Python os 模块知识点整理
Python os模块知识点整理
先引用 os.py 的一段介绍
This exports:
all functions from posix, nt or ce, e.g. unlink, stat, etc.
os.path is either posixpath or ntpath
os.name is either ‘posix’, ‘nt’ or ‘ce’.
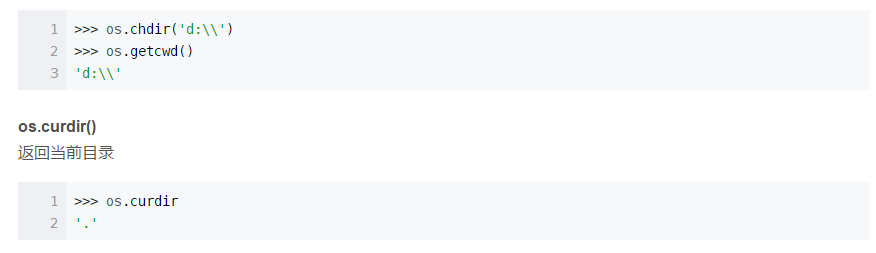
os.curdir is a string representing the current directory (‘.’ or ‘:’)
os.pardir is a string representing the parent directory (‘..’ or ‘::’)
os.sep is the (or a most common) pathname separator (‘/’ or ‘:’ or ‘\’)
os.extsep is the extension separator (always ‘.’)
os.altsep is the alternate pathname separator (None or ‘/’)
os.pathsep is the component separator used in $PATH etc
os.linesep is the line separator in text files (‘\r’ or ‘\n’ or ‘\r\n’)
os.defpath is the default search path for executables
os.devnull is the file path of the null device (‘/dev/null’, etc.)
Programs that import and use ‘os’ stand a better chance of being
portable between different platforms. Of course, they must then
only use functions that are defined by all platforms (e.g., unlink
and opendir), and leave all pathname manipulation to os.path
(e.g., split and join).
简单说明:os 模块提供了一个统一的操作系统接口函数, 这些接口函数通常是平台指定的,os 模块能在不同操作系统平台如 nt 或 posix中的特定函数间自动切换,从而能实现跨平台操作。
os模块的作用:os,语义为操作系统,所以这个模块就是操作系统相关的功能了,可以处理文件和目录这些我们日常手动需要做的操作,就比如说:显示当前目录下所有文件/删除某个文件/获取文件大小……另外,os模块不受平台限制,也就是说:当我们要在linux中显示当前命令时就要用到pwd命令,而Windows中cmd命令行下就要用到dir,这时候我们使用python中os模块的os.path.abspath(name)功能,甭管是linux或者Windows都可以获取当前的绝对路径。
