TensorFlow2.1入门学习笔记(8)——欠拟合与过拟合(正则化)
TensorFlow2.0入门学习笔记(8)——欠拟合与过拟合(正则化)
欠拟合与过拟合
- 欠拟合:模型不能有效拟合数据集对现有数据集学习的不够彻底
- 过拟合:模型对训练集拟合的太好,而缺失了泛化力
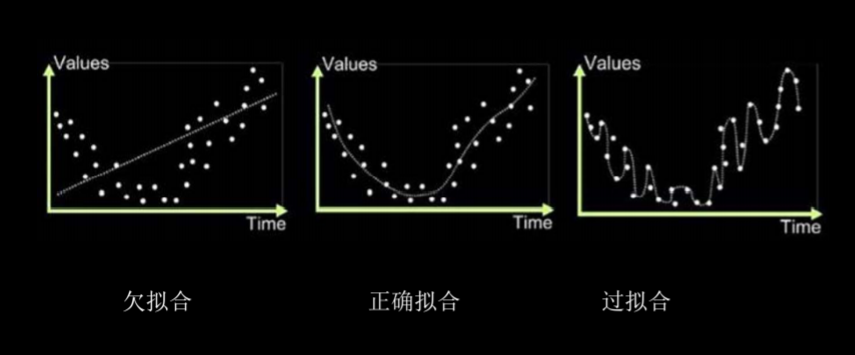
- 欠拟合的解决方法:
增加输入特征项
增加网络参数
减少正则化参数 - 过拟合的解决方法:
数据清洗
增大训练集
采用正则化
增大正则化参数
正则化缓解过拟合
正则化在损失函数中引入模型复杂度指标,利用给W加权值,弱化了训练
数据的噪声(一般不正则化b)

- 常见的正则化:
\(loss_{l_1}(w)=\sum_i |w_i|\)
\(loss_{l_1}(w)=\sum_i |w_i ^2|\) - 正则化的选择:
L1正则化大概率会使很多参数变为零,因此该方法可通过稀疏参数,即减少参数的数量,降低复杂度。
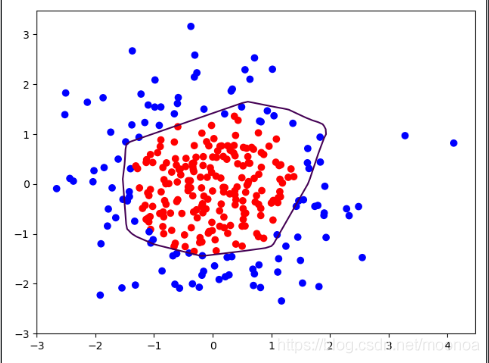
L2正则化会使参数很接近零但不为零,因此该方法可通过减小参数值的大小降低复杂度。 - 例如:给出一个dot.csv数据集,判断y_是1的可能性大还是0的可能性大。
- 思路:可以将x1、x2分别作为横纵坐标,y_为1的点标为红色,为0的点标为蓝色,在坐标系中展示出来,通过神经网络离合出分界线模型。
- 采用l2正则化的源码:
# 导入所需模块
import tensorflow as tf
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 读入数据/标签 生成x_train y_train
df = pd.read_csv('dot.csv')
x_data = np.array(df[['x1', 'x2']])
y_data = np.array(df['y_c'])
x_train = x_data
y_train = y_data.reshape(-1, 1)
Y_c = [['red' if y else 'blue'] for y in y_train]
# 转换x的数据类型,否则后面矩阵相乘时会因数据类型问题报错
x_train = tf.cast(x_train, tf.float32)
y_train = tf.cast(y_train, tf.float32)
# from_tensor_slices函数切分传入的张量的第一个维度,生成相应的数据集,使输入特征和标签值一一对应
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train)).batch(32)
# 生成神经网络的参数,输入层为4个神经元,隐藏层为32个神经元,2层隐藏层,输出层为3个神经元
# 用tf.Variable()保证参数可训练
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2, 11]), dtype=tf.float32)
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.01, shape=[11]))
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([11, 1]), dtype=tf.float32)
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.01, shape=[1]))
lr = 0.005 # 学习率为
epoch = 800 # 循环轮数
# 训练部分
for epoch in range(epoch):
for step, (x_train, y_train) in enumerate(train_db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # 记录梯度信息
h1 = tf.matmul(x_train, w1) + b1 # 记录神经网络乘加运算
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1)
y = tf.matmul(h1, w2) + b2
# 采用均方误差损失函数mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2)
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_train - y))
# 添加l2正则化
loss_regularization = []
# tf.nn.l2_loss(w)=sum(w ** 2) / 2
loss_regularization.append(tf.nn.l2_loss(w1)) #对w1使用l2正则化处理
loss_regularization.append(tf.nn.l2_loss(w2))
# 求和
# 例:x=tf.constant(([1,1,1],[1,1,1]))
# tf.reduce_sum(x)
# >>>6
loss_regularization = tf.reduce_sum(loss_regularization)
loss = loss_mse + 0.03 * loss_regularization # REGULARIZER = 0.03
# 计算loss对各个参数的梯度
variables = [w1, b1, w2, b2]
grads = tape.gradient(loss, variables)
# 实现梯度更新
# w1 = w1 - lr * w1_grad
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0])
b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1])
w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2])
b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3])
# 每200个epoch,打印loss信息
if epoch % 20 == 0:
print('epoch:', epoch, 'loss:', float(loss))
# 预测部分
print("*******predict*******")
# xx在-3到3之间以步长为0.01,yy在-3到3之间以步长0.01,生成间隔数值点
xx, yy = np.mgrid[-3:3:.1, -3:3:.1]
# 将xx, yy拉直,并合并配对为二维张量,生成二维坐标点
grid = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
grid = tf.cast(grid, tf.float32)
# 将网格坐标点喂入神经网络,进行预测,probs为输出
probs = []
for x_predict in grid:
# 使用训练好的参数进行预测
h1 = tf.matmul([x_predict], w1) + b1
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1)
y = tf.matmul(h1, w2) + b2 # y为预测结果
probs.append(y)
# 取第0列给x1,取第1列给x2
x1 = x_data[:, 0]
x2 = x_data[:, 1]
# probs的shape调整成xx的样子
probs = np.array(probs).reshape(xx.shape)
plt.scatter(x1, x2, color=np.squeeze(Y_c))
# 把坐标xx yy和对应的值probs放入contour函数,给probs值为0.5的所有点上色 plt.show()后 显示的是红蓝点的分界线
plt.contour(xx, yy, probs, levels=[.5])
plt.show()
# 读入红蓝点,画出分割线,包含正则化
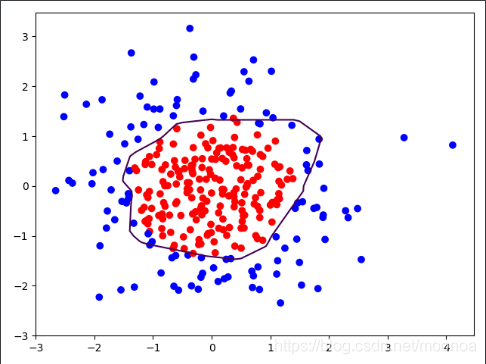
- 学习结果
相比于不使用正则化,分界线更平滑有效缓解了过拟合,泛化性更好
主要学习的资料,西安科技大学:神经网络与深度学习——TensorFlow2.0实战,北京大学:人工智能实践Tensorflow笔记


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号