2, 0])
>>> order.szie
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object has no attribute 'szie'
>>> order.size
3
>>> order.size
3
>>> order.size
3
>>> index = order[-1]
>>> index
0
>>> bounding_boxes[index]
(187, 82, 337, 317)
>>> confidence_score[index]
0.9
>>> start_x[index]
187
>>> start_x[order[:-1]]
array([150, 246])
>>> np.maximum(start_x[index], start_x[order[:-1]])
array([187, 246])
>>> x1 = np.maximum(start_x[index], start_x[order[:-1]])
>>> x1
array([187, 246])
>>> x2 = np.minimum(end_x[index], end_x[order[:-1]])
>>> x2
array([305, 337])
>>> y1 = np.maximum(start_y[index], start_y[order[:-1]])
>>> y1
array([ 82, 121])
>>> y2 = np.minimum(end_y[index], end_y[order[:-1]])
>>> y2
array([282, 304])
>>> w = np.maximum(0.0, x2 - x1 + 1)
>>> w
array([119., 92.])
>>> h = np.maximum(0.0, y2 - y1 + 1)
>>> h
array([201., 184.])
>>> intersection = w * h
>>> intersection
array([23919., 16928.])
>>> areas[index]
35636
>>> areas[order[:-1]]
array([33696, 22632])
>>> (areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]]
...
...
...
...
...
KeyboardInterrupt
>>> temp = areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]]
>>> temp
array([69332, 58268])
>>> temp = areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]] - intersection
>>> temp
array([45413., 41340.])
>>> ratio = intersection / (areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]] - intersection)
>>> ratio
array([0.5266994 , 0.40948234])
>>> left = np.where(ratio < threshold)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'threshold' is not defined
>>> left = np.where(ratio < 0.4)
>>> left
(array([], dtype=int64),)
>>> order = order[left]
>>> order
array([], dtype=int64)
>>> order
array([], dtype=int64)
>>> order = np.argsort(score)
>>> order
array([1, 2, 0])
>>> left = np.where(ratio < 0.5)
>>> left
(array([1]),)
>>> order = order[left]
>>> order
array([2])
>>> picked_boxes.append(bounding_boxes[index])
>>> picked_boxes
[(187, 82, 337, 317)]
>>> picked_score.append(confidence_score[index])
>>> picked_score
[0.9]
>>>
转载于 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37489043
1. 什么是非极大值抑制
非极大值抑制,简称为NMS算法,英文为Non-Maximum Suppression。其思想是搜素局部最大值,抑制极大值。NMS算法在不同应用中的具体实现不太一样,但思想是一样的。非极大值抑制,在计算机视觉任务中得到了广泛的应用,例如边缘检测、人脸检测、目标检测(DPM,YOLO,SSD,Faster R-CNN)等。
2. 为什么要用非极大值抑制
以目标检测为例:目标检测的过程中在同一目标的位置上会产生大量的候选框,这些候选框相互之间可能会有重叠,此时我们需要利用非极大值抑制找到最佳的目标边界框,消除冗余的边界框。Demo如下图:
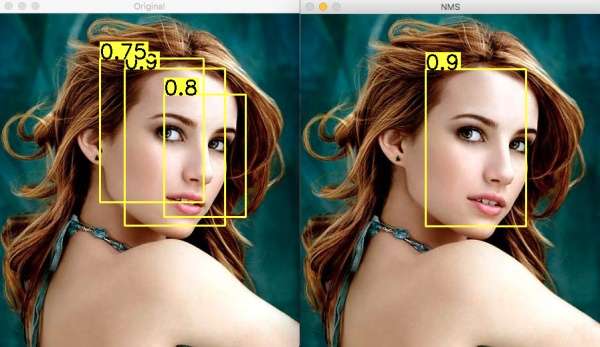
左图是人脸检测的候选框结果,每个边界框有一个置信度得分(confidence score),如果不使用非极大值抑制,就会有多个候选框出现。右图是使用非极大值抑制之后的结果,符合我们人脸检测的预期结果。
3. 如何使用非极大值抑制
前提:目标边界框列表及其对应的置信度得分列表,设定阈值,阈值用来删除重叠较大的边界框。
IoU:intersection-over-union,即两个边界框的交集部分除以它们的并集。
非极大值抑制的流程如下:
- 根据置信度得分进行排序
- 选择置信度最高的比边界框添加到最终输出列表中,将其从边界框列表中删除
- 计算所有边界框的面积
- 计算置信度最高的边界框与其它候选框的IoU。
- 删除IoU大于阈值的边界框
- 重复上述过程,直至边界框列表为空。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号