import os

2 目录操作
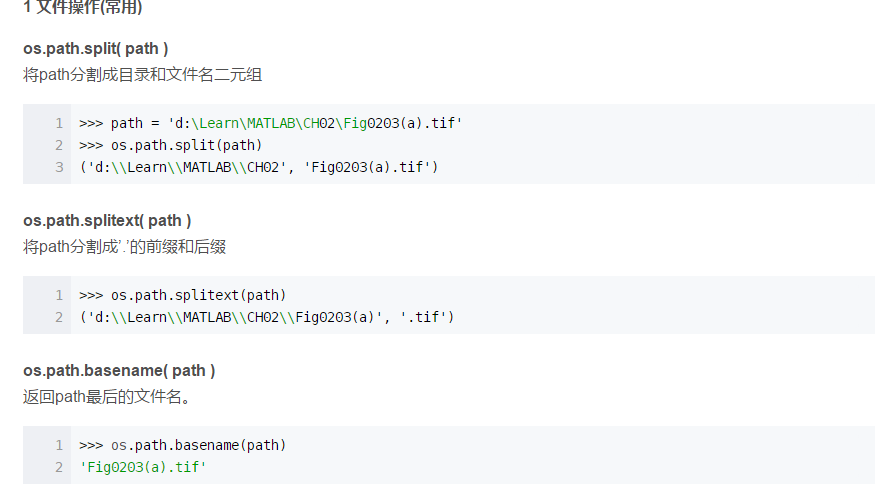
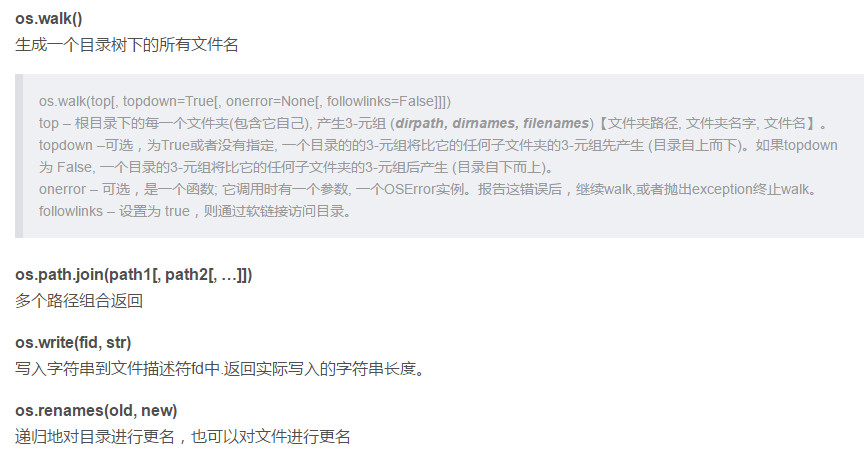
os.listdir( path )
返回指定目录下的所有目录和文件
Python中的join()函数的用法
函数:string.join()
Python中有join()和os.path.join()两个函数,具体作用如下:
join(): 连接字符串数组。将字符串、元组、列表中的元素以指定的字符(分隔符)连接生成一个新的字符串
os.path.join(): 将多个路径组合后返回
一、函数说明
1、join()函数
语法: 'sep'.join(seq)
参数说明
sep:分隔符。可以为空
seq:要连接的元素序列、字符串、元组、字典
上面的语法即:以sep作为分隔符,将seq所有的元素合并成一个新的字符串
返回值:返回一个以分隔符sep连接各个元素后生成的字符串
2、os.path.join()函数
语法: os.path.join(path1[,path2[,......]])
返回值:将多个路径组合后返回
注:第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
#对序列进行操作(分别使用' '与':'作为分隔符) >>> seq1 = ['hello','good','boy','doiido']>>> print ' '.join(seq1)hello good boy doiido>>> print ':'.join(seq1)hello:good:boy:doiido #对字符串进行操作 >>> seq2 = "hello good boy doiido">>> print ':'.join(seq2)h:e:l:l:o: :g:o:o:d: :b:o:y: :d:o:i:i:d:o #对元组进行操作 >>> seq3 = ('hello','good','boy','doiido')>>> print ':'.join(seq3)hello:good:boy:doiido #对字典进行操作 >>> seq4 = {'hello':1,'good':2,'boy':3,'doiido':4}>>> print ':'.join(seq4)boy:good:doiido:hello #合并目录 >>> import os>>> os.path.join('/hello/','good/boy/','doiido')'/hello/good/boy/doiido' |
3 其他
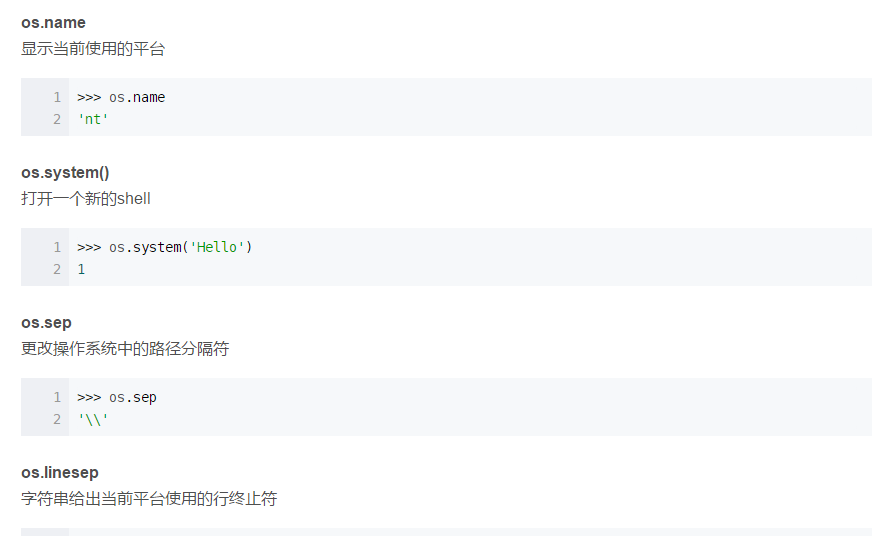
os.environ
获取系统环境变量


